This document contains code and explanations for image processing tasks involving edge detection, thresholding, and segmentation.
It includes:
1) Code to perform spatial filtering of an image using a 3x3 mask and Sobel edge detection filters.
2) Application of the code to detect edges and segment a large blood vessel in a kidney image.
3) Implementation of Otsu's thresholding algorithm to automatically select a threshold for segmentation.
4) Comparison of Otsu's method to global thresholding on a polymersomes image, finding Otsu's performs better.
![% we have a1 to a9 as variables
w =[a1 a2 a3;a4 a5 a6;a7 a8 a9] % w is the filter (assumed to be 3x3)
g=zeros(x+2,y+2);% The original image is padded with 0's
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
g(i+1,j+1)=f(i,j);
end
end
%cycle through the array and apply the filter
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
img(i,j)=g(i,j)*w(1,1)+g(i+1,j)*w(2,1)+g(i+2,j)*w(3,1) ... %first column
+ g(i,j+1)*w(1,2)+g(i+1,j+1)*w(2,2)+g(i+2,j+1)*w(3,2)... %second column
+ g(i,j+2)*w(1,3)+g(i+1,j+2)*w(2,3)+g(i+2,j+2)*w(3,3);
end
end
figure
imshow(img,[])
(b).
f=imread('..');
figure
imshow(f); %original figure
w =[a1 a2 a3;a4 a5 a6;a7 a8 a9] %filter from (a)
c = conv2(f,w,'same'); %image after convolution with mask
s1 = [-1 -2 -1;0 0 0;1 2 1]; % sobel operator in horizontal
s2 = [-1 0 1;-2 0 2;-1 0 1]; % sobel operator in vertical
