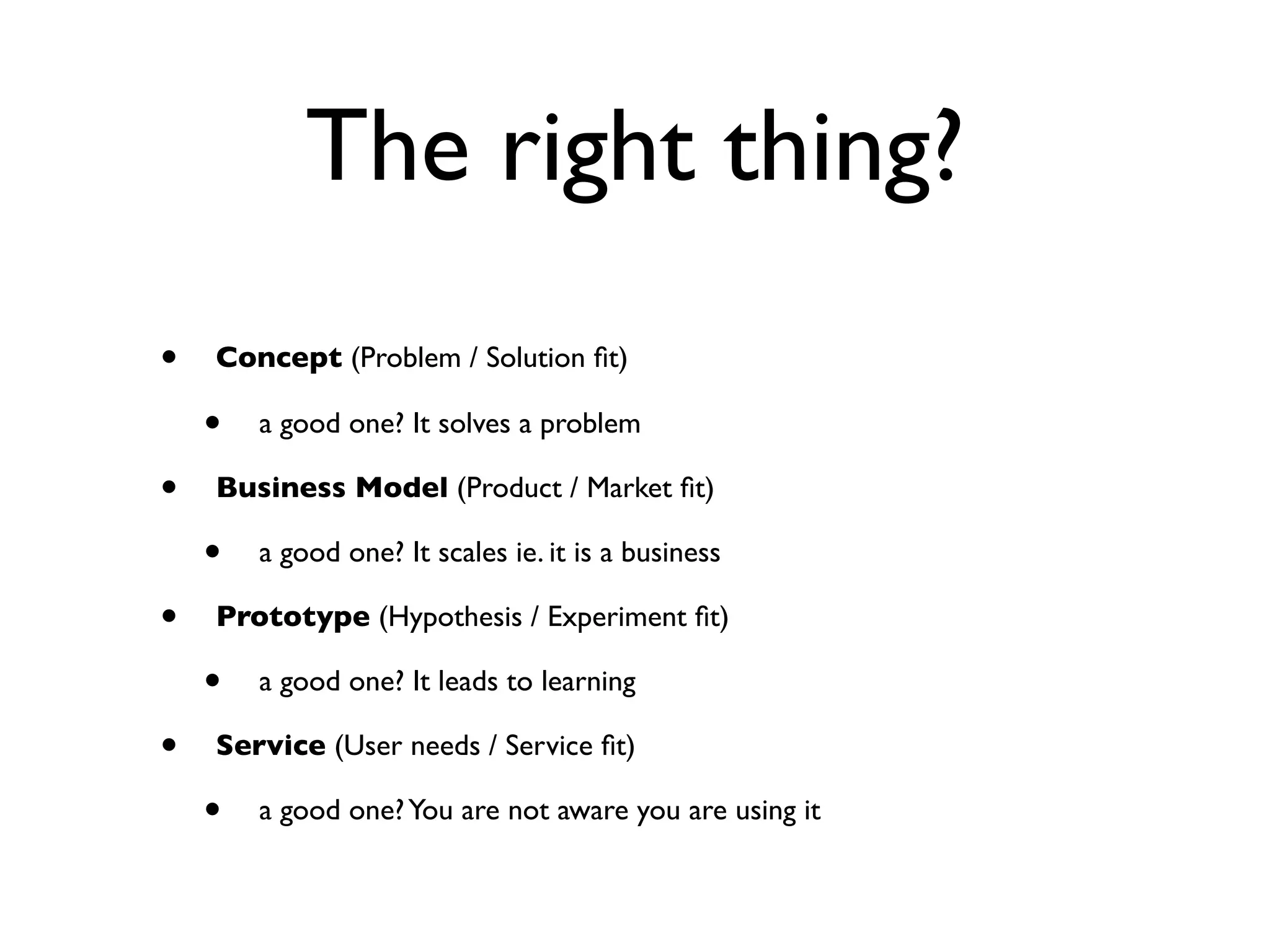
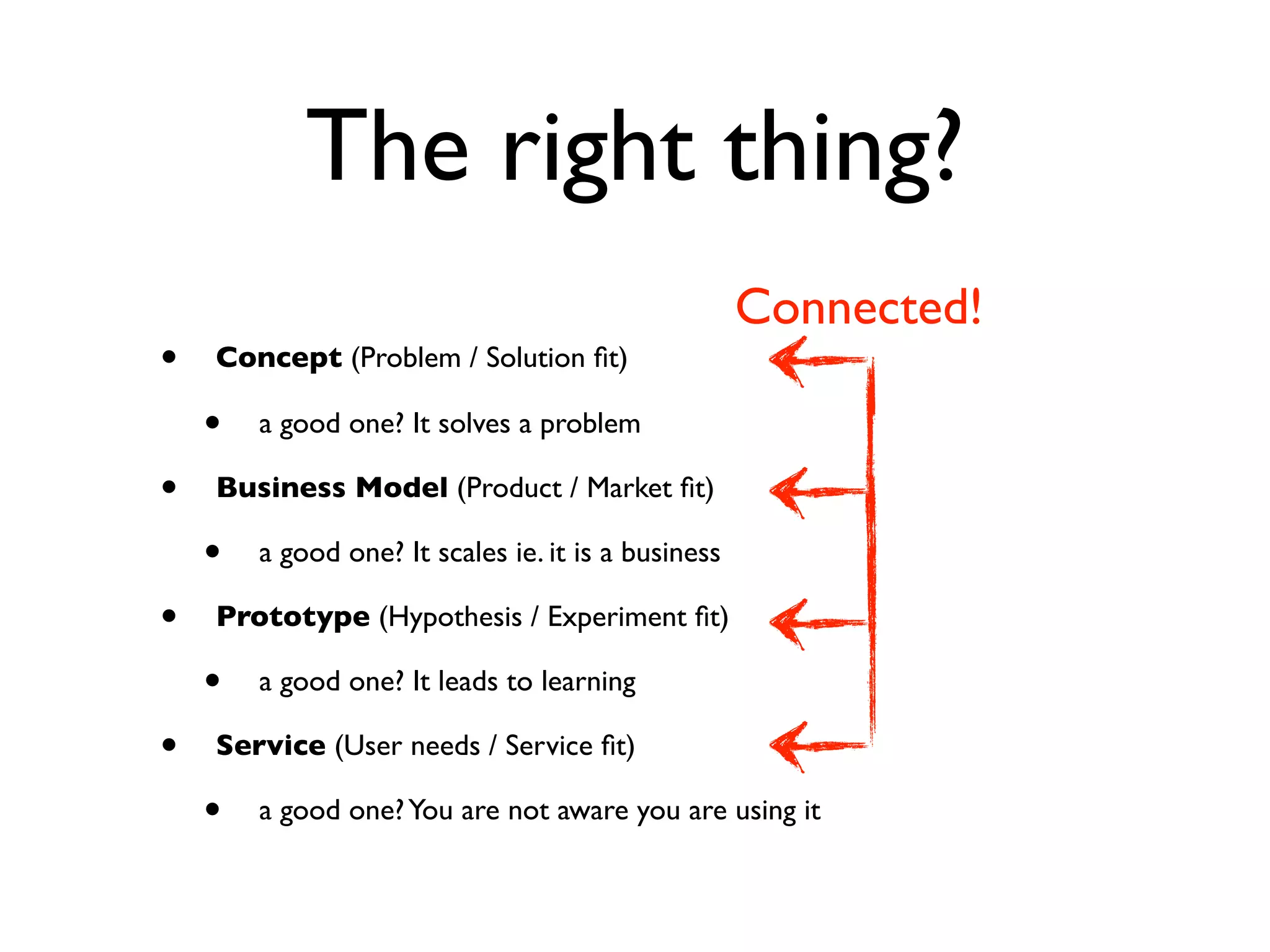
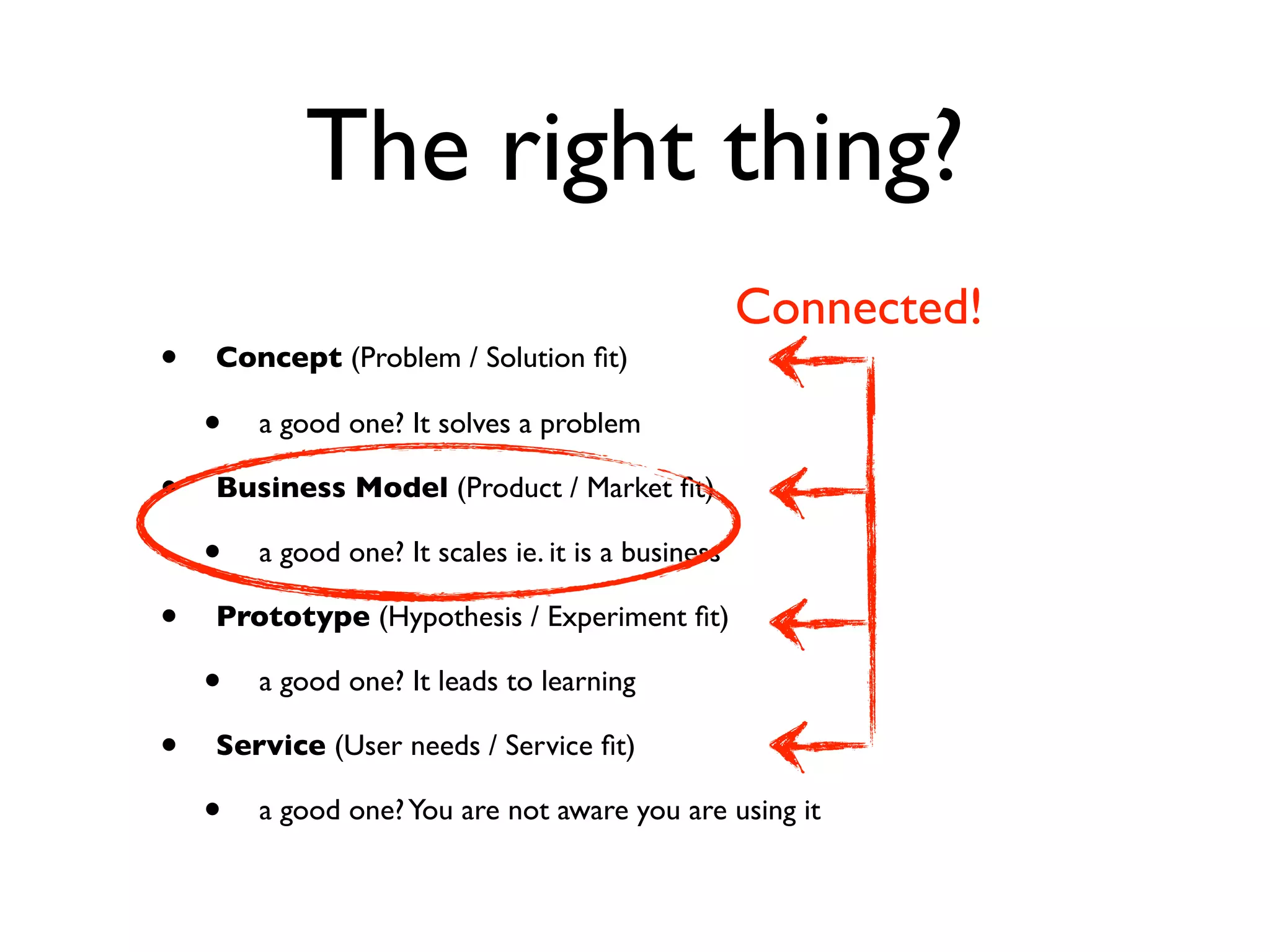
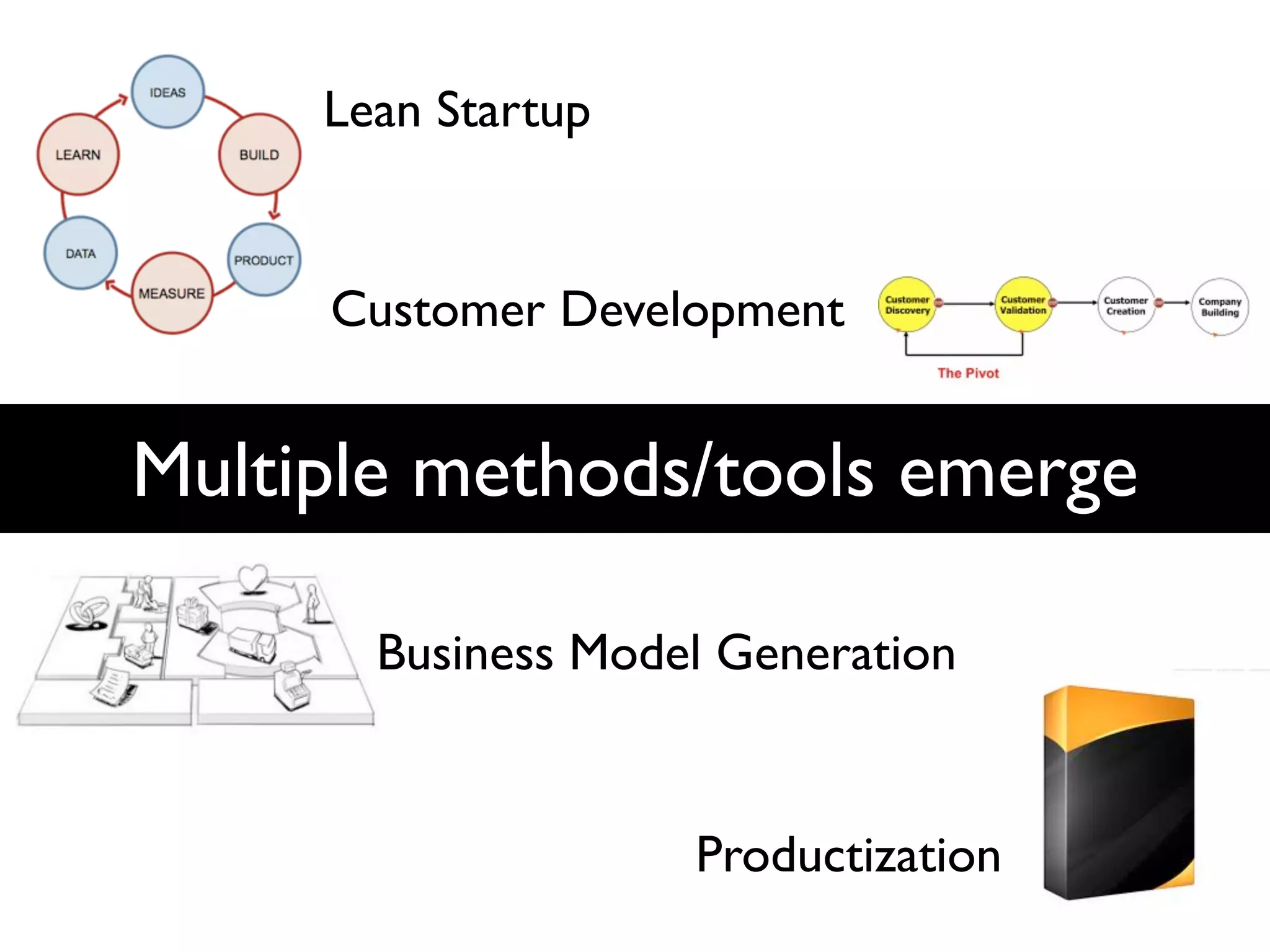
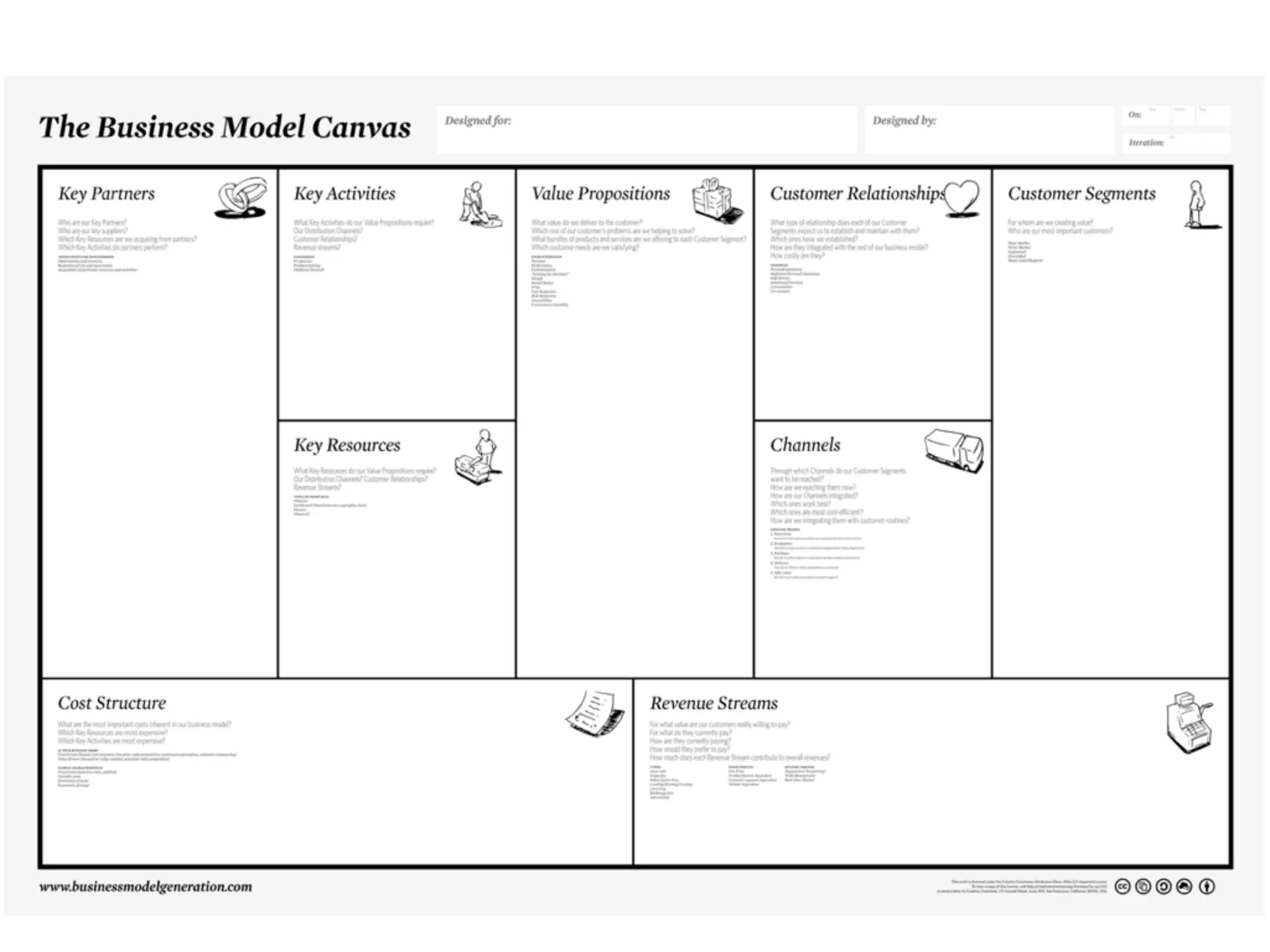
