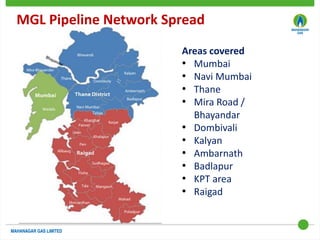
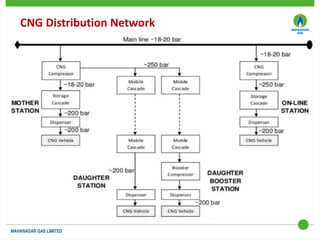
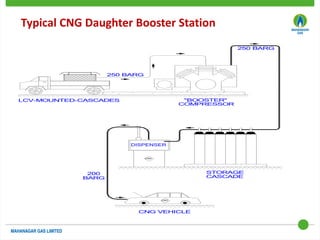
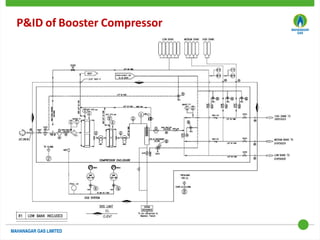
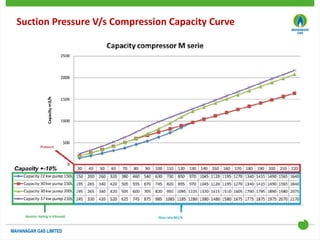
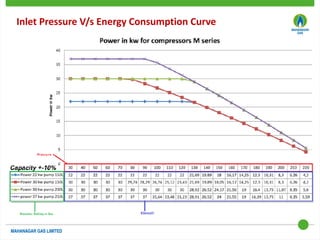
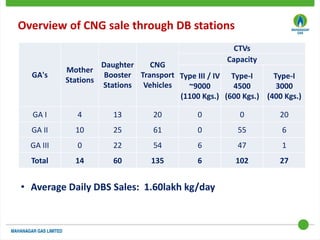
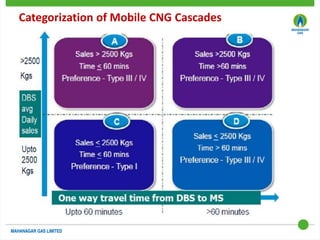
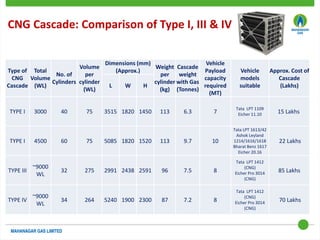
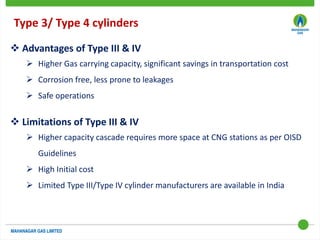
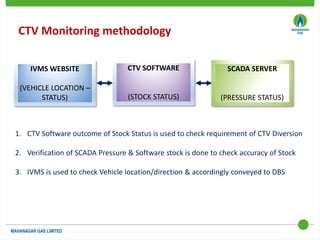
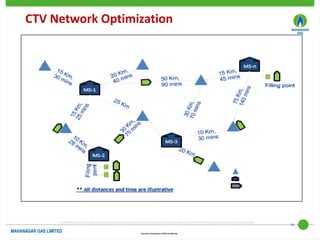
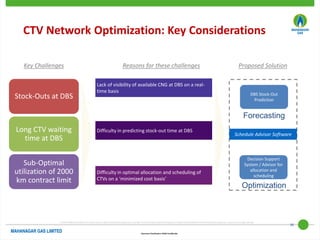
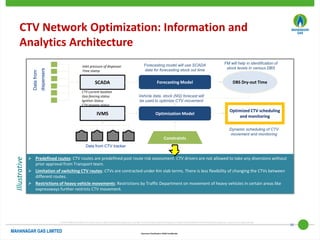
This document discusses Mahanagar Gas Limited's compressed natural gas (CNG) distribution network in Mumbai and surrounding areas. It outlines MGL's pipeline network and CNG daughter booster stations. It describes the types of mobile CNG cascades used (Type I, III, IV) and challenges related to operating daughter booster stations and transporting CNG via cascades, such as dependency on transport vehicles, transportation costs, and machine downtime due to remote locations. It also discusses actions taken to reduce instances when daughter booster stations run out of gas.