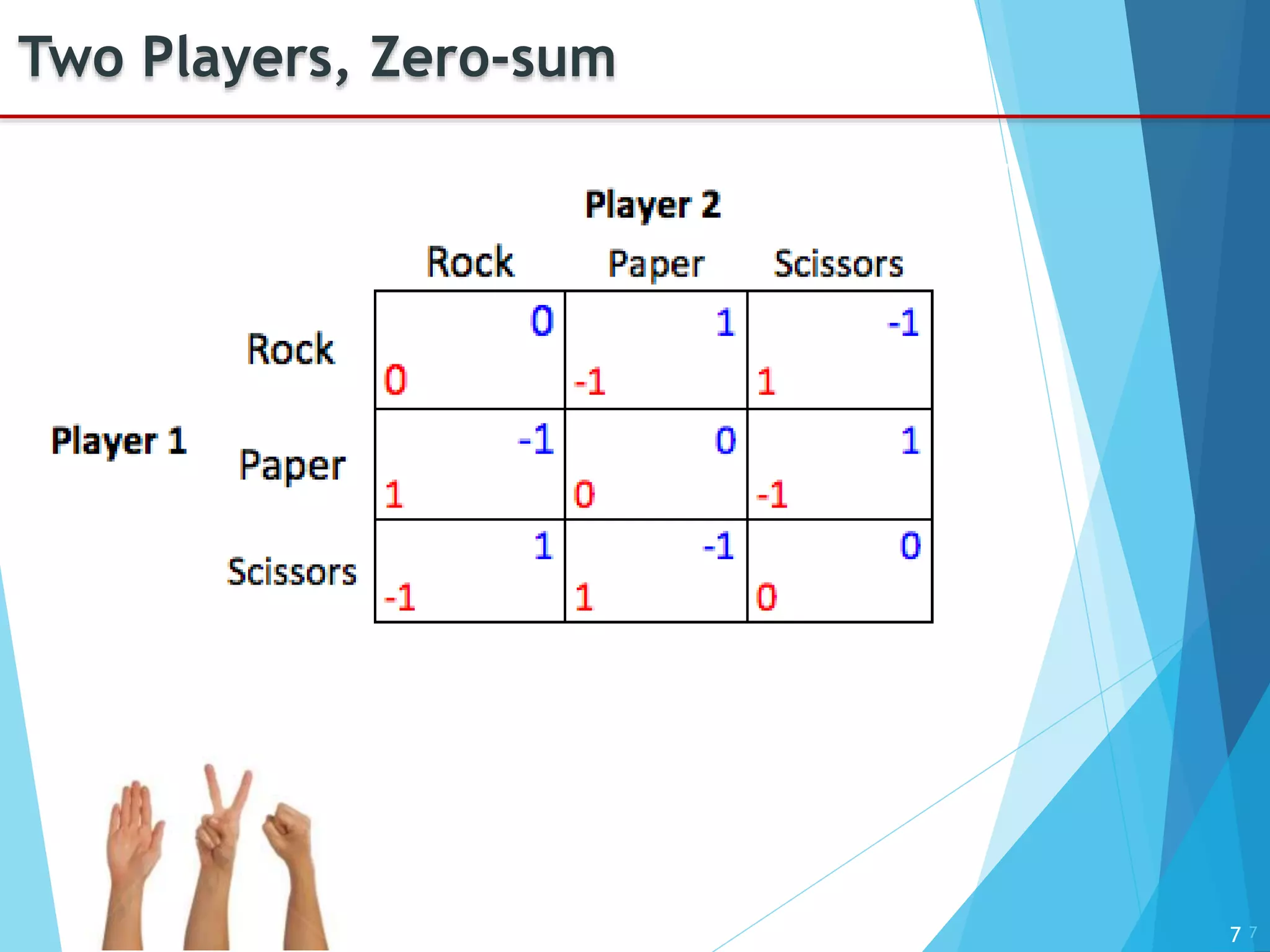
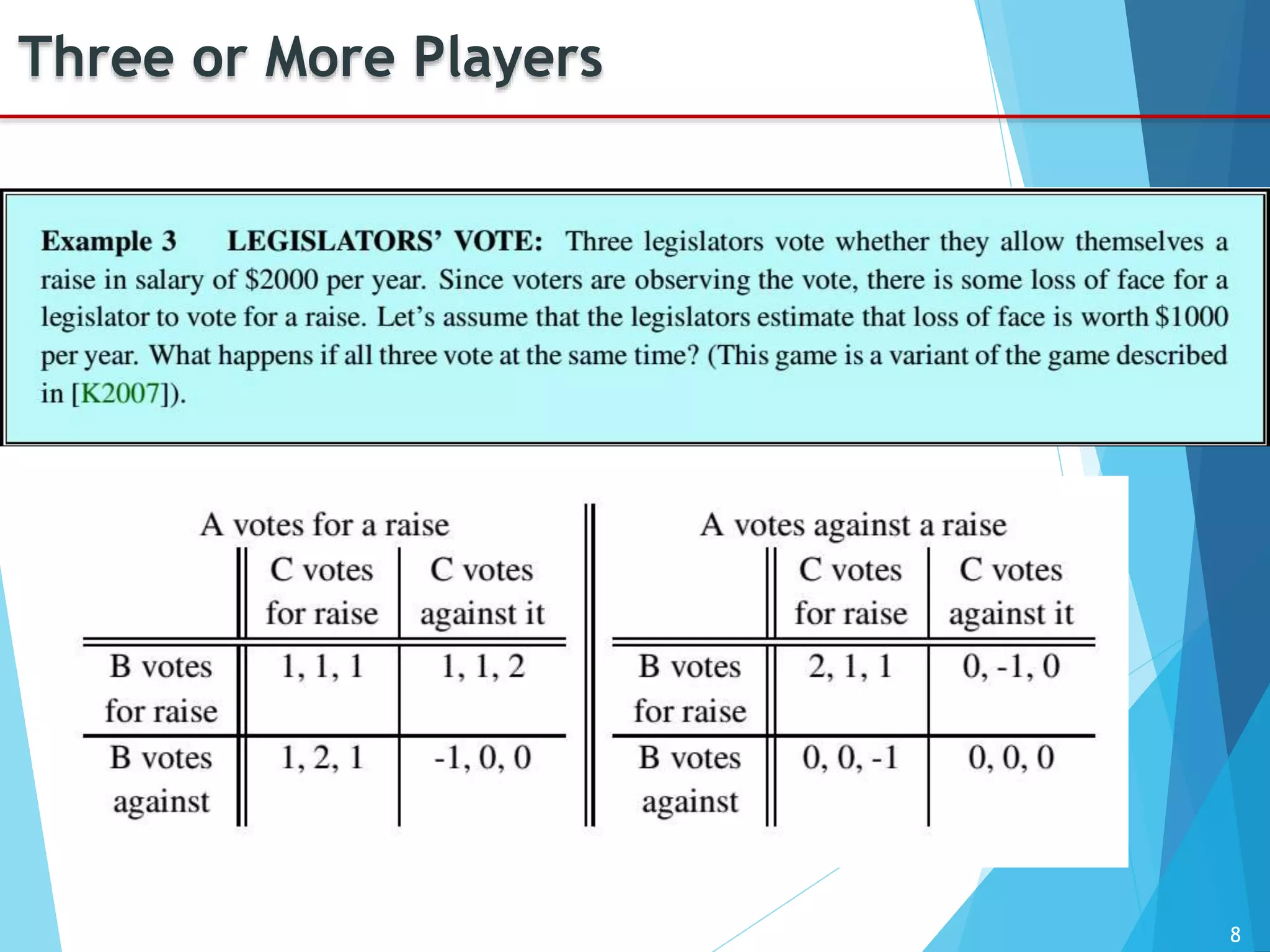
