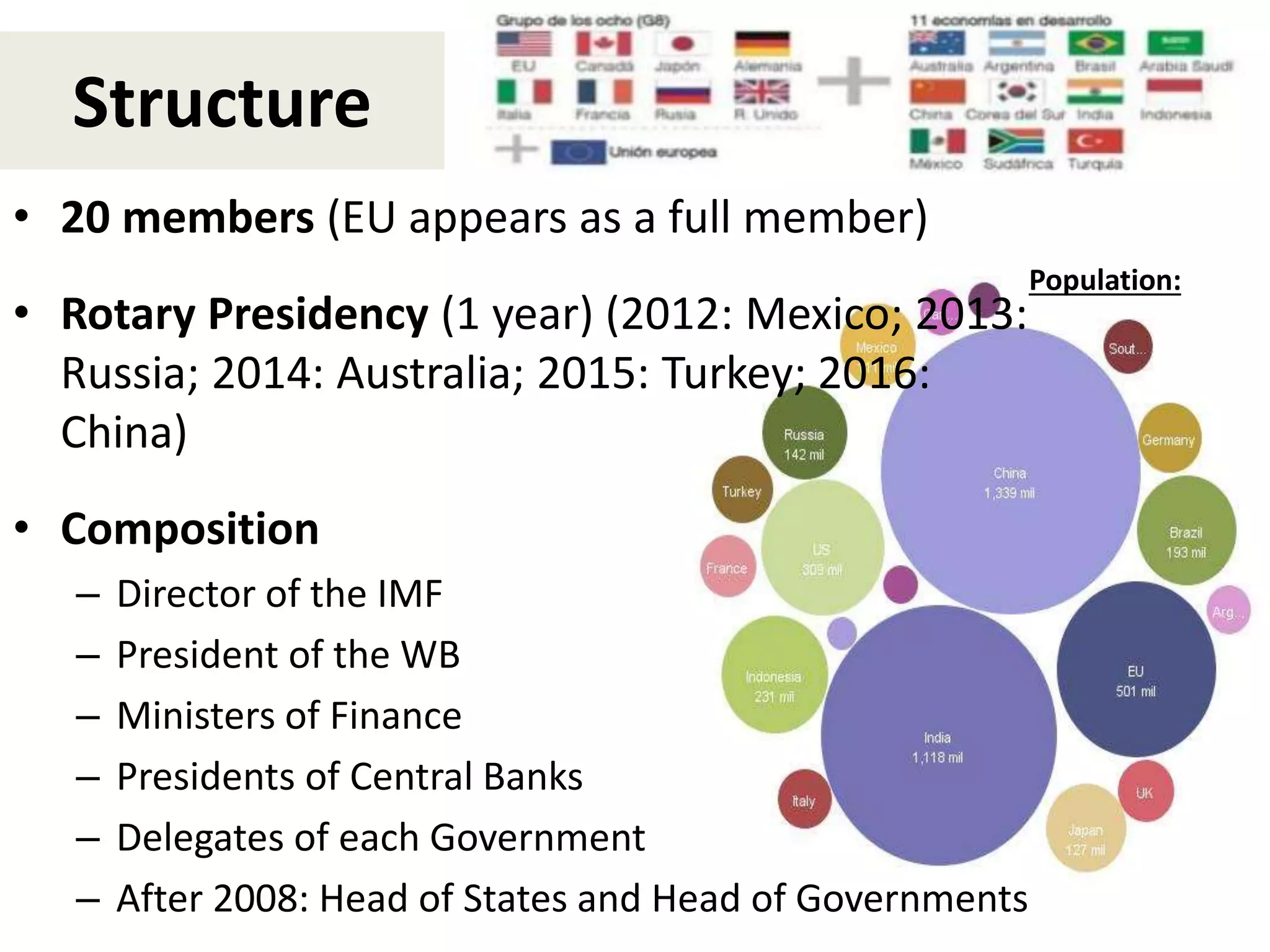
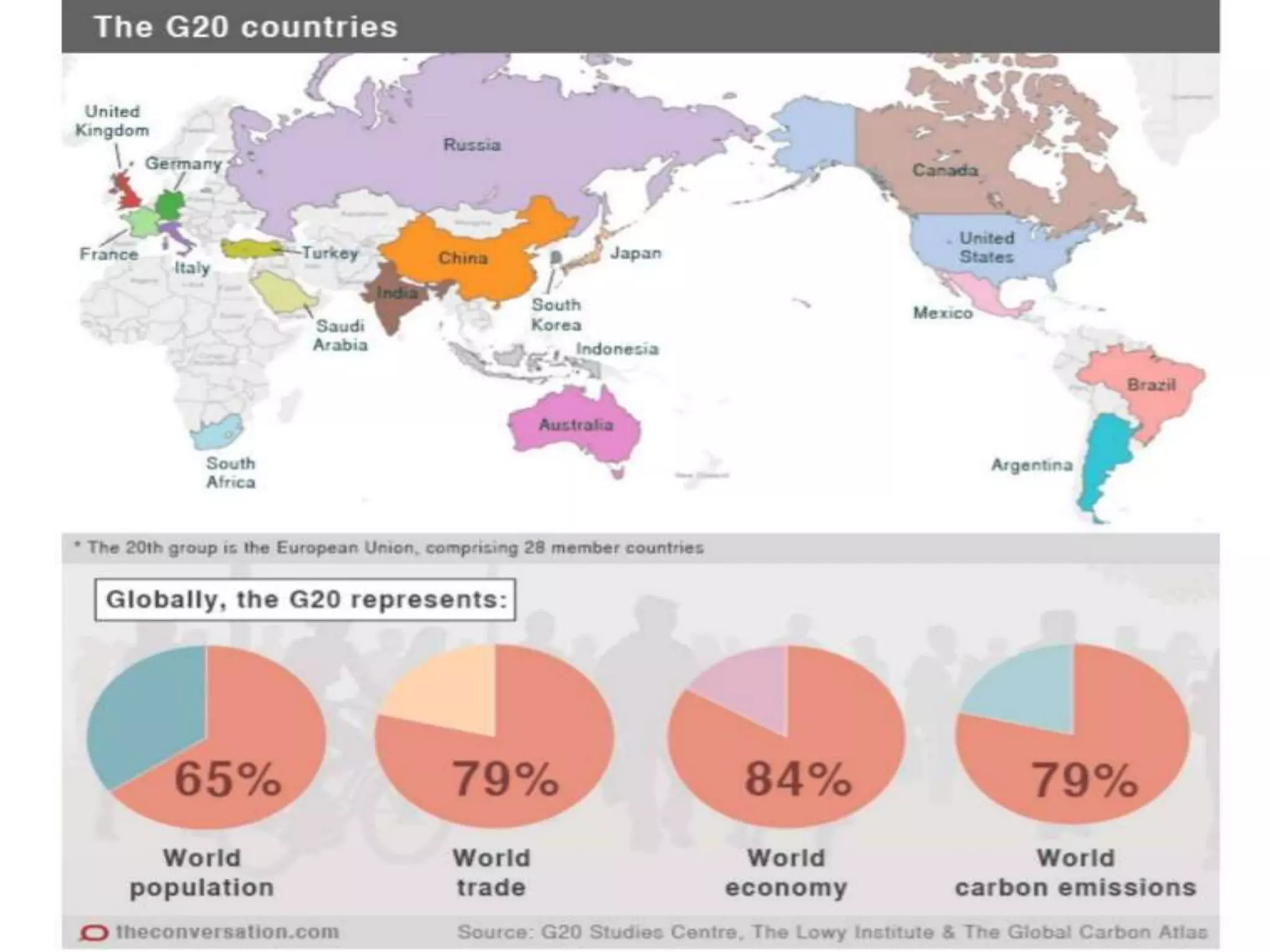
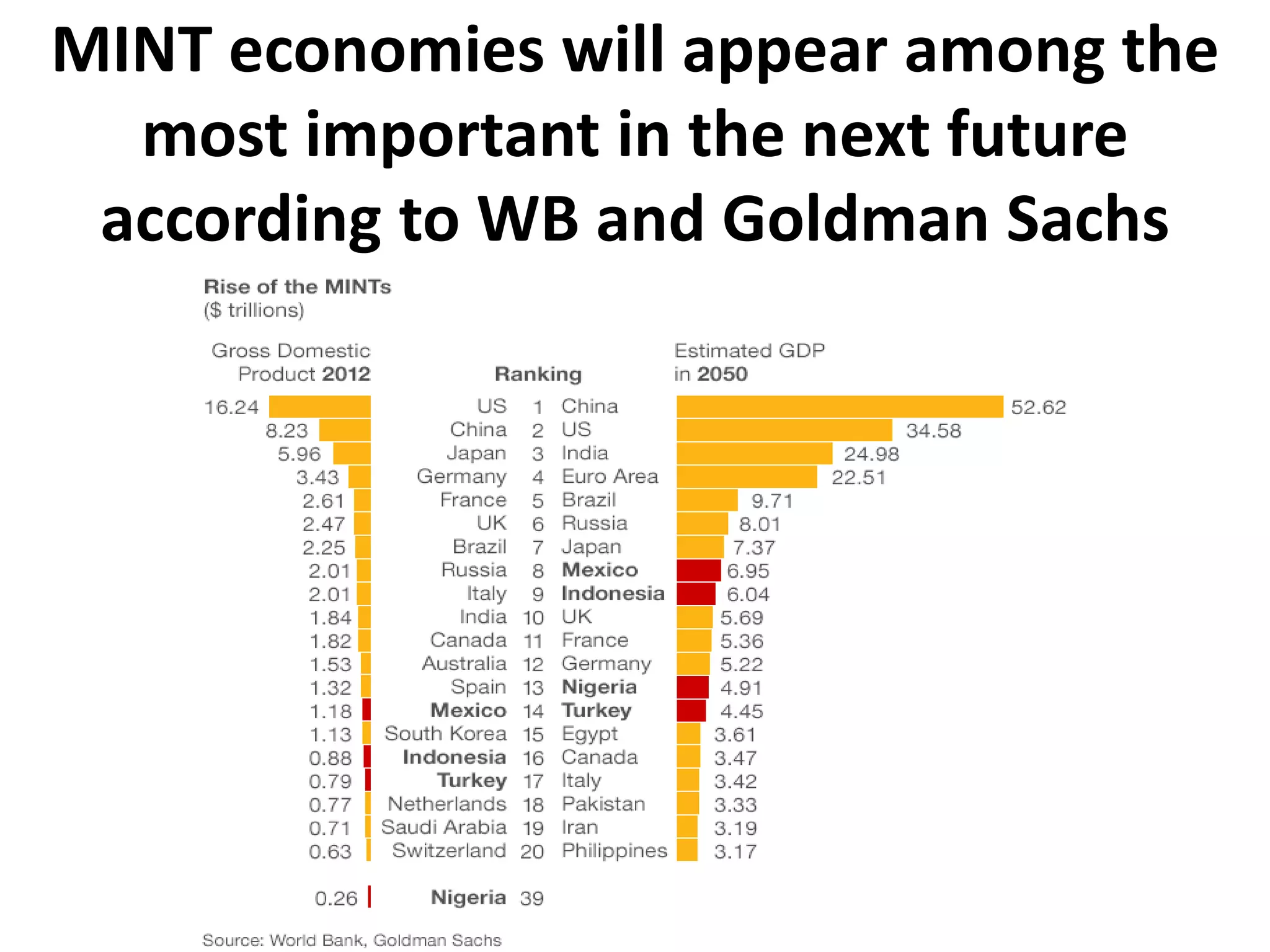
