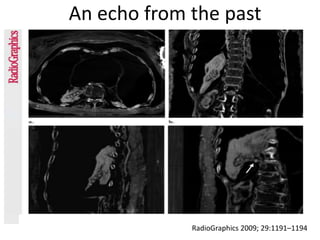
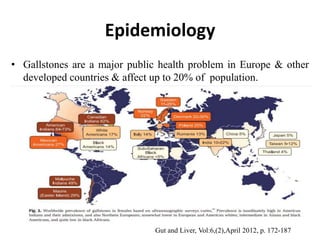
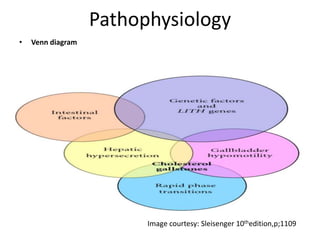
1) Gallbladder stones, or cholelithiasis, affect up to 20% of populations in developed countries. Risk factors include age, diet, rapid weight loss, certain drugs, obesity, and diseases of the liver and bile ducts.
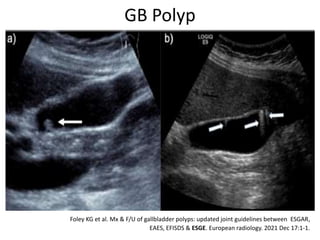
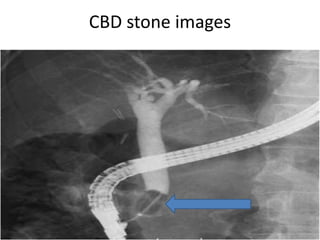
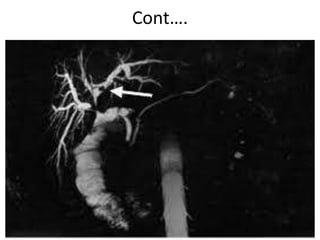
2) Gallbladder stones are usually diagnosed using abdominal ultrasound, while MRCP or EUS may be used if ultrasound is negative but clinical suspicion remains high. Complications include cholecystitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis, and fistula formation.
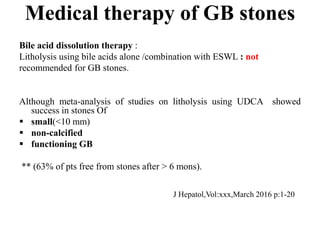
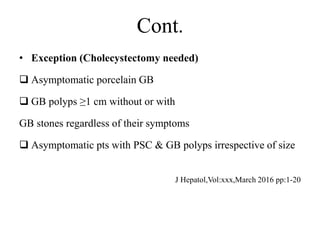
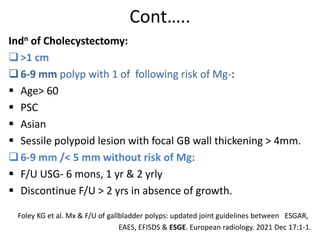
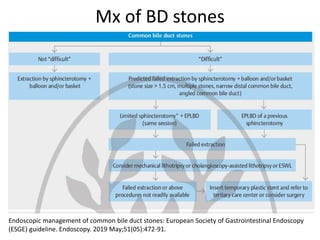
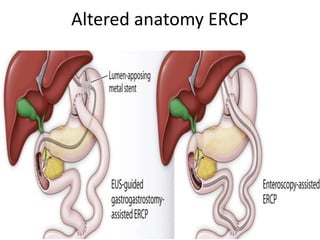
3) Treatment of gallbladder stones is typically laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic stones. Medical dissolution therapy is not usually recommended. For bile duct stones, endoscopic sphincterotomy and