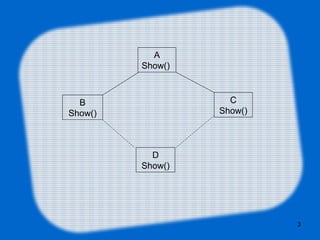
The document explains Java's approach to interfaces and multiple inheritance, highlighting that Java does not support multiple inheritance due to the diamond problem. It details the characteristics and functionalities of interfaces in Java, including the implementation requirements and the ability to extend interfaces. Additionally, it addresses the evolution of interfaces and the introduction of default methods, providing examples for clarity.