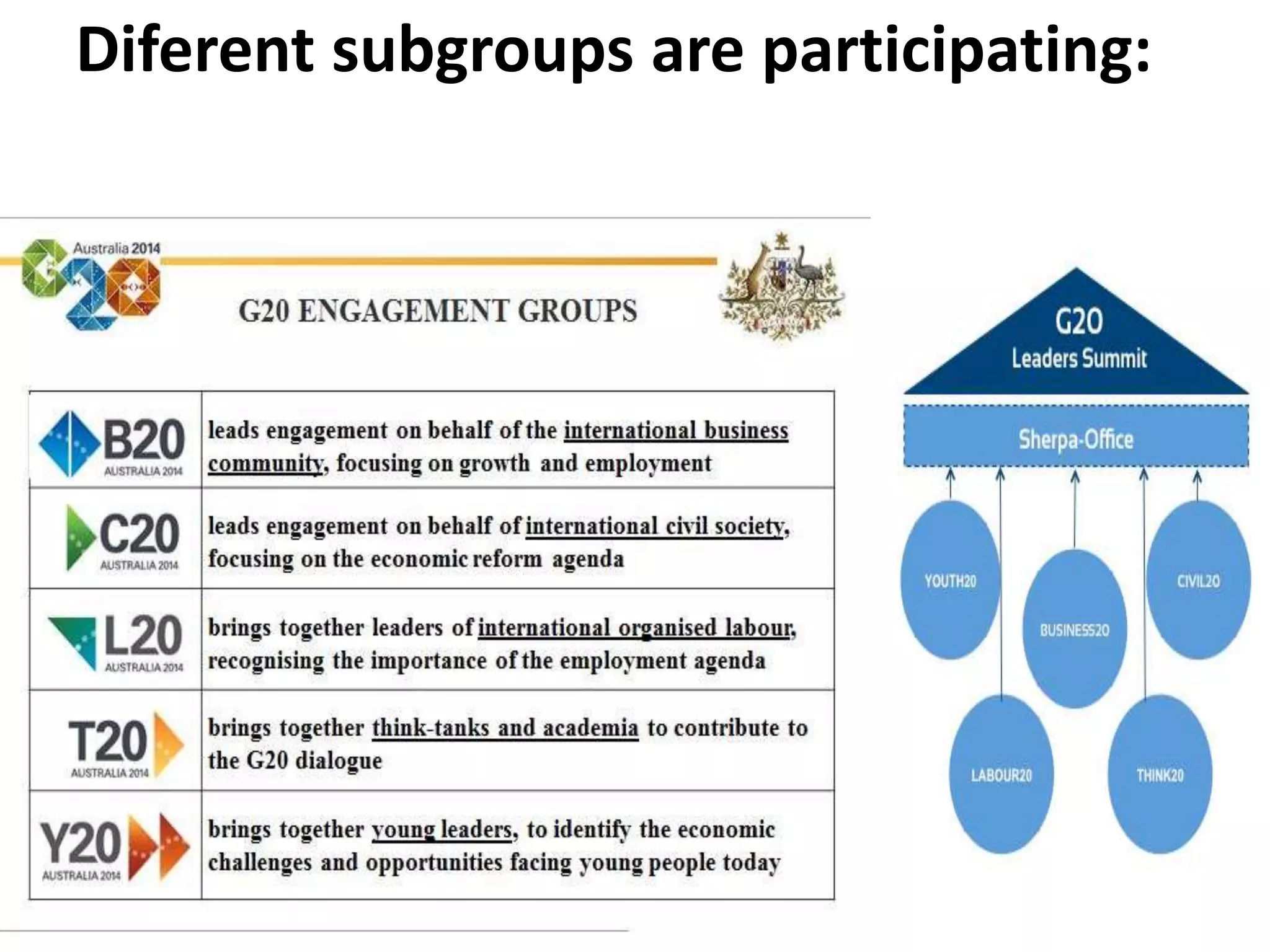
- The G20 was created in 1999 by the G7 countries in response to financial crises to help stabilize global markets and the international monetary system.
