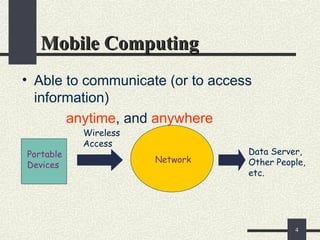
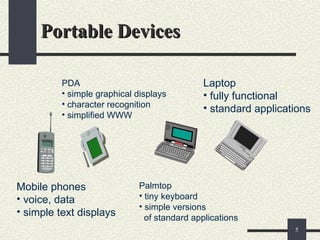
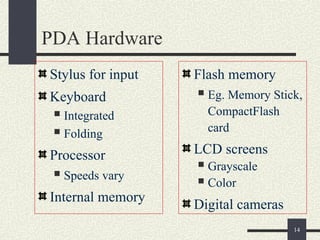
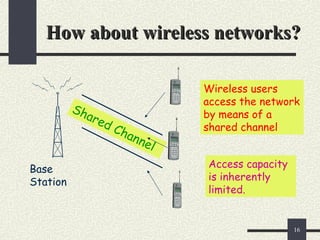
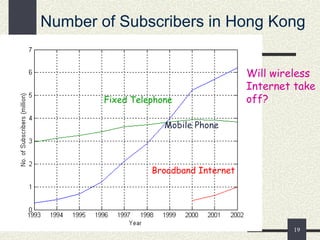
The document provides an overview of mobile computing, including definitions, types of portable devices such as mobile phones, PDAs, and laptops, along with their features and advantages. It highlights the capabilities of these devices to access information anywhere via wireless networks, while also acknowledging their limitations like battery life and connectivity issues. Additionally, it mentions various components and functionalities of devices like MP3 players, cell phones, and tablet PCs, as well as the role of wireless networks in mobile computing.