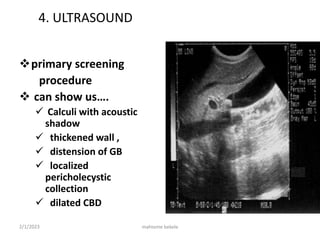
This document discusses gall bladder disease, including common diseases like cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. It identifies the gall bladder's location and function. Symptoms of gall bladder disease are outlined, along with risk factors, pathogenesis, investigations, and management options. Conservative and definitive treatments are described for conditions like acute cholecystitis and stones in the common bile duct.