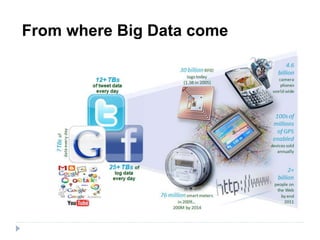
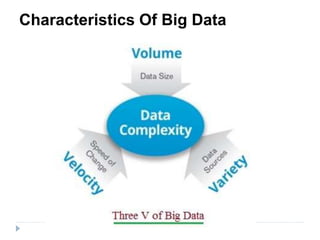
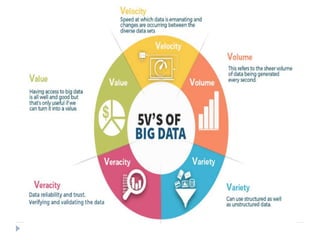
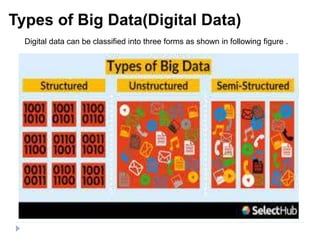
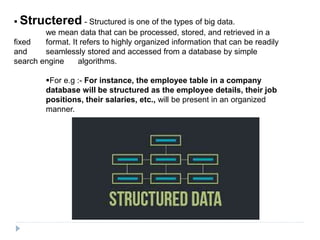
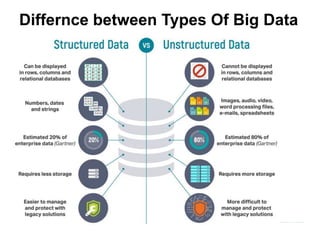
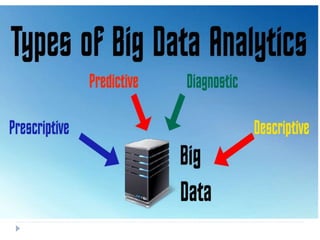
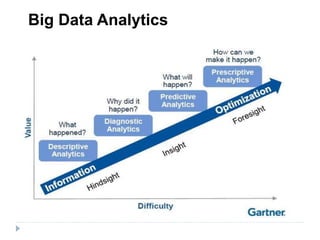
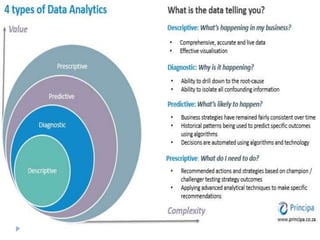
Big data is data that is too large or complex for traditional data processing applications to analyze in a timely manner. It is characterized by high volume, velocity, and variety. Big data comes from a variety of sources, including business transactions, social media, sensors, and call center notes. It can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. Tools used for big data include NoSQL databases, MapReduce, HDFS, and analytics platforms. Big data analytics extracts useful insights from large, diverse data sets. It has applications in various domains like healthcare, retail, and transportation.