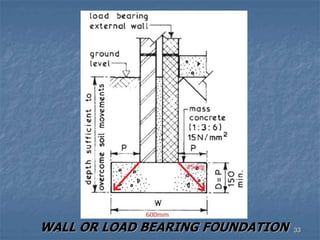
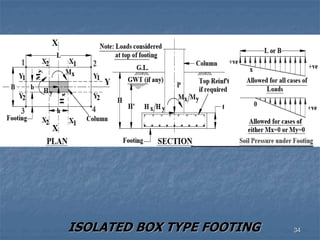
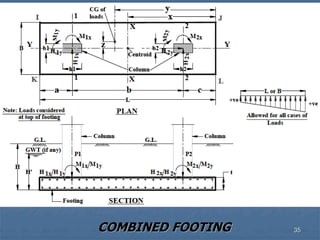
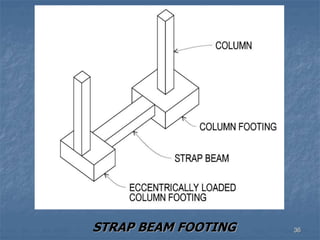
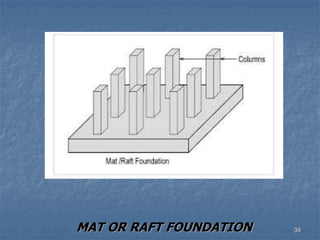
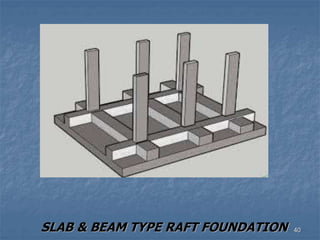
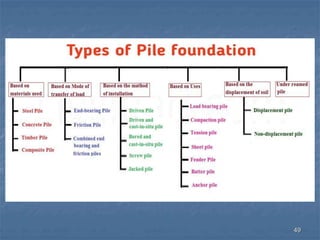
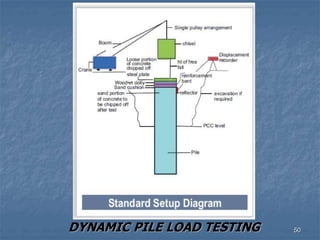
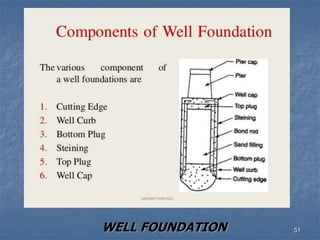
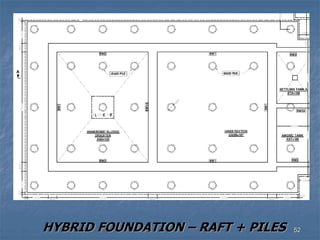
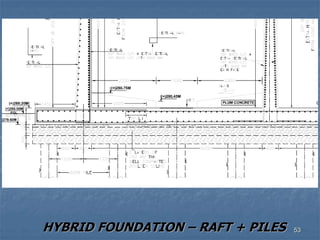
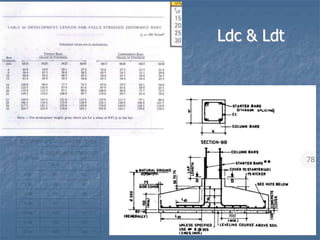
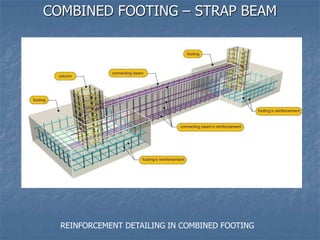
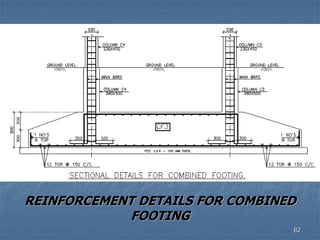
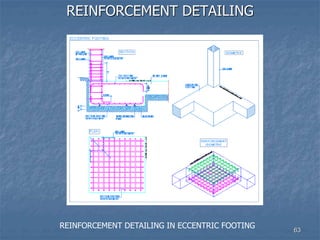
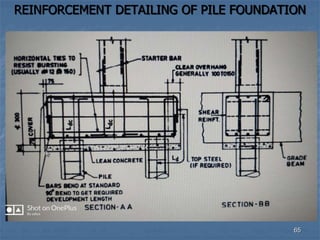
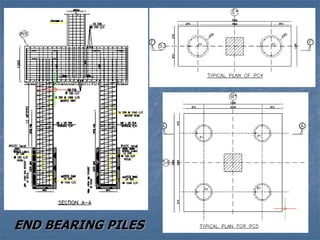
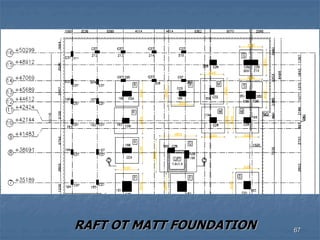
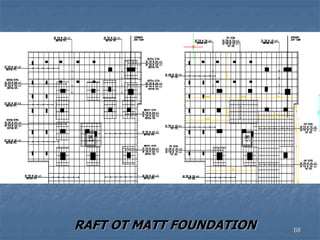
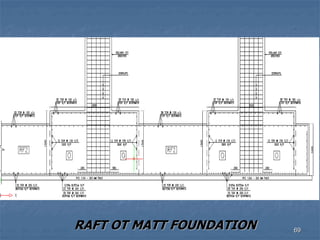
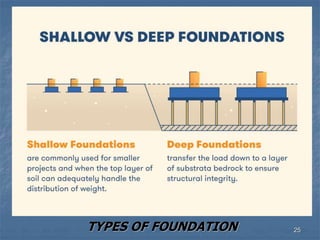
This document provides an overview of structural foundations and related topics. It discusses the importance of structural design and geotechnical investigations. The main types of foundations are described, including shallow foundations like isolated, combined and strip footings, as well as deep foundations like piles. Load combinations, design methods, and reinforcement detailing are also covered. The document emphasizes the importance of proper foundation design and highlights potential problems to avoid in excavation and construction.
















