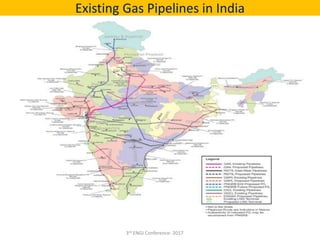
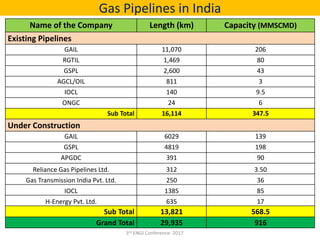
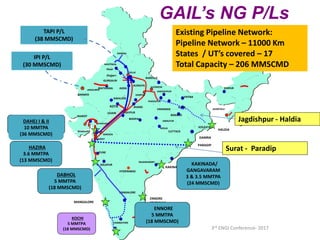
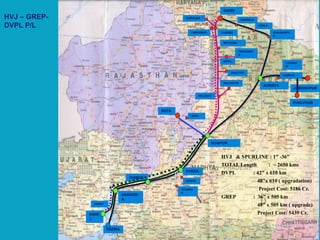
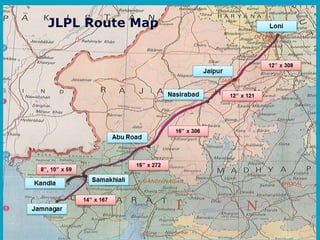
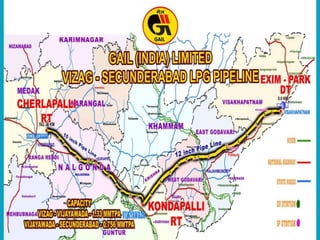
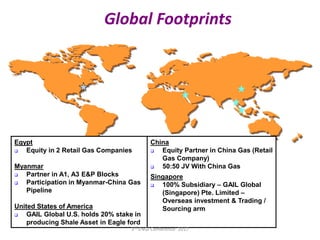
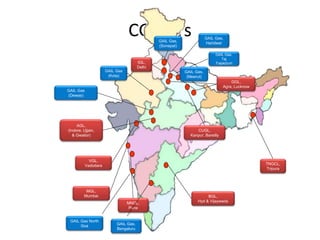
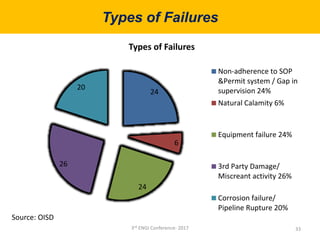
This document summarizes a presentation on safety and integrity measures for natural gas pipelines in India. It discusses the importance of gas pipelines, existing pipeline infrastructure in India, and safety considerations in pipeline design and operations. It focuses on GAIL's pipeline network and safety practices, including following national and international design standards, installing remotely operated valves and pressure safety valves, corrosion protection, emergency response planning, and 24/7 monitoring of pipelines.