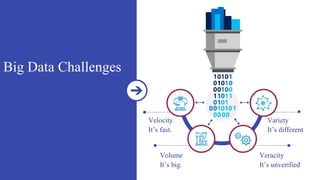
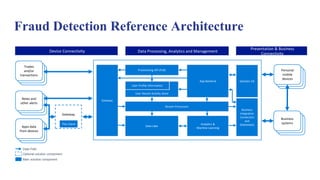
The document discusses the significance of big data in the IT landscape, emphasizing its ability to drive cost reductions and enhance computing tasks. It also examines the various types of fraud, including corporate and credit card fraud, and highlights the importance of risk management in data-driven decision-making. Additionally, the text outlines the challenges and benefits of using big data for fraud detection and customer analytics in financial operations.