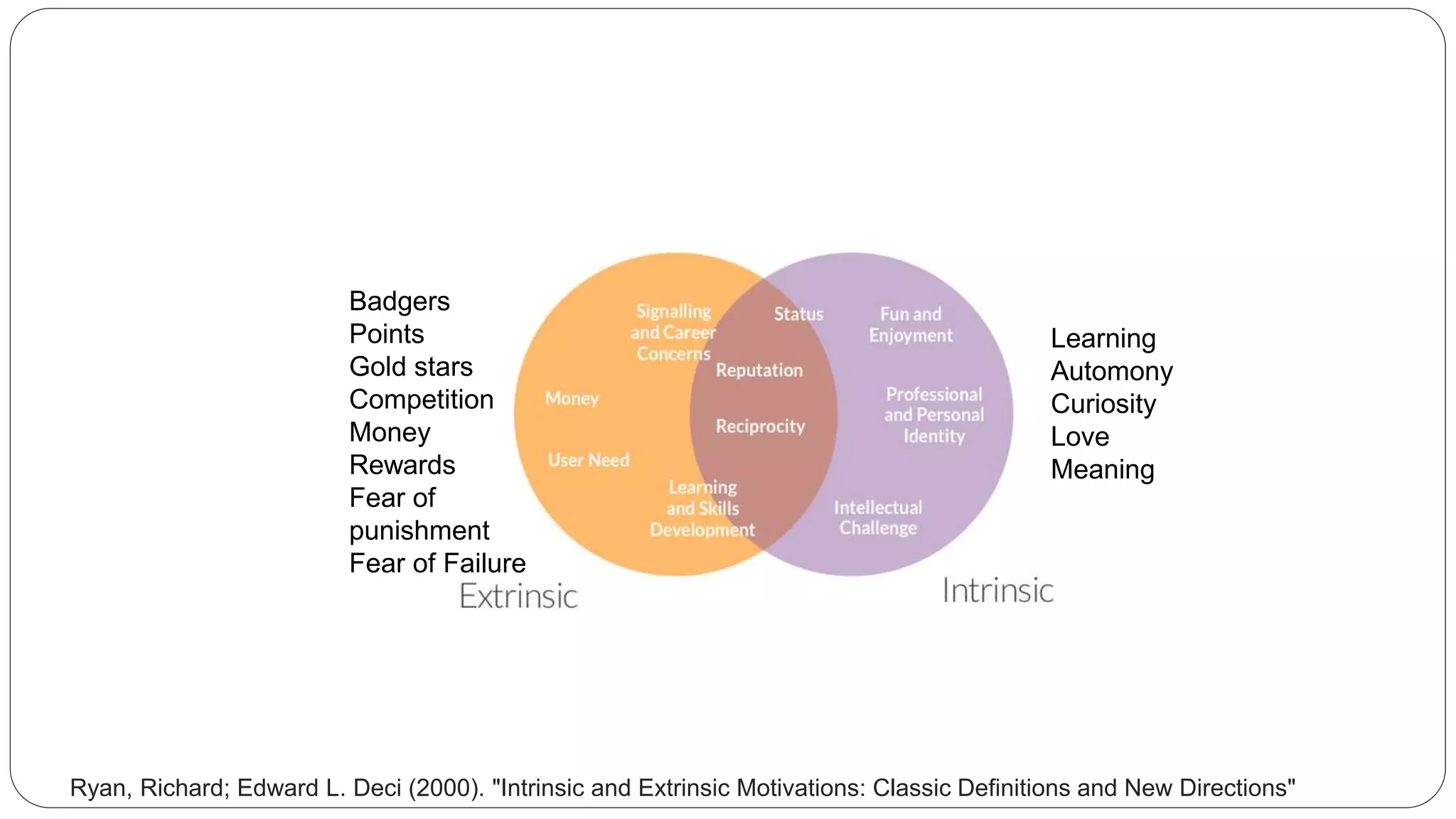
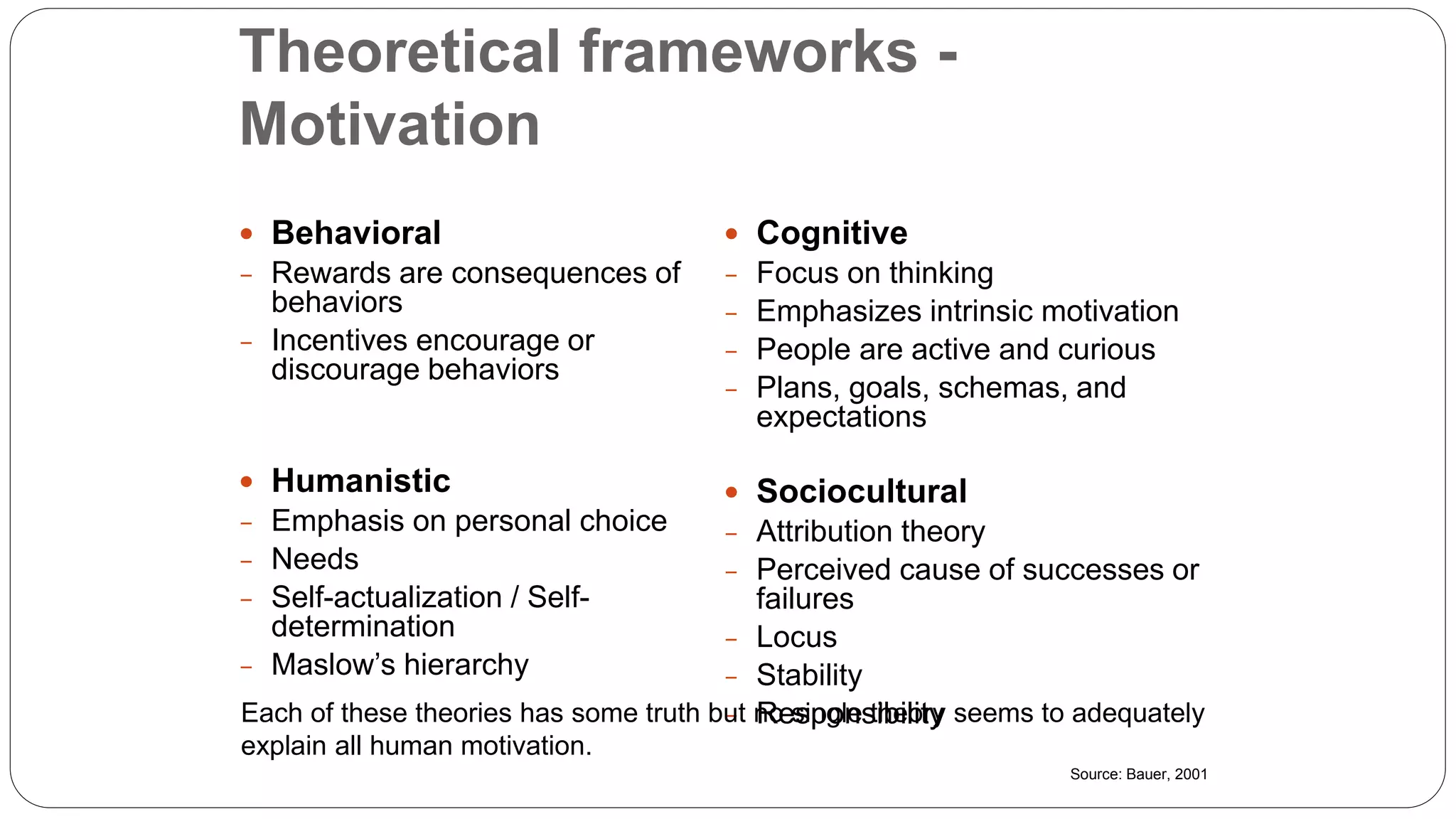
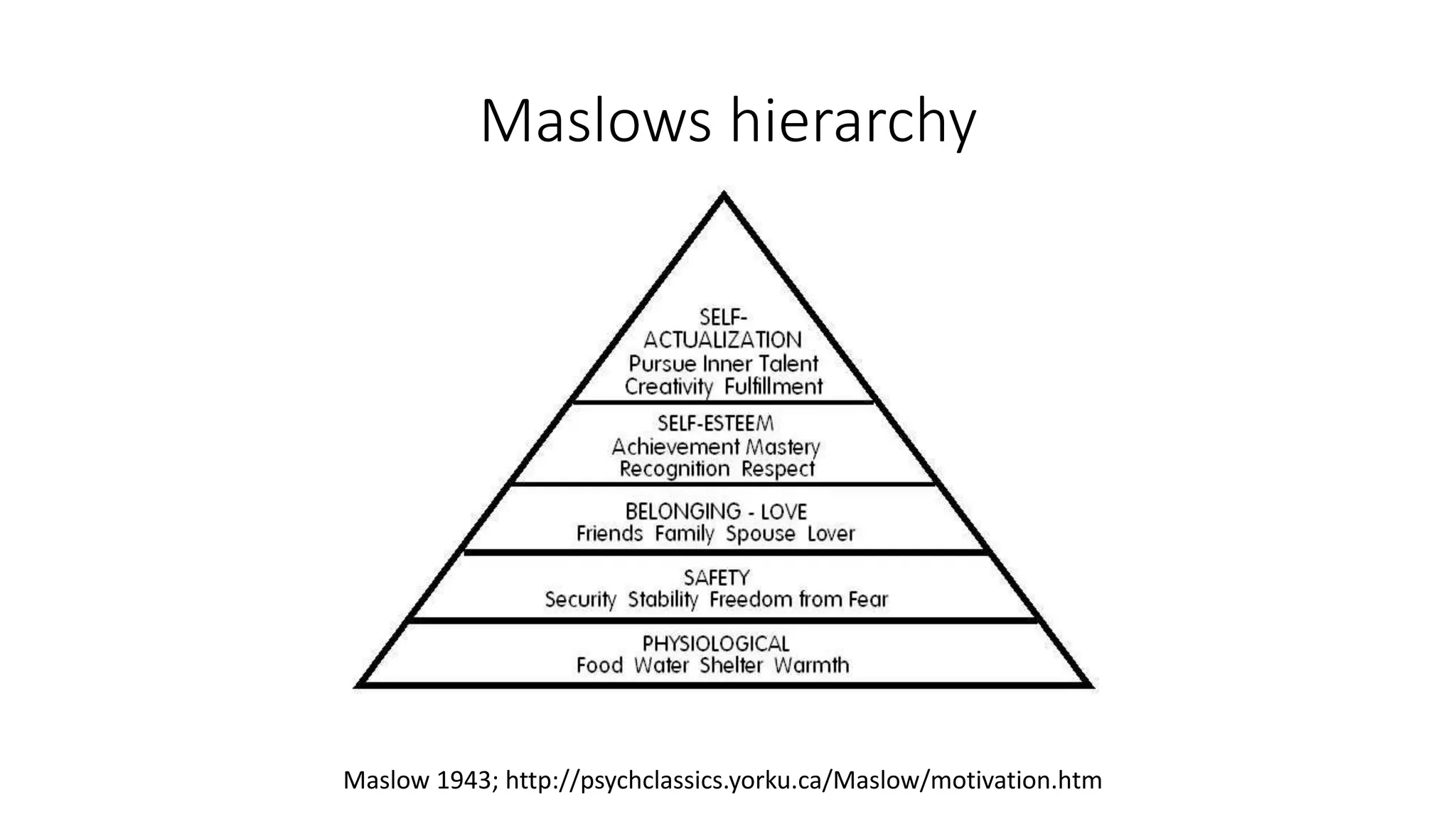
