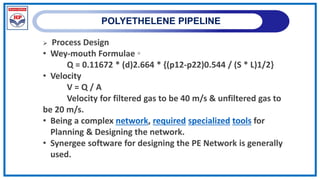
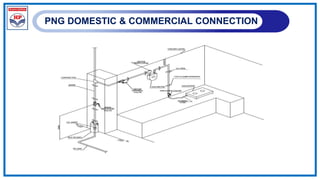
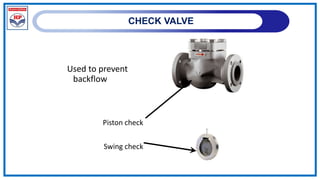
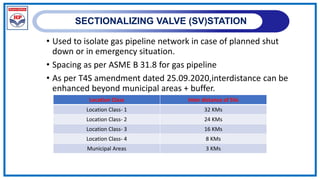
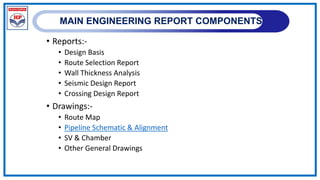
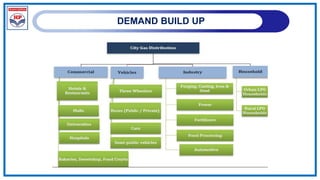
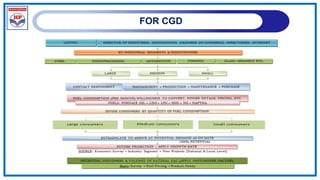
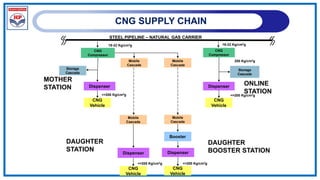
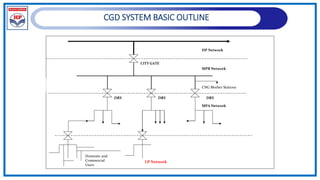
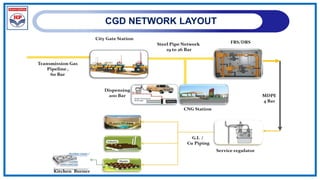
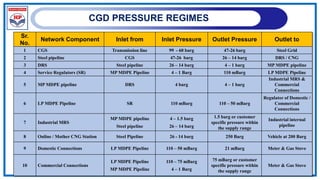
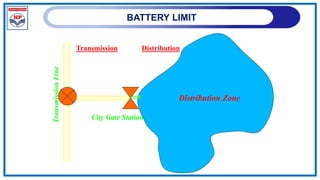
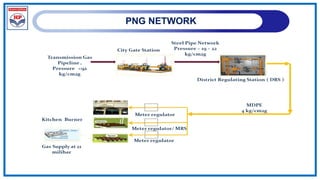
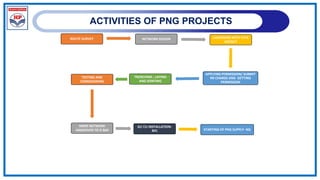
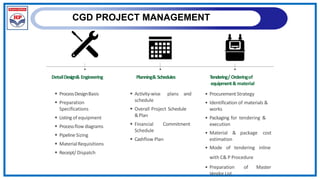
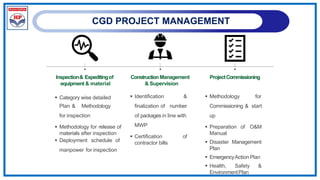
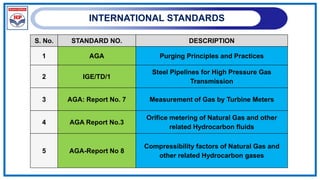
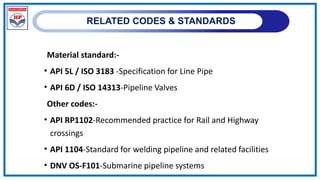
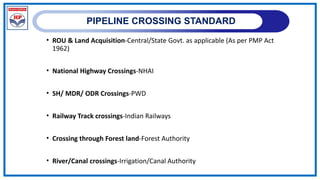
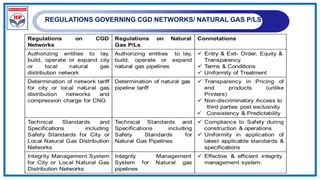
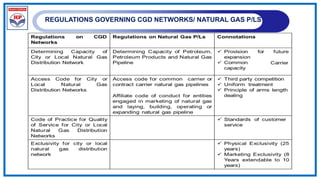
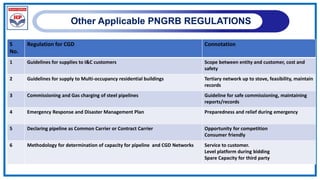
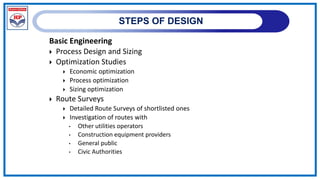
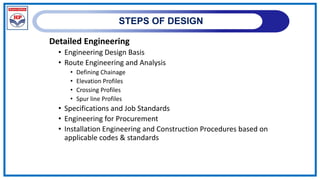
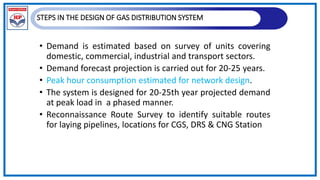
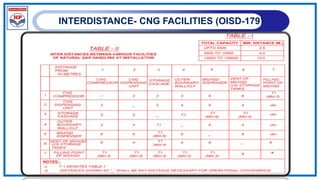
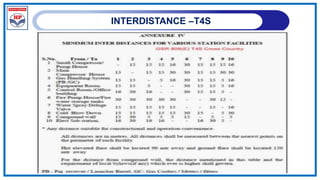
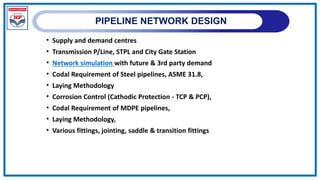
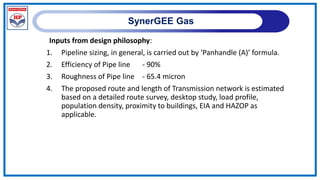
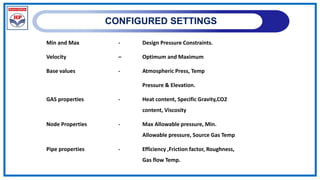
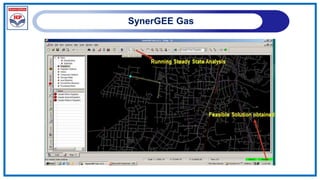
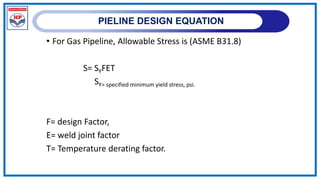
