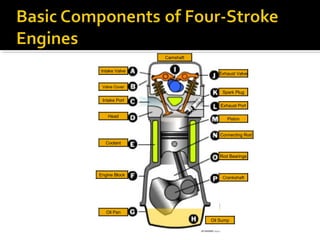
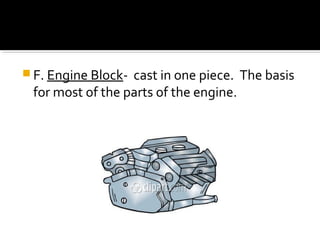
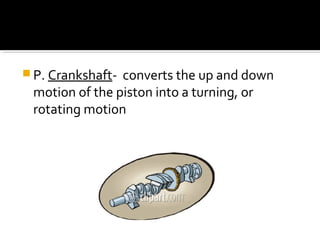
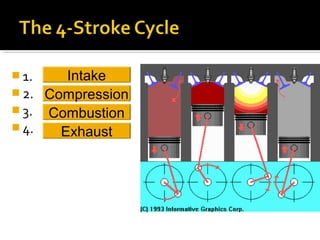
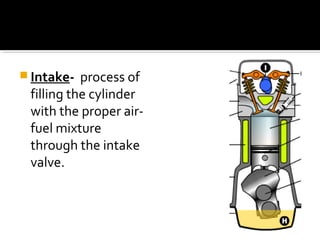
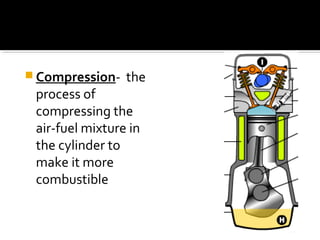
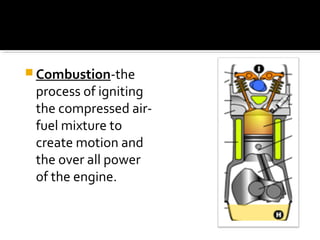
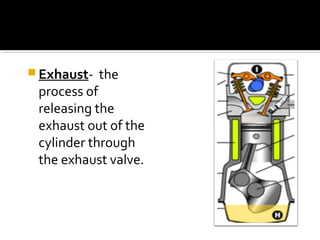
The document discusses the basic components and functions of a four-stroke internal combustion engine. It explains that a four-stroke engine converts gasoline into motion through intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust strokes. The key internal parts include the piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, spark plug, cylinders, and ports that allow air-fuel intake and exhaust gases out.