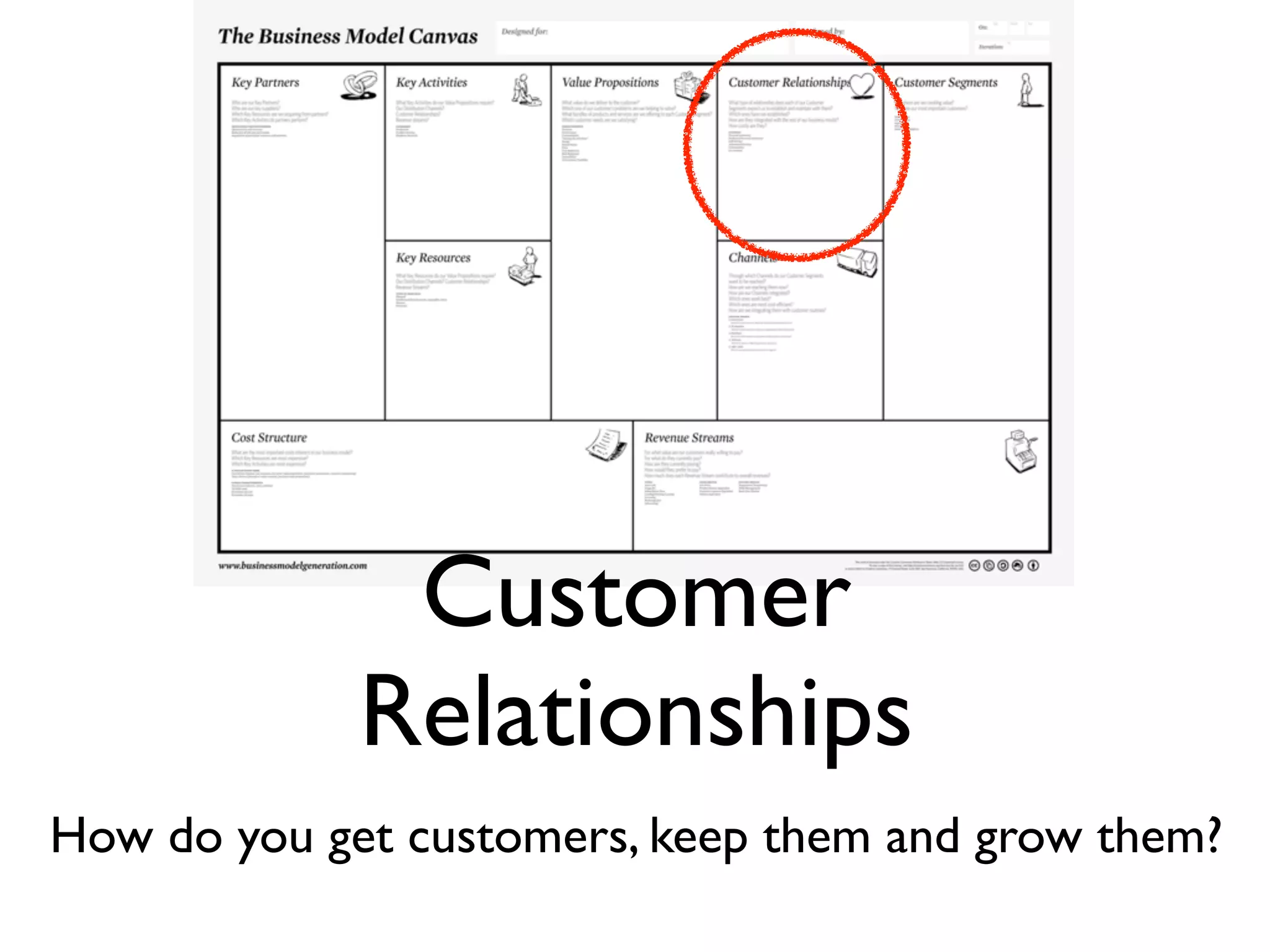
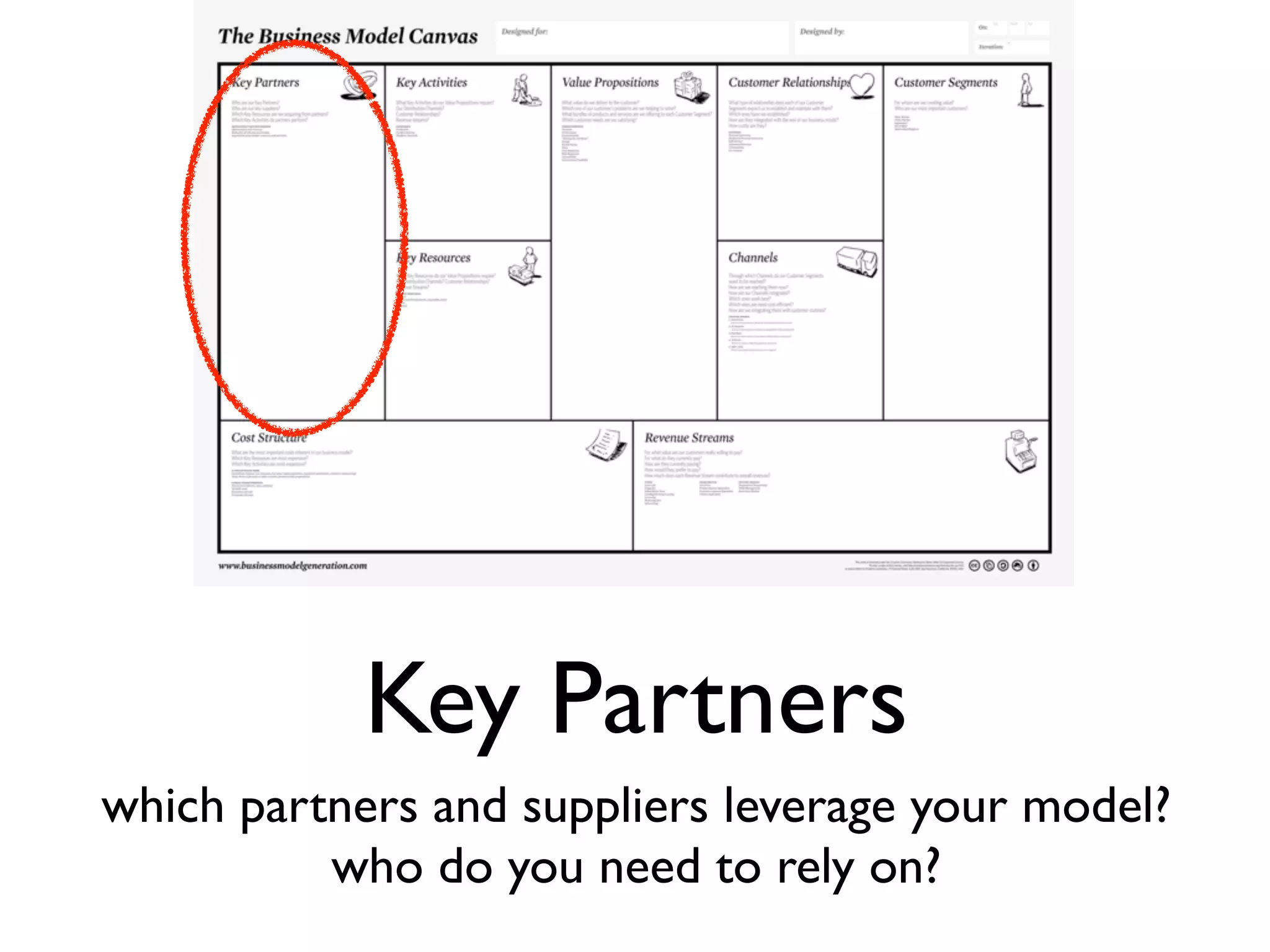
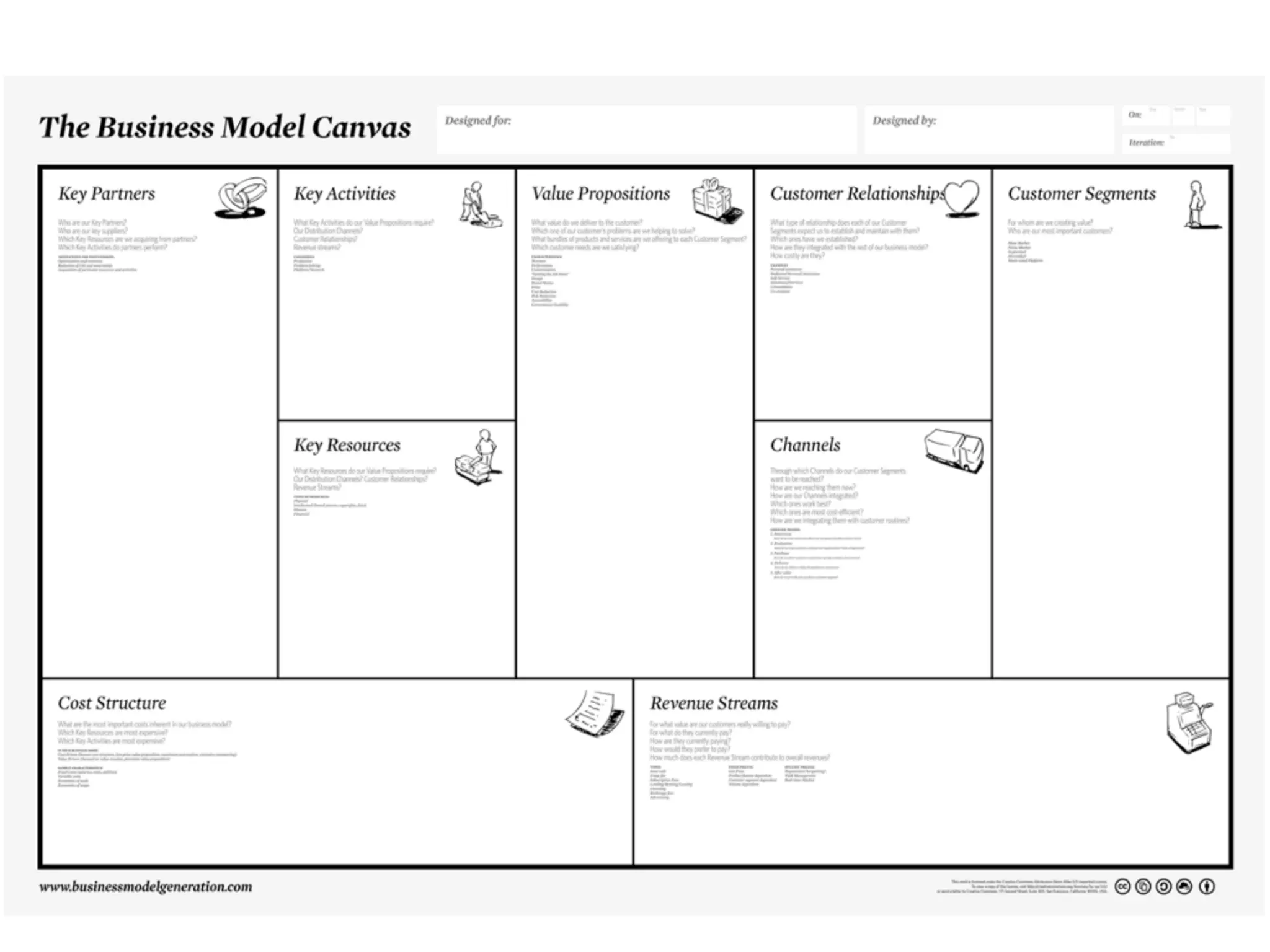
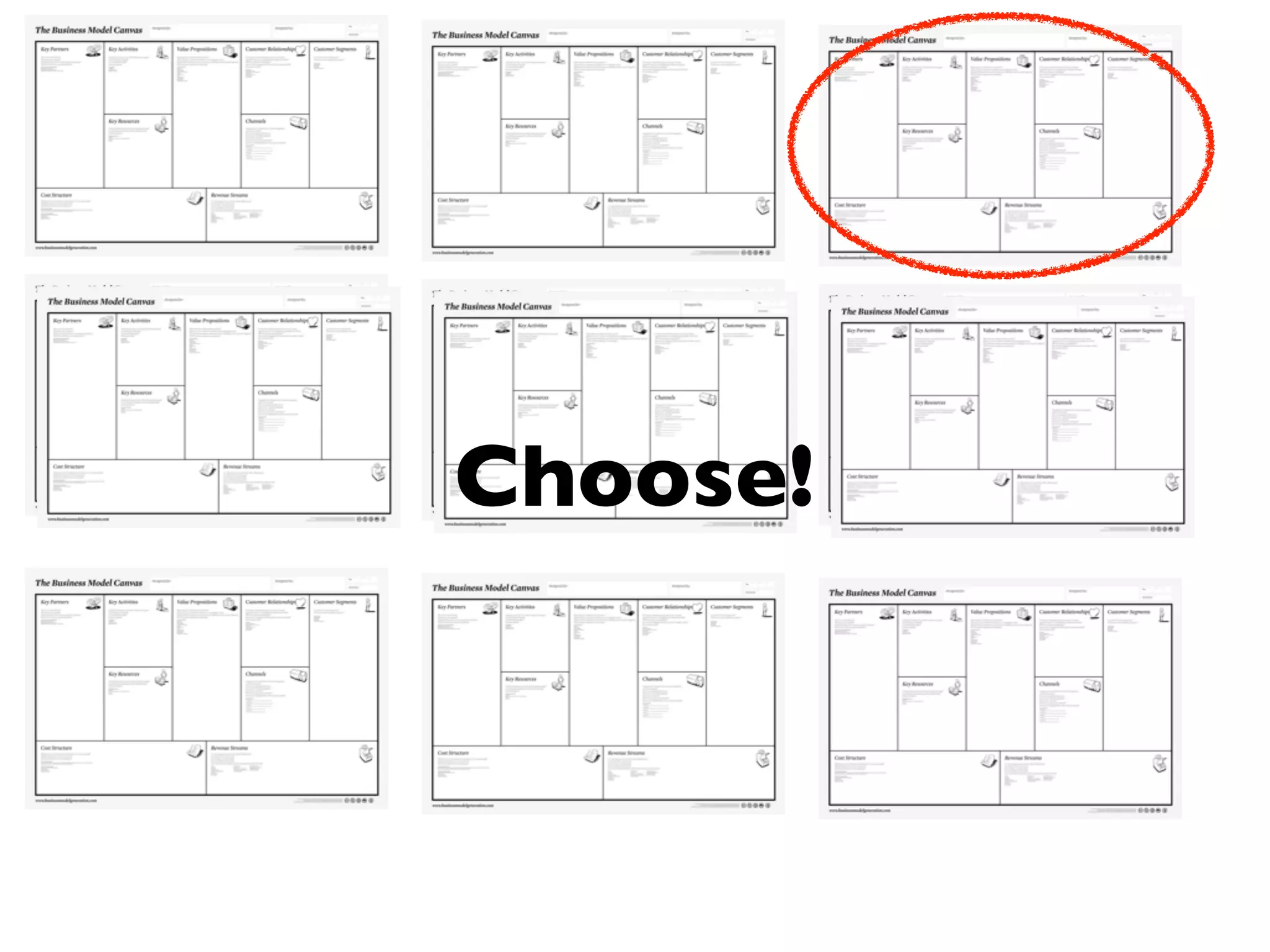
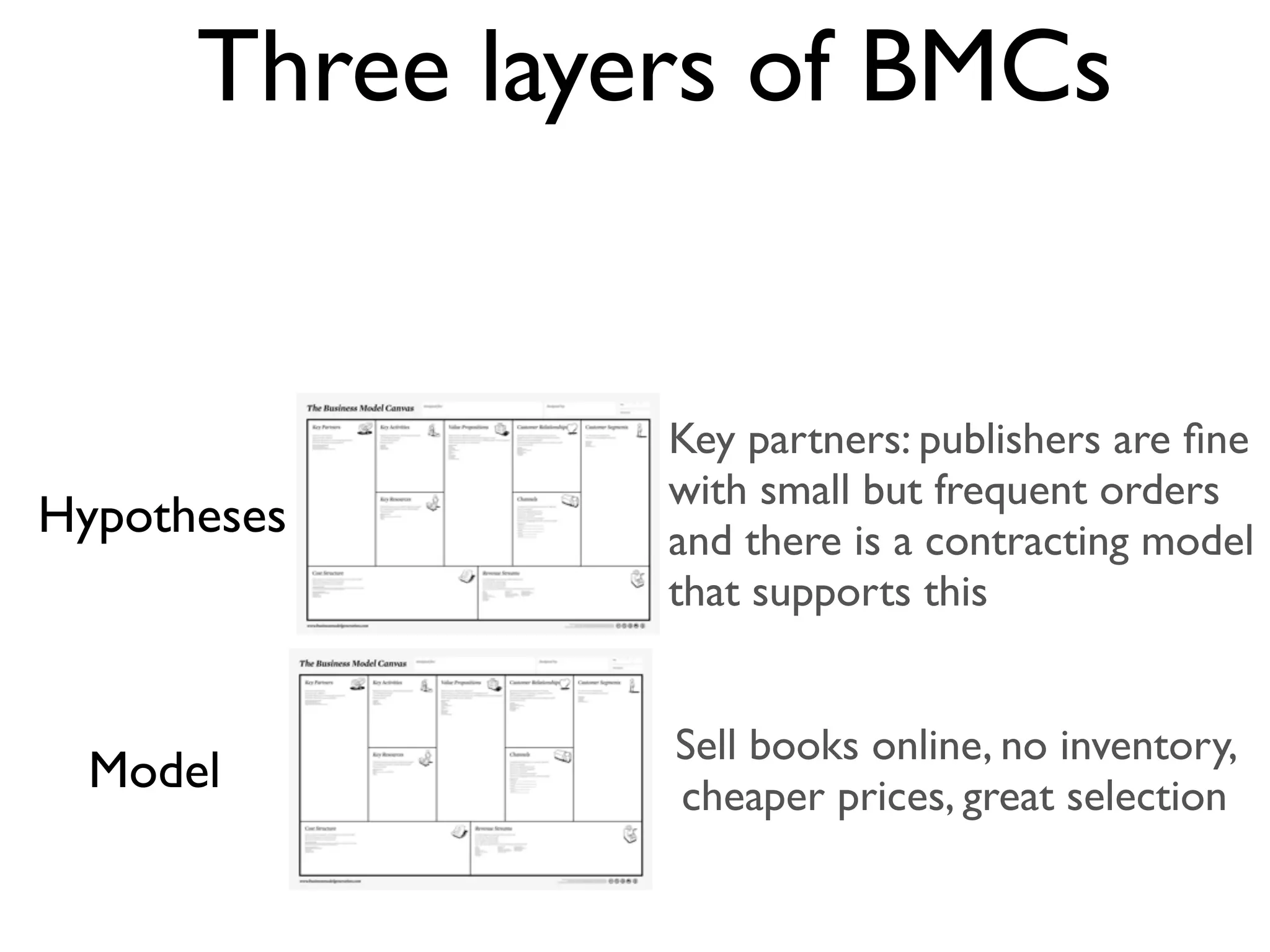
