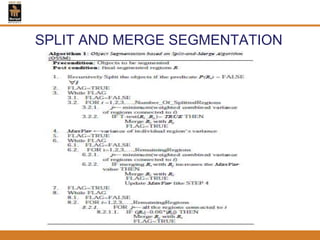
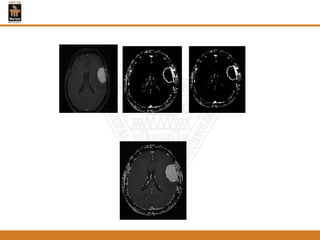
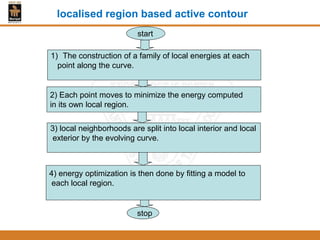
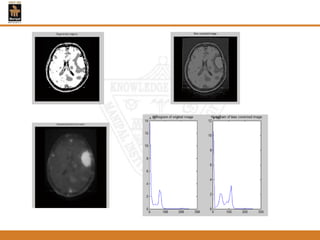
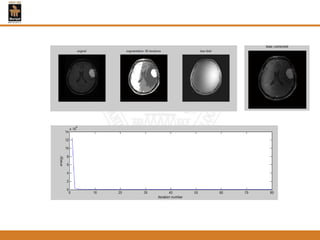
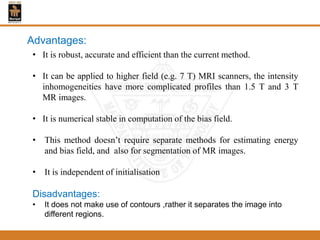
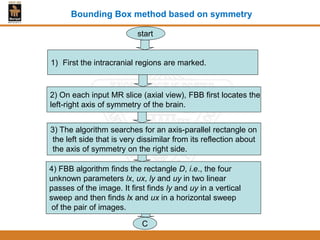
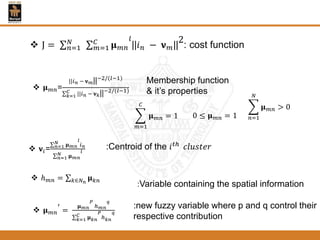
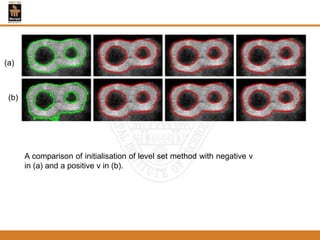
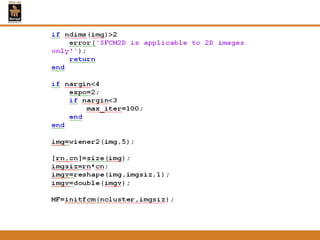
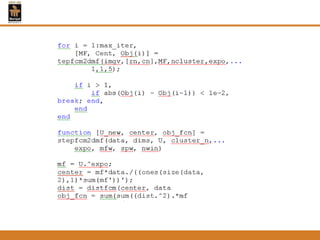
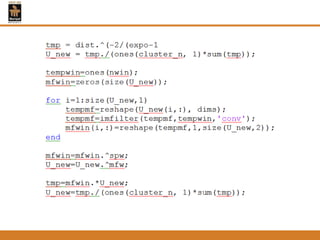
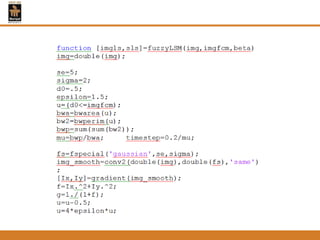
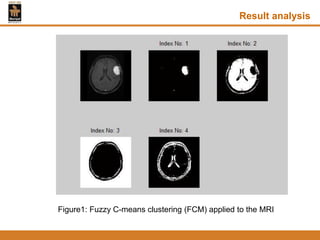
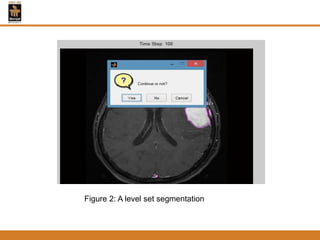
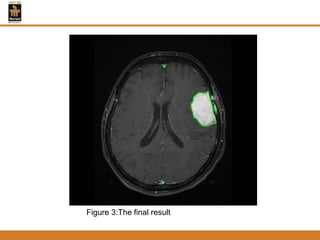
This document provides an overview of different techniques for segmenting brain tumours from MRI images using MATLAB. It includes flowcharts and descriptions of watershed transform, split and merge segmentation, localised region active contours, fuzzy c-means clustering with level sets, bounding box segmentation based on symmetry, and a spatial fuzzy clustering level set method. The document analyzes sample results and concludes the fuzzy level set method overcomes issues with other techniques like needing reinitialization or not handling multiple regions well. Future work could make the methods fully automated and extend them to 3D segmentation.