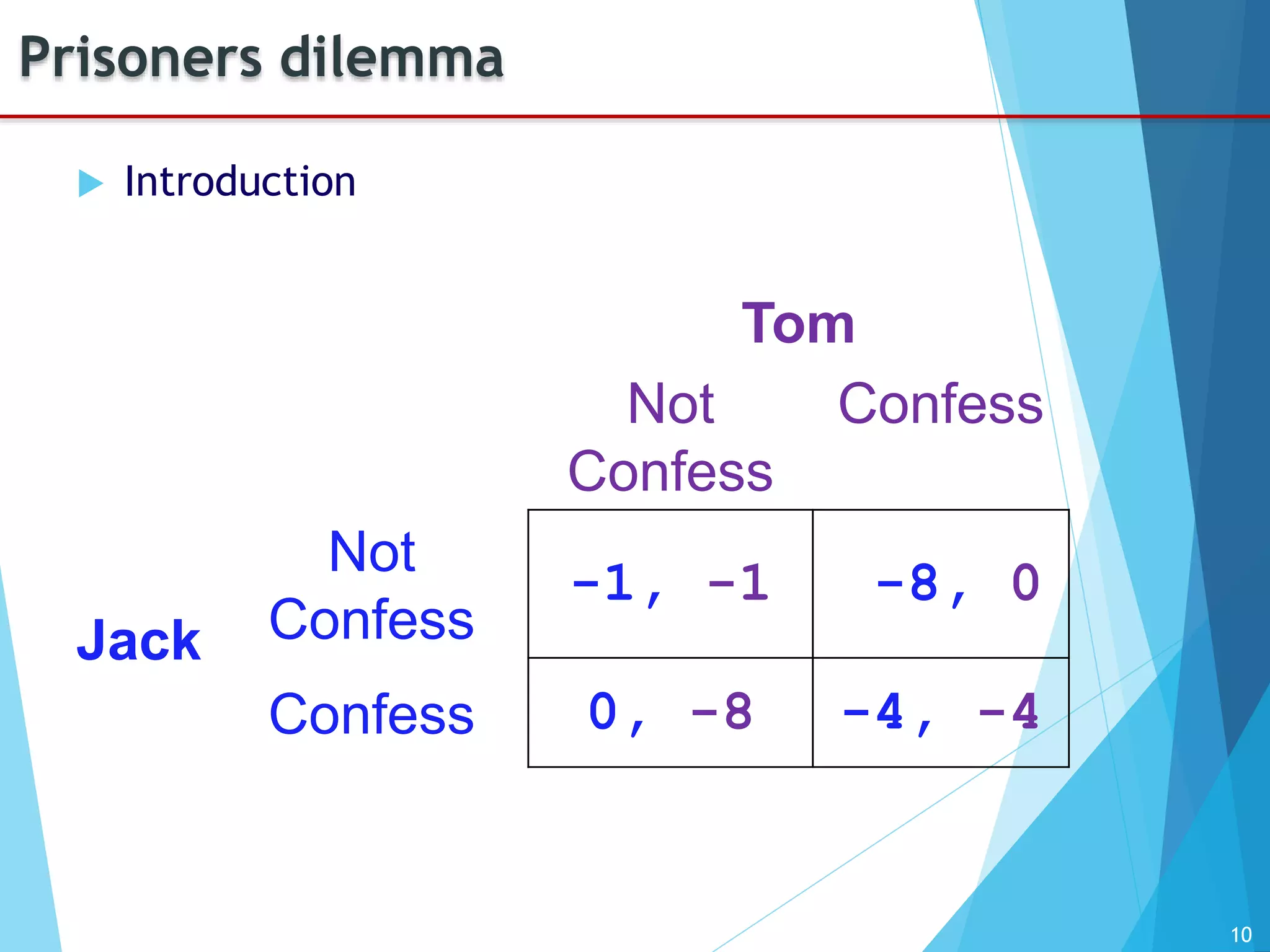
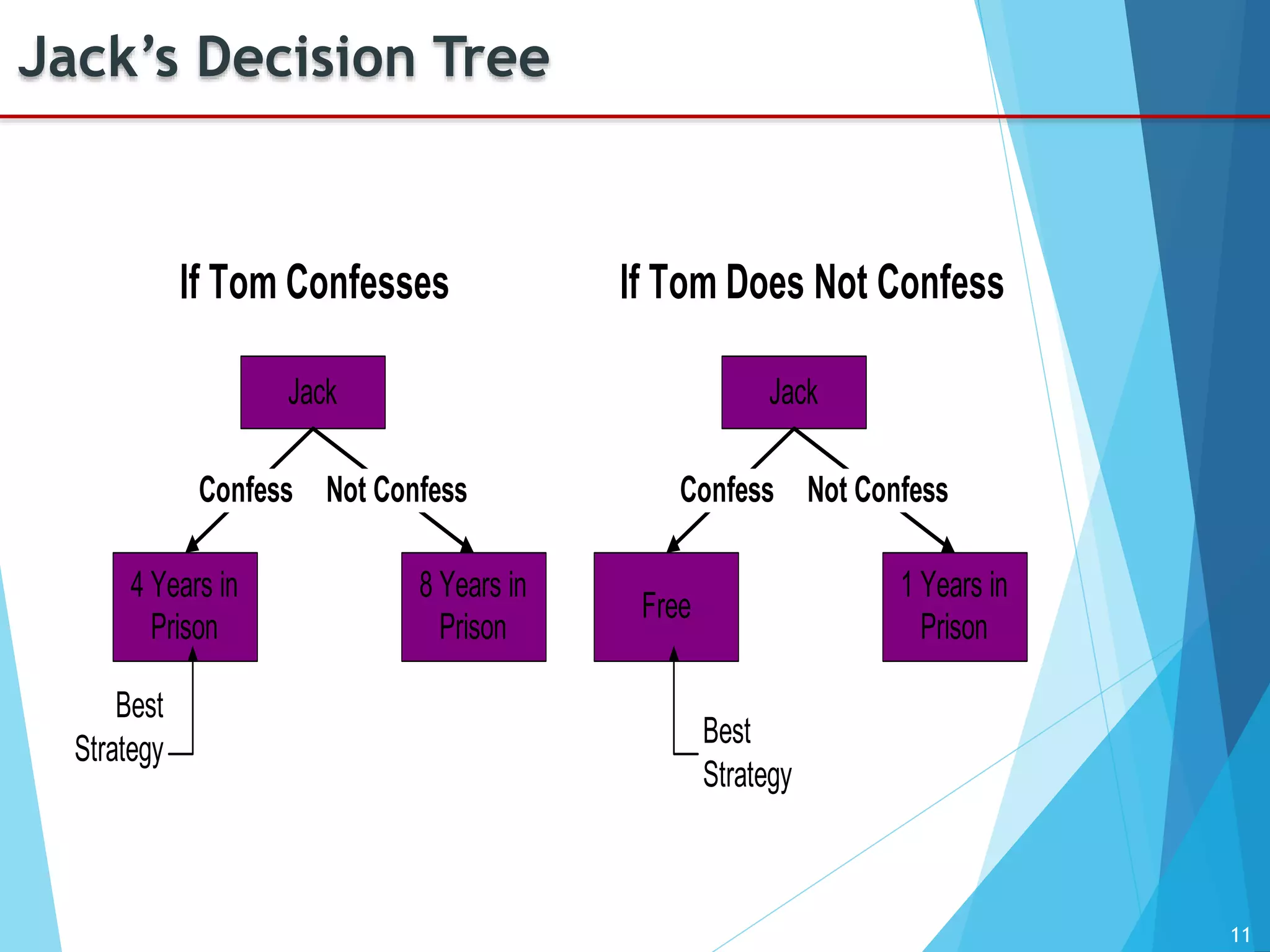
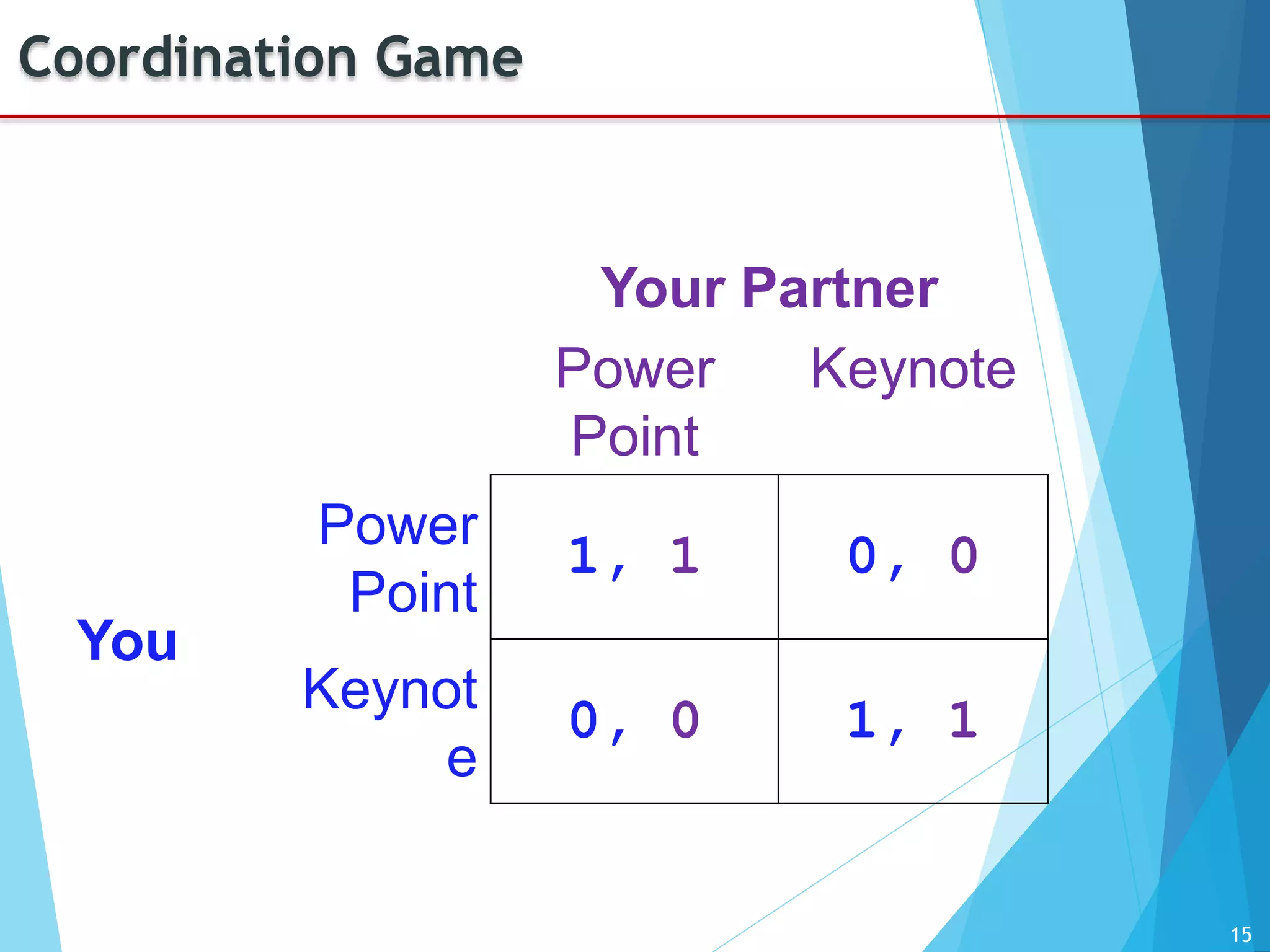