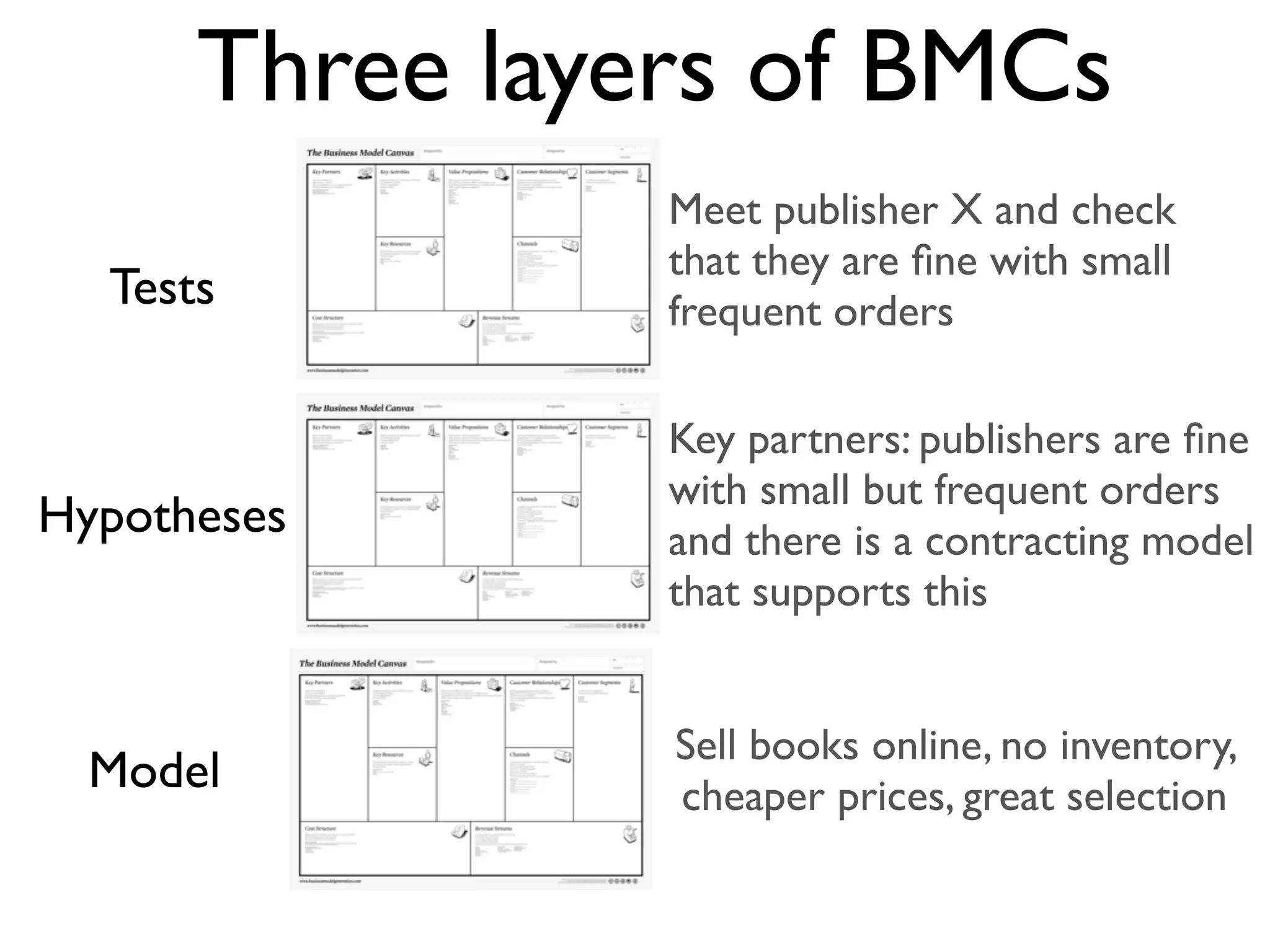
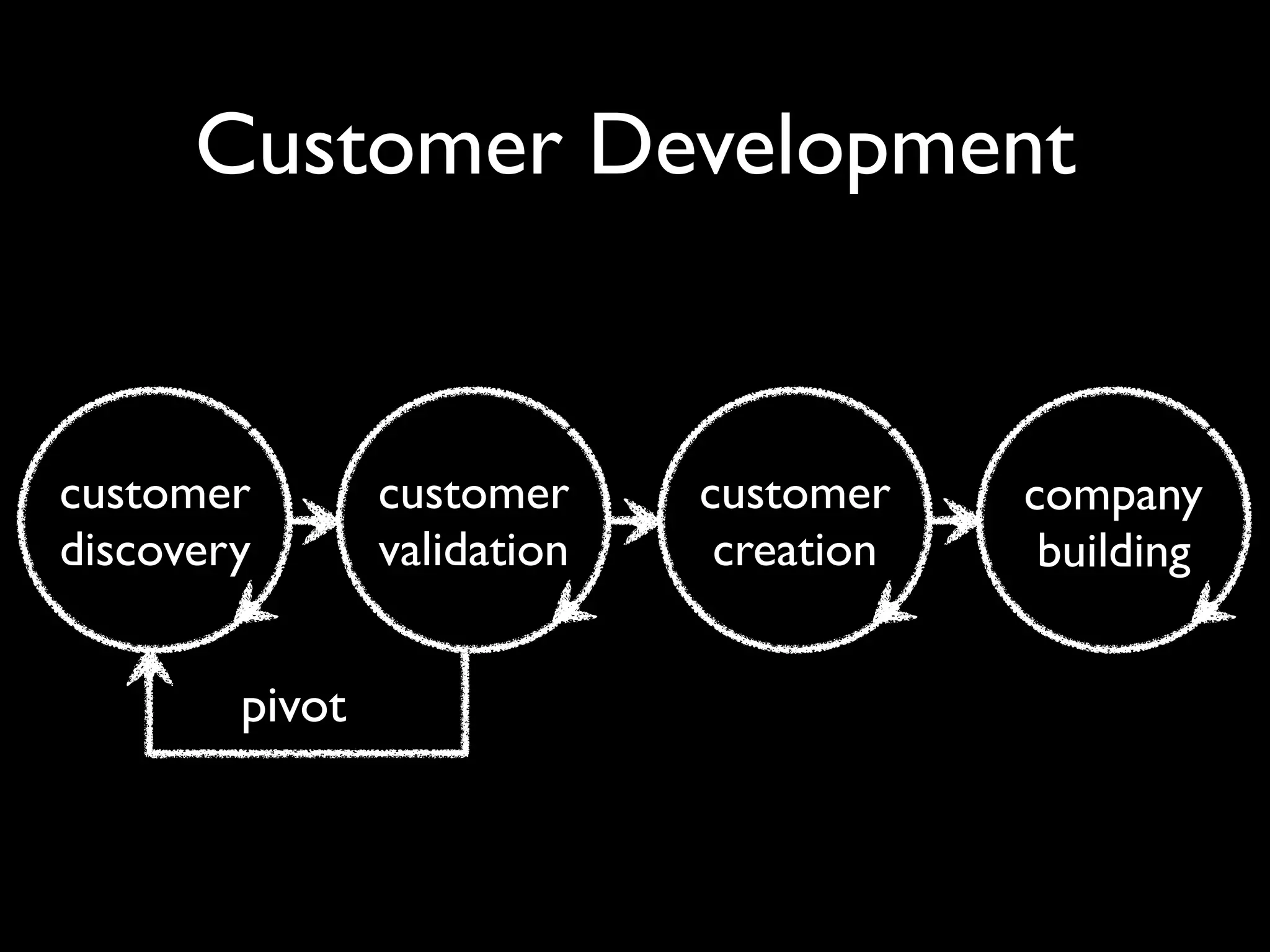
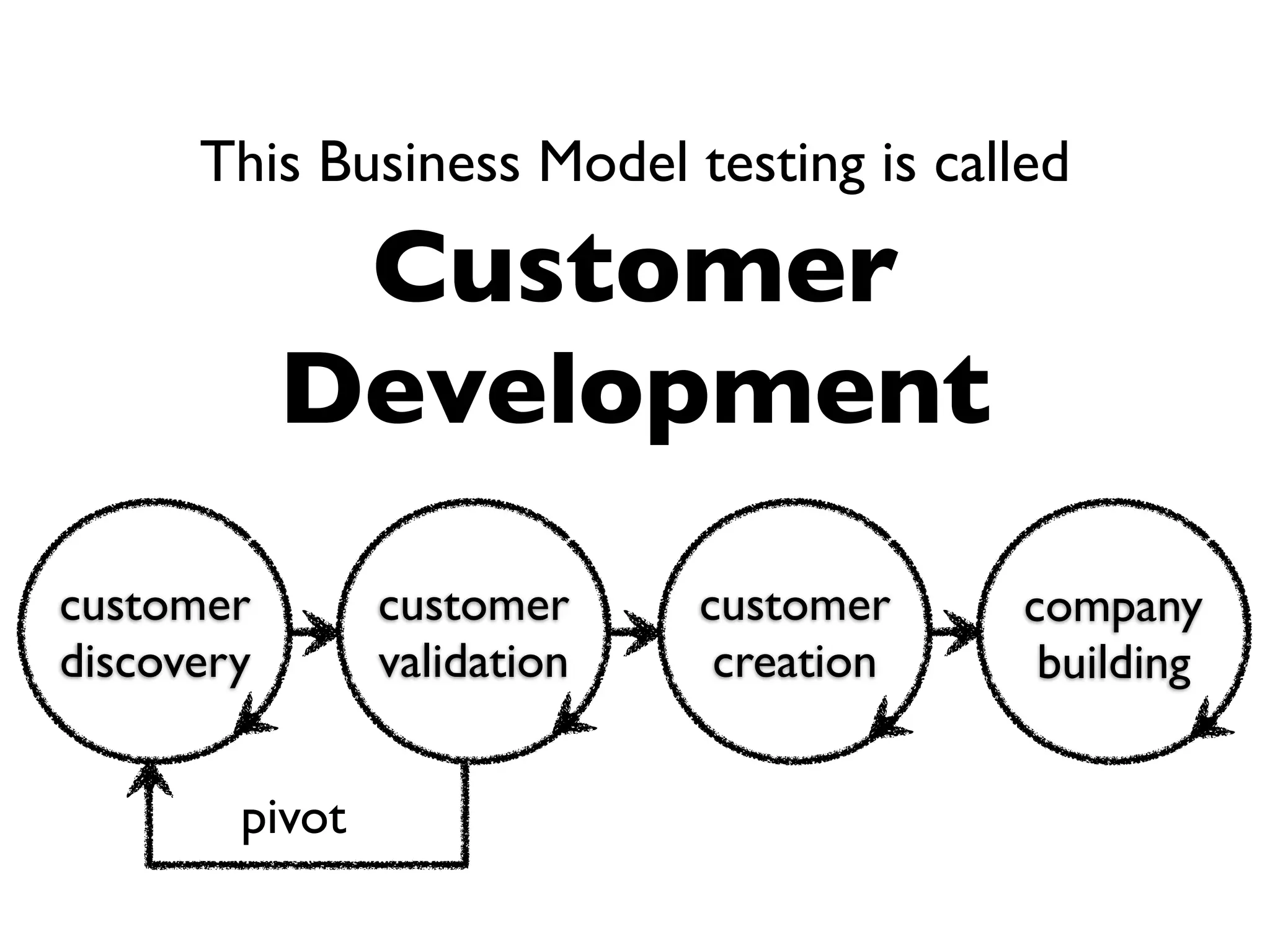
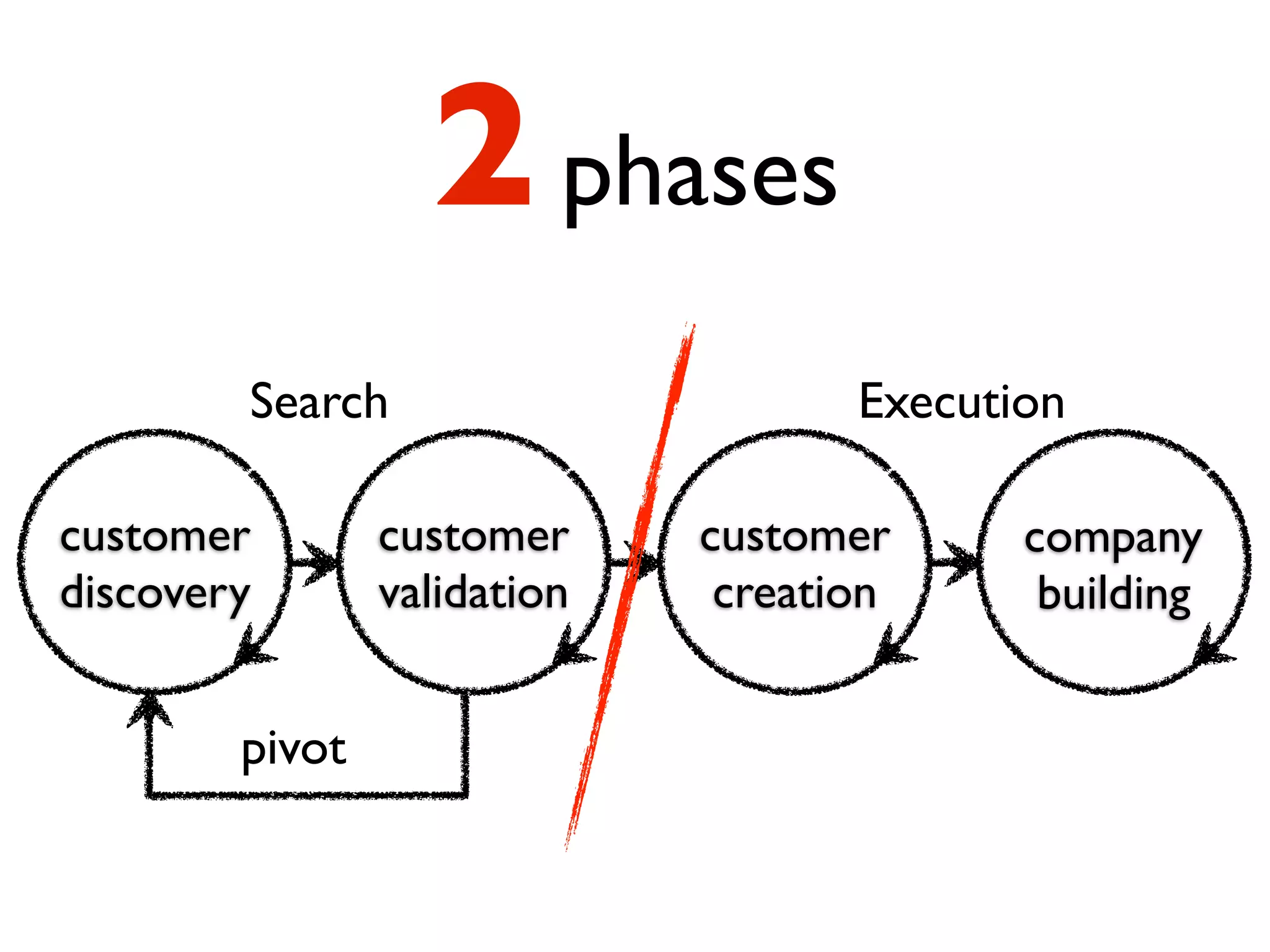
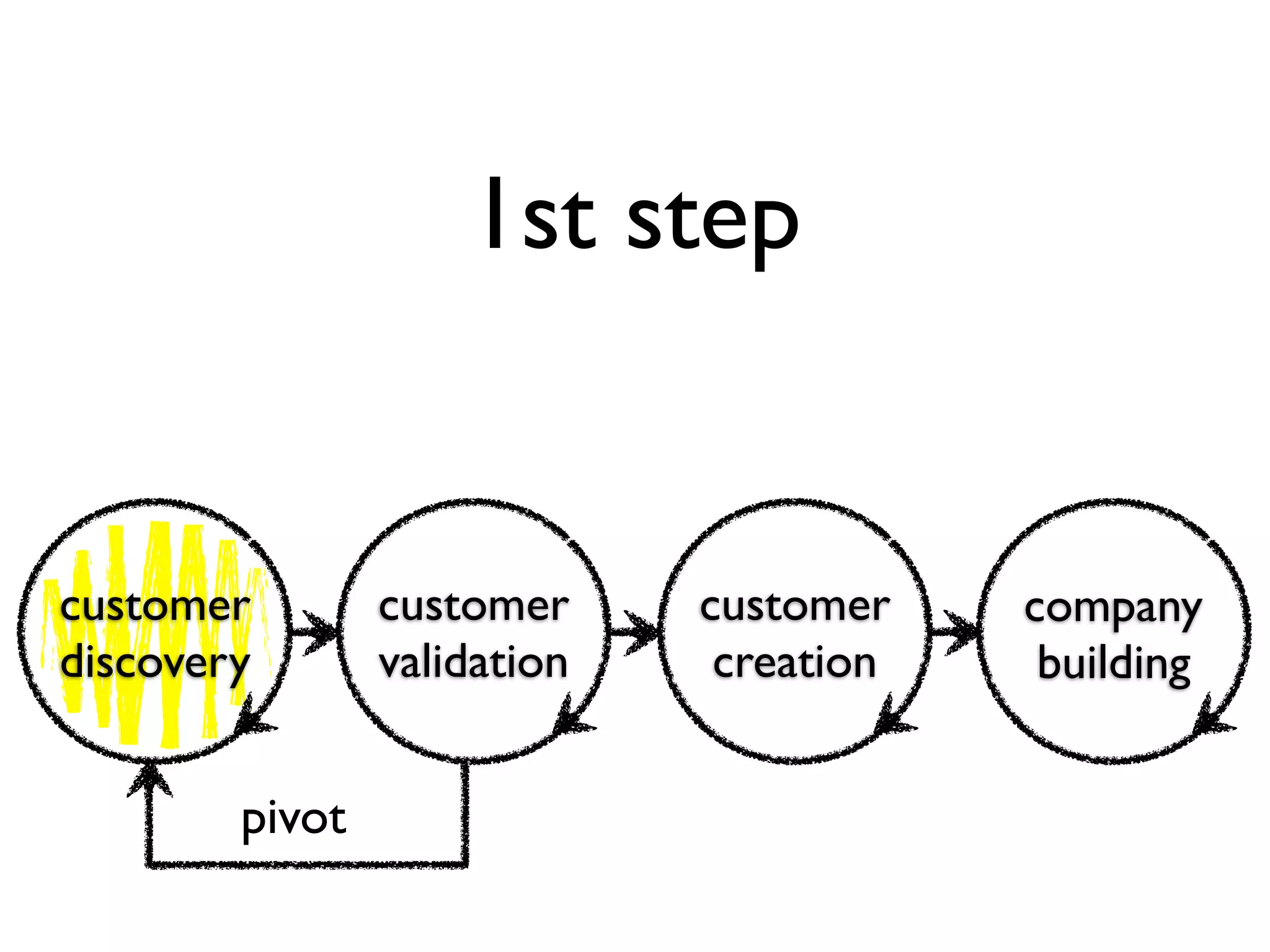