![𝝓 𝑡, 𝑥, 𝑦 < 0 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑖𝑠 𝑖𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝝘(𝑡)
𝝓 𝑡, 𝑥, 𝑦 = 0 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑖𝑠 𝑎𝑡 𝝘(𝑡)
𝝓 𝑡, 𝑥, 𝑦 > 0 𝑖𝑠 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝝘(𝑡)
𝜕𝝓
𝜕𝑡
+ 𝐹 𝛻𝝓 = 0
𝝓 0, 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝝓0(𝑥, 𝑦)
𝑔 =
1
1 + |𝛻( 𝐺 𝝈 ∗ 𝐼)|
𝜕𝝓
𝜕𝑡
= 𝛍𝛇 𝝓 + 𝛏(𝗴, 𝝓)
𝛇 𝝓 = ∆𝝓 − div (
𝛻𝝓
𝛻𝝓
)
𝛏(𝗴, 𝝓)=λ𝛅(𝝓)div ਣ
𝛻𝝓
|𝛻𝝓 |
+ 𝛎ਣ𝛅(𝝓)
𝝓0(𝑥, 𝑦) =
−𝐶, 𝝓0 𝑥, 𝑦 < 0
𝐶, 𝑜𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑤𝑖𝑠𝑒
𝝓 𝑘+1
𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝝓 𝑘
𝑥, 𝑦 +𝞽[𝛍𝛇(𝝓 𝑘
)+𝛏(ਣ, 𝝓 𝑘
)]
The new level set method:The traditional level set formulation:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myproject-150521114705-lva1-app6892/85/various-methods-for-image-segmentation-29-320.jpg)







![References
[1] Ammara Masood, Adel Ali Al-Jumaily, Fuzzy C Mean Thresholding based
Level Set for Automated Segmentation of Skin Lesions, Journal of Signal
and Information Processing, 4, 66-71,2013.
[2] A.B.M. Faruquzzaman1, Nafize Rabbani Paiker1, Jahidul Arafat1, Ziaul
Karim1 , and M. Ameer Ali2, Object Segmentation Based on Split and
Merge Algorithm, 978-1-4244-2409-2, 19-21 Nov. 2008.
[3]D. Chaudhuri, B.B. Chaudhuri and C.A. Murthy, A New Split–and-Merge
Clustering Technique, Pattern Recognition Letters 13, pp. 399-409, 1998.
[4]D. Mumford and J. Shah, “Optimal approximation by piecewise smooth
functions and associated variational problems,” Commun. Pure Appl. Math,
vol. 42, pp. 577–685,1989.
[5] Li F, Ng M, Li C. Variational fuzzy Mumford-Shah model for image
segmentation. SIAM J Appl Math 2010;70(7):2750–70,2010.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myproject-150521114705-lva1-app6892/85/various-methods-for-image-segmentation-50-320.jpg)
![[6] Lions P, Mercier B. Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators.
SIAM J Numer Anal 1979;16(6):964–79,1979.
[7] M. E. Brummer, R. M. Mersereau, R. L. Eisner, R. J. Lewine, “Automatic
detection of brain contours in MRI data sets”, IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, vol. 12,
no. 2, pp. 153 -166,1993.
[8] Rachana Rana1, H.S. Bhadauria2, Annapurna Singh, Study of Various Methods
for brain Tumour Segmentation from MRI Images, International Journal of Emerging
Technology and Advanced Engineering, (pp. 2250-2459), Volume 3, Issue 6, June
2013.
[9] Rajesh C. Patil, Dr. A. S. Bhalchandra, Brain Tumour Extraction from MRI Images
Using MATLAB, International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Soft
Computing Science and Engineering, 2277-9477, Volume 2, Issue 1,2011.
[10] Shawn Lankton, Student Member, IEEE, and Allen Tannenbaum, Member,
IEEE, Localizing Region-Based Active Contours,Year of Publication 2008 IEEE
transactions on image processing, vol. 17, no. 11, Nov. 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myproject-150521114705-lva1-app6892/85/various-methods-for-image-segmentation-51-320.jpg)
