The document discusses arrays in C++. It defines an array as a group of consecutive memory locations with the same name and type. Arrays allow storing multiple values using a single name. The document covers one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays, including how to declare, initialize, access elements, and write programs to input and output array values. It provides examples of programs that input values into arrays, find the maximum/minimum values, and store/display 2D arrays.




![Declaring One dimensional
Array:
The syntax of declaring one-dimensional array is:
Data_type Identifier[length];
Data_type Indicates data type of values.
Identifier Indicates the name of array.
Length Indicates total number of elements in
array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-5-2048.jpg)
![For Example:
int marks[5];
Index of each element 0 1 2 3 4
Name of array marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-6-2048.jpg)
![Array initialization
The syntax of array initialization is :
Data_type Identifier[length]={list of values};
List of values It indicates the values to initialize the array. These
values must b constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-7-2048.jpg)
![Example:
int marks[5]={70,75,90,60,85};
Index of each element 0 1 2 3 4
Name of array marks 70 75 90 60 85](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-8-2048.jpg)
![Accessing individual elements in an
array:
The syntax for accessing element is as follows :
Array_Name[index];
Array_Name Indicates the name of array.
Index Indicates the index element
to be accessed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-9-2048.jpg)
![Example:
int marks[5];
int marks[0]=70;
int marks[1]=75;
int marks[2]=90;
int marks[3]=60;
int marks[4]=85;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-10-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream>
Int main( )
{
int array[3];
cout<<“enter five integers: “<<endl;
cin>>array[0];
cin>>array[1];
cin>>array[2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-12-2048.jpg)
![cin>>array[3];
cin>>array[5];
Cout<<“the values in array are : “<<endl;
cout<<array[0]<<endl;
cout<<array[1]<<endl;
cout<<array[2]<<endl;
cout<<array[3]<<endl;
cout<<array[4]<<endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-13-2048.jpg)


![#include<iostream>
Int main( )
{
int arr[5],i;
for(i=0 ; i<5 ; i++)
{
cout<<“Enter an integer : “;
cin>>arr[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-16-2048.jpg)
![cout<<“The values in array are : n
for(i=0 ; i<5 ; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-17-2048.jpg)


![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int a[5],i,max;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<"Enter number : ";
cin>>a[i];
}
max=a[0];
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
if(max<a[i])
max=a[i];
cout<<"Maximum Number is : "<<a[i];
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-20-2048.jpg)


![Syntax:
Data_type identifier[Rows][Cols];
For Example:
The following statement declares a 2-D array with four rows and three
columns.
Int Arr[4][3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-23-2048.jpg)

![Accessing elements of 2-D array
The array name and indexes of row and column are used to access
individual element of a 2-D array. For example, the following statement will
store 20 in the second column of first row.
Int Arr[0][1]=100;
OR
By assigning variables to indexes:
R=0;
C=1;
Arr[R][C]=100;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-25-2048.jpg)



