The document discusses future trends on the web, including moving from a web of documents to a web of structured data and services through technologies like semantic web and linked data. Other trends discussed include cloud computing, mobile web, internet of things, and new forms of user interfaces using technologies like augmented reality. The document also addresses social implications such as the effects of information overload and the trade-off between personalization and privacy.




![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 5December 19, 2014
Structured Data
Web of data instead of Web of documents
Semantic Web
linked data as part of the Semantic Web
- based on URI, HTTP and RDF
various applications already make use of structured data on
the Web
- search engines start to process microformats (e.g. hproduct) or RDFa markup
[http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/23/Lod-datasets_2010-09-22_colored.png]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture12-futuretrends-091210131440-phpapp02/75/Future-Trends-Lecture-12-Web-Information-Systems-4011474FNR-5-2048.jpg)












![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 20December 19, 2014
Digital Documents as a Paper Simulator?
Vannevar Bush
Ted Nelson
Most people don't understand the logic of the
concept: "What You See Is What You Get" is
based on printing the document out ("get"
means "get WHEN YOU PRINT IT OUT"). And that
means a metaphysical shift: a document can
only consist of what can be printed! [...] No
overlays [...] – PAPER UNDER GLASS.
When data of any sort are placed in storage,
they are filed alphabetically or numerically,
and information is found (when it is) by
tracing it down from subclass to subclass. It
can be in only one place, unless duplicates
are used [...] The human mind does not work
that way. It operates by association.
As We May Think, Atlantic Monthly, July 1945
Geeks Bearing Gifts: How the Computer World Got This Way, Mindful Press 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture12-futuretrends-091210131440-phpapp02/75/Future-Trends-Lecture-12-Web-Information-Systems-4011474FNR-20-2048.jpg)




![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 31December 19, 2014
Other Courses
Advanced Topics in Information Systems
seminar about recent developments in information systems
information systems and information management
