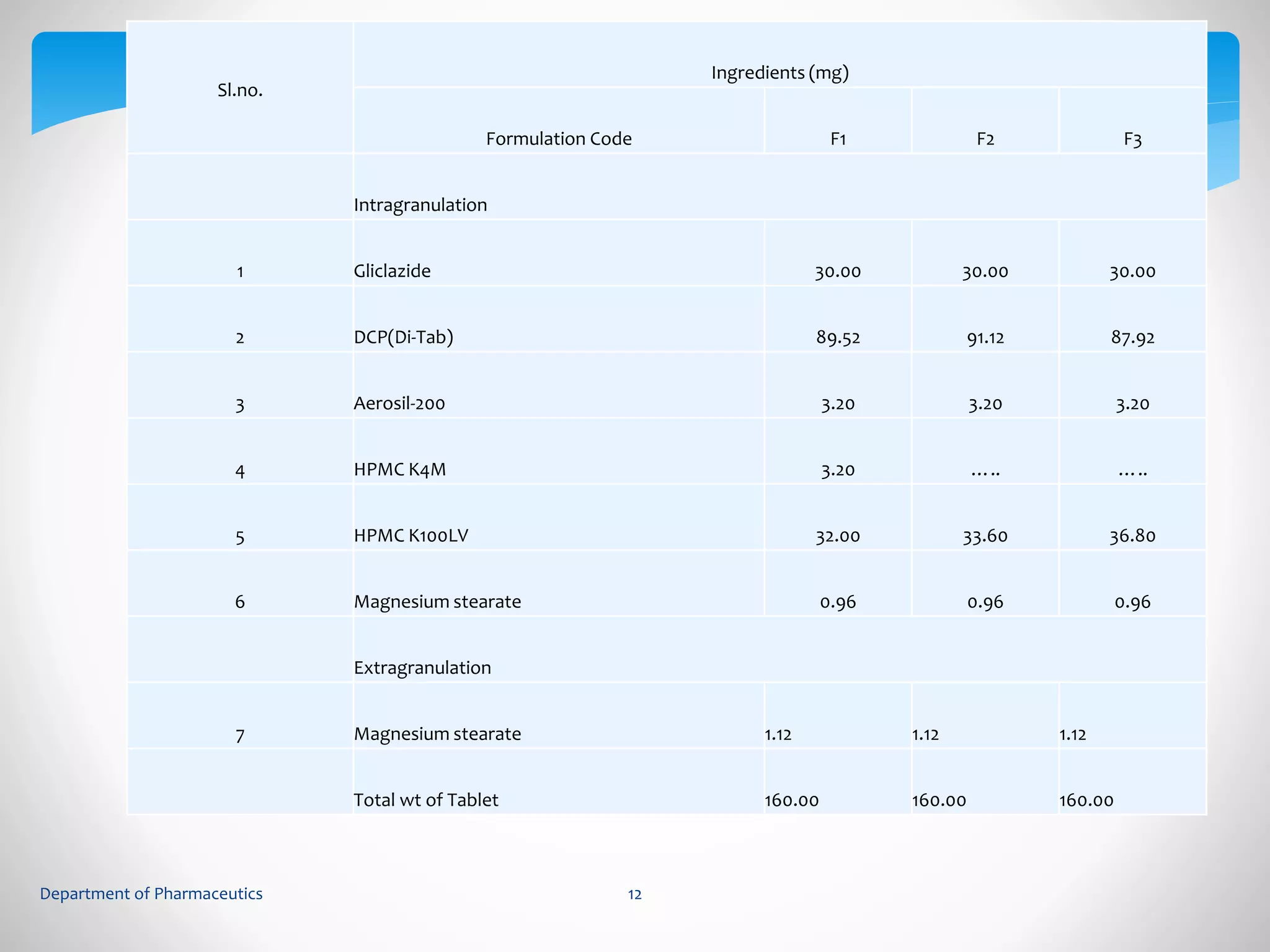
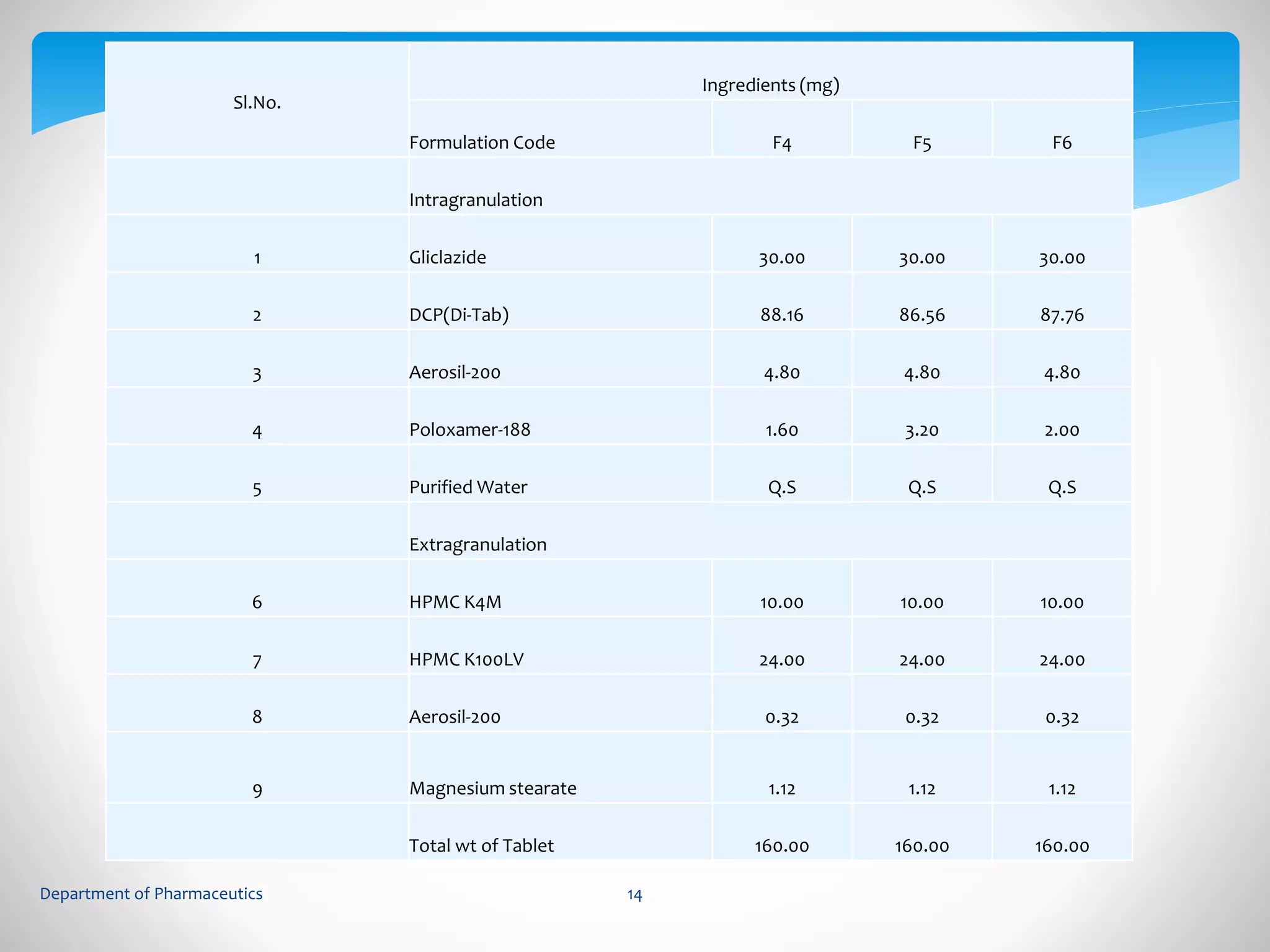
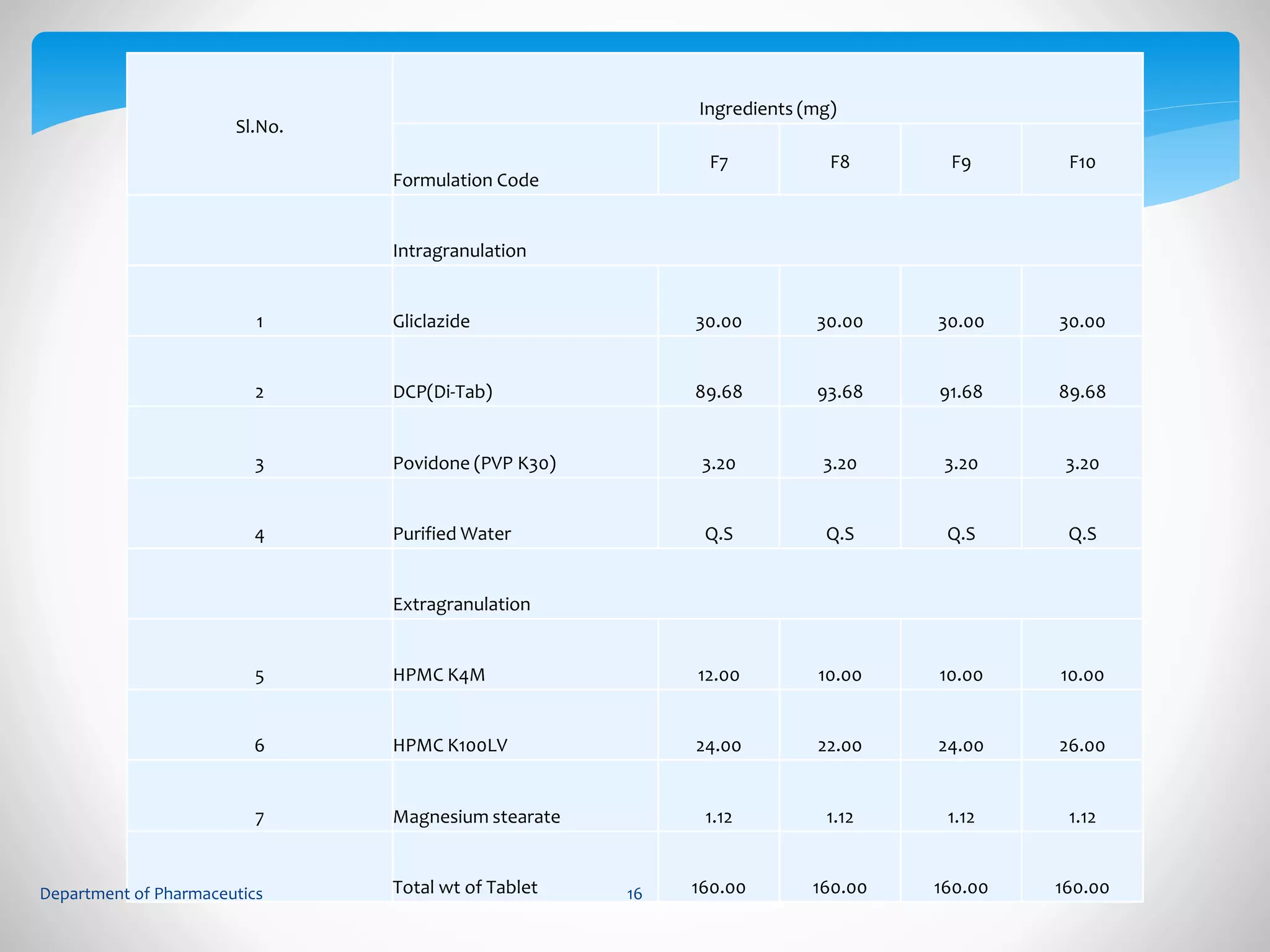
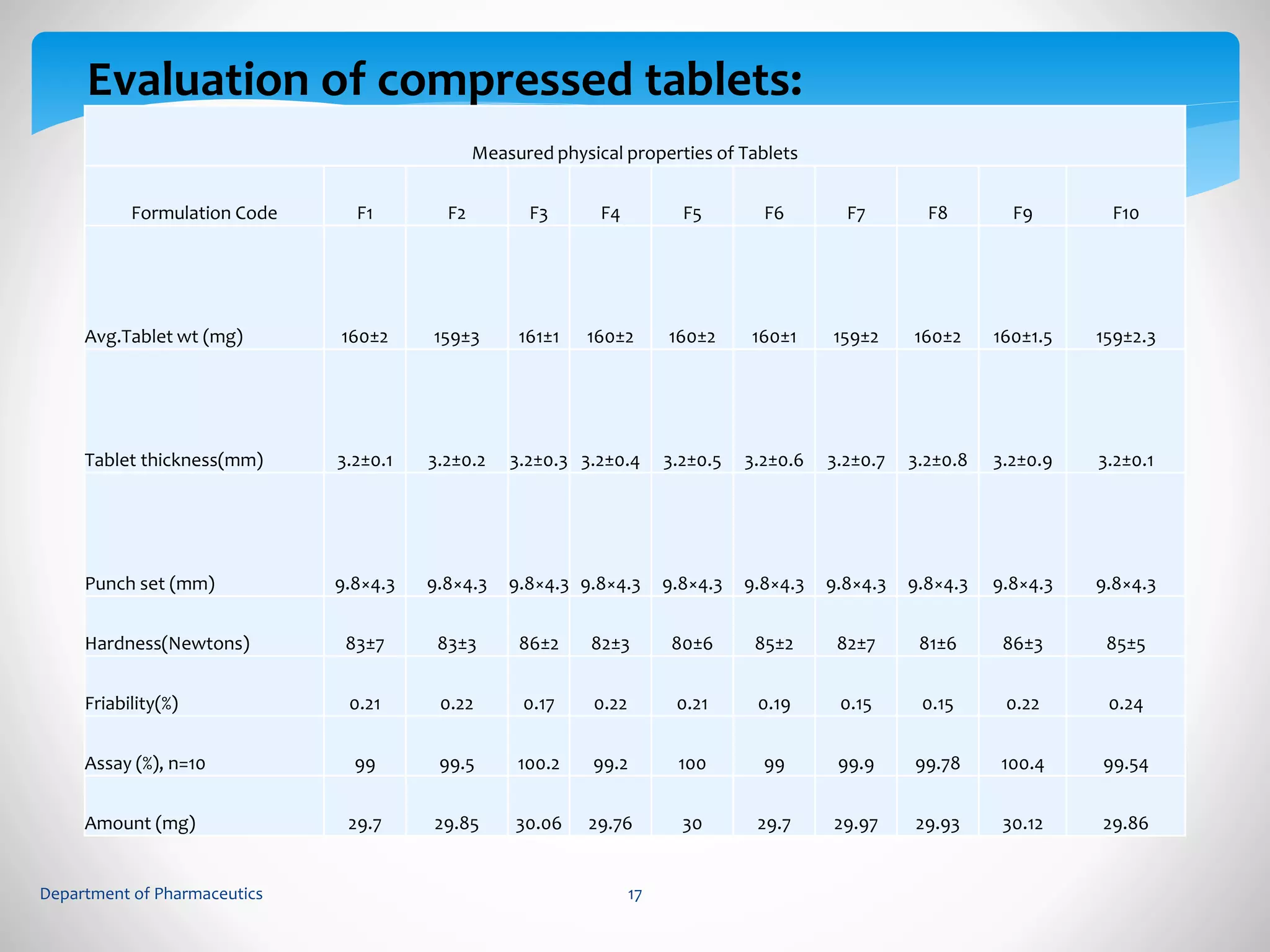
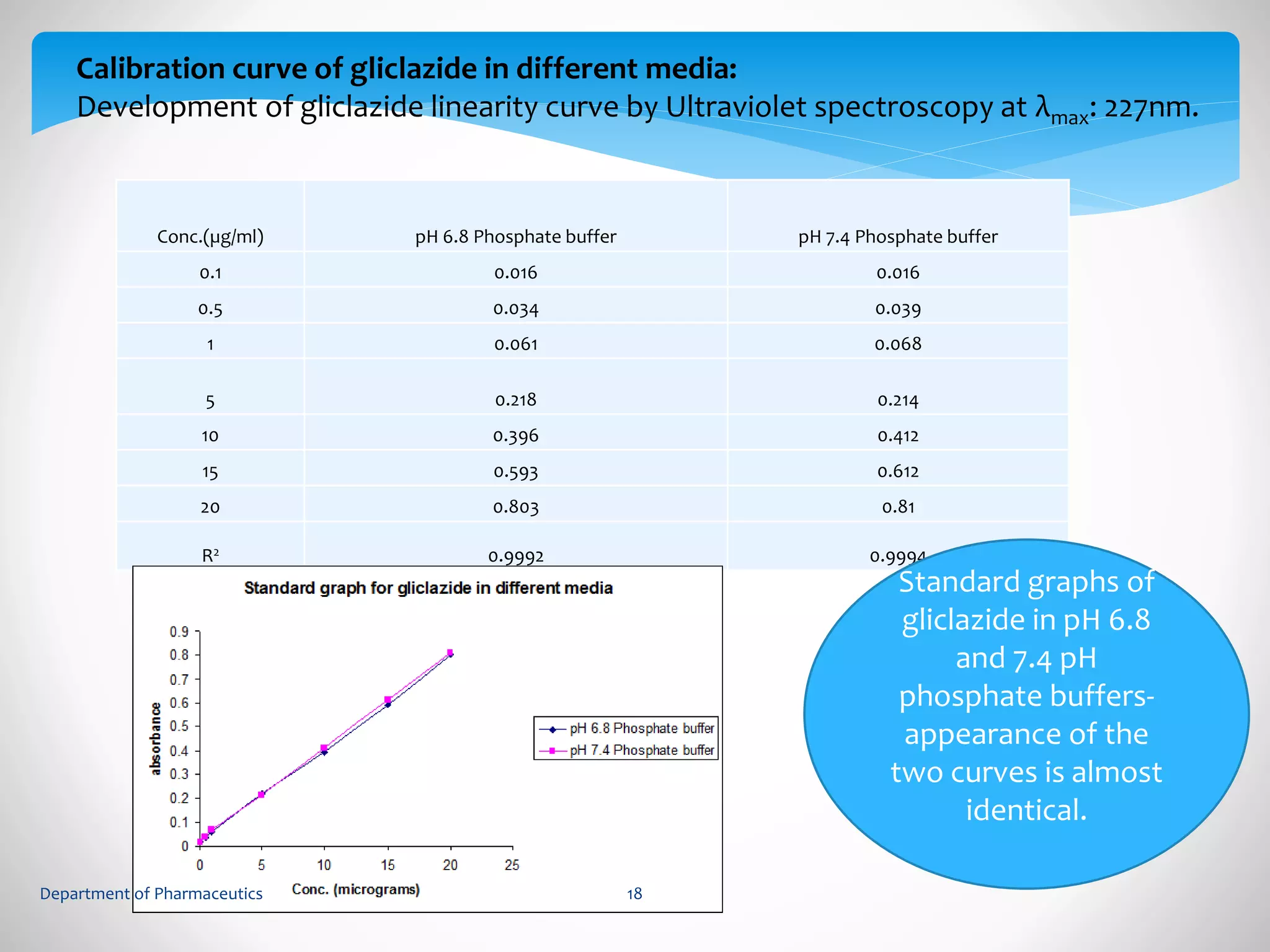
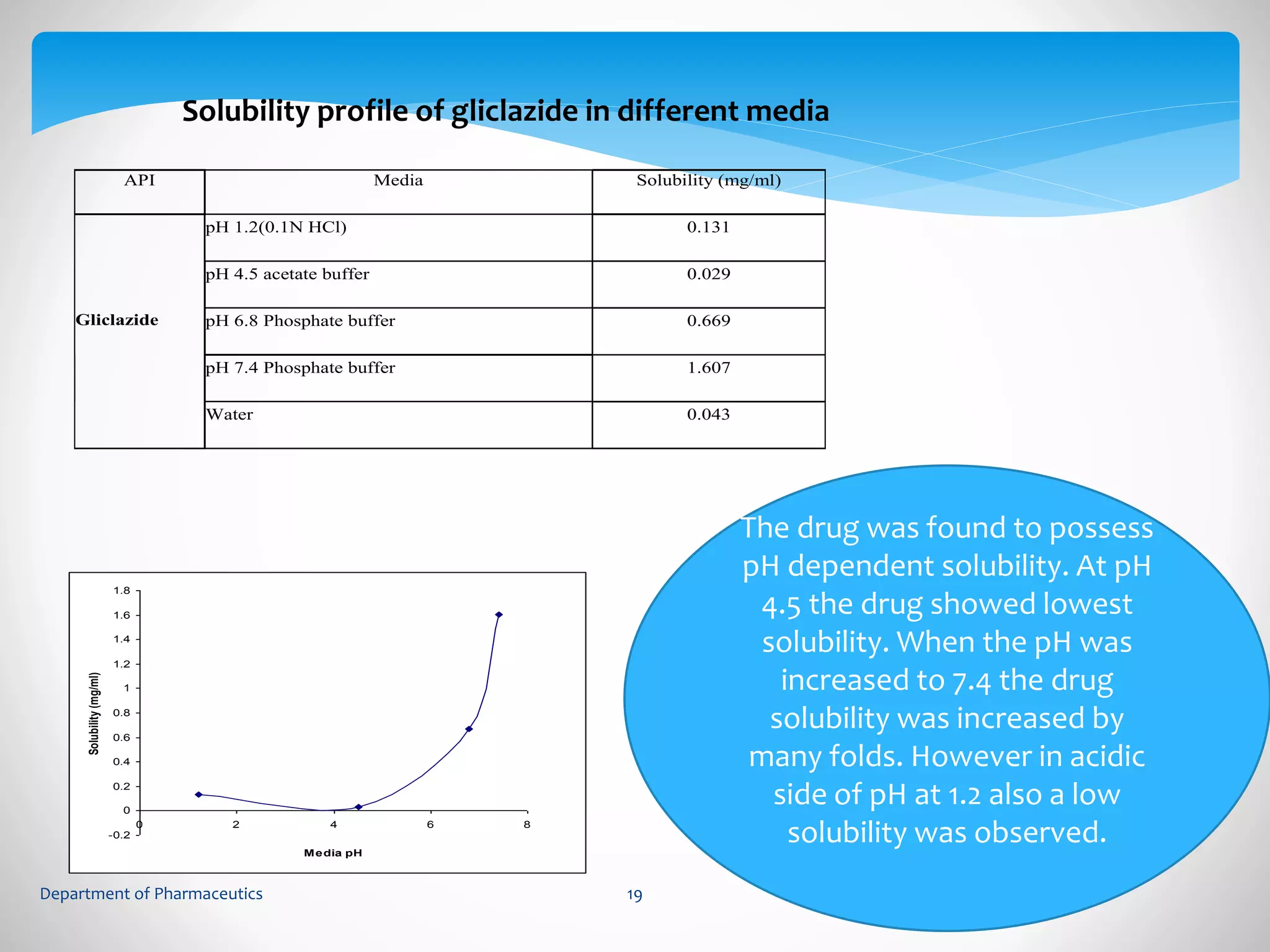