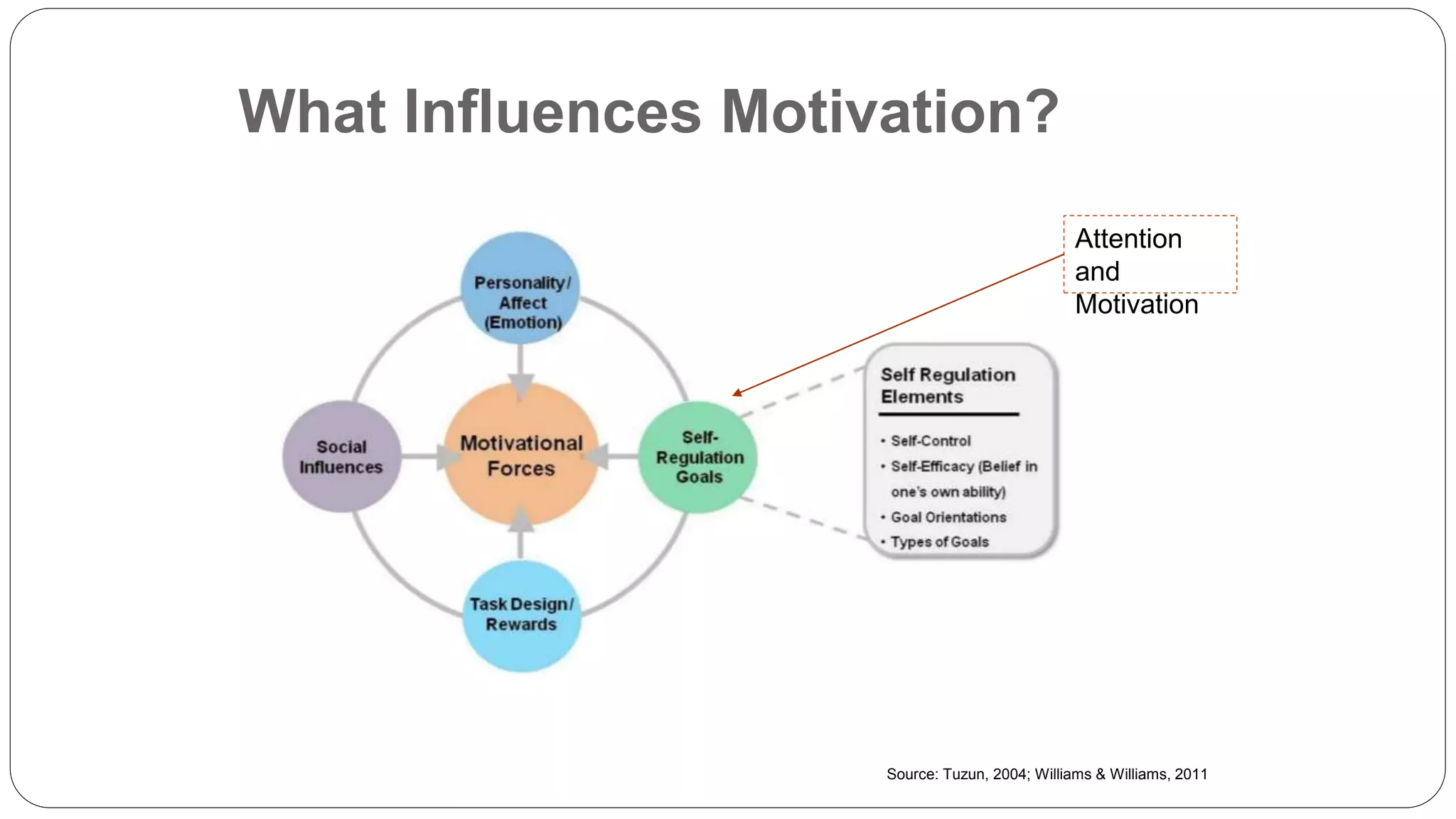
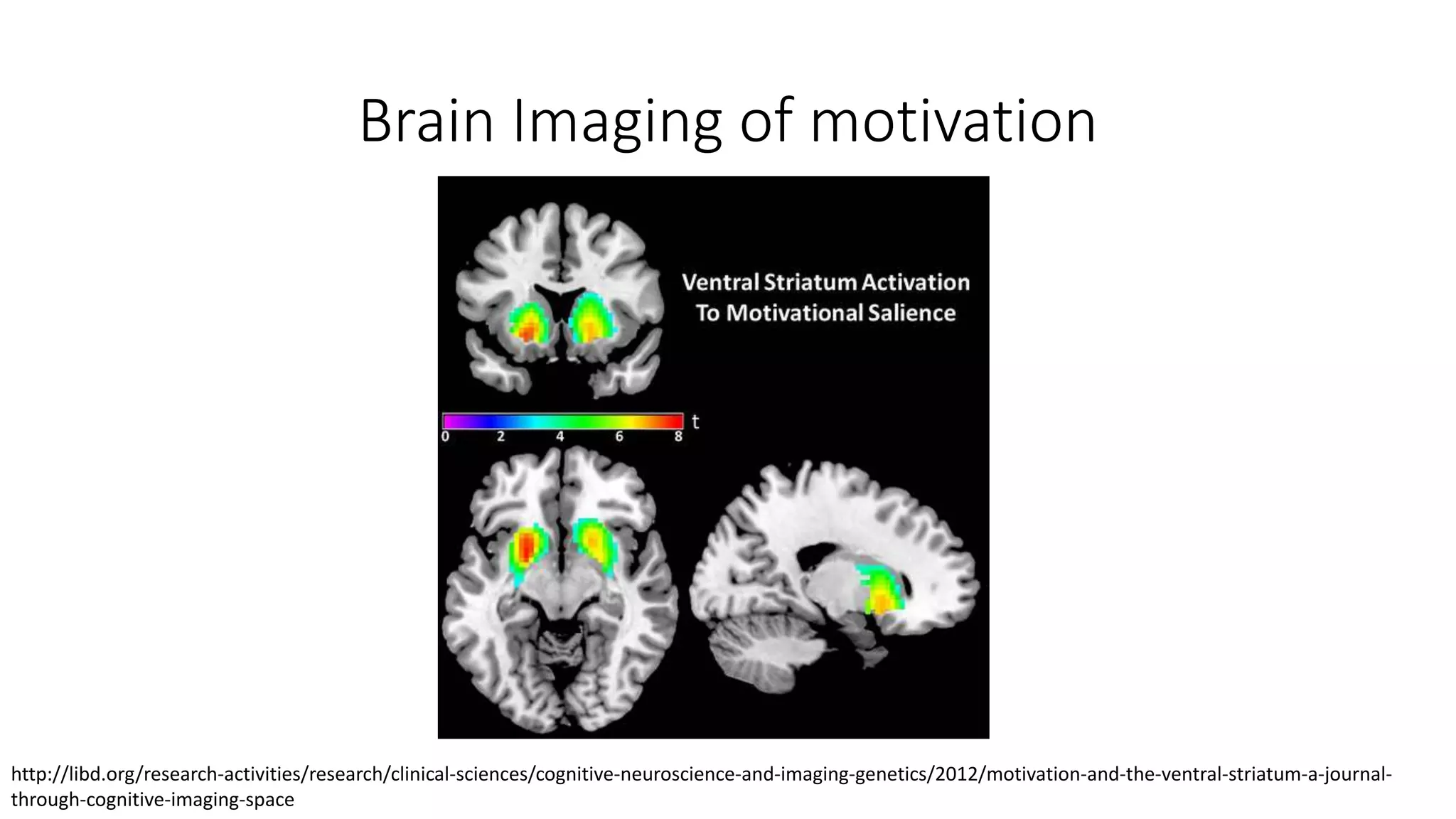
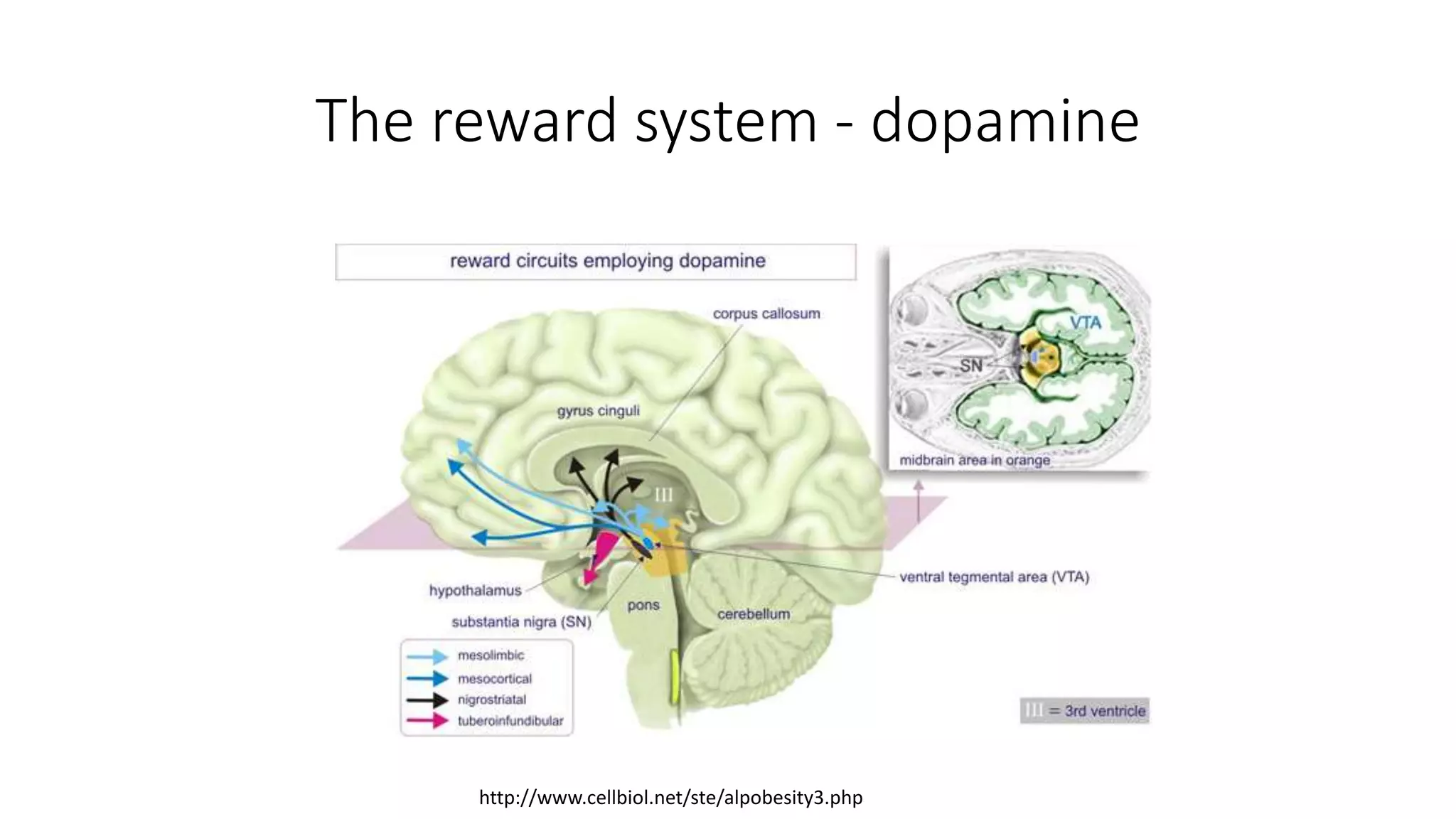