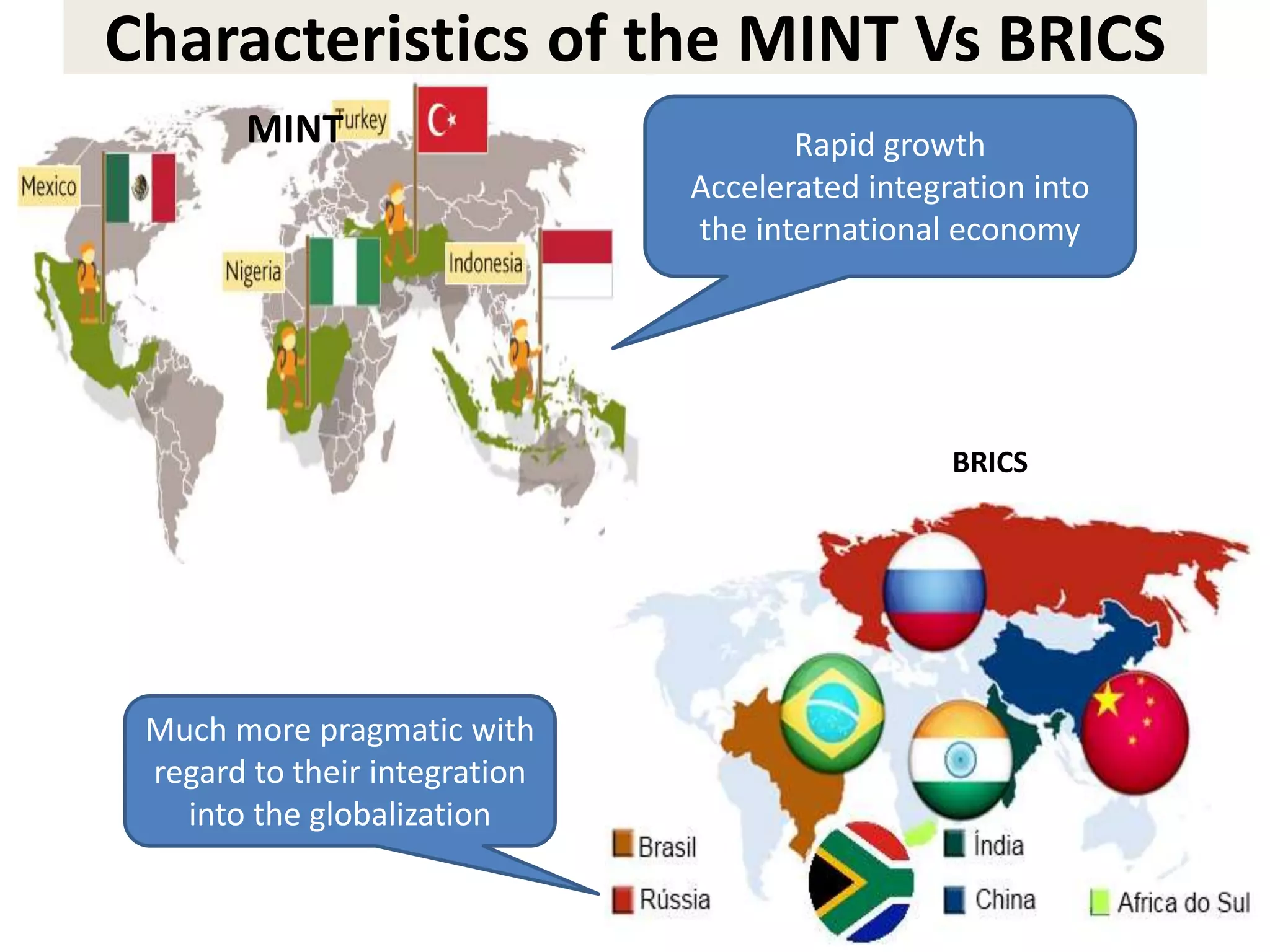
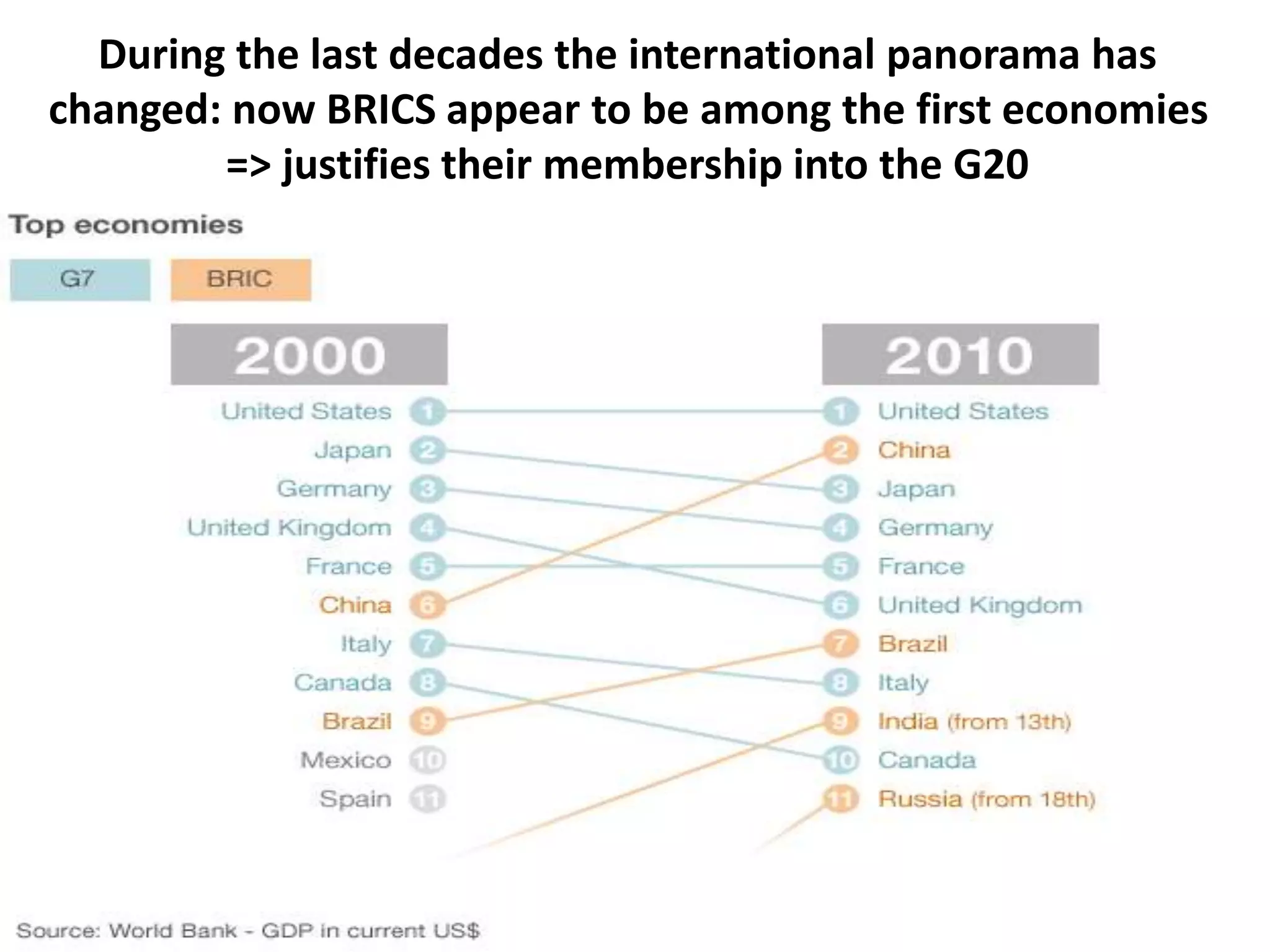
- It has taken on a larger role since the 2008 crisis and expanded its membership to include both creditor and emerging economies.
