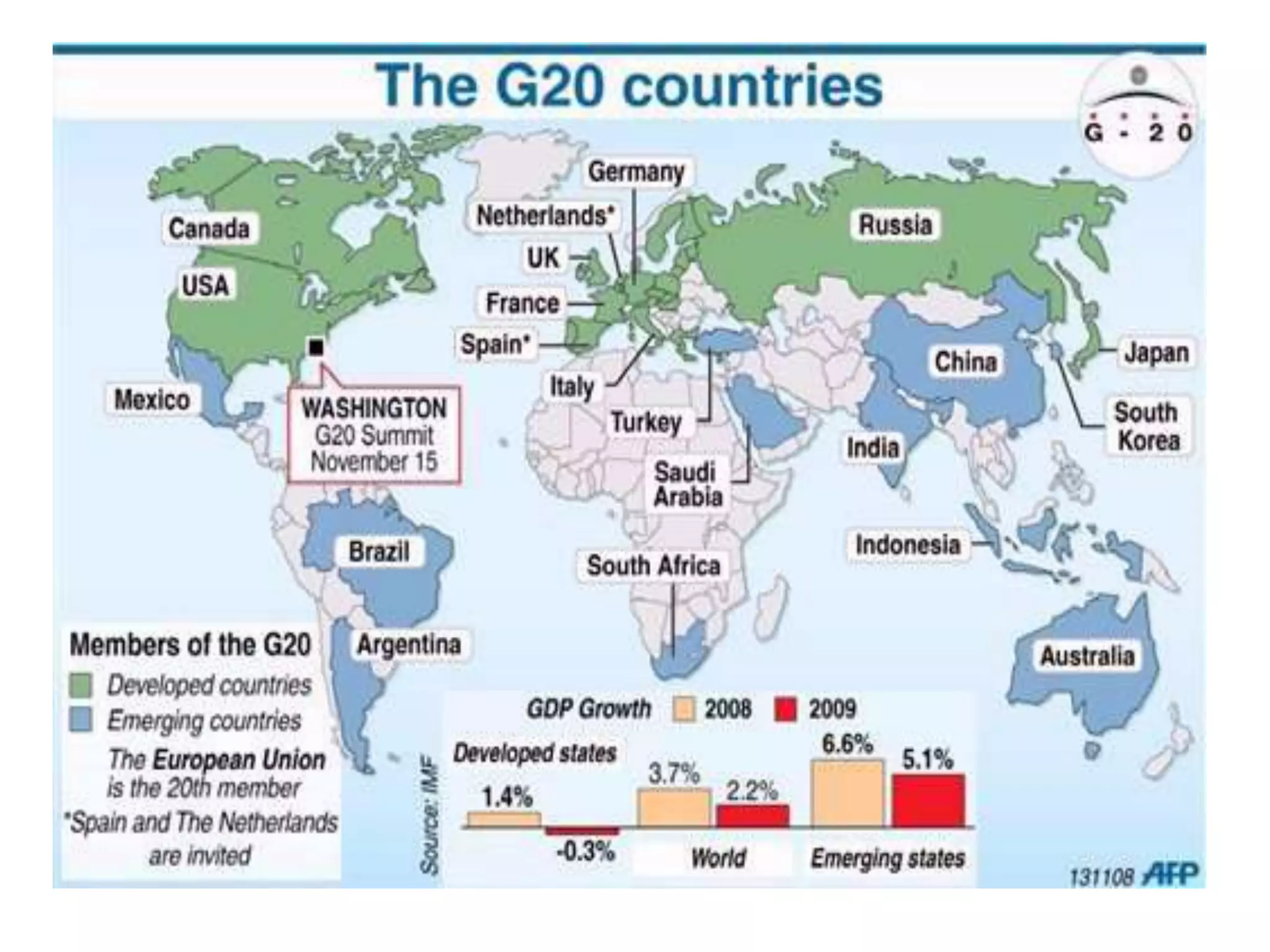
A summit is a high-level meeting between heads of state to discuss important issues. Summits were not commonly called that until the Cold War era. Over time, the number of summit meetings has increased, including the G6/G7/G8 meetings of economically powerful countries. The G20 was formed in the late 1990s as a meeting of finance ministers in response to economic crises and grew to address the 2008 global financial crisis. Recent G20 summits have focused on economic growth, financial regulation, development, and other issues. The next G20 summit will be in Turkey in 2015.