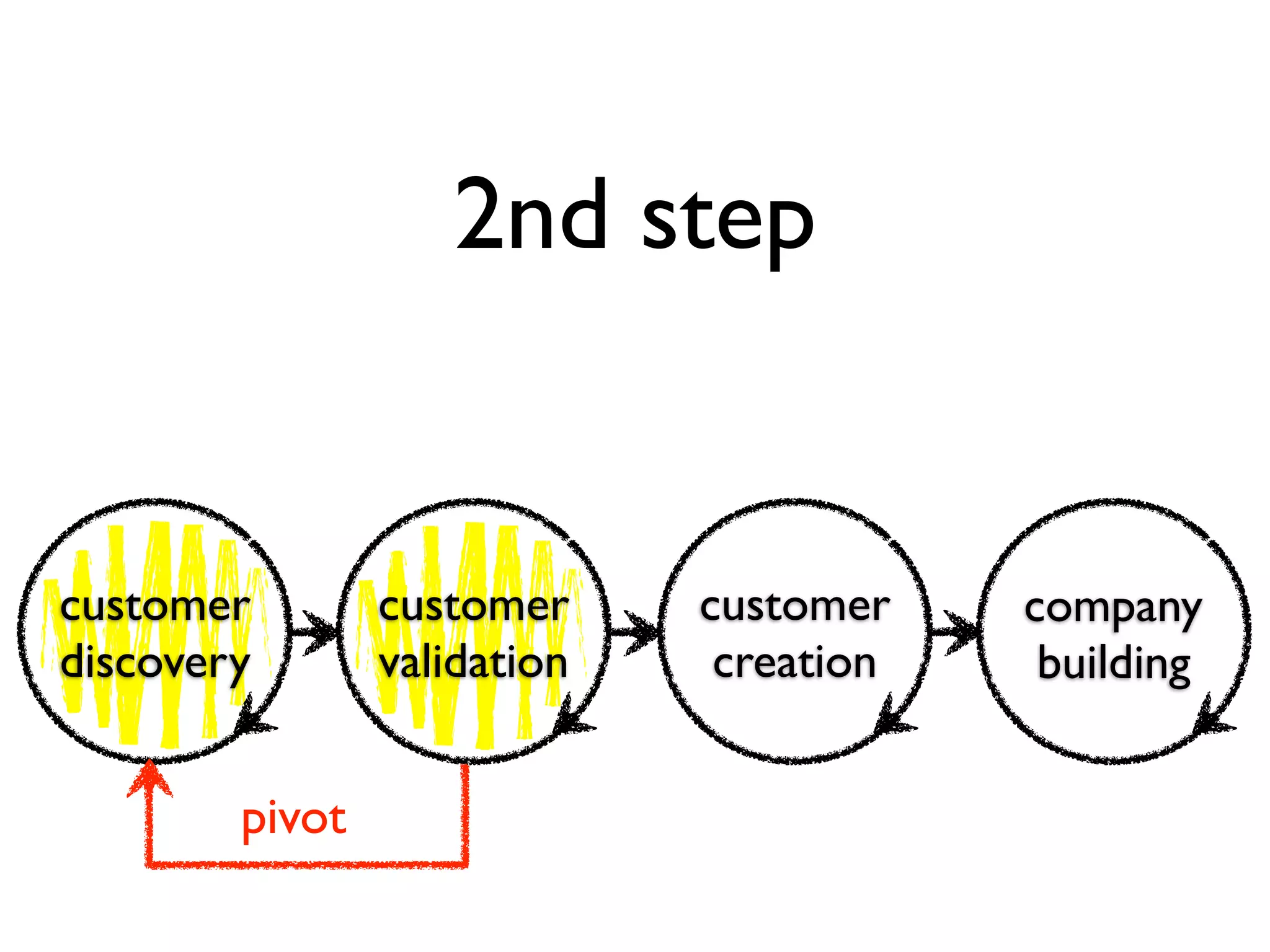
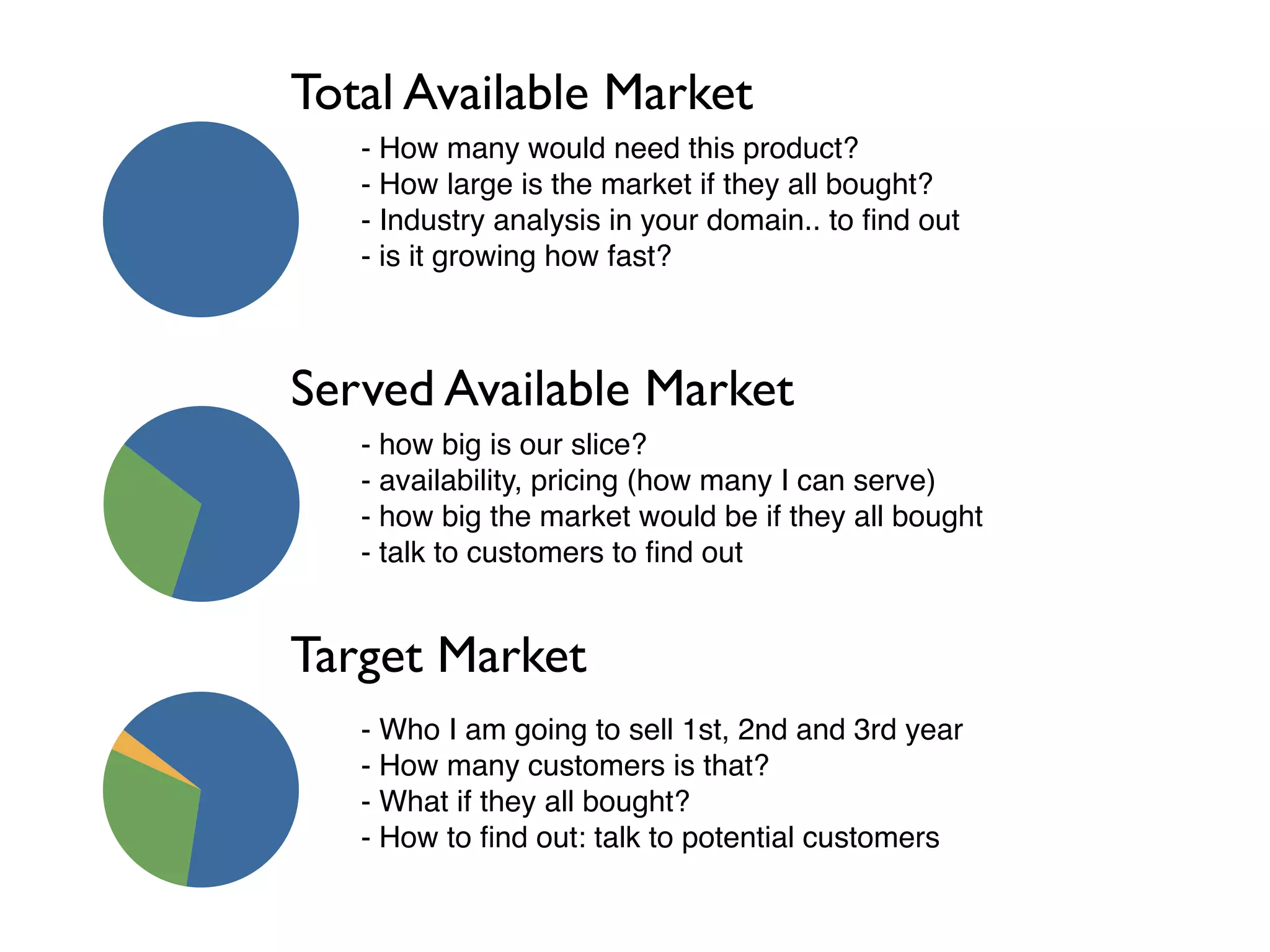
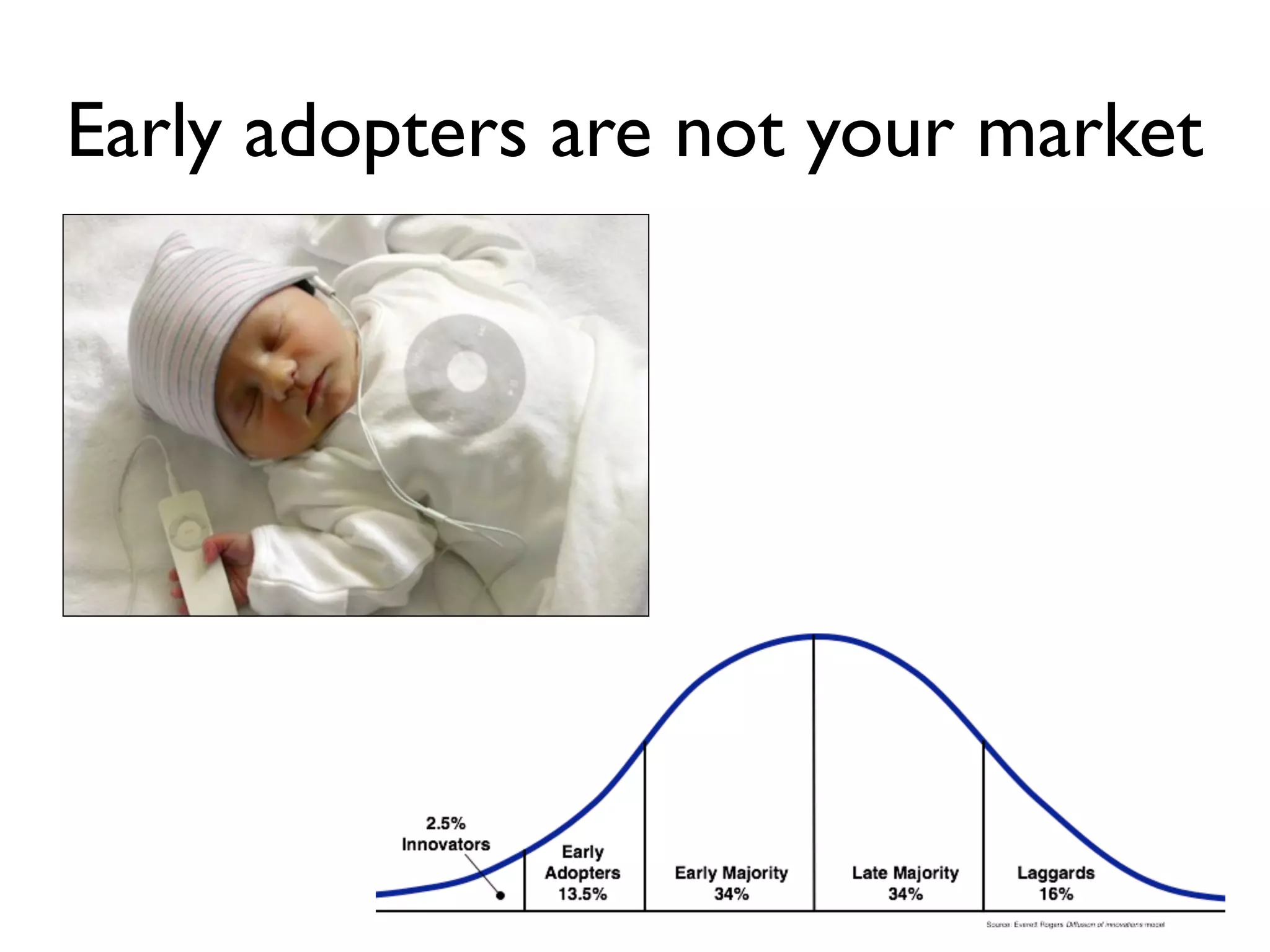
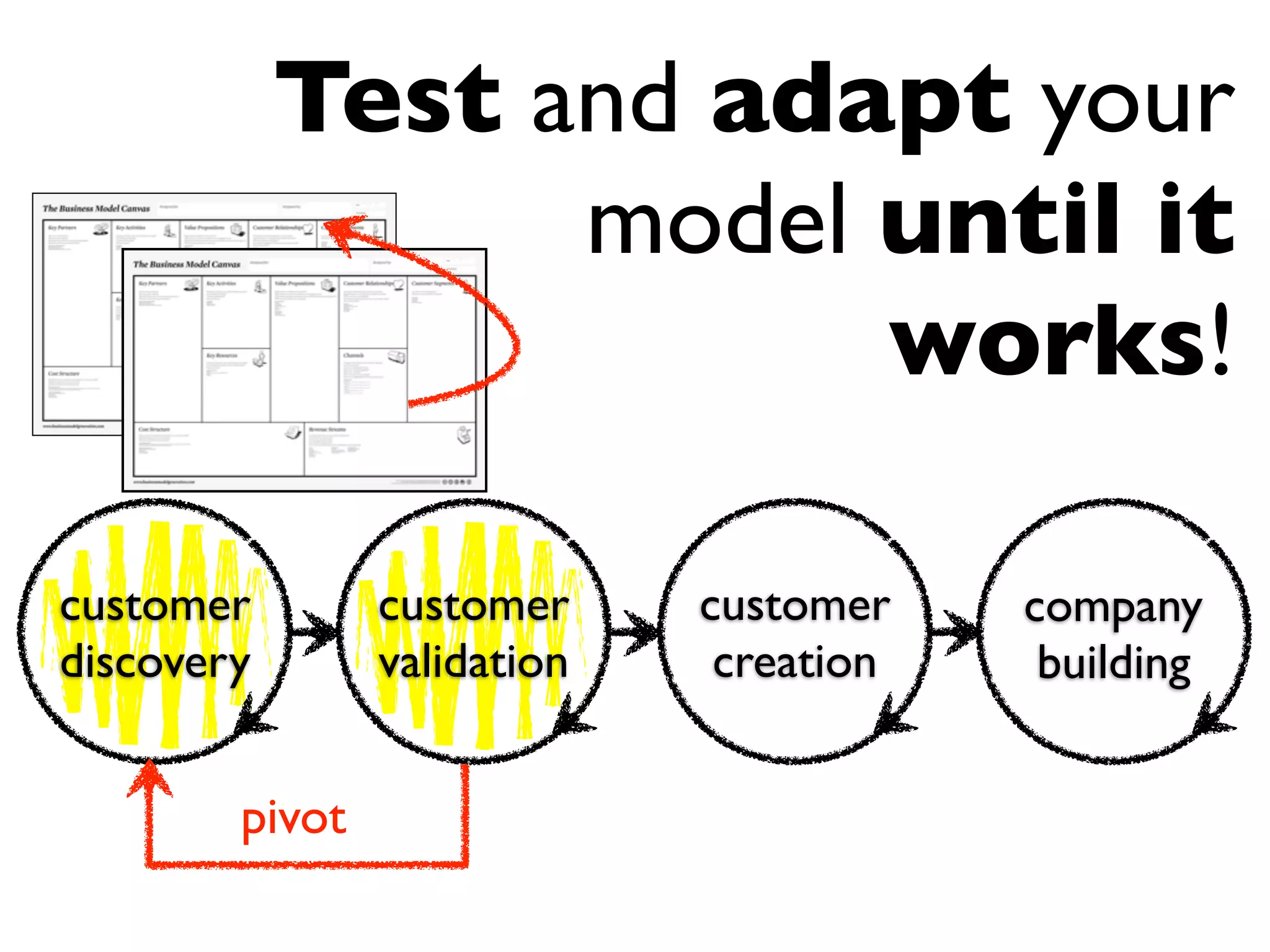