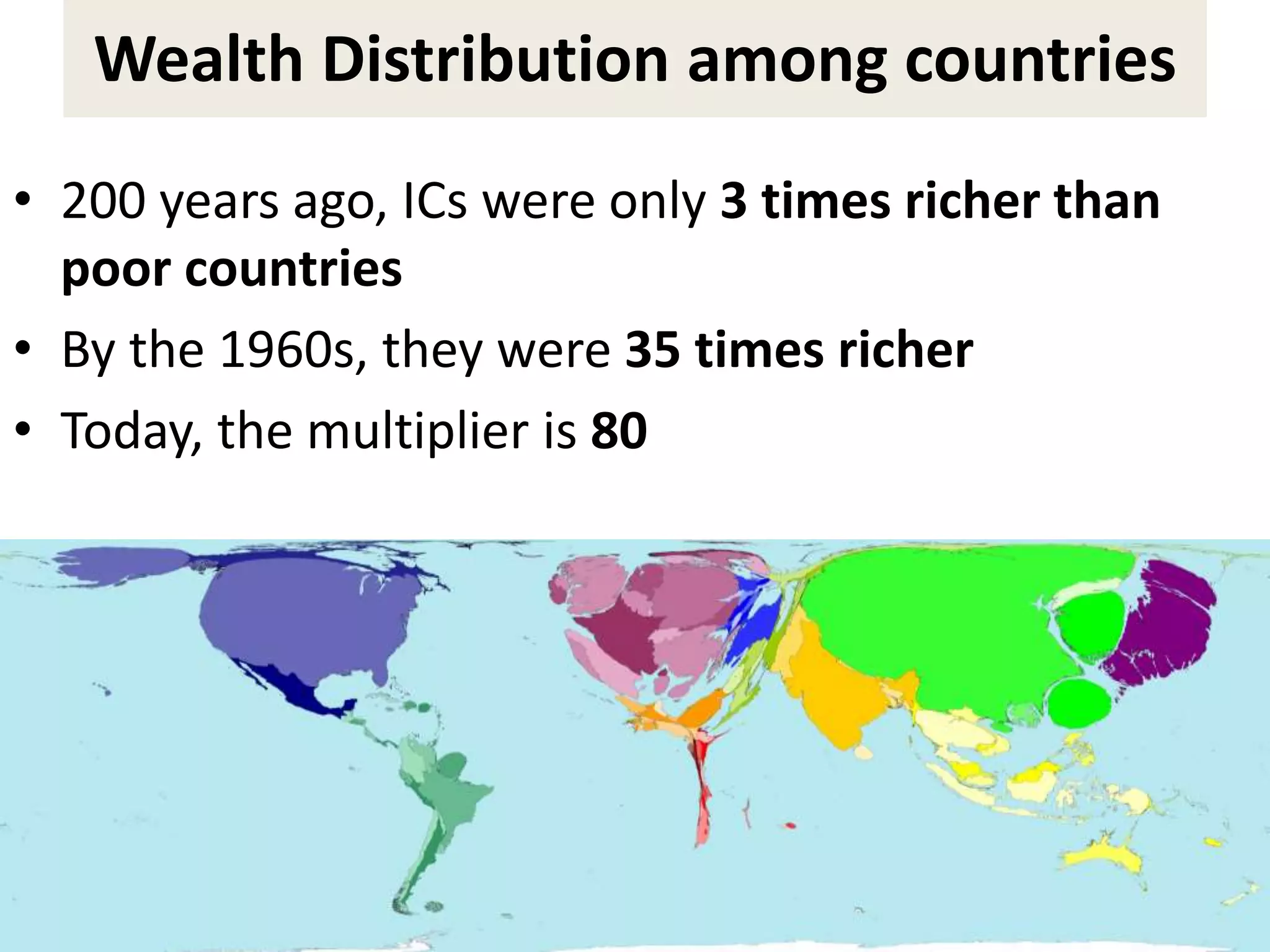
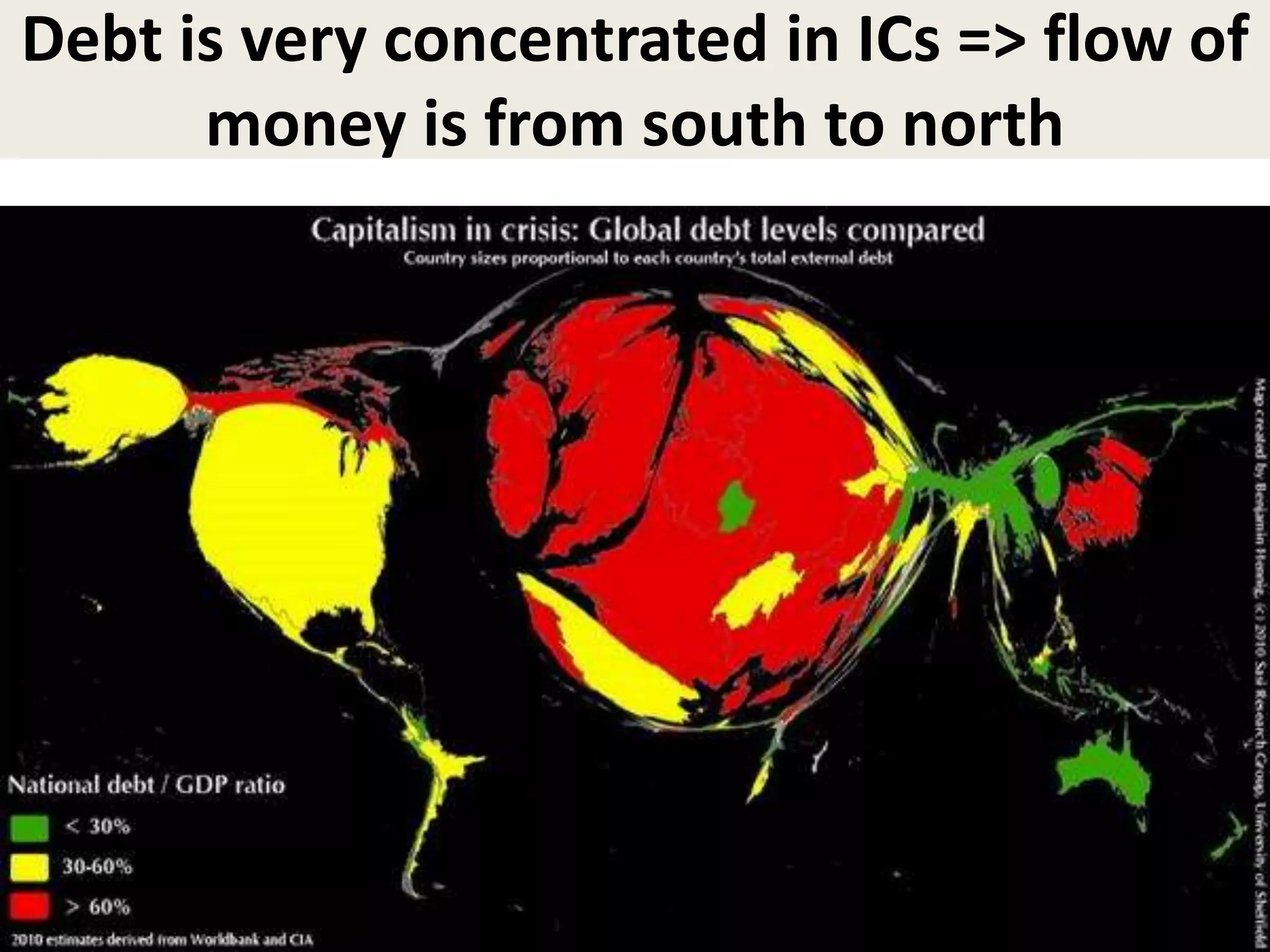
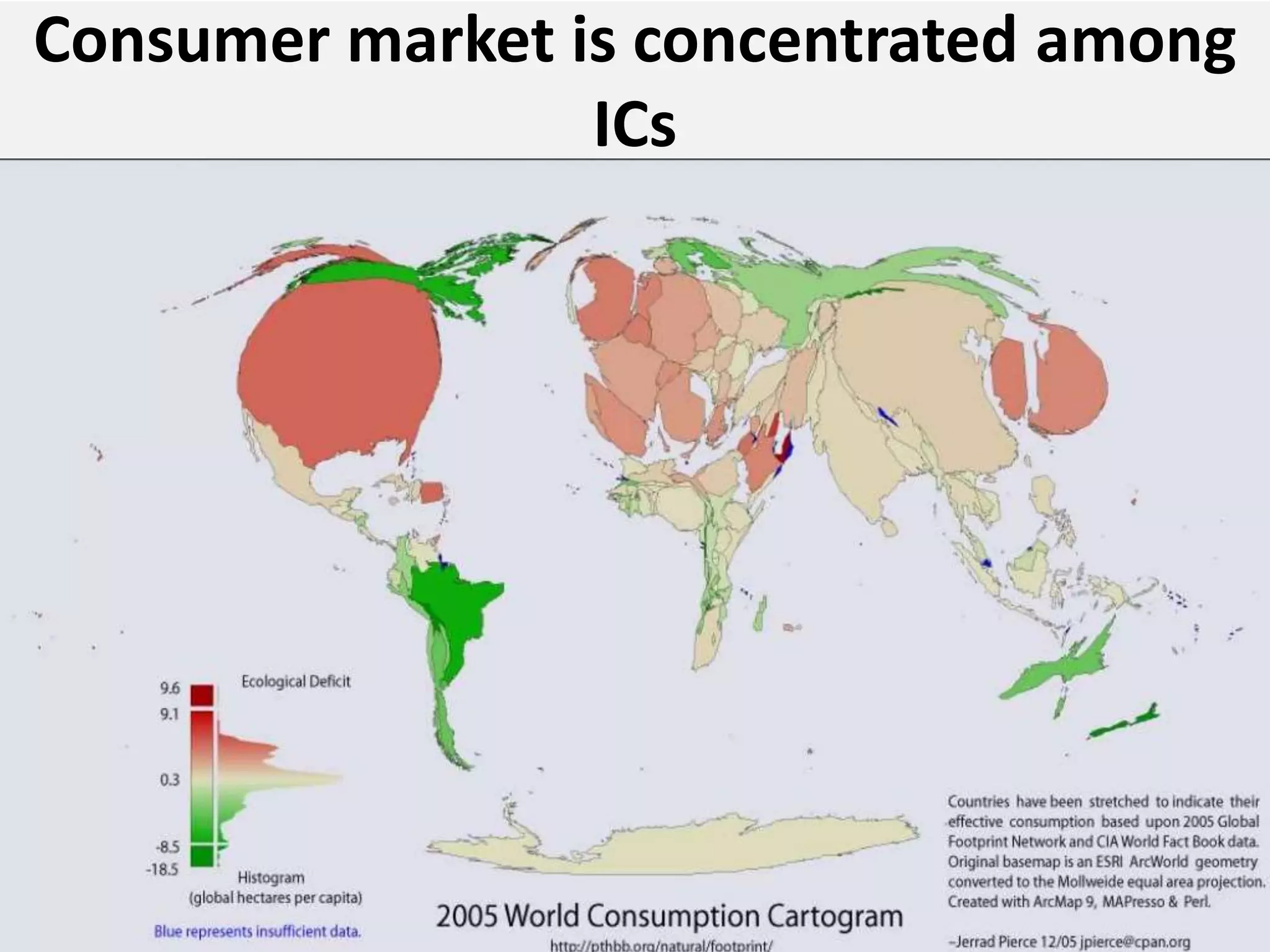
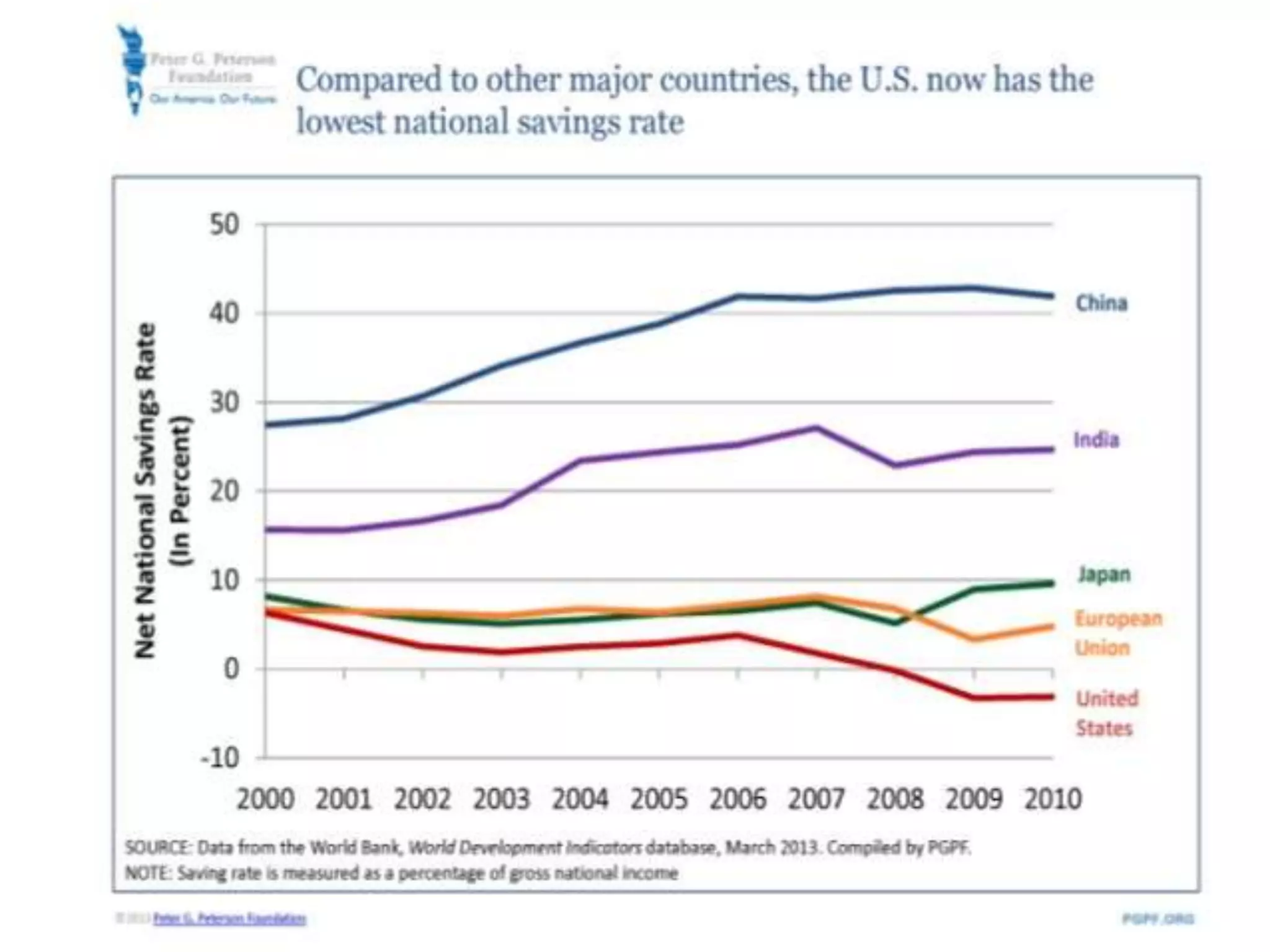
- However, the G20 and other global institutions have struggled to anticipate and resolve major issues like inequality, unemployment, climate change, and have focused more on short-term banking rescues in developed countries. Significant obstacles remain to establishing a new economic governance with more justice for developing countries.