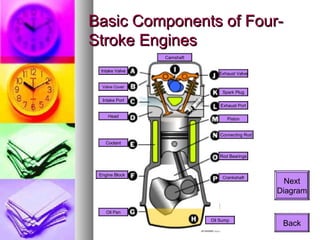
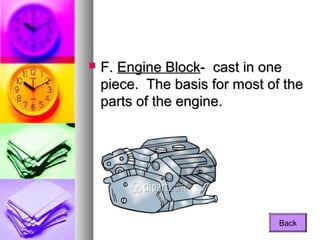
1. Understanding how your car's engine works allows you to properly maintain it through regular oil changes and tune-ups.
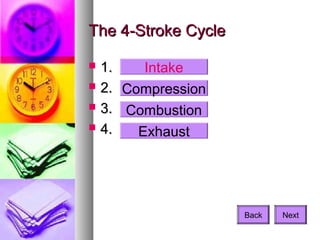
2. The four-stroke cycle principle is applied in many engines beyond automobiles, such as motorcycles, boats, lawnmowers, and generators.
3. An awareness of the basic components and combustion process in a four-stroke engine helps develop troubleshooting skills for mechanical issues.