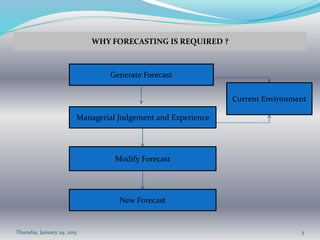
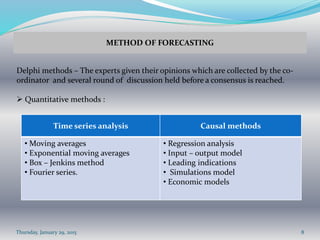
This document discusses forecasting methods. It states that forecasting is both an art and a science, requiring subjective assessment of historical and current data as well as numerical methods. Forecasting is important for planning production, personnel, capacity, and supply chains. Accurate forecasting can improve employee relations, material management, capital usage, customer service, and reduce costs. Forecasts contain best demand estimates and allowances for errors. Qualitative methods include surveys and expert opinions, while quantitative methods use time series analysis and causal models. The appropriate forecasting method depends on the required format, time horizon, data availability, needed accuracy, process behavior, and costs.