This document discusses fuzzy clustering, which allows data points to belong to multiple clusters with a degree of membership. It describes fuzzy c-means clustering, which was improved in 1981 by Bezdek. The algorithm involves initializing membership values, computing centroids, recomputing membership values iteratively until convergence. Pros include a more natural representation of overlapping clusters, while cons include sensitivity to initialization and needing to specify the number of clusters. Applications include image segmentation, enhancement, and change detection.












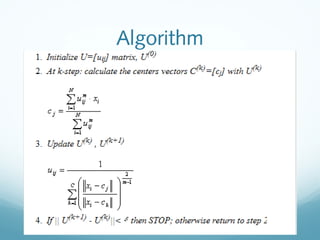
![An example
X=[3 7 10 17 18 20] and assume C=2
0.1 0.2 0.6 0.3 0.1 0.5
Initially, set U randomly U=
0.9 0.8 0.4 0.7 0.9 0.5
N
∑u m
x
ij i
cj = i =1
N
∑u
i =1
m
ij
Compute centroids, cj using , assume m=2
1
uij = 2
C
|| xi − c j || m −1
c1=13.16; c2=11.81
∑ || x − c ||
k =1
i k
Compute new membership values, uij using
0.43 0.38 0.24 0.65 0.62 0.59
U=
New U: 0.57 0.62 0.76 0.35 0.38 0.41
Repeat centroid and membership computation until changes in
membership values are smaller than say 0.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzydm-130415131742-phpapp02/85/Fuzzy-dm-14-320.jpg)



