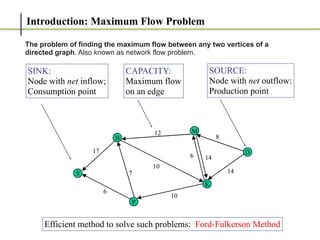
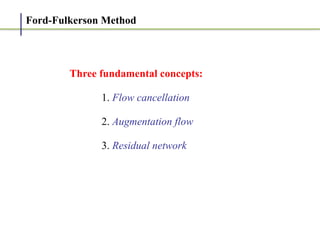
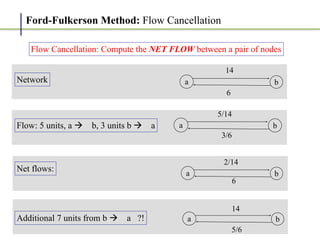
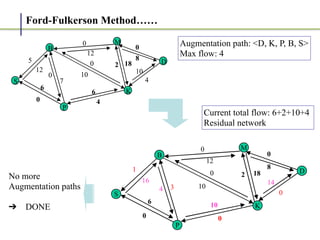
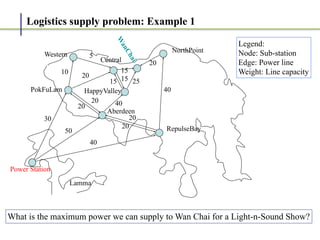
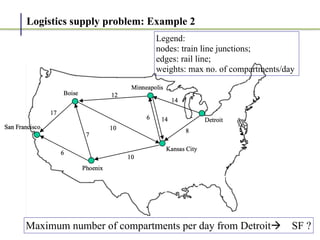
1. The Ford-Fulkerson method is an algorithm for finding the maximum flow in a flow network, also known as the maximum flow problem.
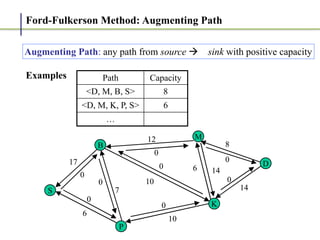
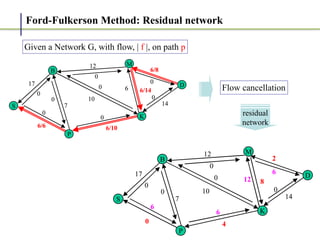
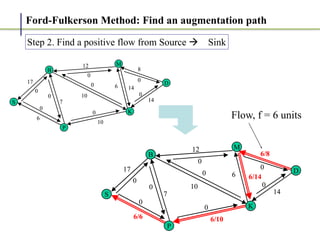
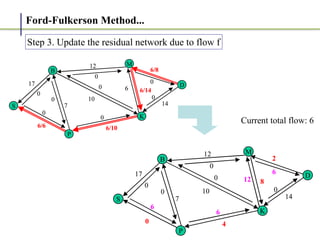
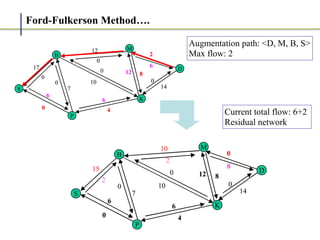
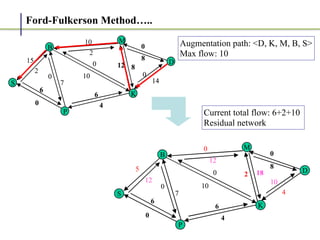
2. It works by finding augmenting paths in the residual network - paths from the source to the sink with available capacity. It then pushes additional flow along this path.
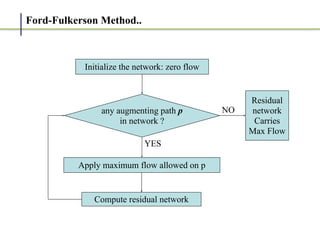
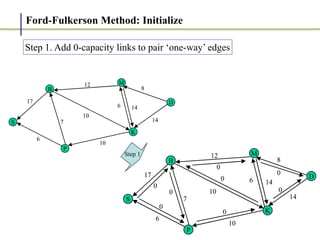
3. The key steps are: (1) finding an augmenting path, (2) updating the residual capacities and flows, (3) repeating until no more augmenting paths exist. This guarantees finding the maximum possible flow.