gx = conv2(c,s1,'same');
gy = conv2(c,s2,'same');
M = sqrt(gx.*gx+gy.*gy); % maginitude
figure % image after convolution with horizontal sobel operator
imshow(gx);
figure % image after convolution with vertical sobel operator
imshow(gy)
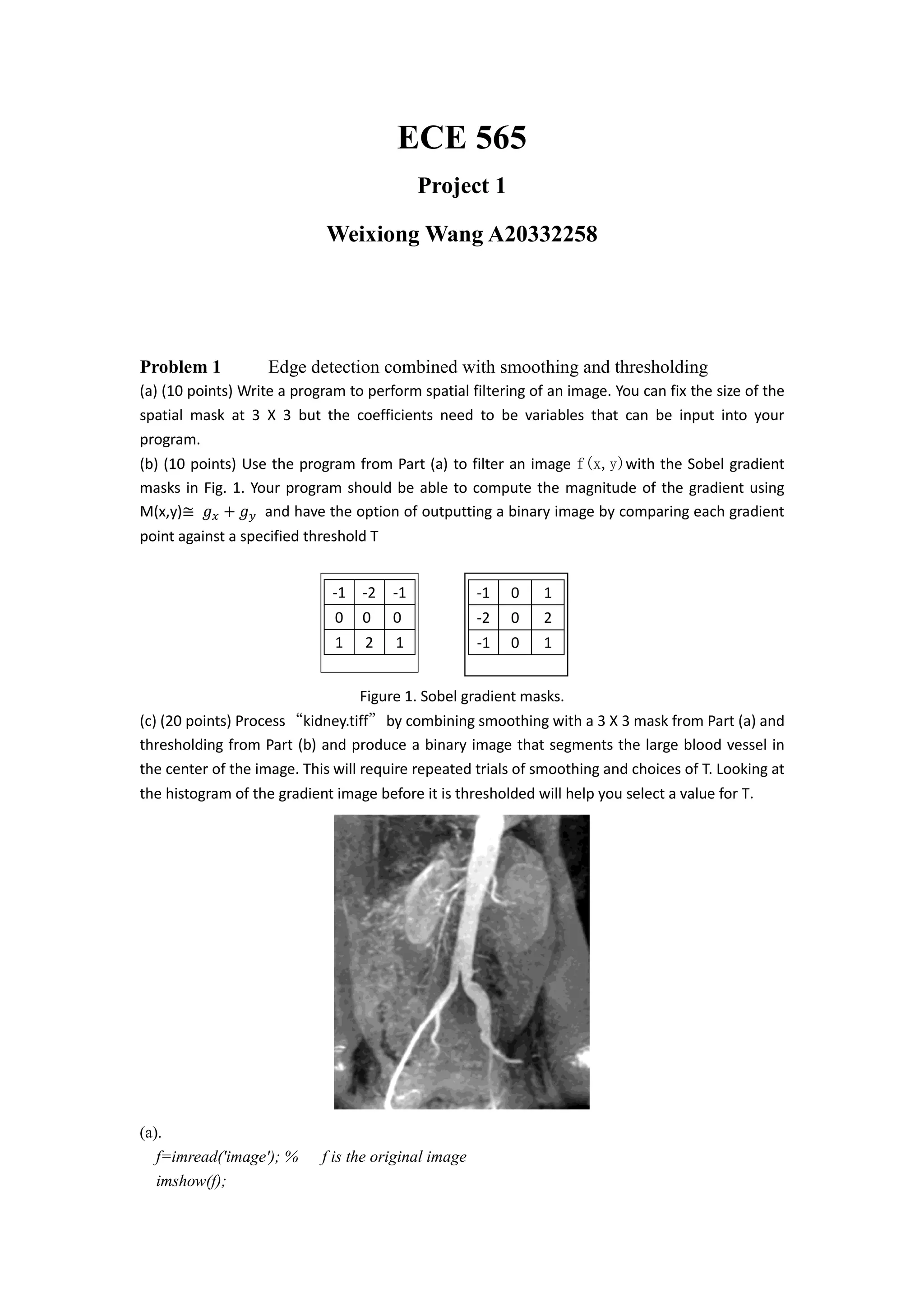
g = gx+gy; % image with horizontal gx plus vertical gy
figure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba4b1a67-e0dc-44f9-bef4-291be5a9cc58-160523230201/75/ECE-565-Project1-2-2048.jpg)
![imshow(g)
% historgram stem of image
I = gpuArray(imread('E:myimages¥kidney.tif'));
[counts,x] = imhist(I);
stem(x,counts);
BW = im2bw(f,T);
figure
imshow(BW)
(c).
Figure before smoothing Figure after smoothing
To produce a binary image thatsegments the large blood vessel in the center of the image.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba4b1a67-e0dc-44f9-bef4-291be5a9cc58-160523230201/75/ECE-565-Project1-3-2048.jpg)
![Code:
f=imread('E:myimages¥kidney.tif');
figure
imshow(f); %original figure
w=ones(3)/9; %filter from (a)
c = conv2(f,w,'same'); %image after convolution with mask
s1 = [-1 -2 -1;0 0 0;1 2 1]; % sobel operator in horizontal
s2 = [-1 0 1;-2 0 2;-1 0 1]; % sobel operator in vertical
gx = conv2(c,s1,'same');
gy = conv2(c,s2,'same');
M = sqrt(gx.*gx+gy.*gy); % maginitude
figure % image after convolution with horizontal sobel operator
imshow(gx);
