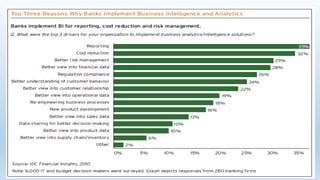
The document discusses the application of data analytics in banking and financial services, highlighting how predictive analytics can enhance customer segmentation, risk management, and personalized marketing. It outlines various use cases, including fraud detection, customer analytics, and operational risk dashboards that enable banks to make data-driven decisions and improve efficiency. Overall, leveraging advanced analytics techniques allows banks to increase profitability by understanding customer behaviors and managing risks effectively.