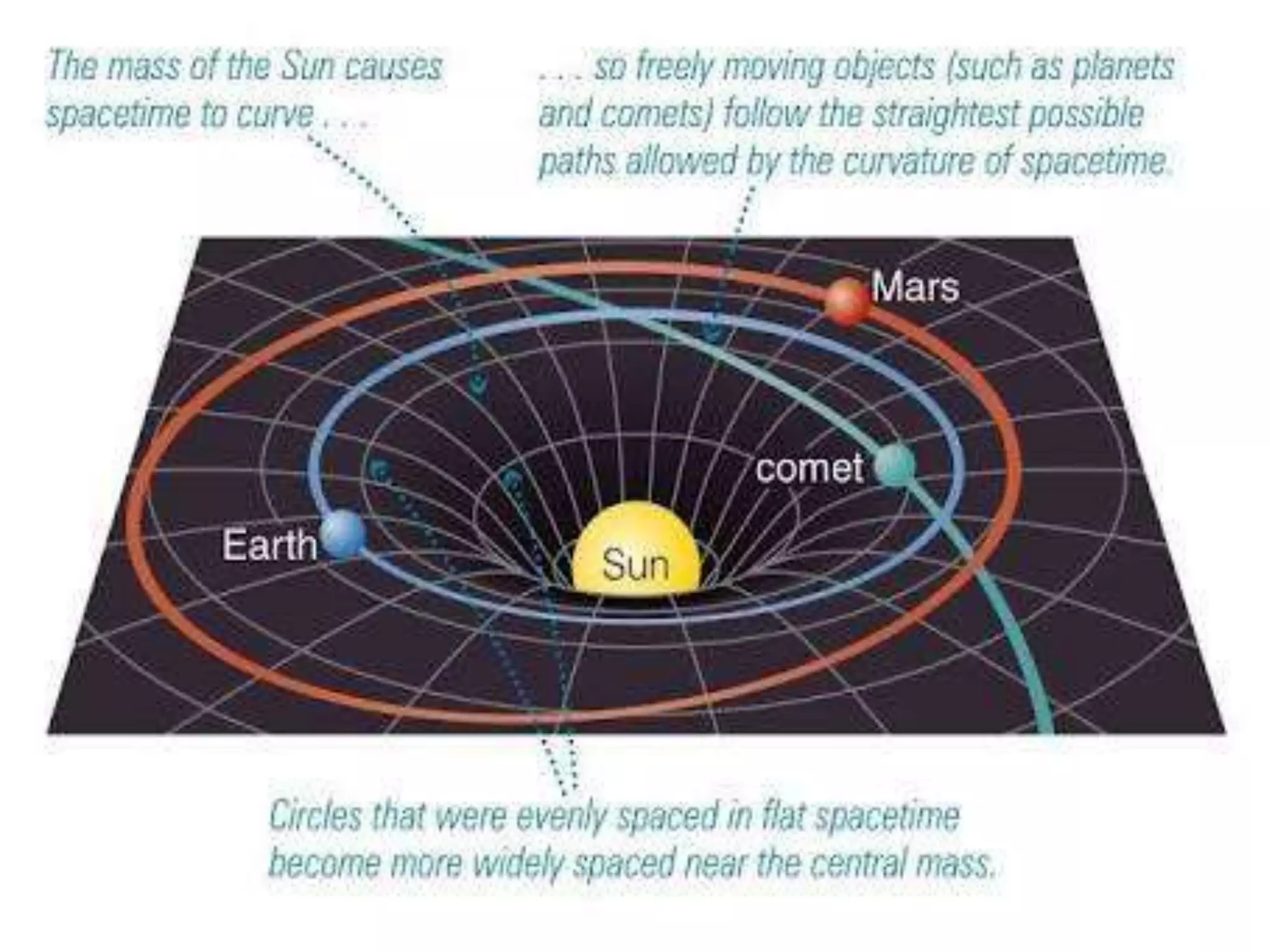
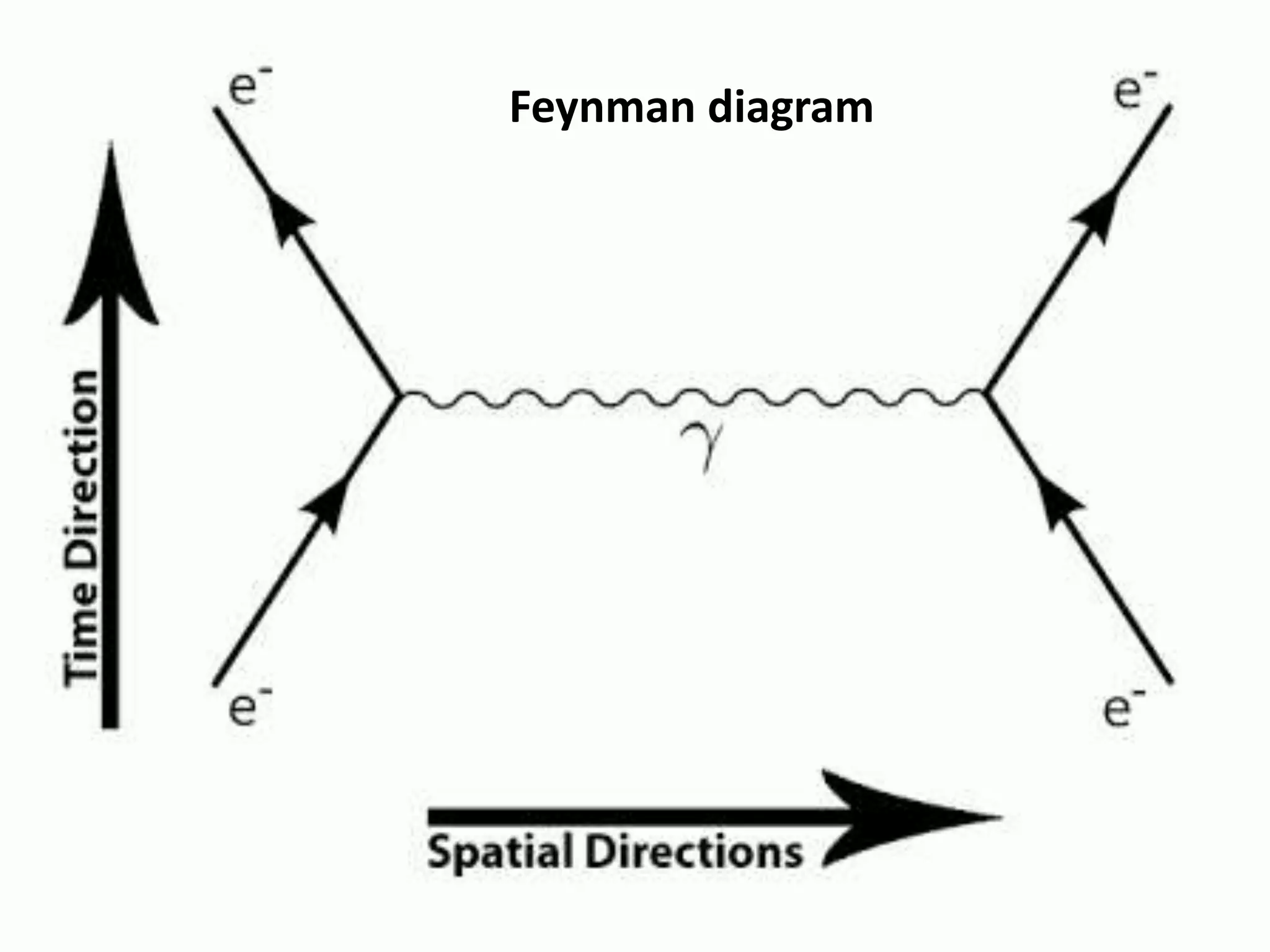
This document discusses the four fundamental forces in nature: gravitational, electromagnetic, weak nuclear, and strong nuclear forces. It provides details on what each force is, how it acts, examples of its effects, and the theories behind it. A key point is that physicists believe these forces may be interrelated and emerged from a single force early in the universe, as described by various grand unified theories that aim to connect fundamental forces and particles.