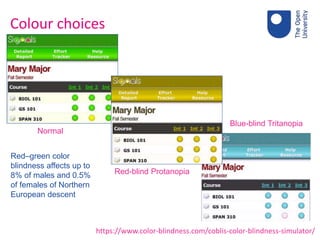
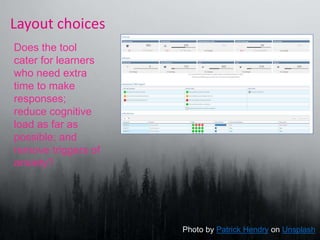
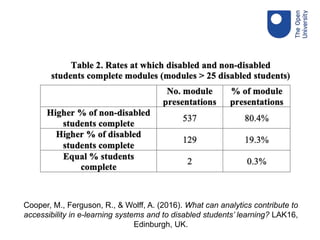
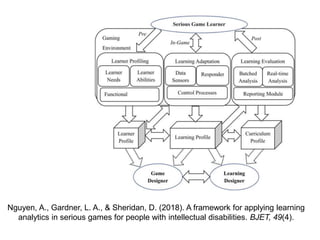
The document discusses the importance of accessible learning analytics for students with disabilities, emphasizing a social model that focuses on societal factors rather than individual deficits. It highlights the need for tools to be designed inclusively, considering color blindness, layout, and the reduction of cognitive load to enhance usability. Overall, it advocates for the adaptation of tools to ensure that all learners can effectively engage with learning analytics.