Physics is the study of natural phenomena in the physical world. It aims to understand and describe nature at its most fundamental level by making observations, performing experiments, and developing theories to explain experimental results. Some key ideas discussed are:
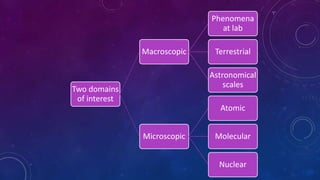
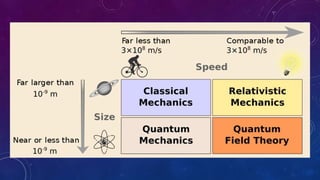
- Physics studies both macroscopic phenomena visible to the naked eye and microscopic phenomena at atomic and nuclear scales.
- The scientific method involves systematic observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling to understand natural phenomena.
- Major forces that govern physical interactions are gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces. The electromagnetic force is the strongest at atomic and molecular scales.