1) Respiration is a vital process for all living organisms to obtain energy by breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water and ATP.
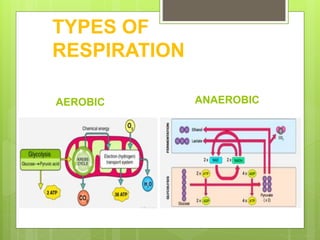
2) Respiration occurs through cellular respiration in the cells of organisms. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen to break down glucose while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen.
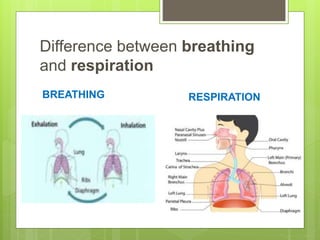
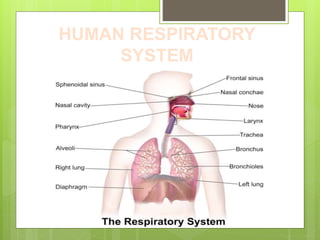
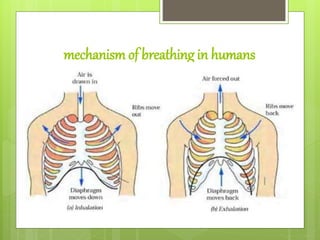
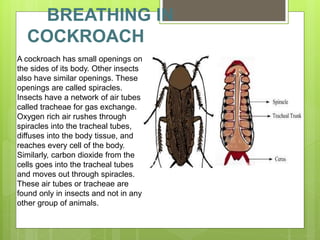
3) Humans and other animals breathe to take in oxygen which is distributed to cells through respiratory organs like lungs. Gases are exchanged through various structures depending on the organism, such as lungs, skin, gills or tracheae.