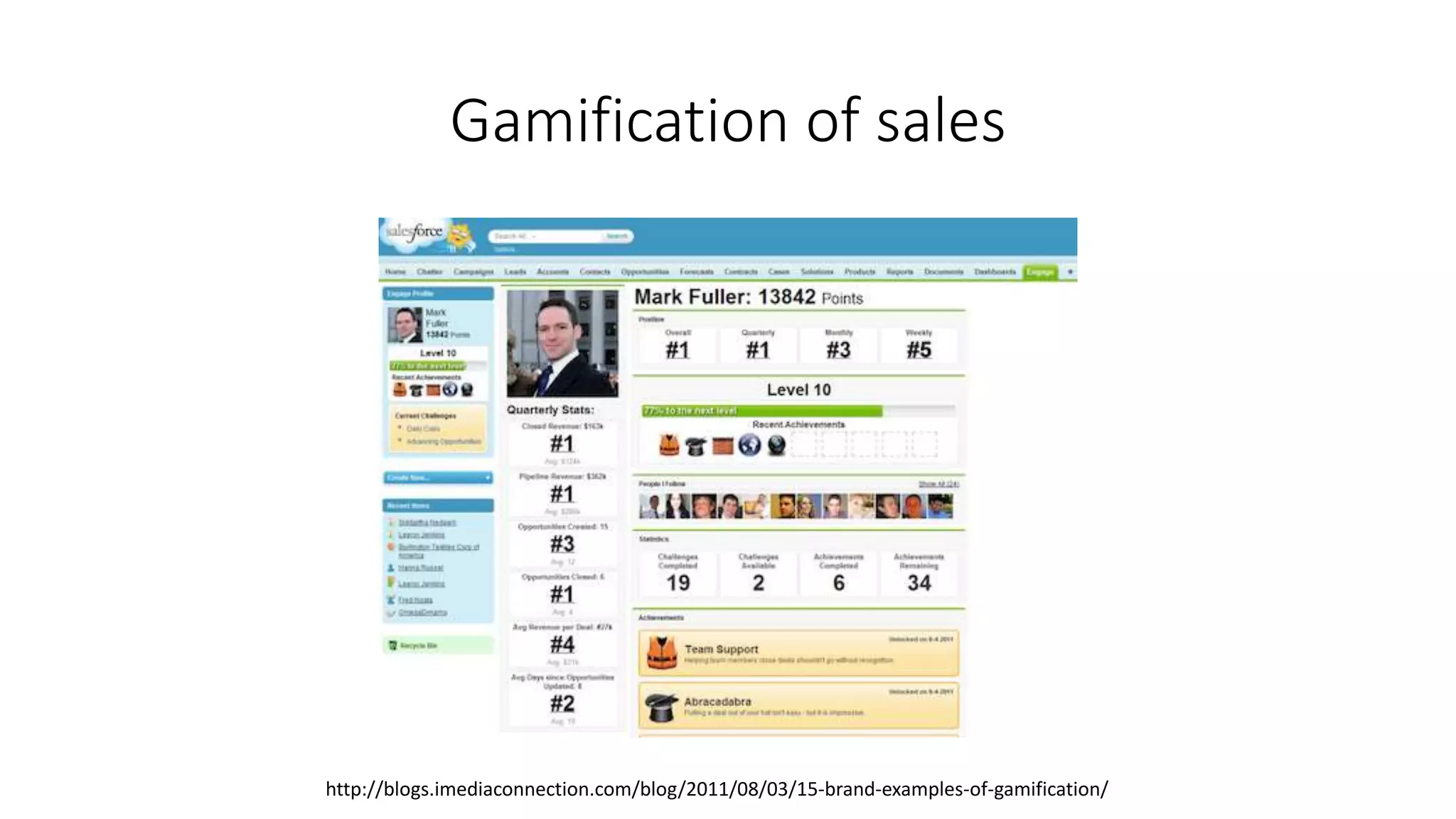
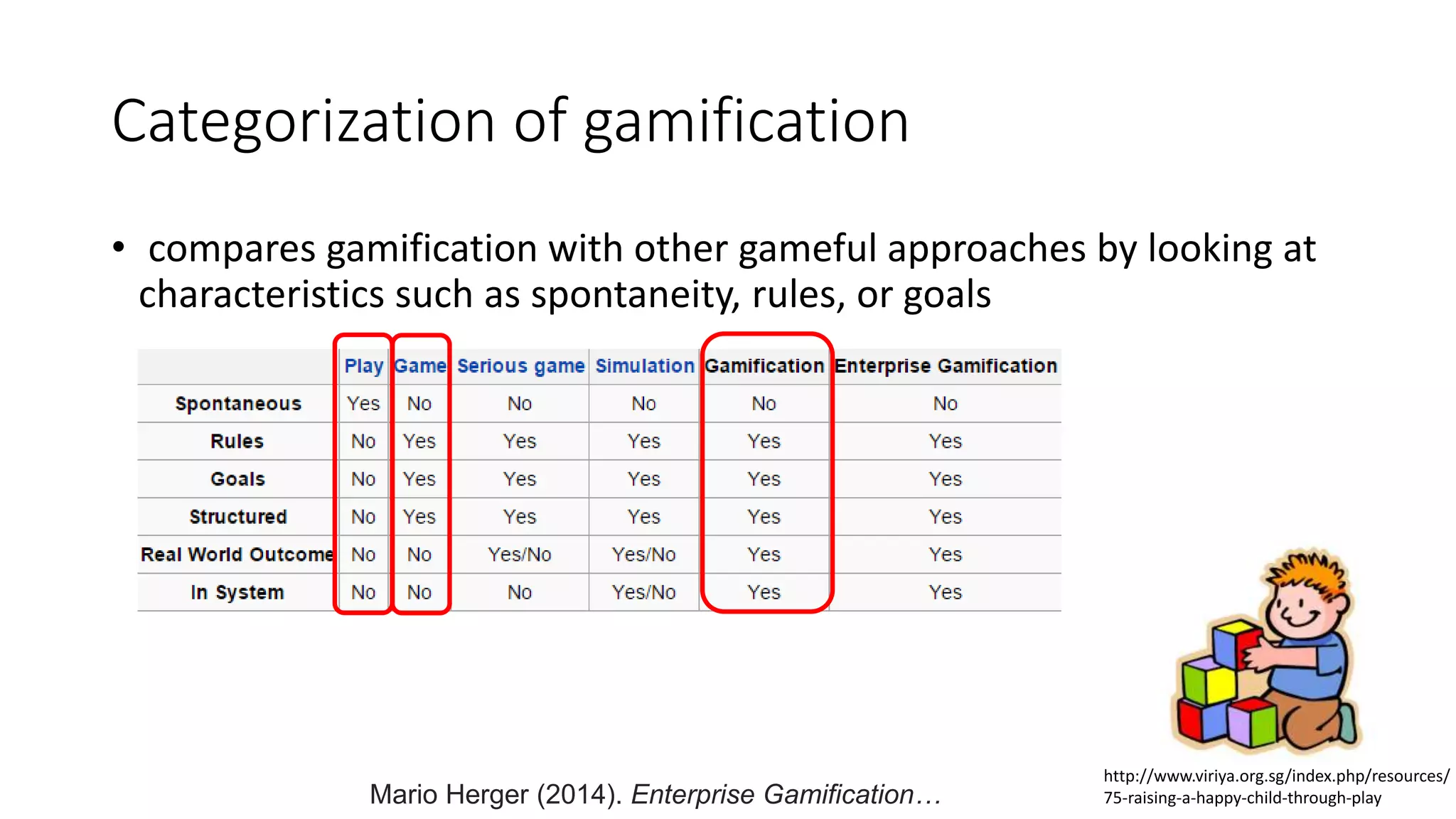
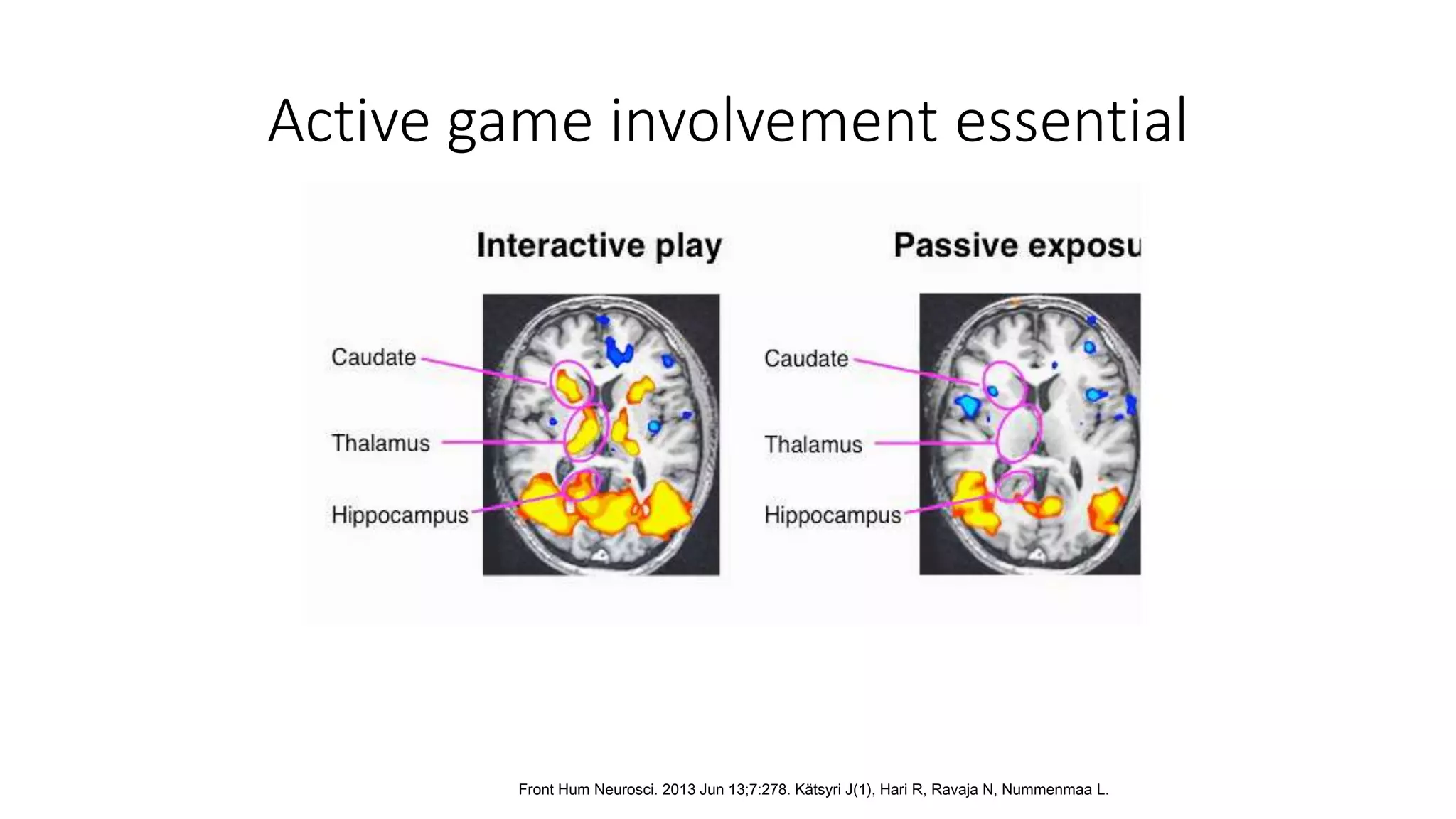
