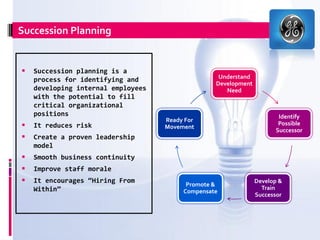
This document discusses succession planning at General Electric (GE). It provides background on GE and describes its business structure. It then defines succession planning and explains how GE implements it through processes like identifying potential successors, developing them, and promoting from within. The document presents GE's succession chart from 1892 to the present and analyzes the succession planning under former CEO Jack Welch and current CEO Jeff Immelt. It compares their leadership styles and comments on GE's performance under Immelt's leadership. Finally, it examines the need for succession planning in companies and potential issues without it.