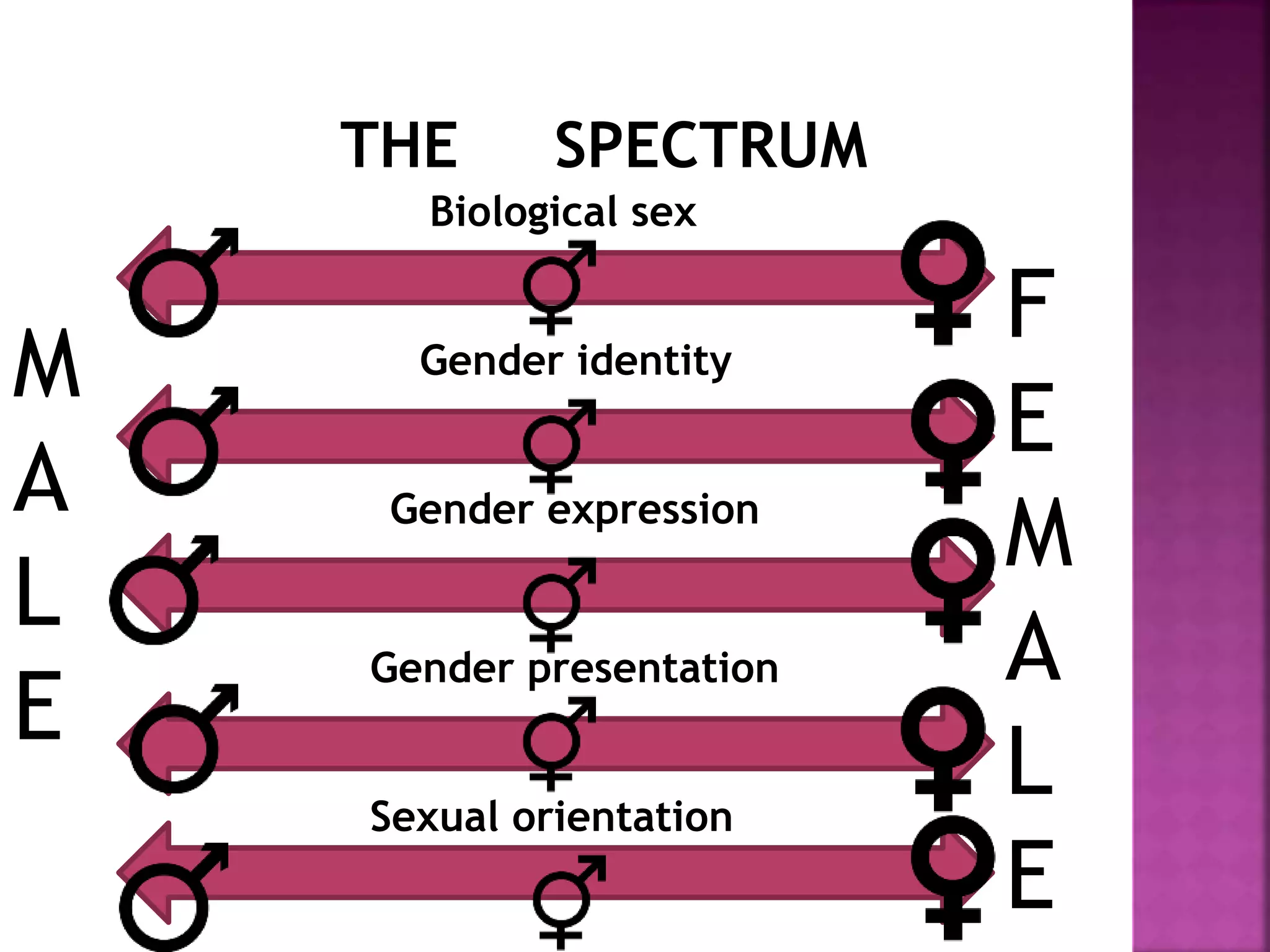
The document discusses the distinctions between biological sex and gender, emphasizing the importance of gender-neutral language to promote inclusivity. It outlines the challenges faced by transgender and intersex individuals, including discrimination and mental health issues, along with rights and protective measures for these communities. Additionally, it highlights government initiatives and organizations aimed at supporting transgender rights, education, and social integration.