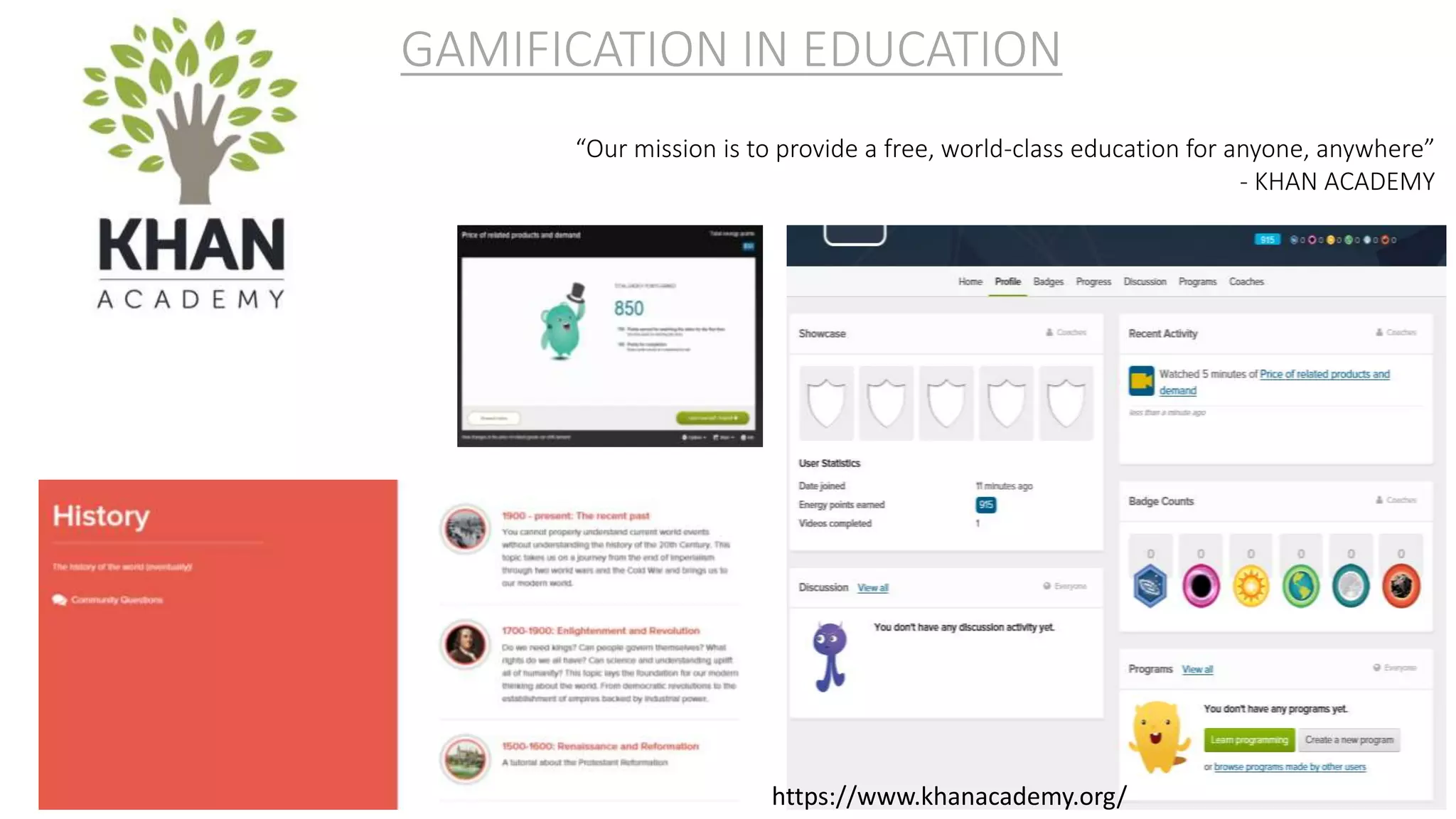
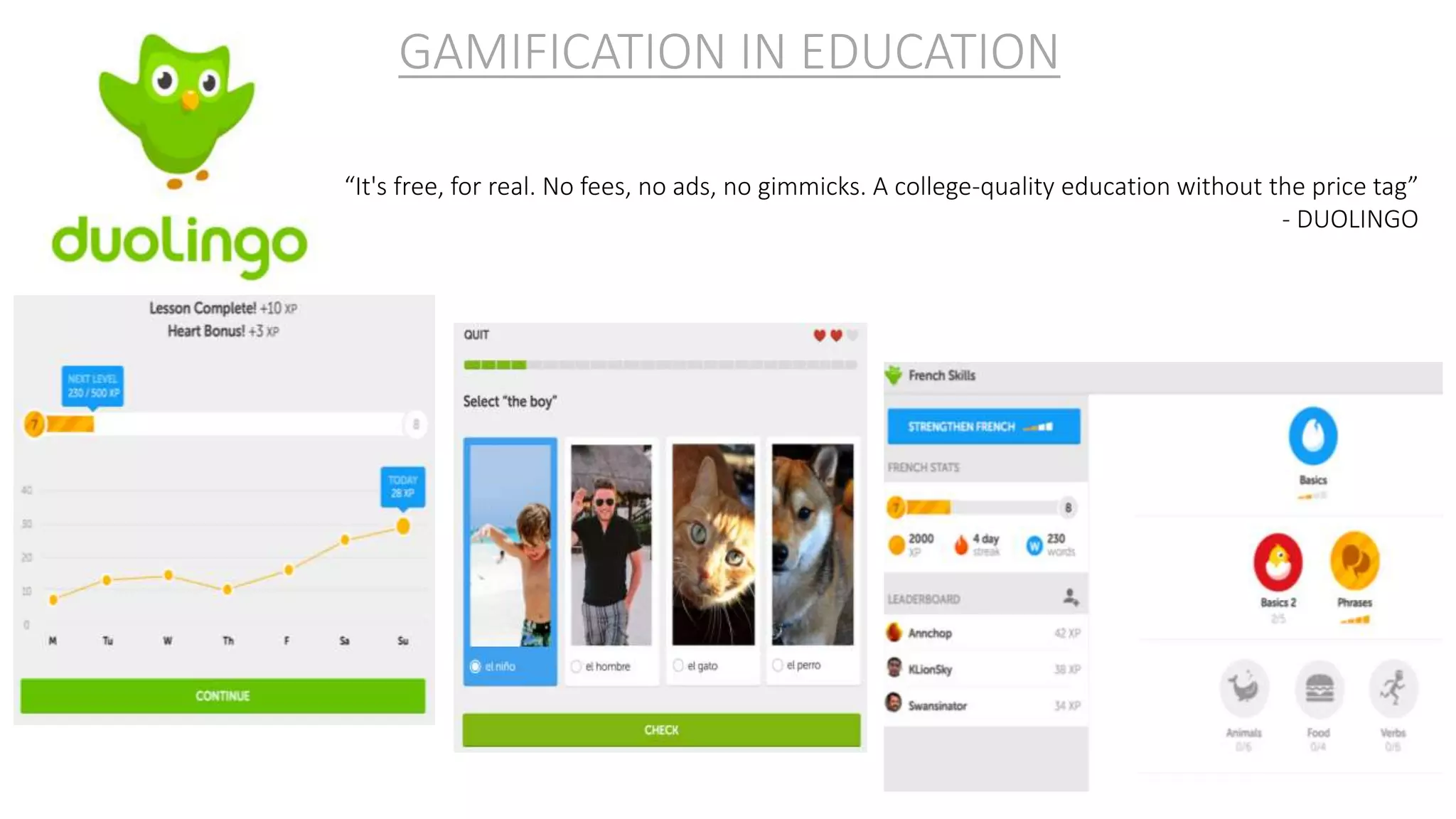
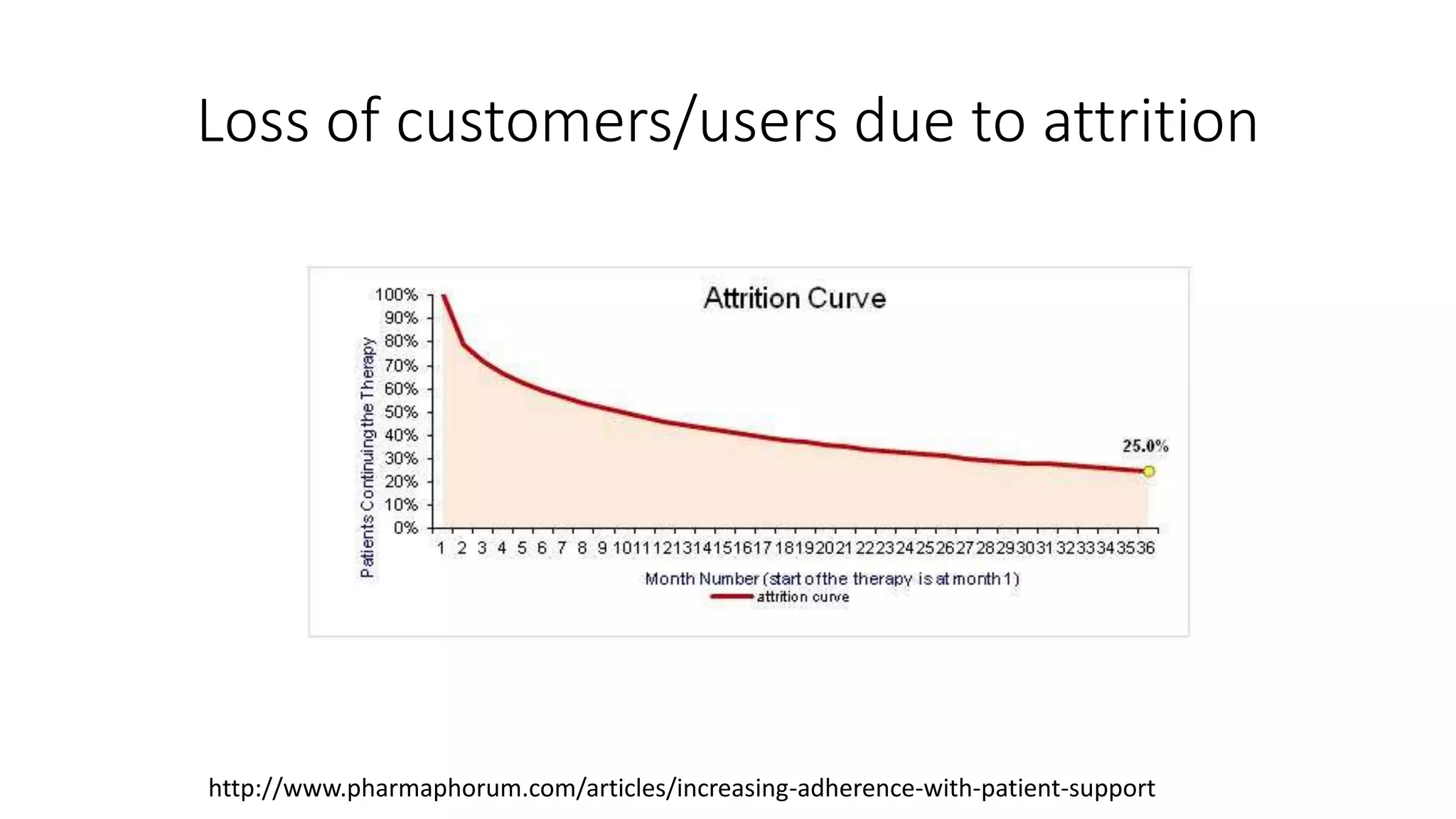
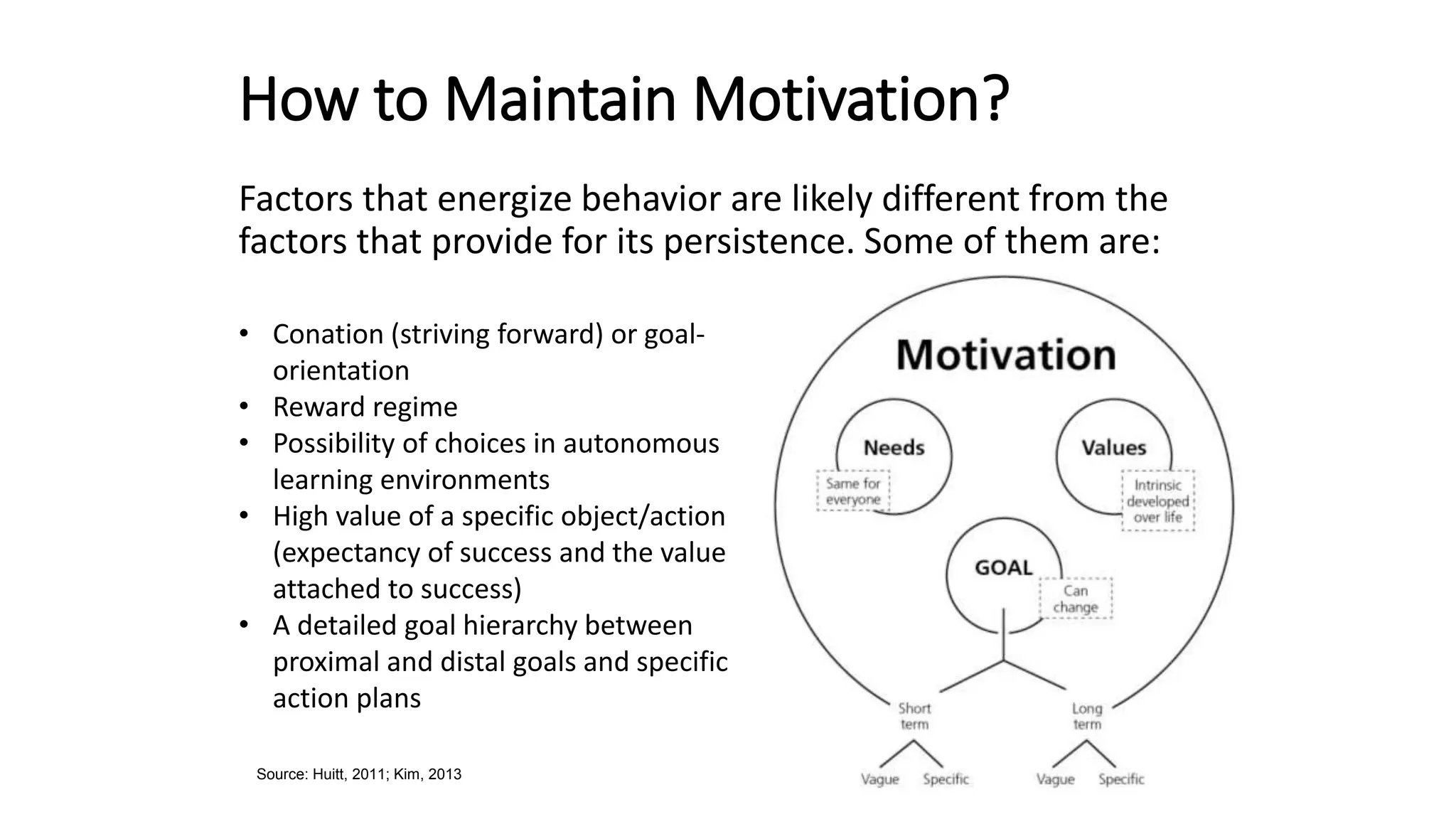
The document discusses gamification, defined as the use of game mechanics in non-game contexts to engage users in learning, innovation, and productivity. It explores the concept of motivation, its components, and how gamification techniques can enhance educational experiences by fostering intrinsic motivation and student engagement. Additionally, it addresses the benefits, criticisms, and potential future use of gamification in various sectors, including education and employee productivity.