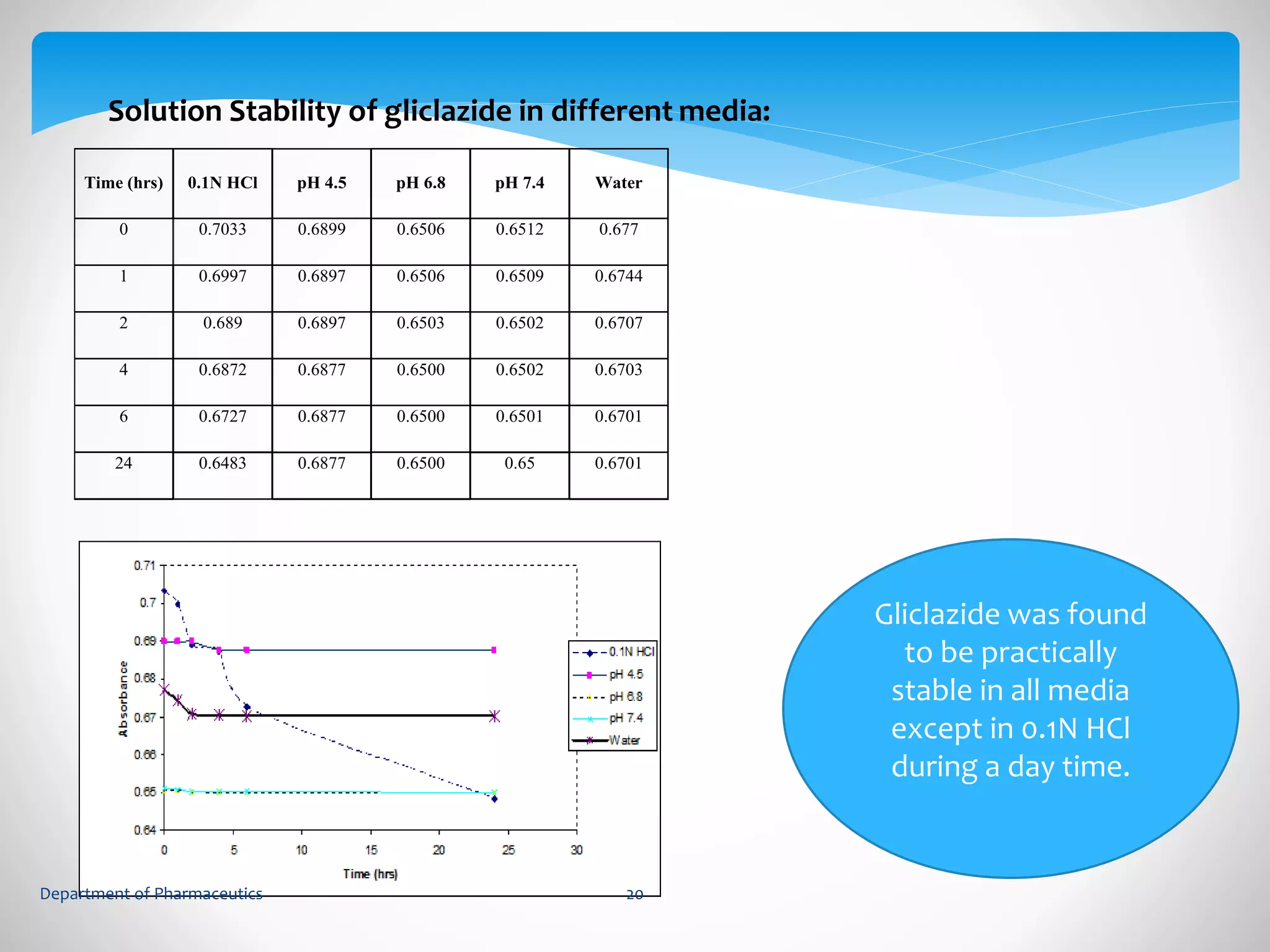
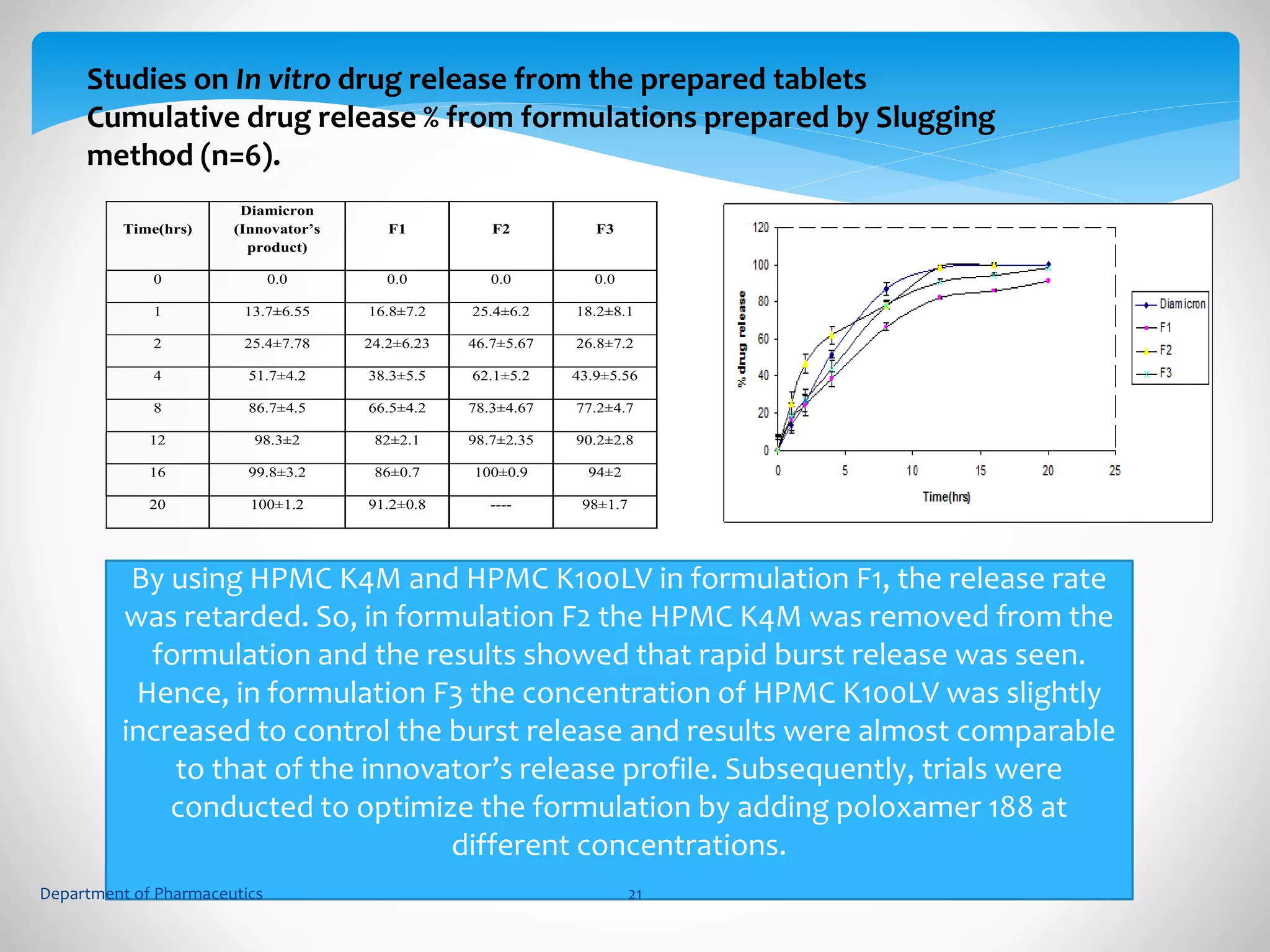
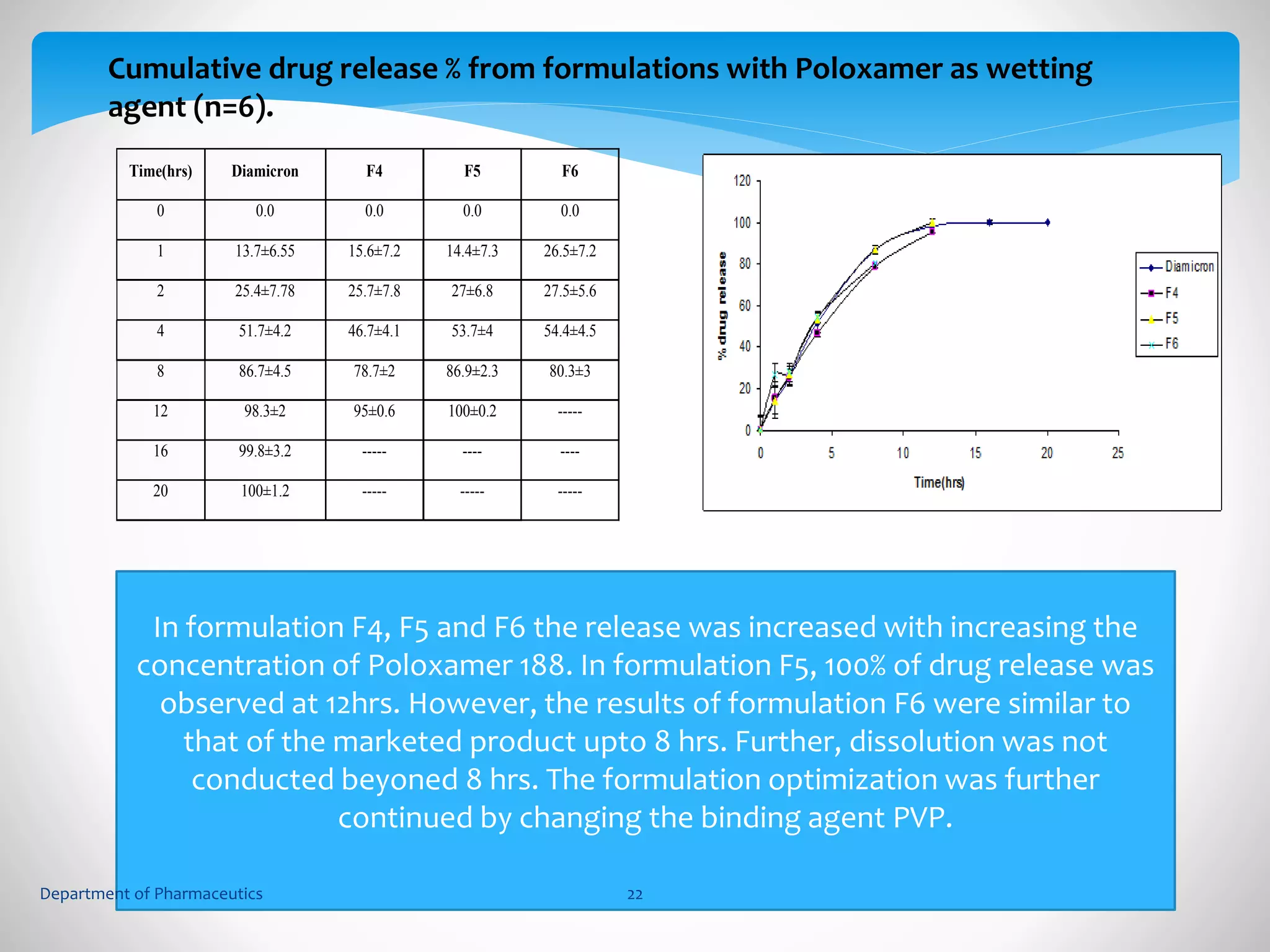
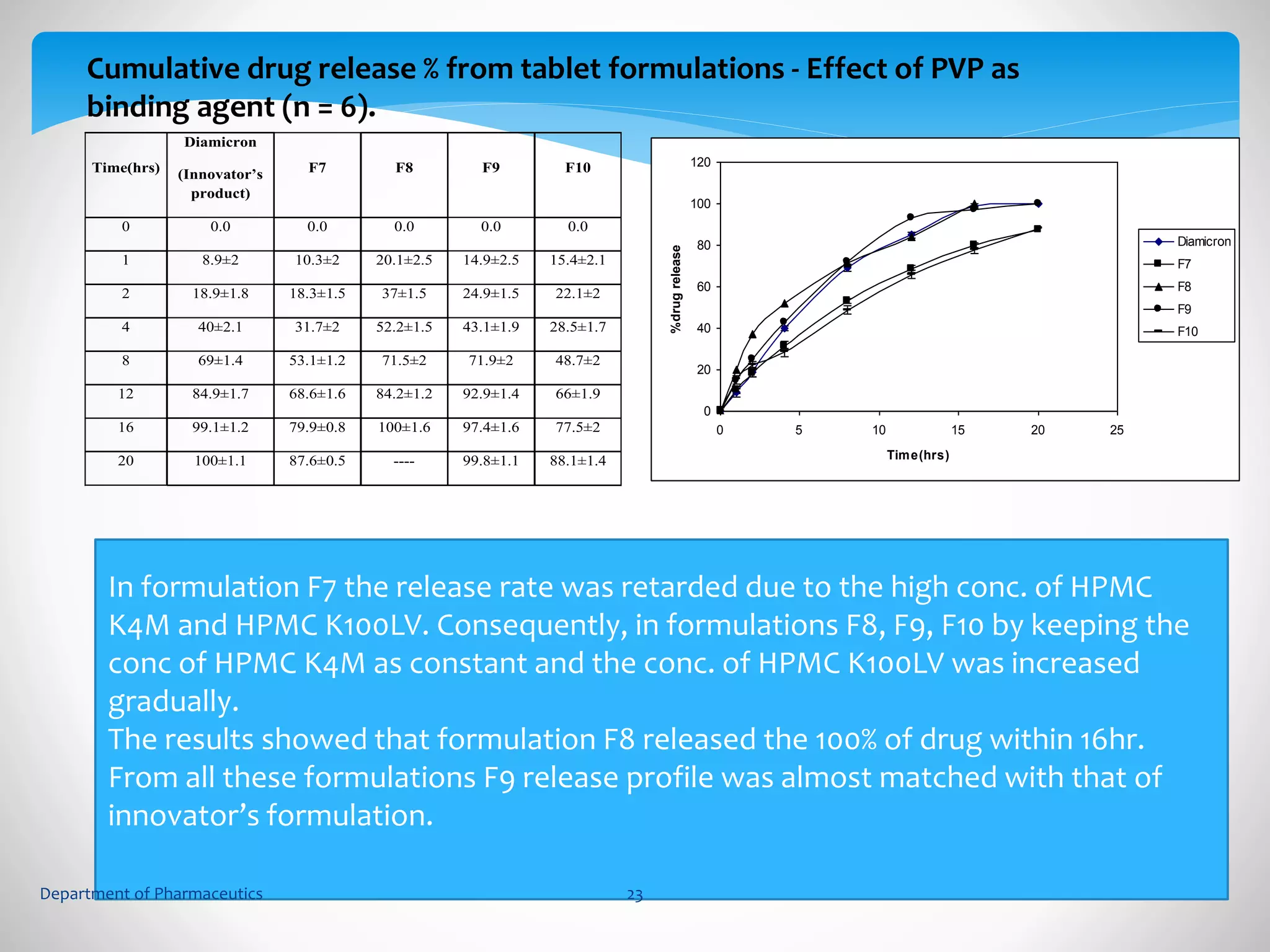
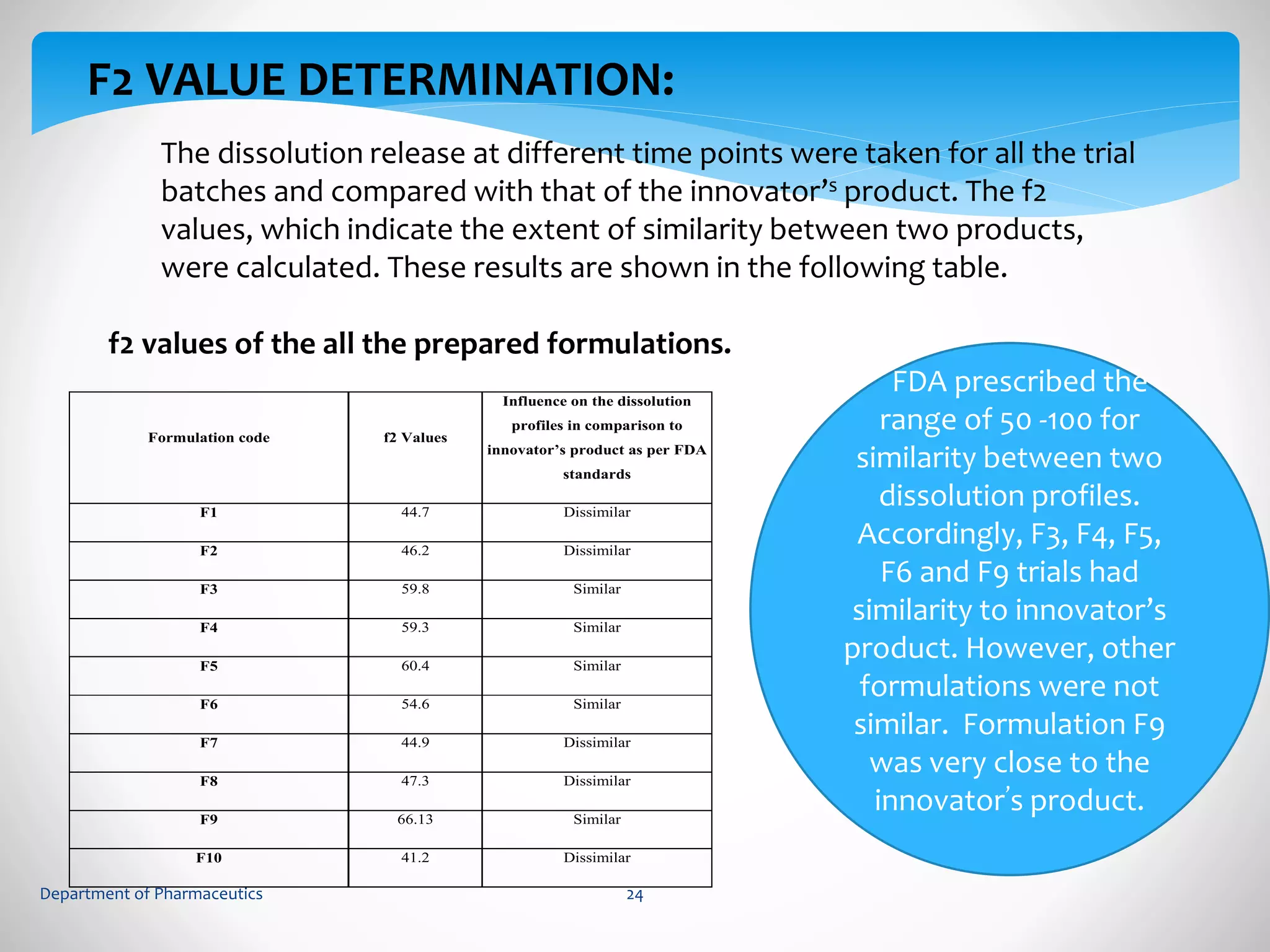
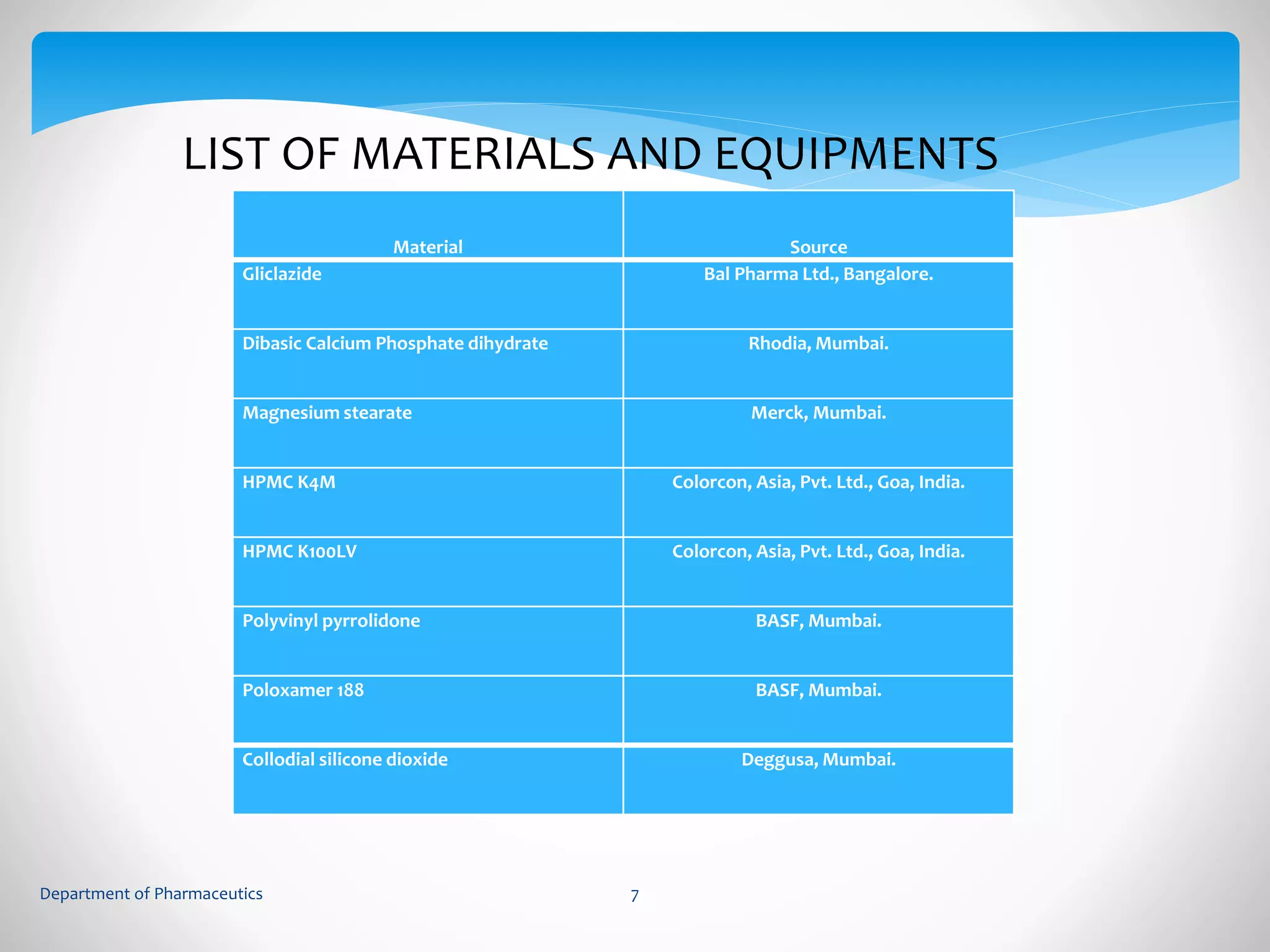
