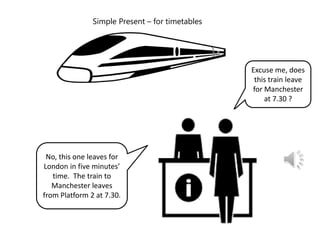
The document discusses several uses of verbs to refer to the future in English:
1) The simple present is used for timetables and fixed future events.
2) The present continuous is used for people's planned actions and future arrangements.
3) "Be going to" expresses intentions or predictions based on evidence of what will happen soon.
4) "Will" is used for requests, promises, snap decisions, predictions, inevitable events, expressions of determination, volunteering, opinions, and conditions in the first conditional.