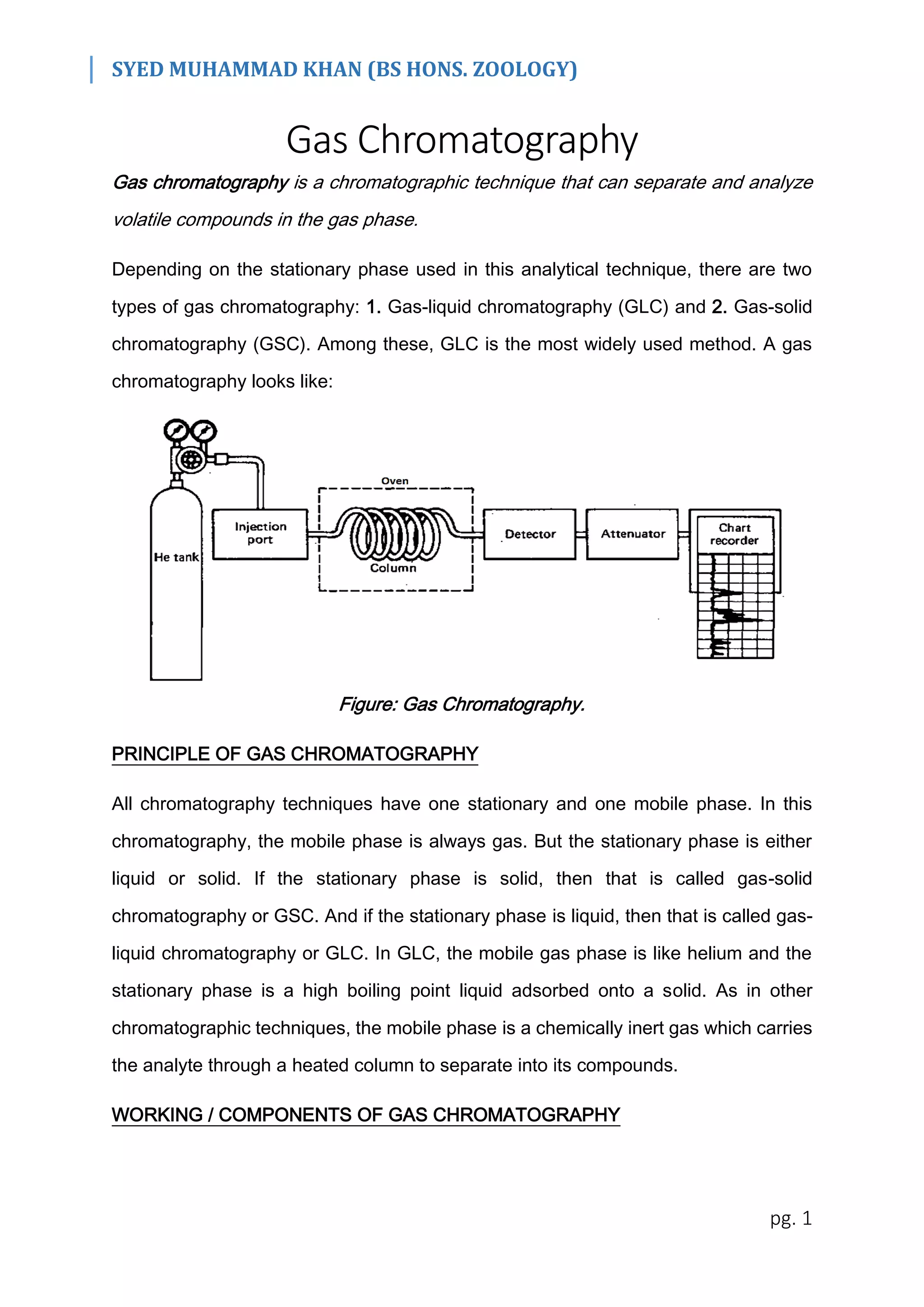
Gas chromatography is a technique that separates and analyzes volatile compounds in the gas phase. There are two main types: gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) and gas-solid chromatography (GSC). GLC is the most widely used method. It works by vaporizing the sample and carrying it through a column using an inert gas such as helium. Components separate based on how strongly they interact with the liquid stationary phase coating the column. A detector then measures the separated components as they exit the column. Gas chromatography has many applications including qualitative and quantitative analysis of compounds, identification of mixtures, isolation of metabolites, and its use in forensics.