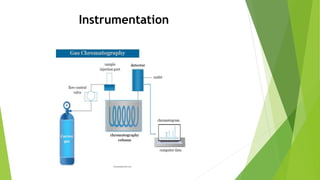
Gas chromatography is a widely used analytical technique for separating and identifying chemical compounds through a sample solution injected into a gas stream that moves it into a separation column. The document details various detectors used in gas chromatography, including thermal conductivity, flame ionization, and others, along with essential instrumentation components. Applications of gas chromatography extend to fields such as food analysis, quality control, forensic analysis, and air pollution assessment.