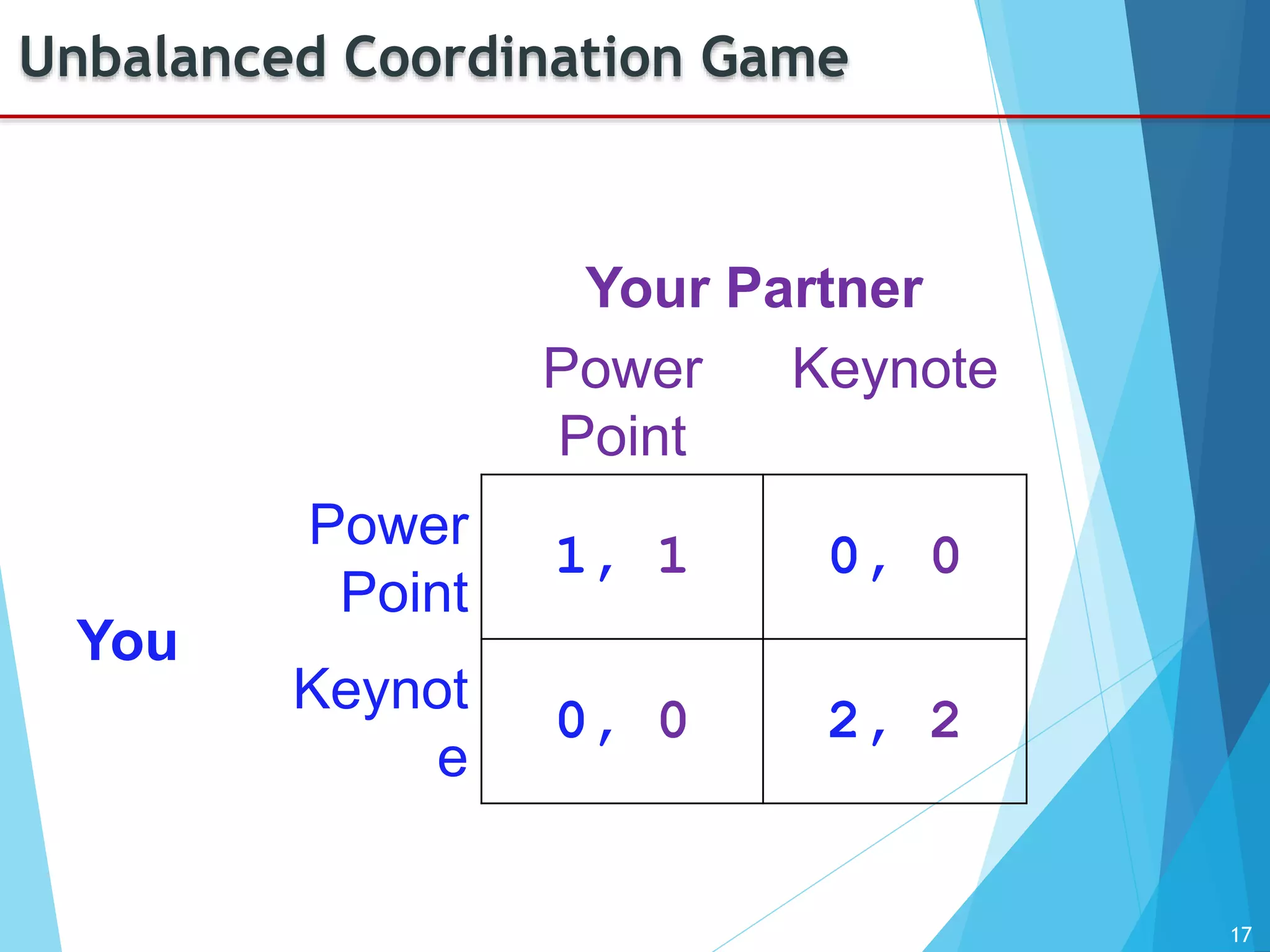
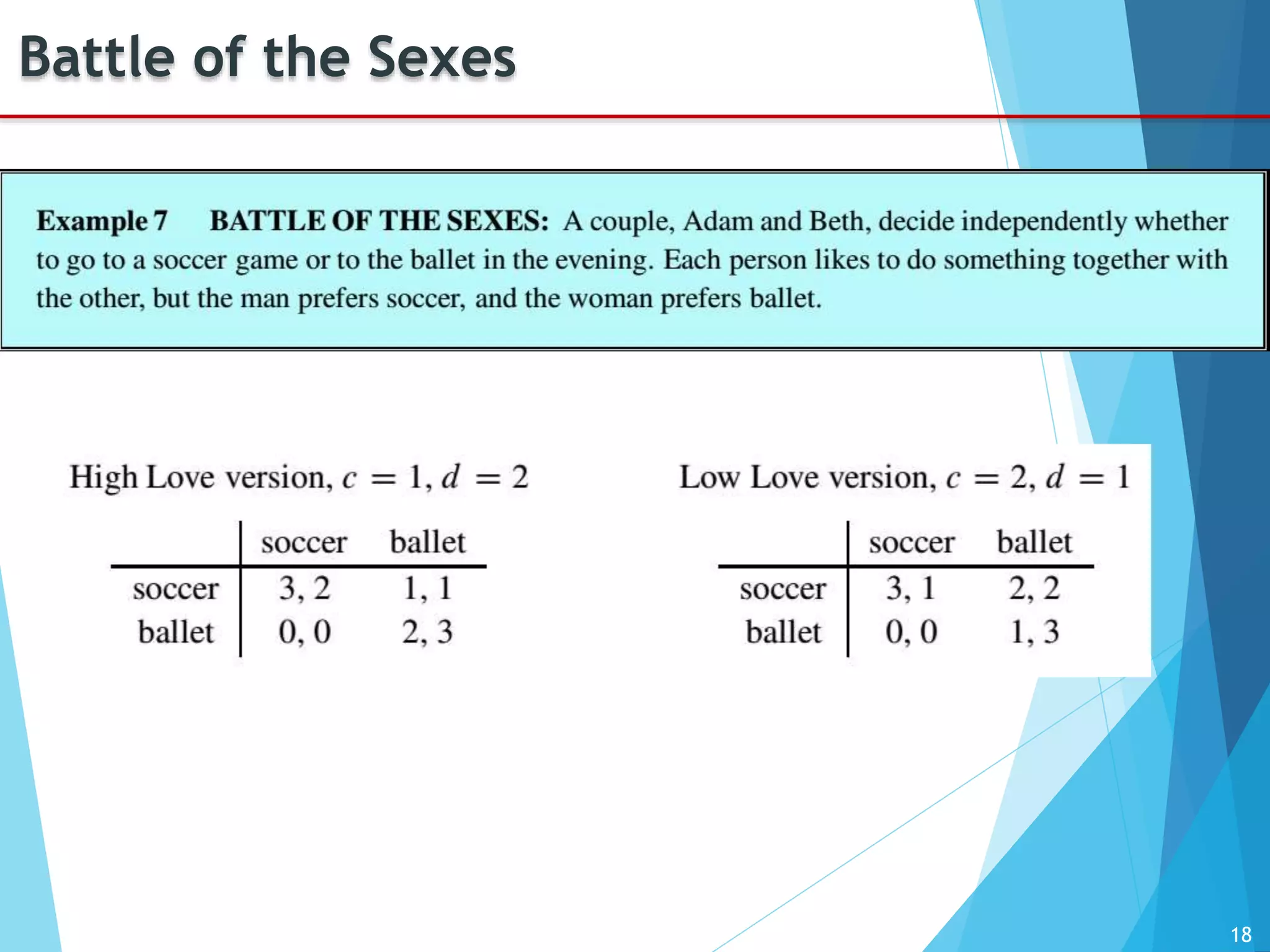
