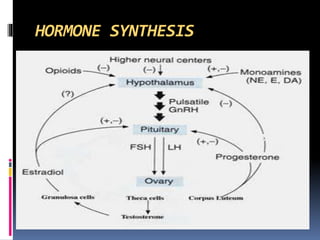
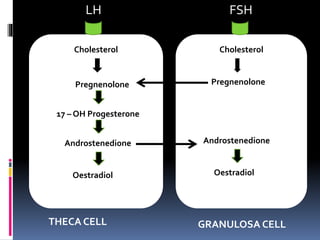
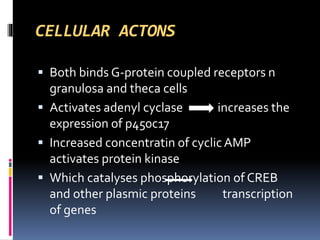
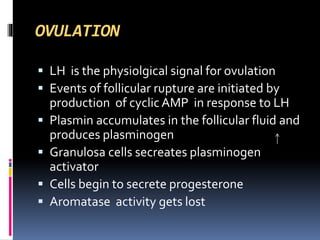
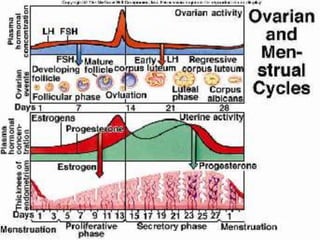
This document summarizes the roles and actions of the gonadotrophins FSH and LH in females. It describes their chemical structure as glycoproteins composed of alpha and beta subunits. FSH stimulates follicular development and estrogen production by granulosa cells. LH triggers ovulation and corpus luteum formation, supporting oocyte maturation and progesterone secretion. Both FSH and LH act through G-protein coupled receptors in theca and granulosa cells to regulate steroidogenesis and gene expression critical for female reproductive functions.