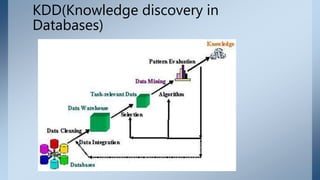
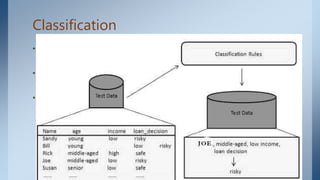
Data mining involves discovering knowledge from large amounts of data through processes like extraction, cleansing, integration, transformation, and analysis. It aims to extract useful information for purposes like market analysis, risk analysis, detecting patterns, and improving websites. Key techniques include association rule mining to analyze customer purchasing patterns, classification to categorize and predict items, and clustering to group similar objects together.