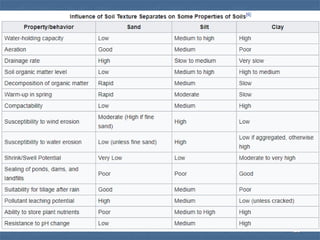
![Classification of Soil As Per
Occupational Safety & Health Administration [OSHA]
• Type A Soil – Include Clay, Silty Clay, Sandy Clay,
And Clay Loam, Most Stable, Cohesive, High
Unconfined Compressive Strength
• Type B Soil – Include Angular Gravel, Silt, Silt
Loam, And Soils That Are Fissured, Medium
Unconfined Compressive Strength
• Type C Soil – Include Gravel And Sand, Granular,
Least Stable, Low Unconfined Compressive
Strength
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk4raipure-210325062723/85/Foundation-Types-22-320.jpg)



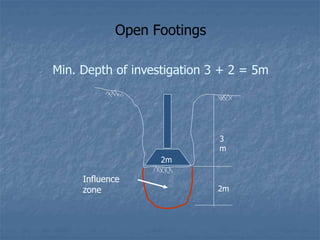
![Isolated or Combined [Open] Footings
• Used for most buildings where the loads are light
and / or there are strong soil at shallow depth.
• These footing deliver the load directly to the
supporting soils.
• Area of footing is = Load / SBC
• Generally suitable for low rise buildings (1-5 floors)
• Requires firm soil conditions that are capable of
supporting the building on the area of the spread
footings.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk4raipure-210325062723/85/Foundation-Types-28-320.jpg)