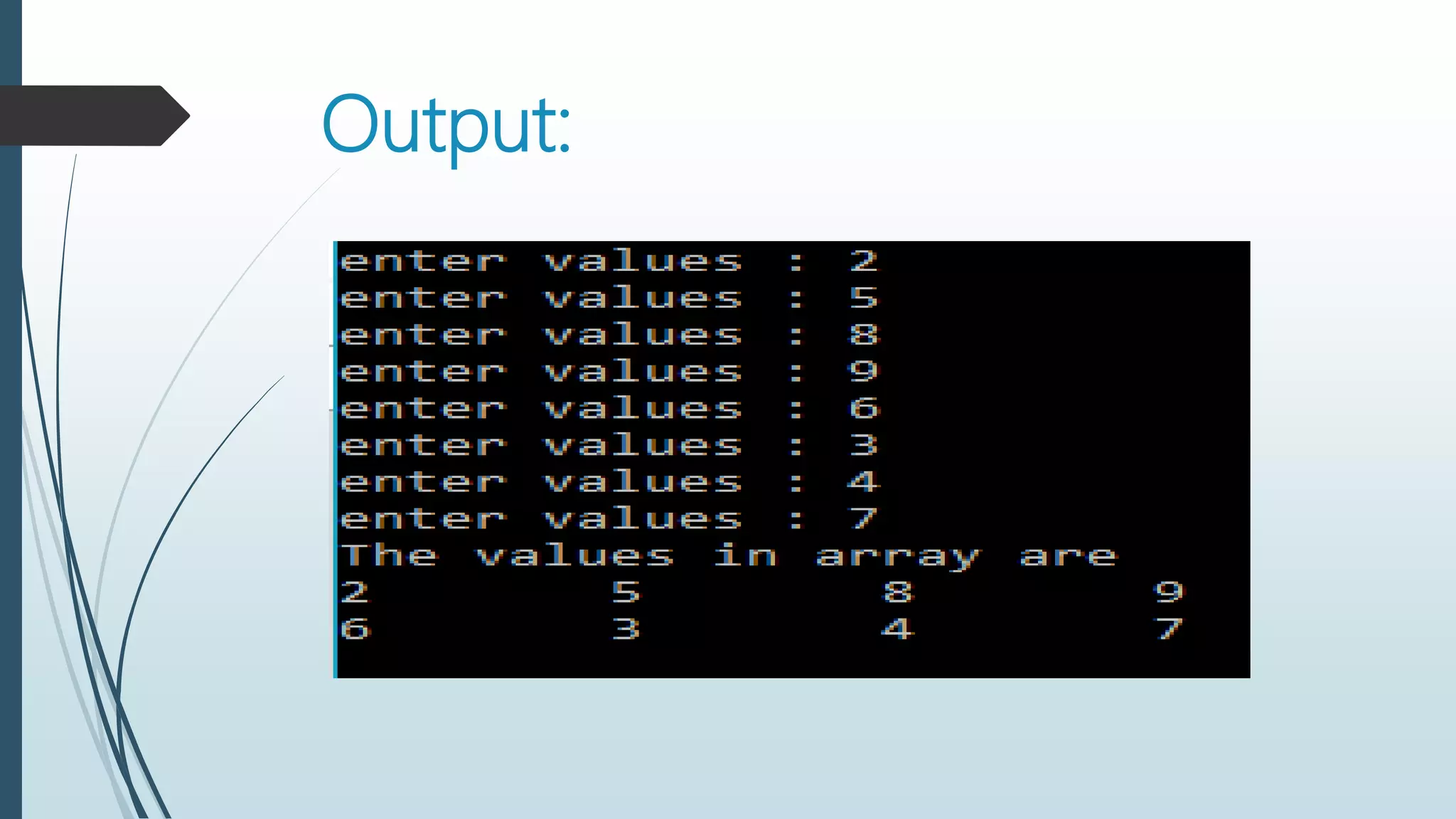
![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int Array[2][4],i,j;
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
cout<<"enter values : ";
cin>>Array[i][ j];
}
cout<<"The values in array aren";
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
cout<<Array[i][ j]<<"t";
cout<<endl;
}
return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-29-2048.jpg)
![Initialization 2-D Arrays
The process of initialization is performed by assigning the initial values in
braces separated by commas at the time of declaration.
For example:
Int array[3][4]={ {12,5,22,84},
{95,3,41,59},
{77,6,53,62} };
OR
Int array[3][4]={ {12,5,22,84}, {95,3,41,59}, {77,6,53,62} };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-31-2048.jpg)
![Initialization can also be performed without using inner braces.
Int array[3][4]={ 12,5,22,84,
95,3,41,59,
77,6,53,62 }
OR
Int array[3][4]= { 12,5,22,84,95,3,41,59,77,6,53,62 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-32-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int i,j,a[2][3]={0,1,2,3,4,5};
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
cout<<"arr["<<i<<"]["<<j<<"] "<<a[i][ j]<<"t";
cout<<"n";
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-34-2048.jpg)


![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int max,min,i,j;
int A[2][4]={15,21,9,84,33,72,18,47};
max=min=A[0][0];
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-37-2048.jpg)
![Program continues
if(A[i][j]>max)
max=A[i][j];
if(A[i][j]<min)
min=A[i][j];
}
cout<<"Maximum number is : "<<max<<endl;
cout<<"Minimum Number is : "<<min<<endl;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-170219112845/75/Arrays-in-C-38-2048.jpg)
