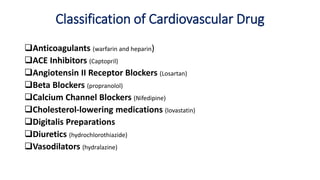
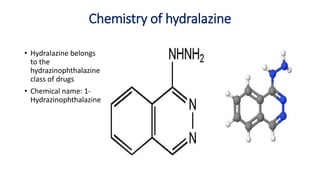
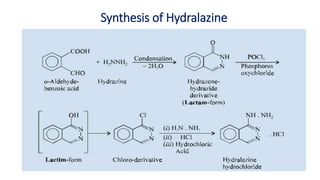
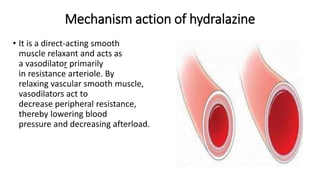
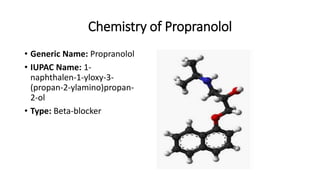
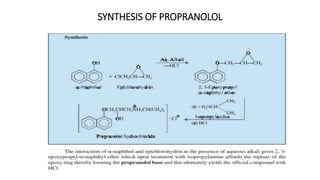
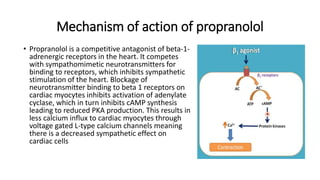
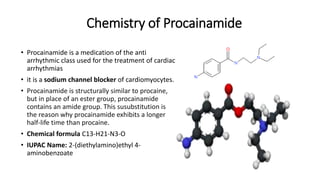
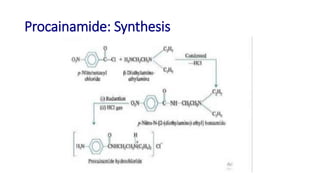
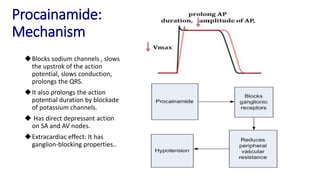
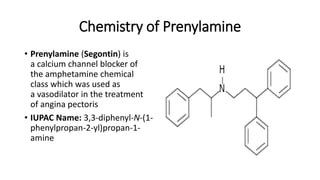
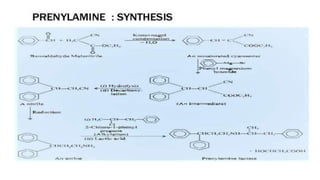
This document discusses several cardiovascular drugs, including their chemistry, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic uses. It describes hydralazine as a vasodilator that acts on resistance arterioles to lower blood pressure. Propranolol is a beta-blocker that competitively blocks beta-1 receptors in the heart to reduce its workload and rate. Procainamide is a sodium channel blocker used to treat arrhythmias by slowing conduction and prolonging the action potential. Prenylamine is a calcium channel blocker and vasodilator formerly used to treat angina by decreasing sympathetic stimulation of the heart.