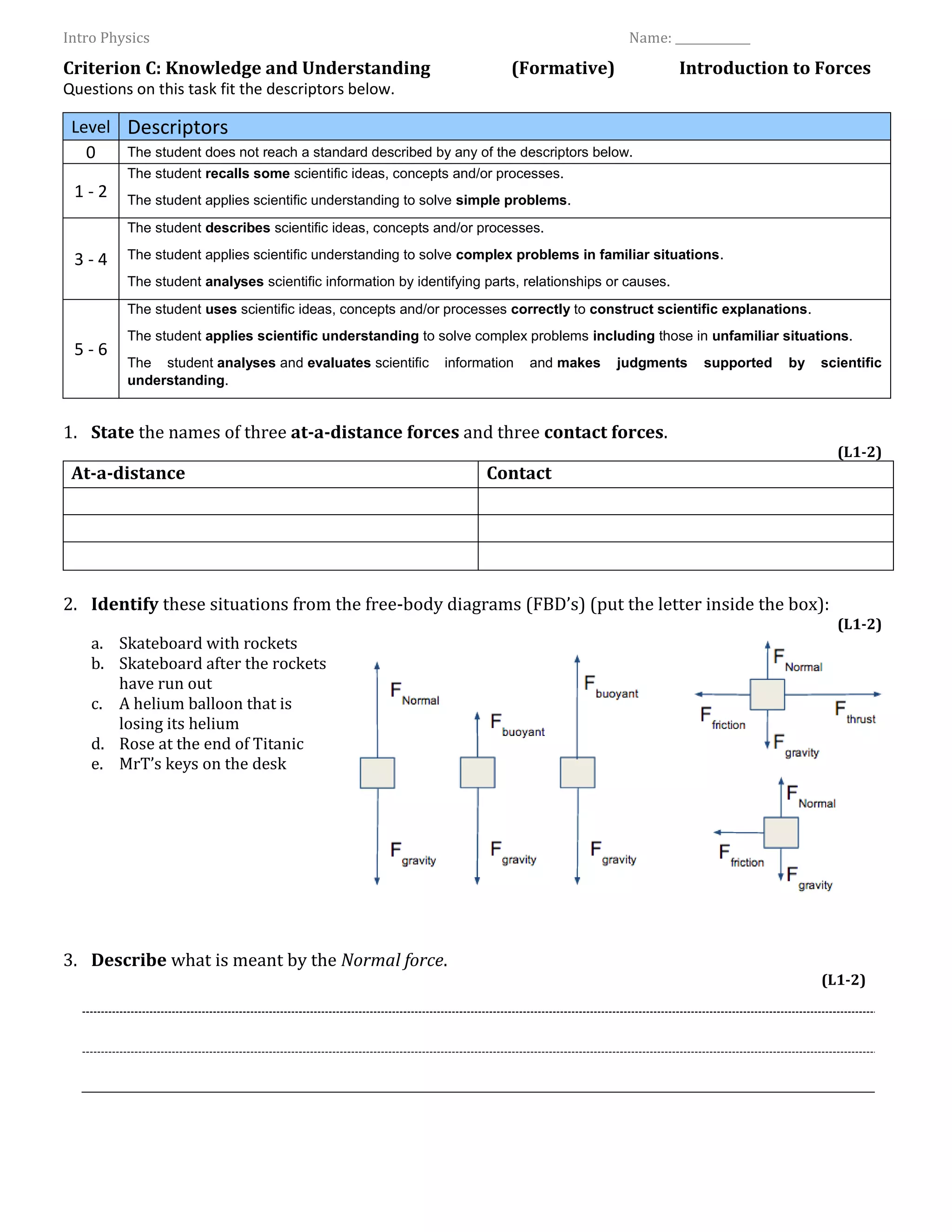
The document outlines a physics assessment focused on understanding forces, including at-a-distance and contact forces, as well as free-body diagram analysis. It includes questions on various topics such as normal force, unbalanced forces, mass versus weight, and calculations related to Felix Baumgartner's freefall jump. The document serves as a formative criterion for evaluating students' knowledge and understanding of these concepts.