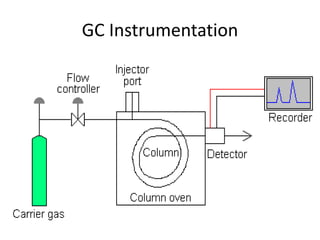
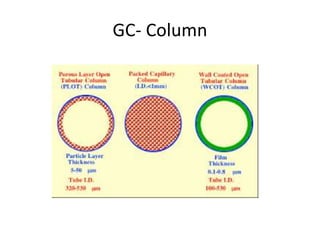
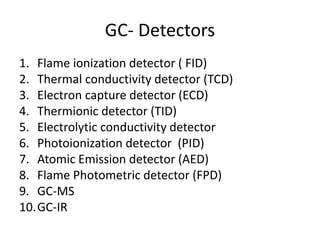
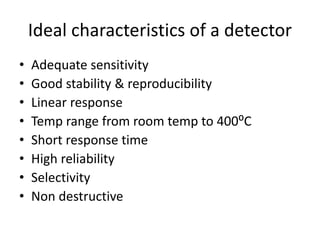
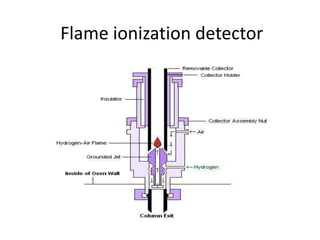
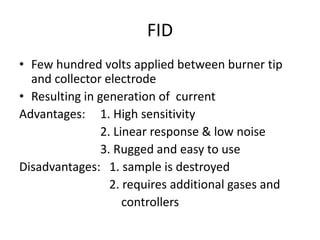
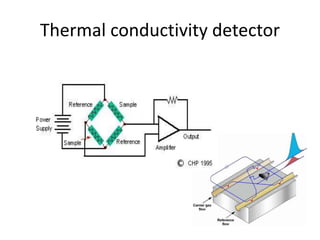
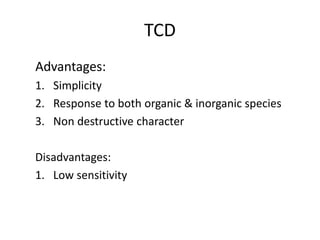
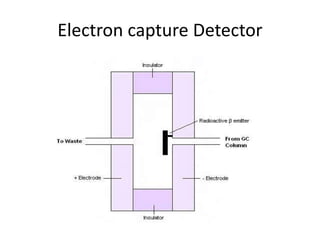
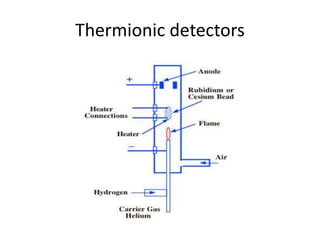
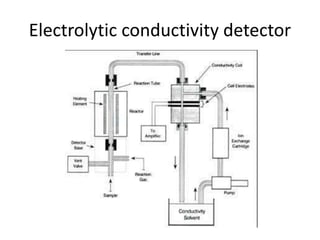
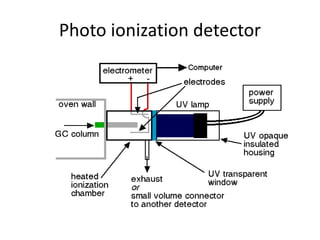
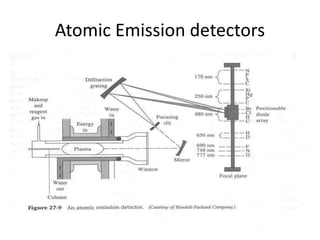
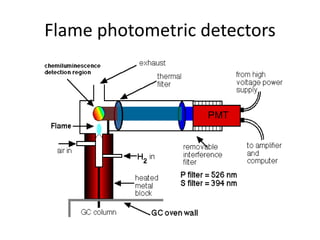
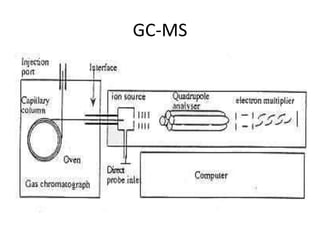
The document describes various gas chromatography detectors including the Flame Ionization Detector (FID), Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD), Electron Capture Detector (ECD), Thermionic Detector (TID), Electrolytic Conductivity Detector, Photoionization Detector (PID), Atomic Emission Detector (AED), Flame Photometric Detector (FPD), GC-MS, and GC-IR. It provides details on the principles, advantages, and disadvantages of some of the main detectors.