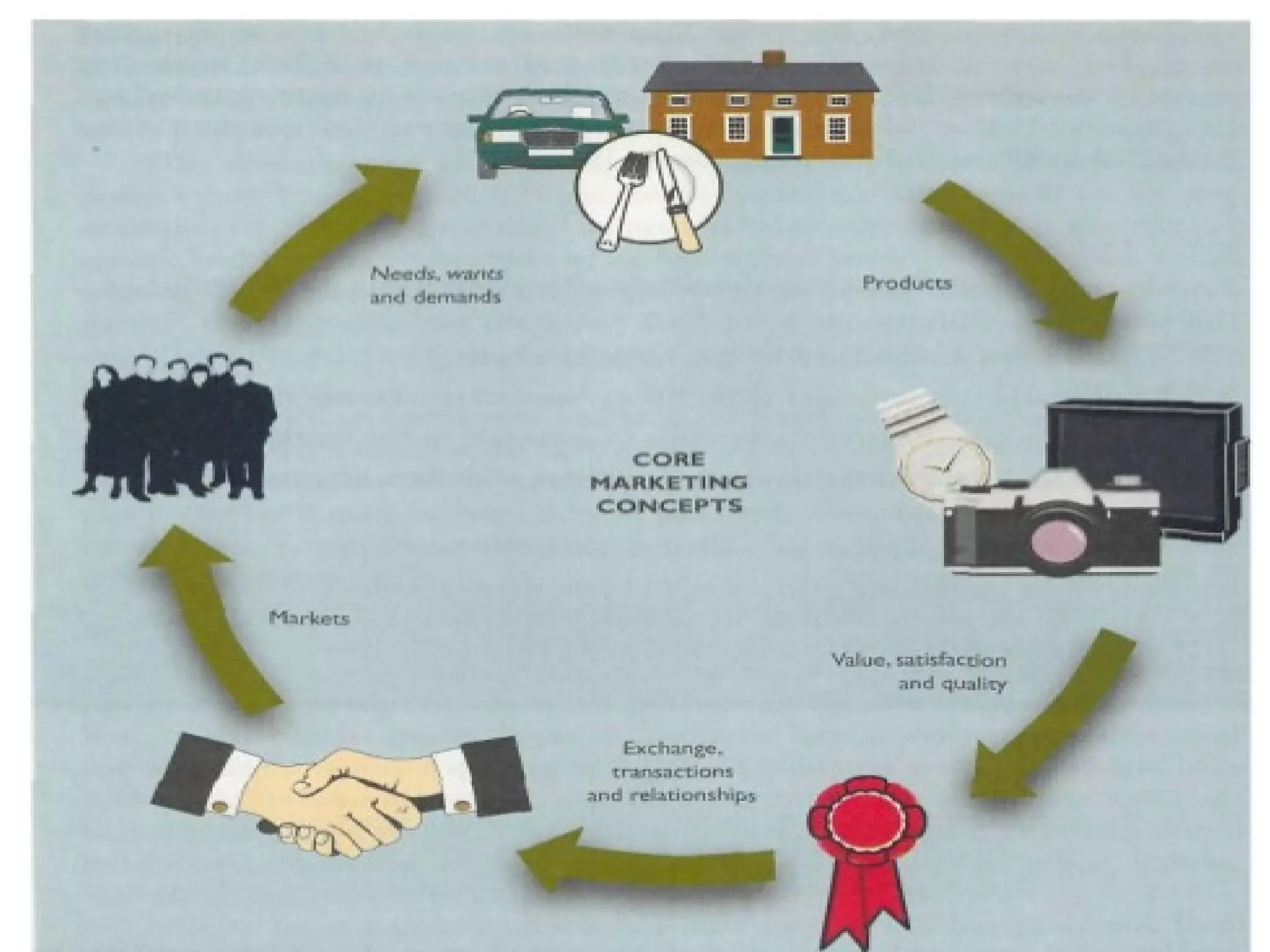
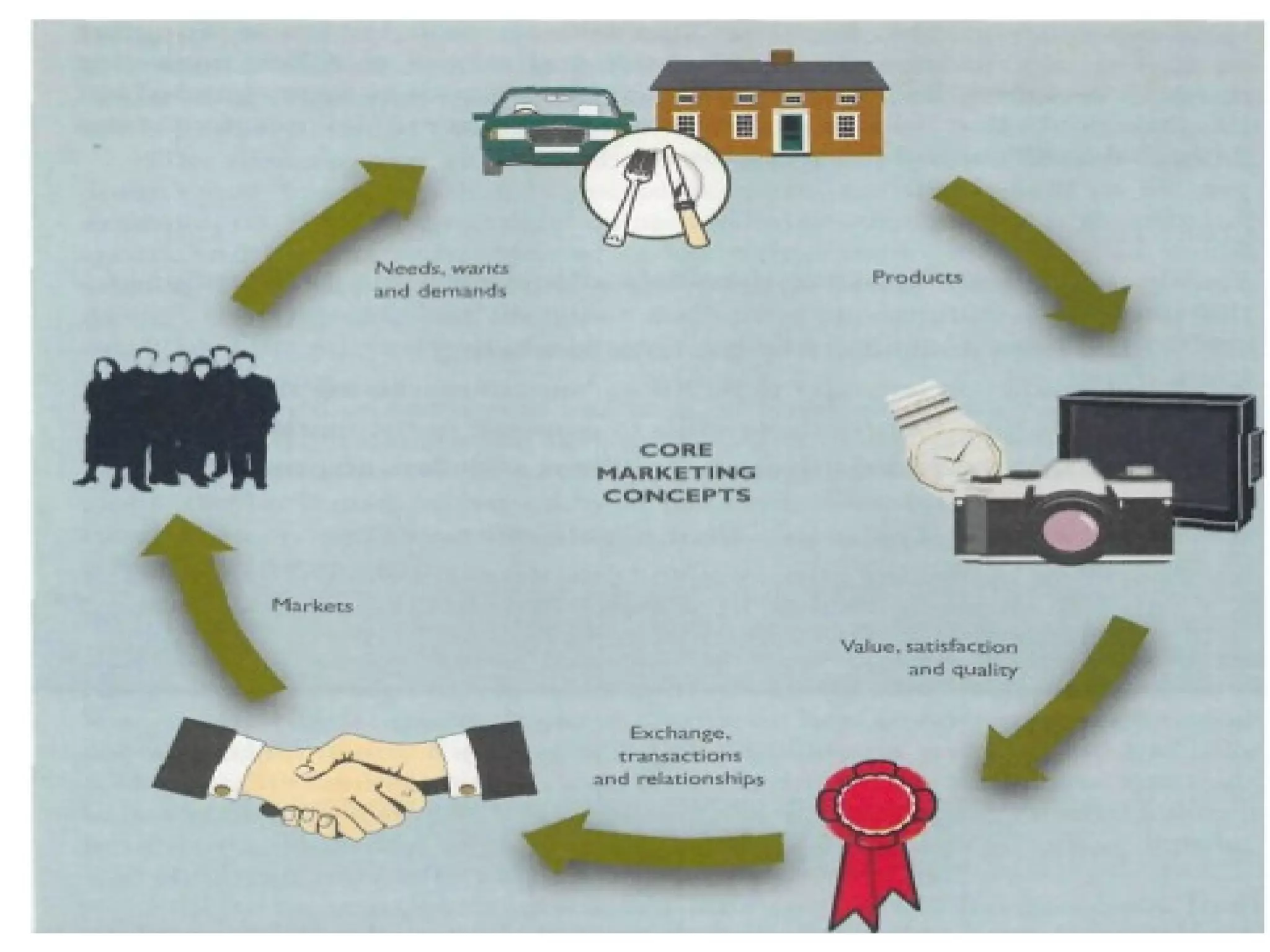
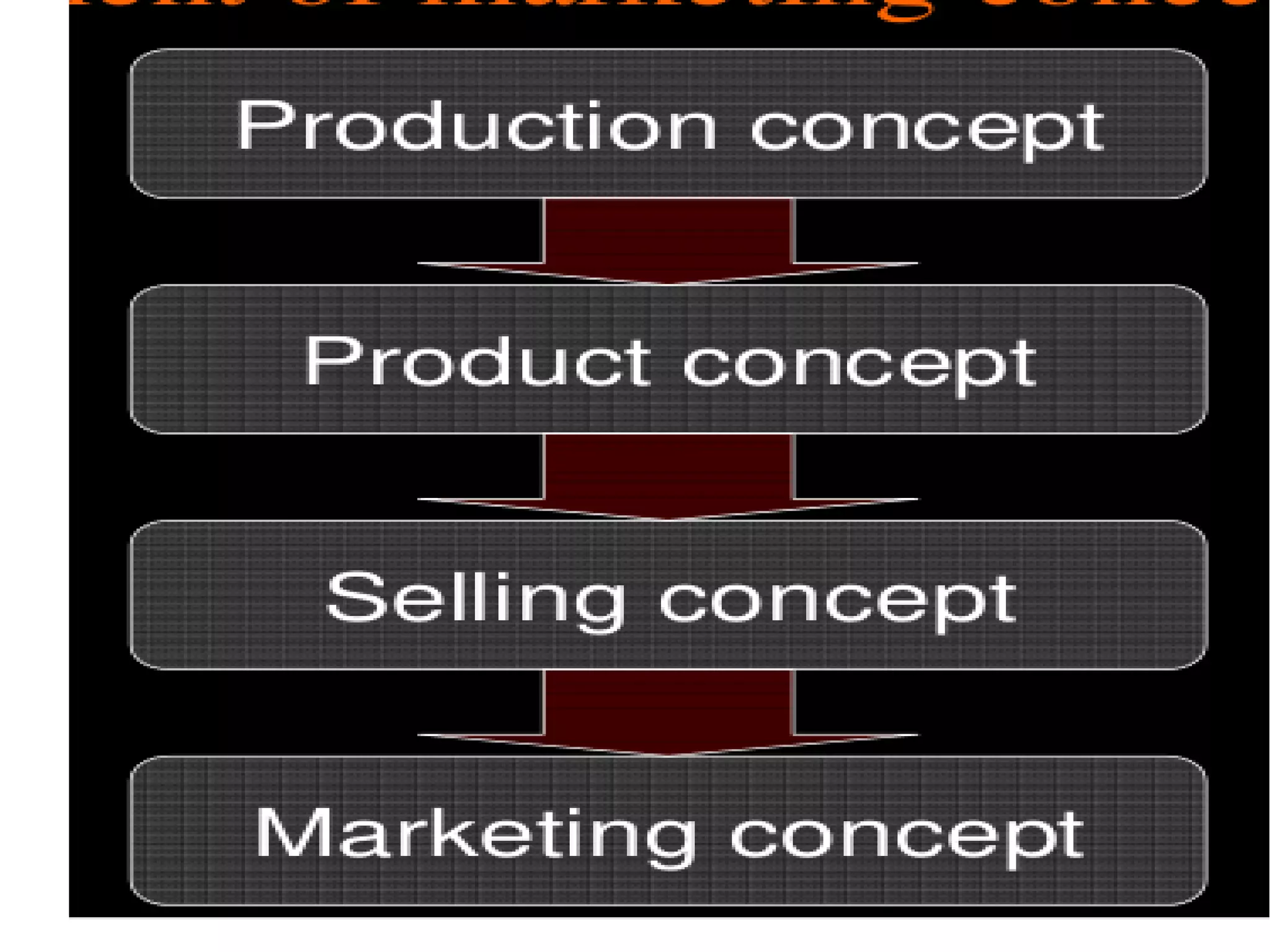
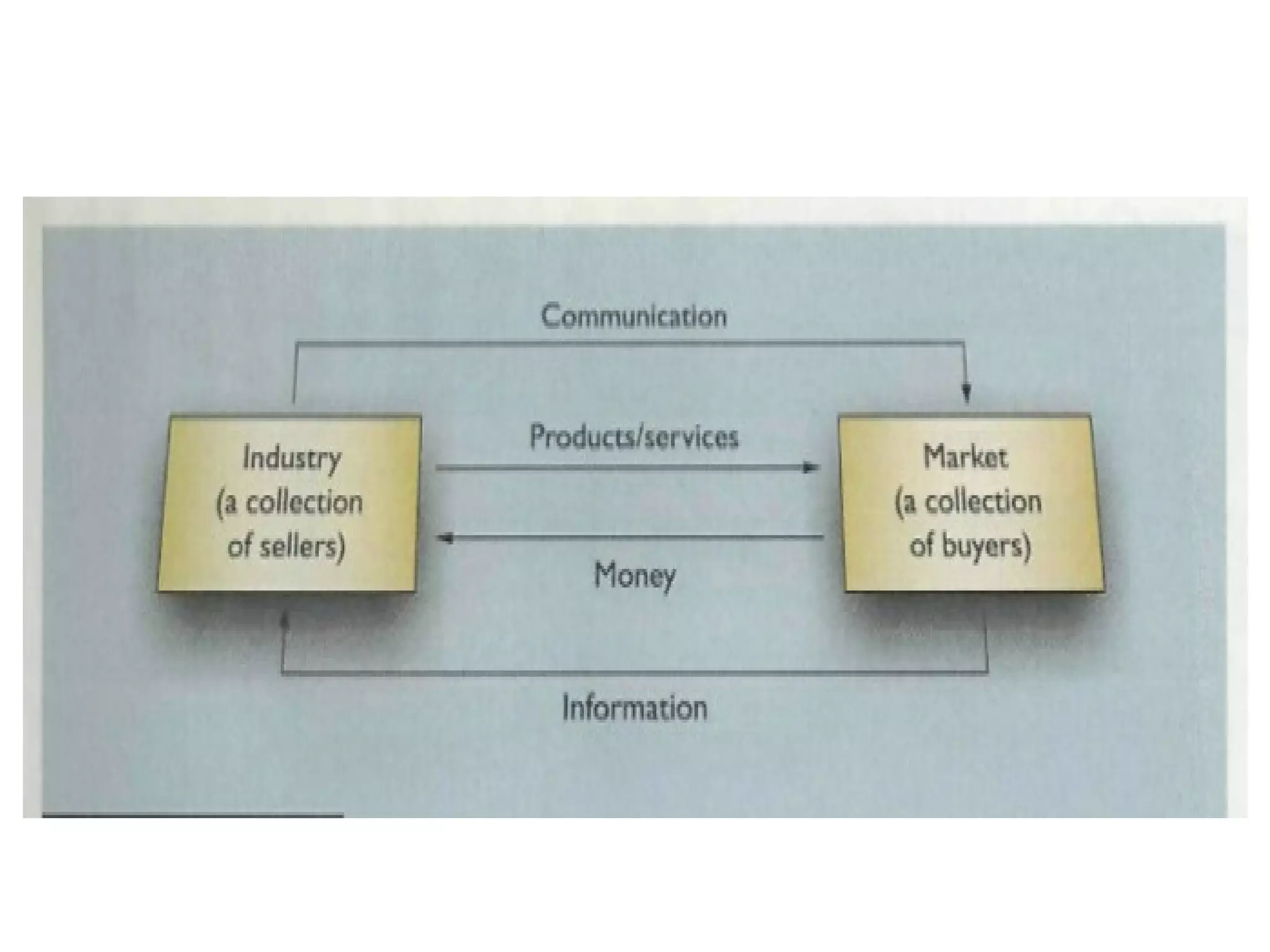
