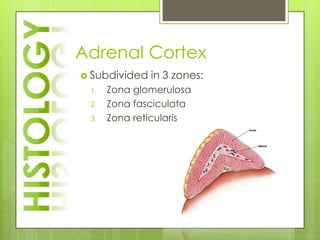
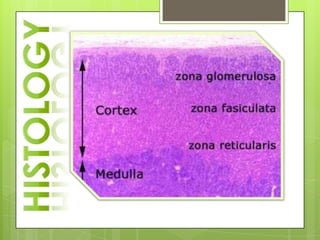
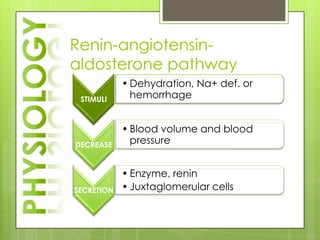
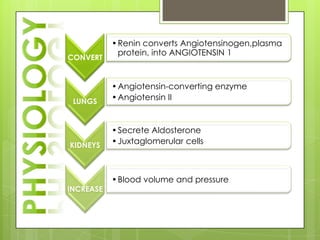
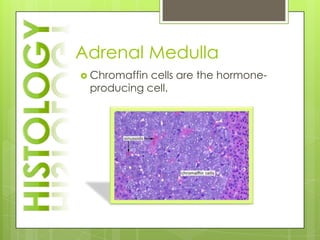
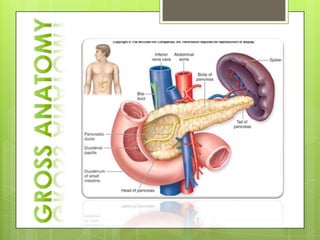
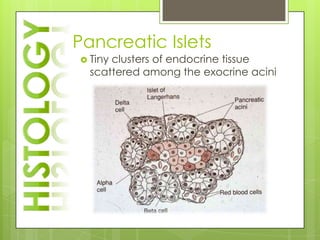
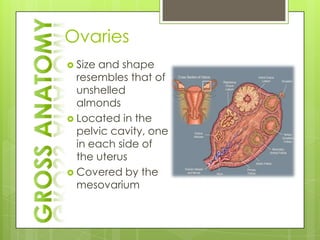
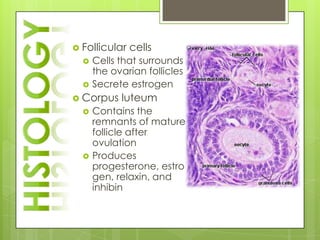
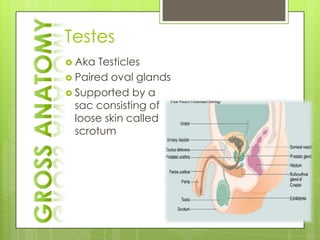
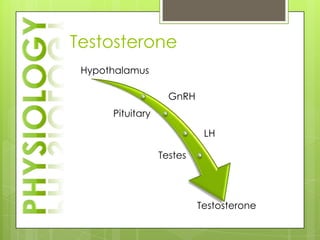
The adrenal glands are located above the kidneys and consist of an outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex secretes mineralocorticoids like aldosterone and glucocorticoids like cortisol. The medulla secretes catecholamines such as norepinephrine and epinephrine. The pancreas contains clusters of cells called islets that secrete glucagon and insulin which regulate blood sugar levels. The ovaries and testes are reproductive endocrine glands. The ovaries secrete estrogens and progesterone while the testes secrete testosterone.