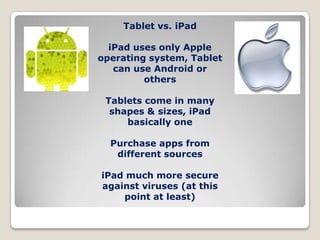
The document outlines the various types of mobile devices, including laptops, smartphones, e-readers, and tablets, emphasizing the importance of connectivity, operating systems, and features. It compares laptops and desktops, discusses the capabilities of smartphones, and details the characteristics of e-readers and tablets, along with considerations for purchasing devices. It also touches on portable music devices and storage options, providing advice on consumer choices.