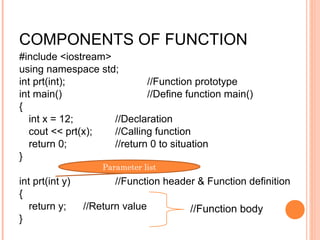
The document discusses functions in C++. It defines a function as a block of code that performs a specific task. There are two types of functions: built-in functions provided by the language and user-defined functions created by the programmer. The components of a function include the function header, body, parameters, return type, local variables, and return statement. Functions can pass arguments either by value or by reference. The document provides examples of built-in and user-defined functions as well as examples demonstrating call by value and call by reference.