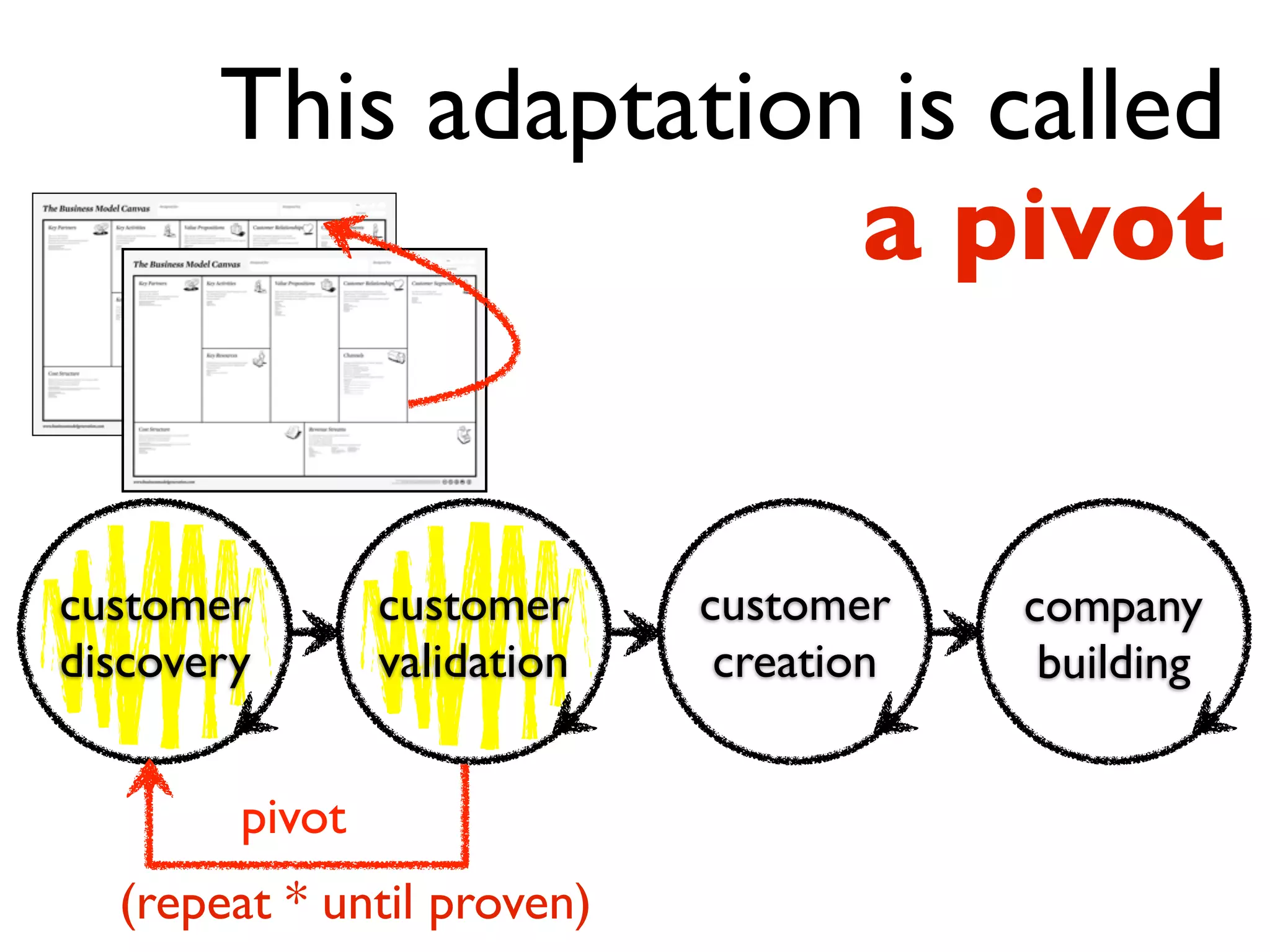
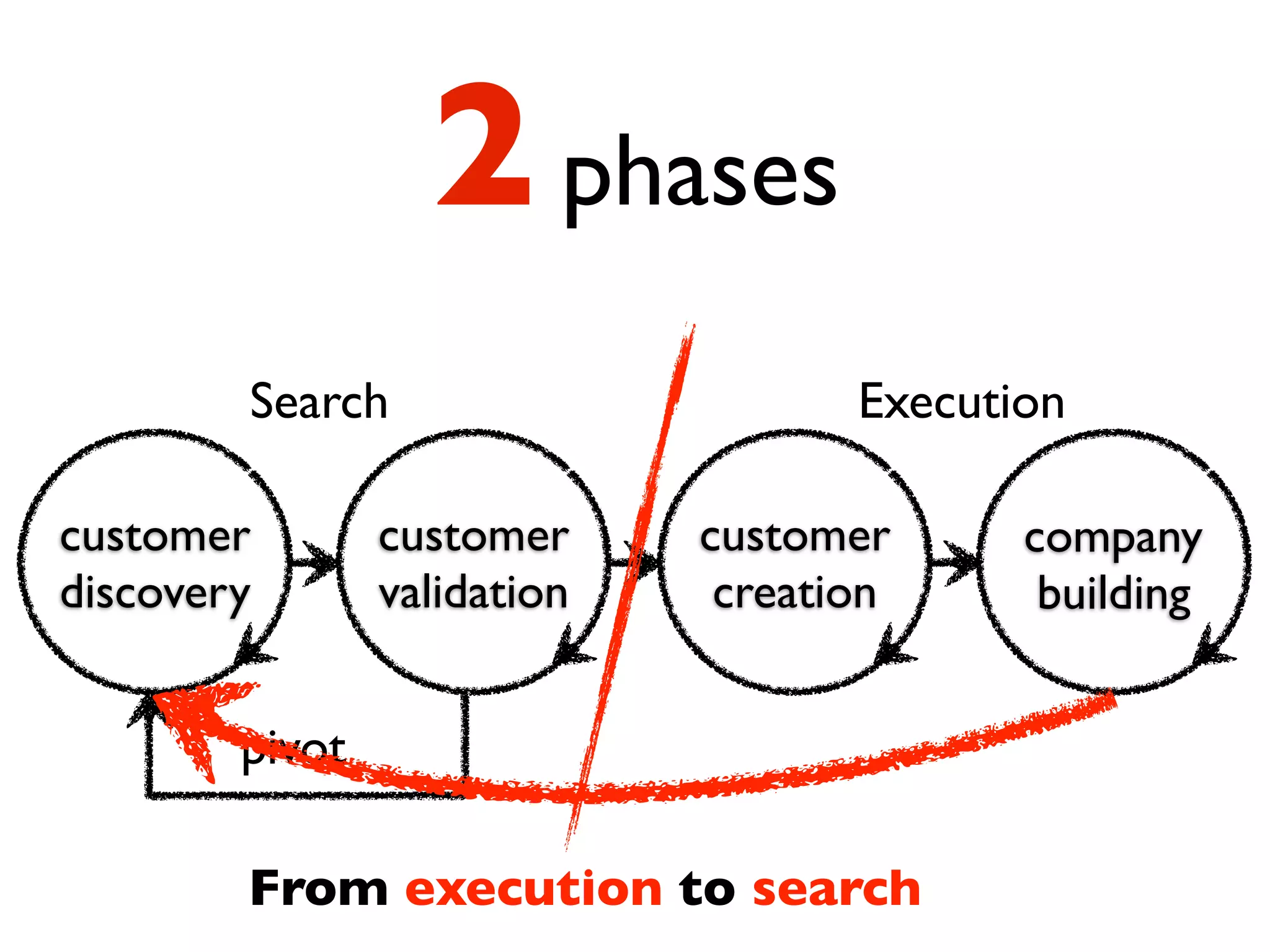
This document discusses building the right product by focusing on problem/solution fit, business model/market fit, hypothesis/experiment fit, and user needs/service fit. It emphasizes the importance of validating your concepts by talking to customers and measuring results rather than assuming you know requirements. The key steps outlined are drawing a business model canvas, stating hypotheses to test, and getting customer feedback through discovery and validation. Pivoting based on learnings is important rather than prematurely scaling execution without verifying the business model. Overall the message is to interface business, design and engineering to create successful businesses by making the business the driver.