The document outlines a training program on City Gas Distribution (CGD) networks, focusing on system design, infrastructure, applicable codes and standards, and project management. It details the design considerations for pipeline networks, including high and medium-pressure systems, safety protocols, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, it emphasizes the steps involved in designing gas distribution systems, including demand forecasting, route surveys, and engineering practices.







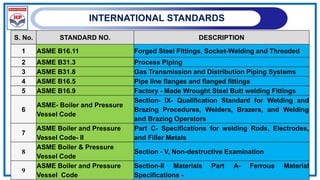
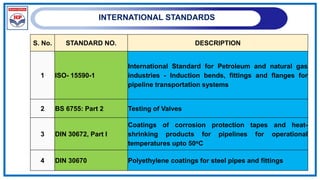
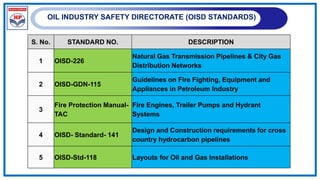
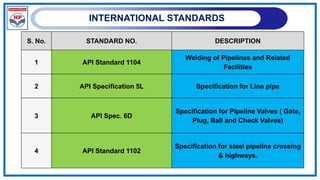








![POLYETHENELENE PIPELINE
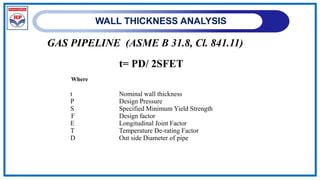
MRS(Minimum Required Strength)
The MRS value represents the long-term circumferential stress in the pipe under which
the break may occur after 50years at the earliest.
Stress = MRS/ C, where C is overall service coefficient
The minimum value of C for the material to be used for Gas application is 2.
MAOP(Max. allowableOperatingPressure)
MAOP= (20* MRS) / [C * (SDR-1)].
Standard Dimension Ratio
SDR= Dn / En
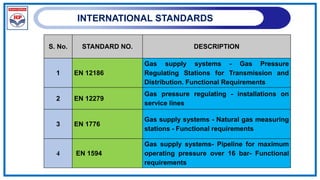
Standard followed by CGD entities - IS 14885:2001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refreshercgdnetworkdesign-240610234213-f55306b9/85/Refresher_City-Gas-network-Design-pptx-53-320.jpg)