figure % image after convolution with vertical sobel operator
imshow(gy)
g = gx+gy; % image with horizontal gx plus vertical gy
figure
imshow(g)
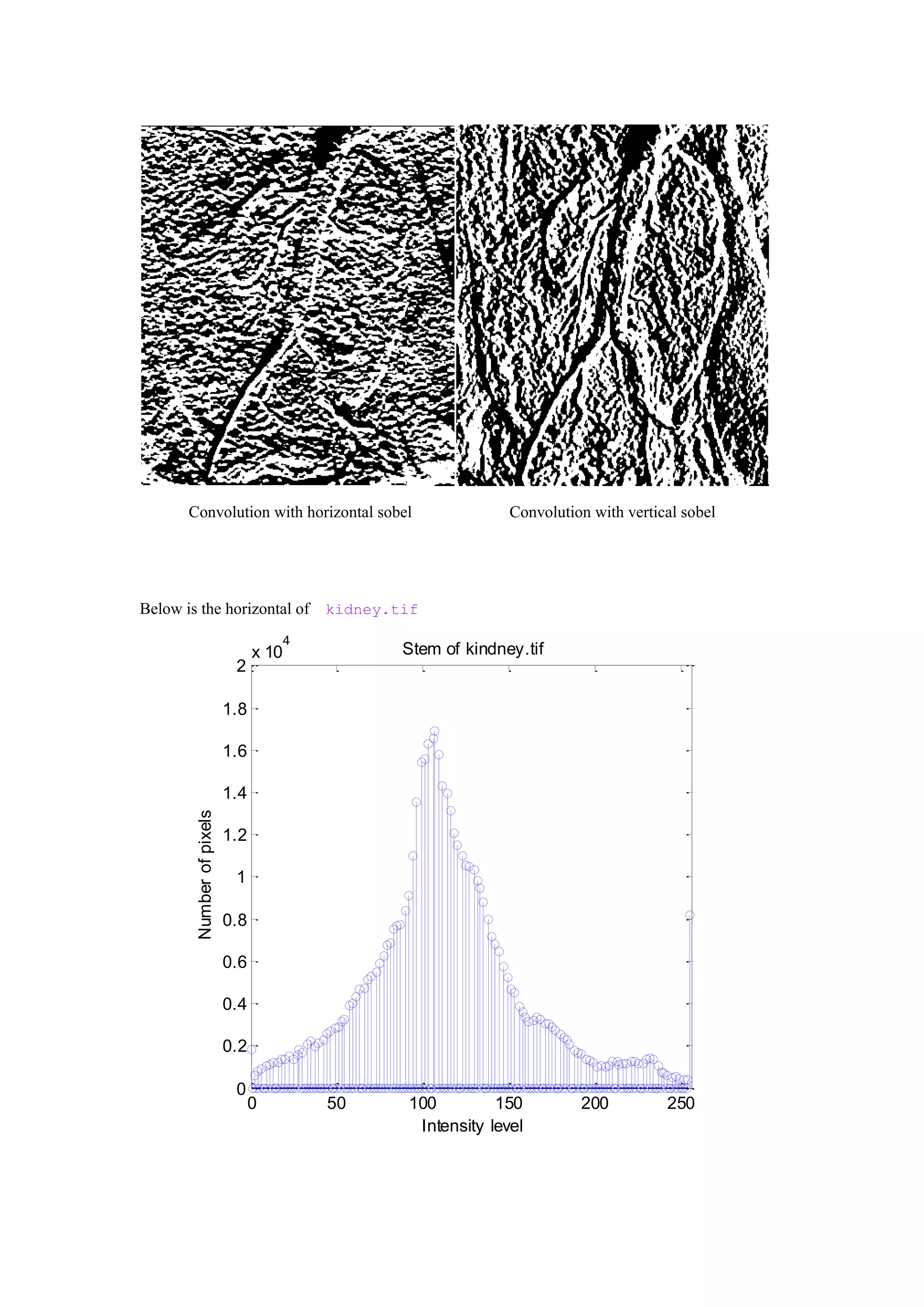
%historgram stem of image
[counts,x] = imhist(f);
stem(x,counts);
title('Stem of kindney.tif')
xlabel('Intensity level')
ylabel('Number of pixels')
axis([0 256 0 20000])
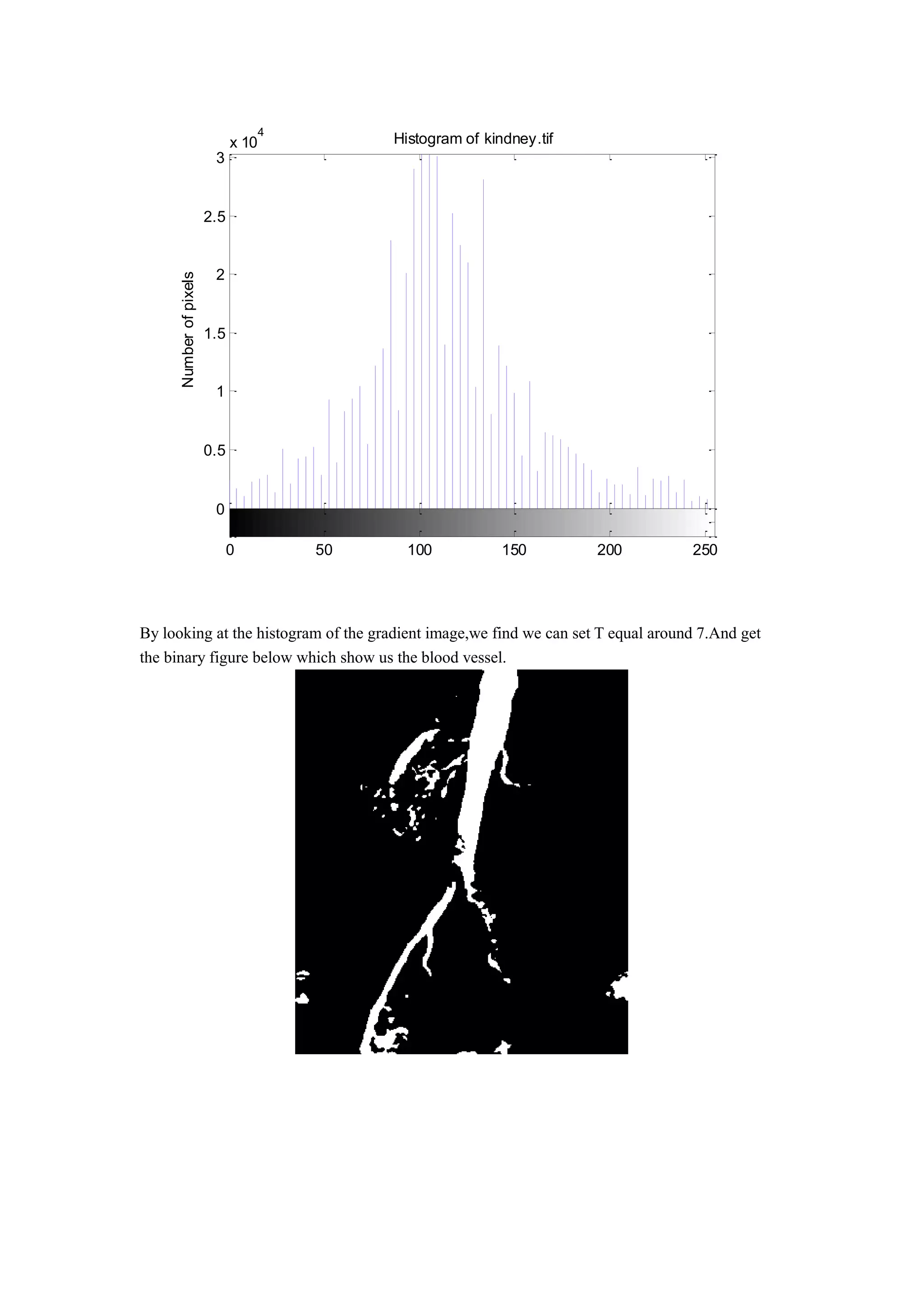
figure;
imhist(f,64)
title('Histogram of kindney.tif')
xlabel('Intensity level')
ylabel('Number of pixels')
BW = im2bw(f,0.72);
figure
imshow(BW)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba4b1a67-e0dc-44f9-bef4-291be5a9cc58-160523230201/75/ECE-565-Project1-6-2048.jpg)

![function level = g_t(I)
I = imread('E:myimages¥noisy_fingerprint.tif');
% STEP 1: Compute mean intensity of image from histogram, set T=mean(I)
[counts,N]=imhist(I);
i=1;
mu=cumsum(counts);
T(i)=(sum(N.*counts))/mu(end);
T(i)=round(T(i));
% STEP 2: compute Mean above T (MAT) and Mean below T (MBT) using T from
% step 1
mu2=cumsum(counts(1:T(i)));
MBT=sum(N(1:T(i)).*counts(1:T(i)))/mu2(end);
mu3=cumsum(counts(T(i):end));
MAT=sum(N(T(i):end).*counts(T(i):end))/mu3(end);
i=i+1;
% new T = (MAT+MBT)/2
T(i)=round((MAT+MBT)/2);
% STEP 3 to n: repeat step 2 if T(i)~=T(i-1)
while abs(T(i)-T(i-1))>=1
mu2=cumsum(counts(1:T(i)));
MBT=sum(N(1:T(i)).*counts(1:T(i)))/mu2(end);
mu3=cumsum(counts(T(i):end));