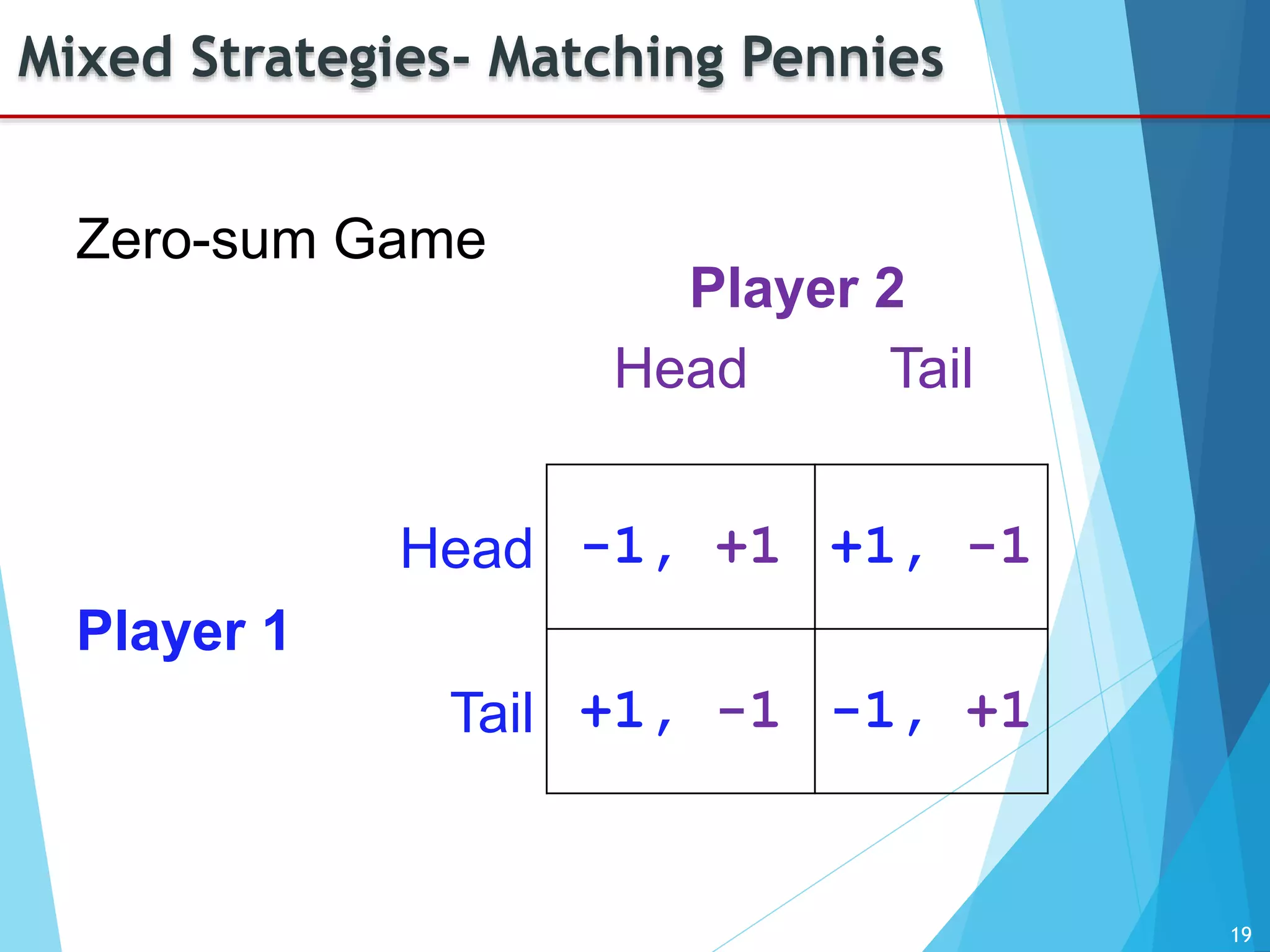
The document provides an introduction to game theory, detailing its history, applications, and key concepts such as the prisoner's dilemma, dominant strategies, and Nash equilibrium. It highlights the interdisciplinary nature of game theory, developed since the 1920s, and its relevance in various fields including economics, politics, and sports. The document also explores different types of games and their classifications based on player interaction and information availability.