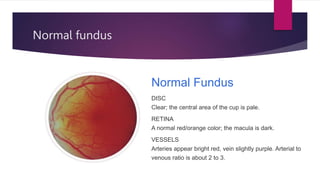
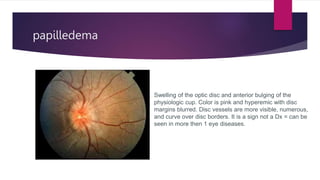
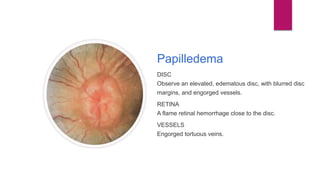
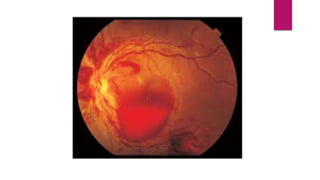
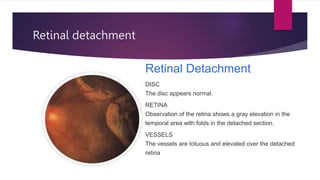
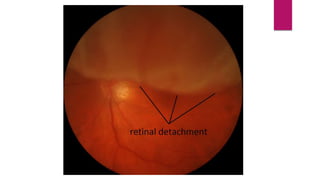
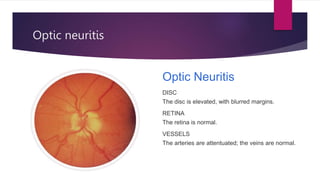
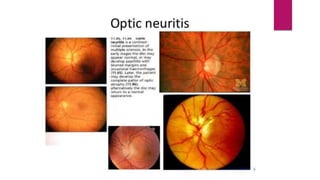
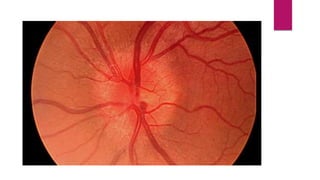
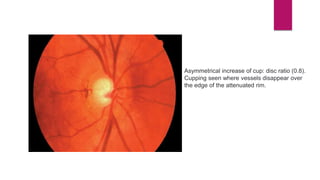
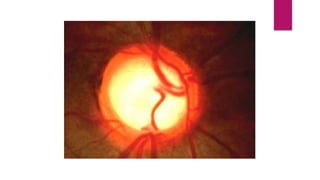
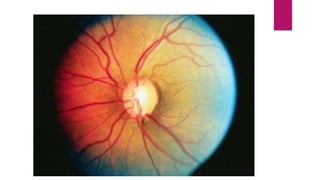
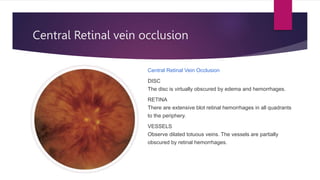
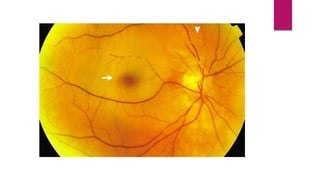
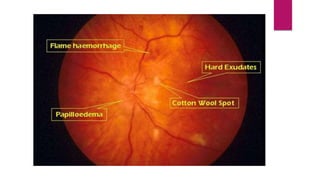
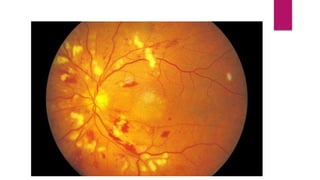
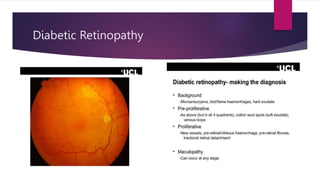
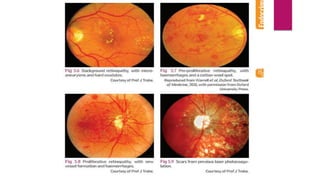
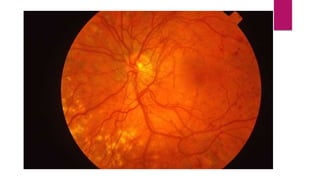
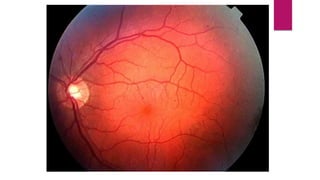
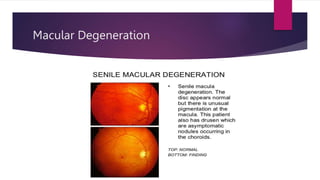
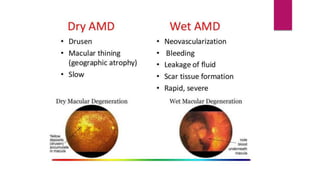
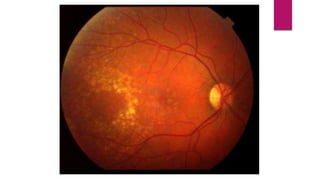
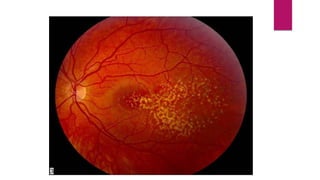
This document summarizes various funduscopic findings for different eye conditions. A normal fundus has a clear optic disc, red/orange retina with a dark macula, and bright red arteries and slightly purple veins. Papilledema shows swelling of the optic disc with blurred margins and engorged tortuous vessels. Retinal detachment appears as a gray retinal elevation with folded detached retina and tortuous elevated vessels. Optic neuritis presents as an elevated disc with blurred margins and normal retina and veins and attenuated arteries. Glaucoma shows cupping of the disc with displaced peripheral vessels and a pale cup. Central retinal vein occlusion fully obscures the disc due to edema and hemorrhages with blot retinal hemorrhages throughout