information visualisation and navigation
human-machine and human-information interaction
[http://wise.vub.ac.be/content/advanced-topics-information-systems]
Next Generation User Interfaces
interaction design
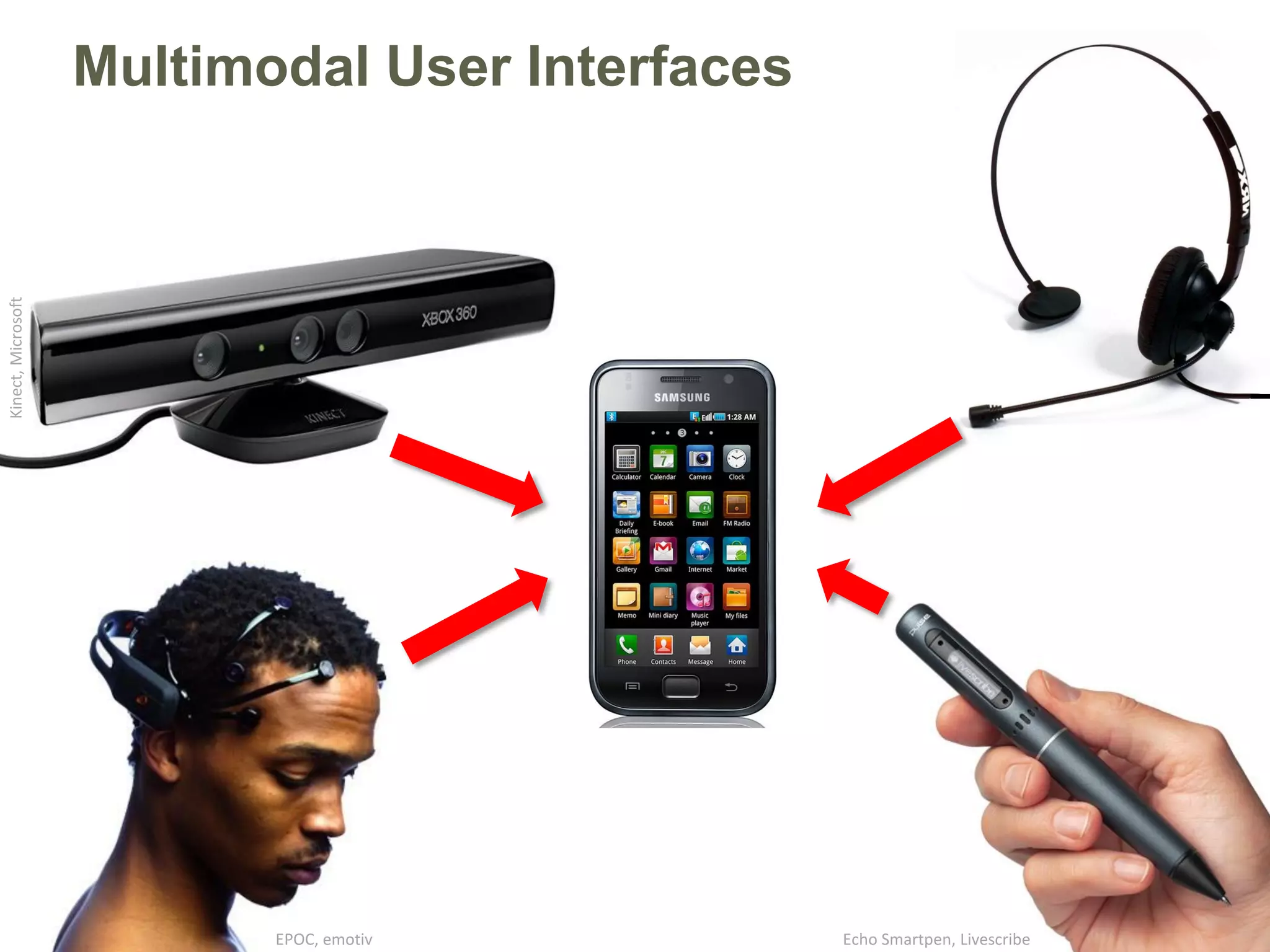
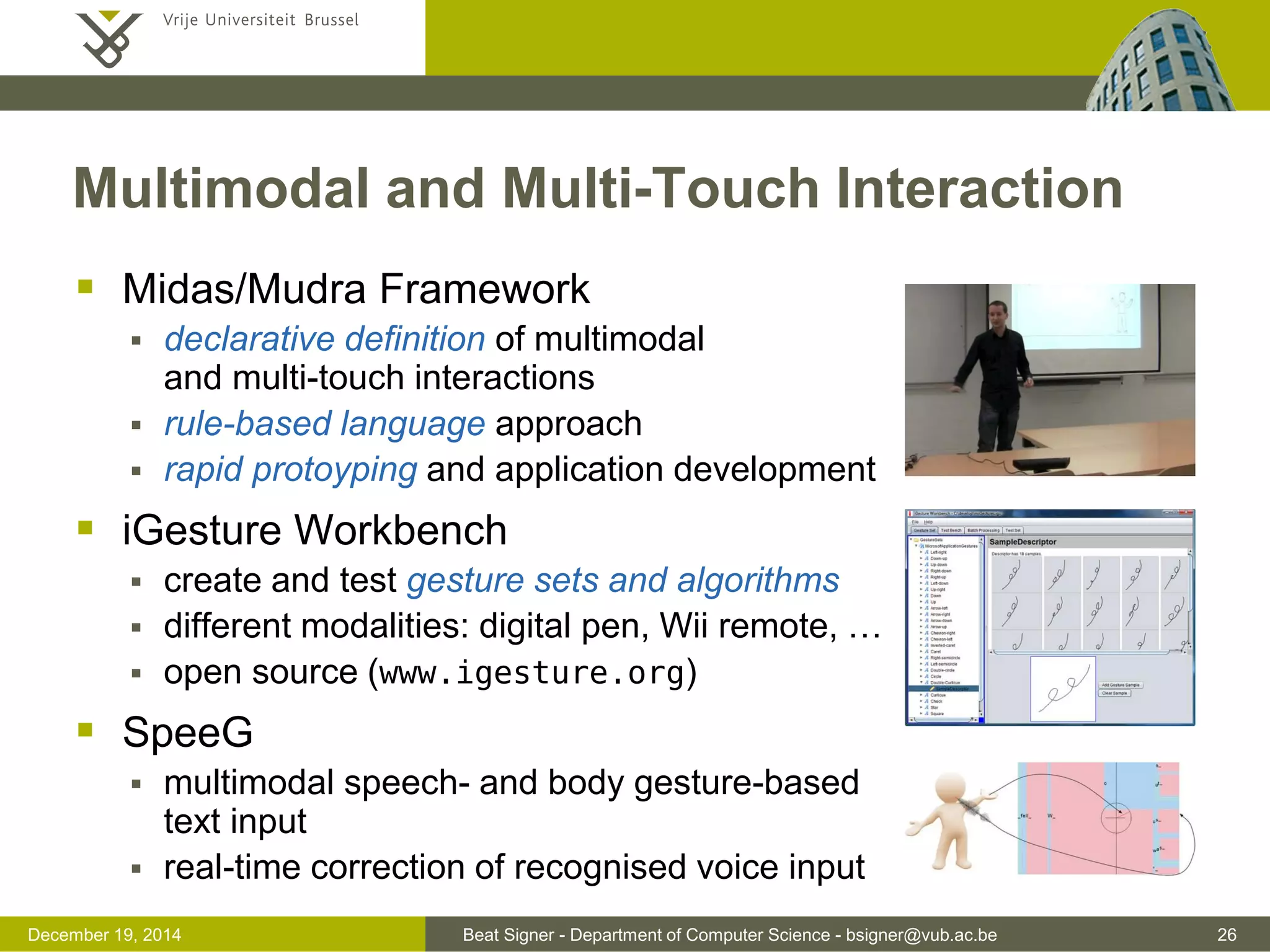
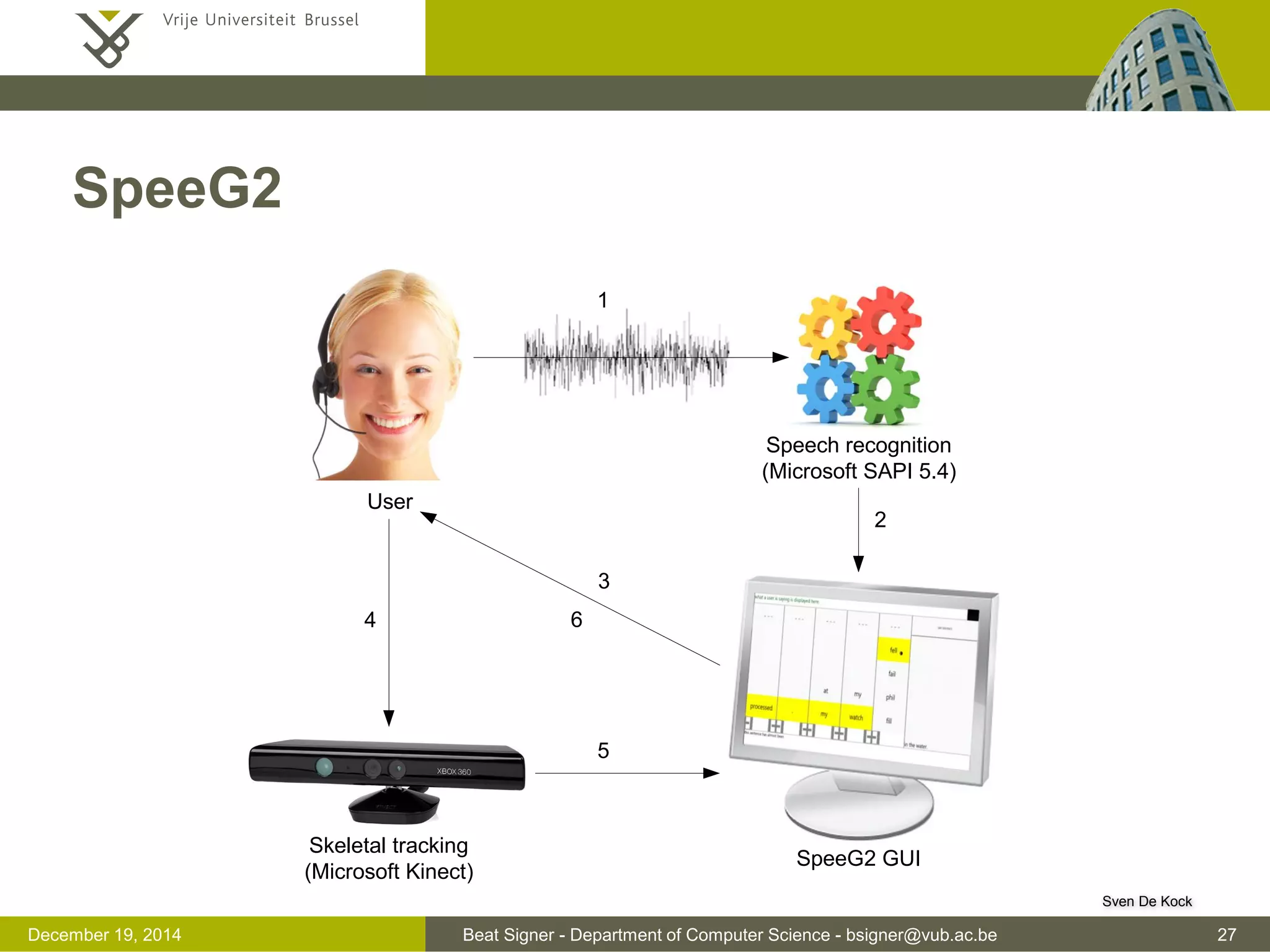
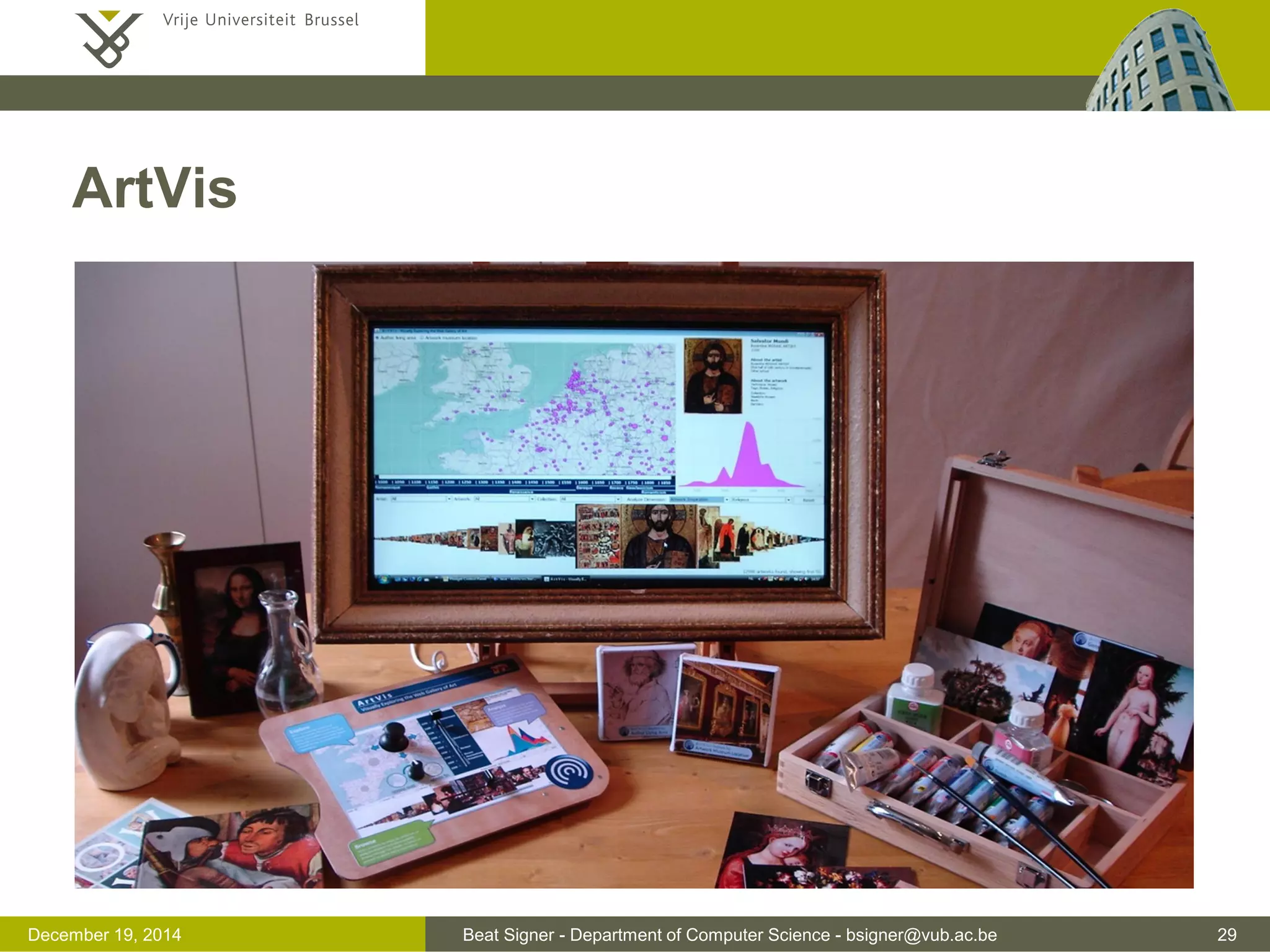
multimodal interaction (theoretical concepts, fusion and fission, ...)
interactive tabletops and surfaces
pen-based interaction and gesture-based interaction
tangible interaction, virtual reality and augmented reality
[http://wise.vub.ac.be/content/next-generation-user-interfaces]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture12-futuretrends-091210131440-phpapp02/75/Future-Trends-Lecture-12-Web-Information-Systems-4011474FNR-31-2048.jpg)