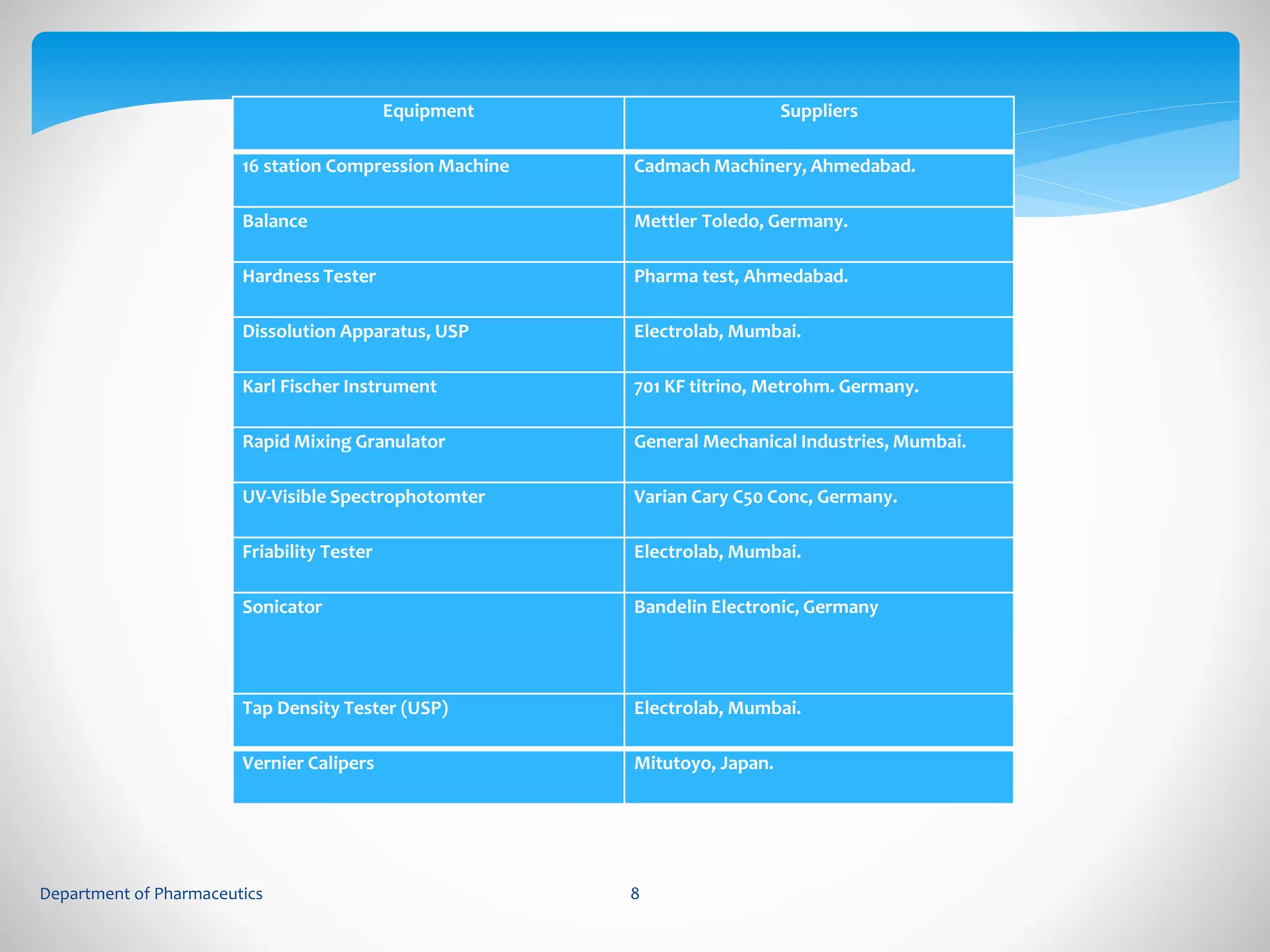
This document summarizes the formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets containing gliclazide. The objectives were to develop a once-daily tablet to reduce side effects and fluctuations in drug levels compared to immediate release tablets. Various polymers like HPMC K4M, HPMC K100LV, poloxamer 188, and PVP K30 were used to formulate sustained release matrix tablets by wet granulation. The tablets were evaluated for weight variation, hardness, friability, drug content and in vitro drug release over 20 hours. The optimized formulation showed comparable drug release to the innovator's product over the tested time period.






![DRUG PROFILE
Synonym : Gliclazidum
Chemical name : N-[[(Hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1H)-yl) amino] carbonyl]-4-
methylbenzenesulfonamide.
Empirical formula : C15H21N3O3S
Molecular weight: 323.4g/mol.
Melting point : 163oC to 165°C
Half-life: 6 to 14 h
Bioavailability: About 79 to 100%
Dissociation Constant: pKa 6.6
Chemical Structure
Mechanism of action:
primary effect is to potentiate glucose-stimulated insulin release from
functioning pancreatic islet β-cells.
Department of Pharmaceutics 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formulationandevalutionofsustainedreleasematrixtablets-141203110427-conversion-gate02/75/Formulation-and-evalution-of-sustained-release-matrix-tablets-9-2048.jpg)