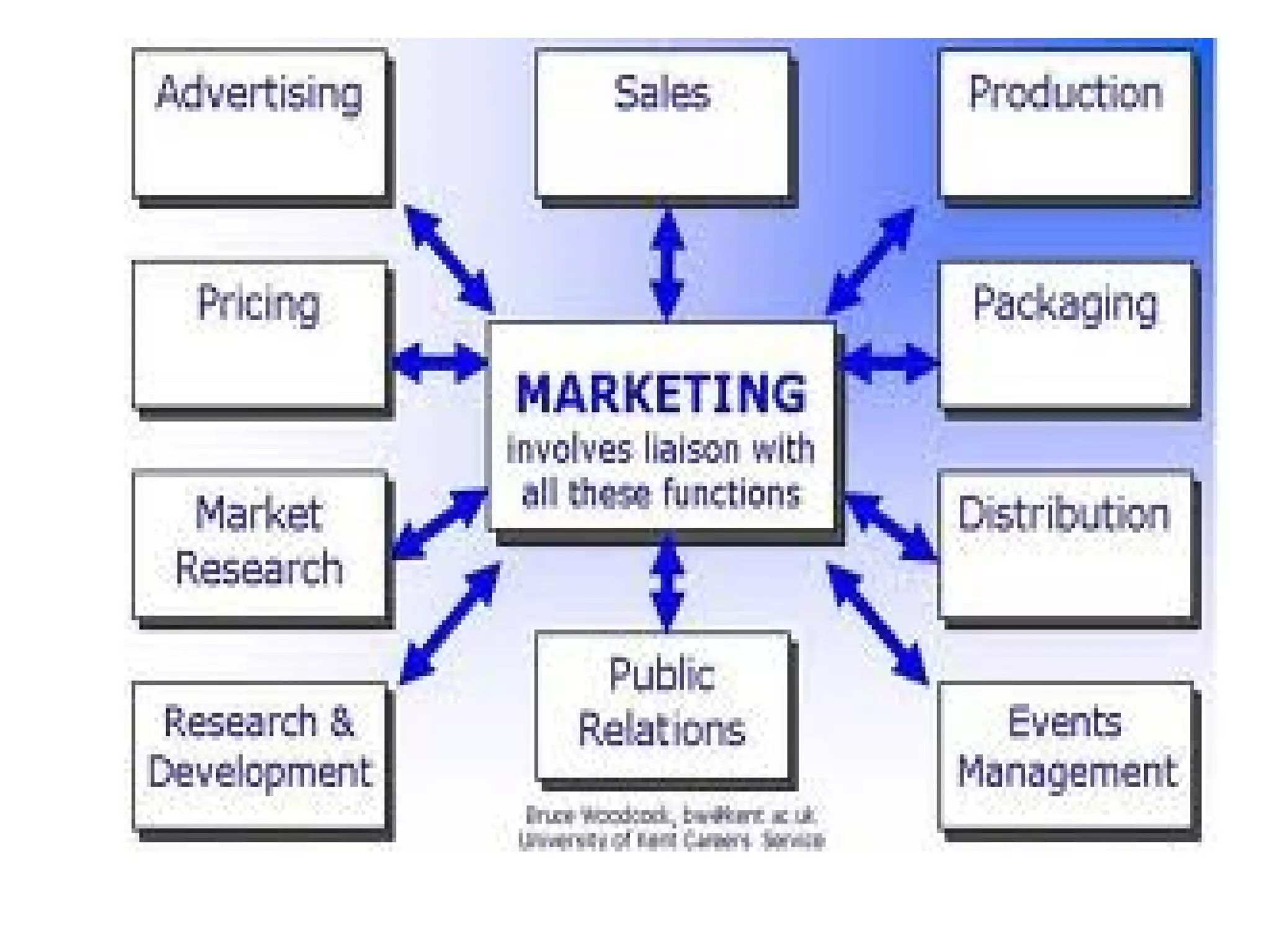
Marketing involves satisfying customer needs rather than just making sales. It encompasses 9 key functions: distribution, selling, financing, market information management, pricing, product/service management, promotion, transportation, and processing. These functions work together to move products from producers to consumers by facilitating buying, selling, financing, storage, transportation, processing, risk management, market research, and quality standards. The ultimate goal is to provide opportunities for consumers to purchase products that fulfill their needs.