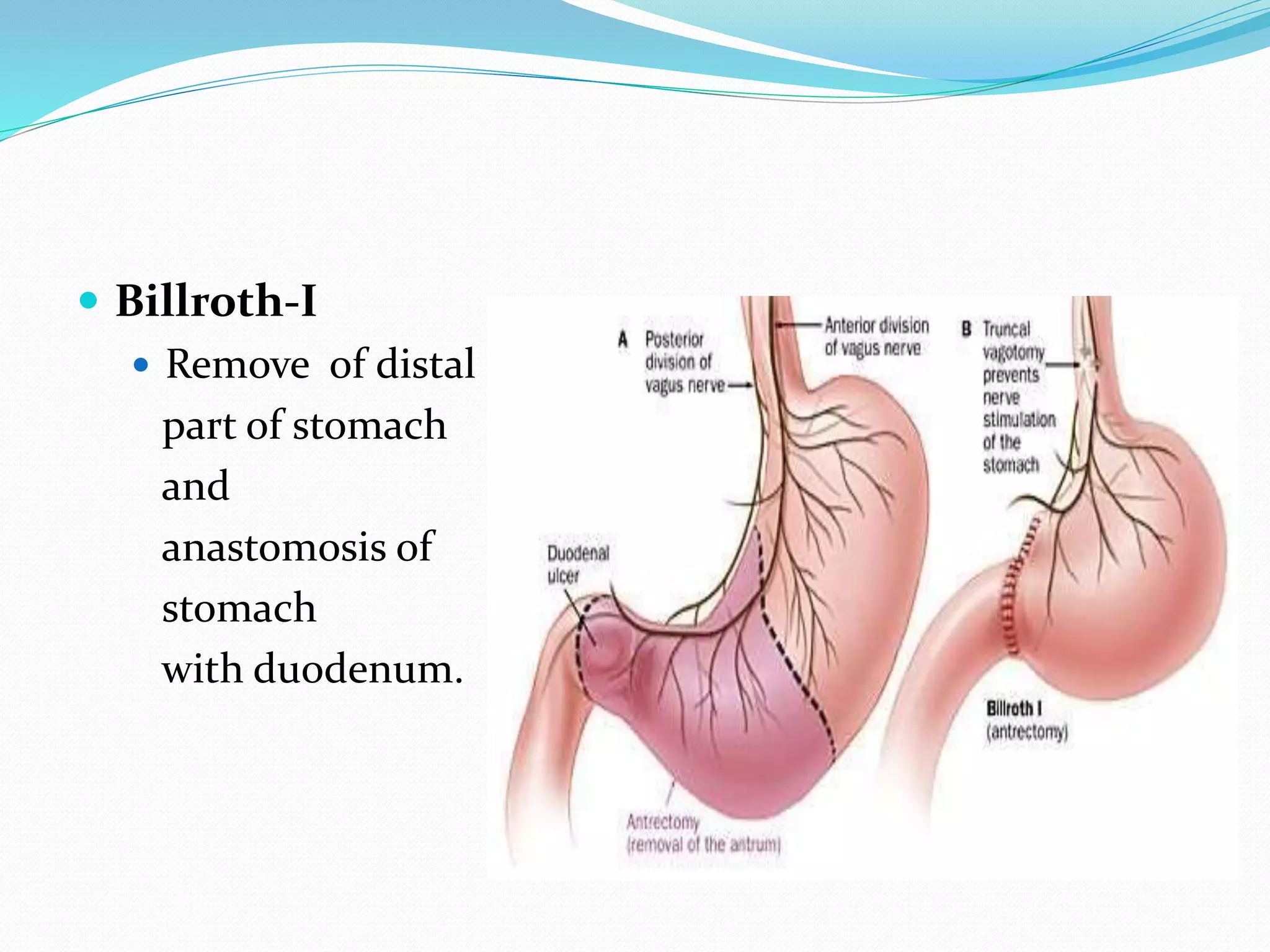
This document discusses various types of gastric surgeries including gastrectomy, vagotomy, and gastrojejunostomy. It outlines indications for gastric surgery such as complicated peptic ulcers, cancer, and obesity. Complications of gastric surgery are discussed, including early complications like bleeding and leaks, and late complications like stenosis and hernias. Specific procedures for ulcers, cancer, and obesity are described. Complications of vagotomy like diarrhea and dumping syndrome are also summarized.