MAT=sum(N(T(i):end).*counts(T(i):end))/mu3(end);
i=i+1;
T(i)=round((MAT+MBT)/2);
Threshold=T(i);
end
% Normalize the threshold to the range [i, 1].
level = (Threshold - 1) / (N(end) - 1);
BW = im2bw(I,level);
imshow(BW)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba4b1a67-e0dc-44f9-bef4-291be5a9cc58-160523230201/75/ECE-565-Project1-8-2048.jpg)

![Compare the result for a) and b)
We see the Otsu has a better performance than global,because Otsu is based on the histogram,so
we can get a good threshold value than in global thresholding.In Otsu,We can’t change the
distributions, but we can adjust where we separate them (the threshold). As we adjust the threshold
one way, we increase the spread of one and decrease the spread of the other.
Code:
I = imread('E:myimages¥polymersomes.tif');
mgk = 0;
mt = 0;
[m,n] = size(I);
h = imhist(I);
pi = h/(m.*n);
for i=1:1:256
if pi(i)~=0
lv=i;
break
end
end
for i=256:-1:1
if pi(i)~=0
hv=i;
break
end
end
lh = hv - lv;
for k = 1:256
p1(k)=sum(pi(1:k));
p2(k)=sum(pi(k+1:256));
end
for k=1:256
m1(k)=sum((k-1)*pi(1:k))/p1(k);
m2(k)=sum((k-1)*pi(k+1:256))/p2(k);
end
for k=1:256
mgk=(k-1)*pi(k)+mgk;
end
for k =1:256
var(k)=p1(k)*(m1(k)-mgk)^2+p2(k)*(m2(k)-mgk)^2;
end
[y,T]=max(var(:));
T=T+lv;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba4b1a67-e0dc-44f9-bef4-291be5a9cc58-160523230201/75/ECE-565-Project1-10-2048.jpg)
