Recommended
PPT
PDF
PPT
FORD-FULKERSON Algorithm.ppt
PPTX
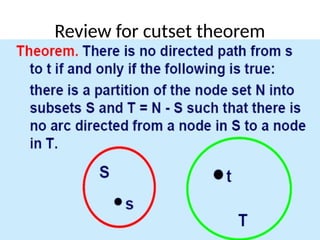
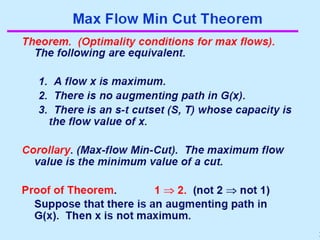
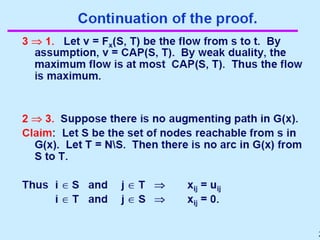
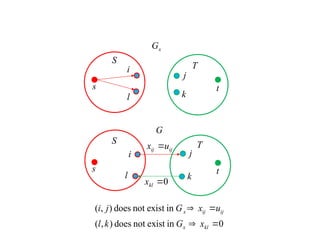
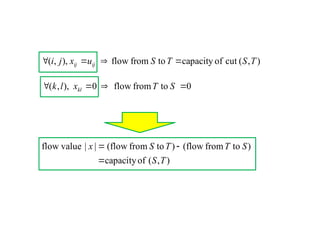
A Maximum Flow Min cut theorem for Optimizing Network
PPT
Ford Fulkerson Algorithm with example .ppt
PDF
CS253: Network Flow (2019)
PPT
PDF
22 - Max Flow Porblem Ford Fulkerson Method.pdf
PPT
PPT
Backtracking is an algorithmic technique used to solve problems by trying all...
PPTX
Chapter 9 DESCRIBE THE CONCEPT OF NETWORK MODELS.pptx
PPTX
Advanced_ Algorithm_ fulk 002410702012.pptx
PPT
PDF
maxflow.4up.pdf for the Maximam flow to solve using flord fulkerson algorithm
PDF
Lecture 3 (Network Flow for optimization course).pdf
PPTX
23-Maximum Flows_ Ford-Fulkerson algorithm-26-02-2025.pptx
PDF
PPTX
Ford_Fulkerson_Algorithm_uptade.ppt[1].pptx
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
08-network-flow-problems that are usefull in Oops
PPT
Network flow algorithm.ppt, Netwok Flow Algorithms, Ford Fulkerson Algorithm
PPT
PPT
PDF
Ford Fulkerson wjgnejgbnhjbdreryjerhsrgjhegeujtgsruyw (1).pdf
PPT
PDF
algorithm_7network_flow.pdf
PPTX
BUSY Software Business Management Solution.pptx
PPTX
GraphQL Day Paris 2025 | Bringing DevOps to GraphQL with the Apollo GraphOS O...
More Related Content
PPT
PDF
PPT
FORD-FULKERSON Algorithm.ppt
PPTX
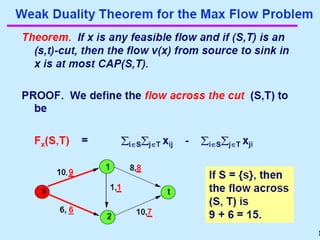
A Maximum Flow Min cut theorem for Optimizing Network
PPT
Ford Fulkerson Algorithm with example .ppt
PDF
CS253: Network Flow (2019)
PPT
PDF
22 - Max Flow Porblem Ford Fulkerson Method.pdf
Similar to Flow networkFlow networkFlow networkFlow network
PPT
PPT
Backtracking is an algorithmic technique used to solve problems by trying all...
PPTX
Chapter 9 DESCRIBE THE CONCEPT OF NETWORK MODELS.pptx
PPTX
Advanced_ Algorithm_ fulk 002410702012.pptx
PPT
PDF
maxflow.4up.pdf for the Maximam flow to solve using flord fulkerson algorithm
PDF
Lecture 3 (Network Flow for optimization course).pdf
PPTX
23-Maximum Flows_ Ford-Fulkerson algorithm-26-02-2025.pptx
PDF
PPTX
Ford_Fulkerson_Algorithm_uptade.ppt[1].pptx
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
08-network-flow-problems that are usefull in Oops
PPT
Network flow algorithm.ppt, Netwok Flow Algorithms, Ford Fulkerson Algorithm
PPT
PPT
PDF
Ford Fulkerson wjgnejgbnhjbdreryjerhsrgjhegeujtgsruyw (1).pdf
PPT
PDF
algorithm_7network_flow.pdf
Recently uploaded
PPTX
BUSY Software Business Management Solution.pptx
PPTX
GraphQL Day Paris 2025 | Bringing DevOps to GraphQL with the Apollo GraphOS O...
PDF
Metrics, Logs, Traces, and Mayhem_ Introducing an observability adventure gam...
PPTX
Device Repair and Maintenance Management
PDF
Project Tracking in Software Project Management
PDF
apidays Australia 2025 | Build Your First MCP Server with Postman Flows
PDF
2026 Safety Roadmap: Systems, Skills, and Scale for EHS Leaders
PPTX
Recent Data Breaches in Cyber World.pptx
PDF
Physiotherapist App Development for Modern Rehabilitation
PDF
On Demand Grocery Delivery App Development
PDF
Monitoring your MySQL Server's Health Trends
PDF
Build a Scalable On-Demand Courier Service App
PDF
20260201 [FOSDEM] gomodjail - library sandboxing for Go modules.pdf
PDF
AI-native development: from Prompt to Platform
PDF
Image and video processing: From Mars to Hollywood with a stop at the hospita...
PDF
Taxi App UIUX Design for Seamless Ride Booking
PDF
Water Delivery App Development Solutions.pdf
PDF
Animated Safety Induction: A Smarter Way to Onboard for Workplace Safety
PDF
Figma systems development services
PPTX
Salesforce Spring '26 Release presentation - Melbourne Salesforce User Group
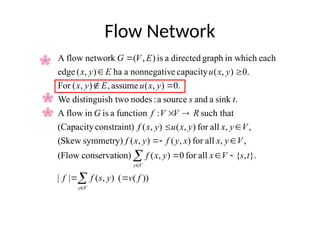
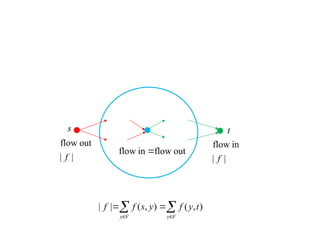
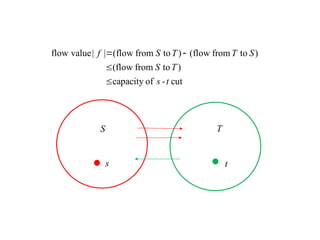
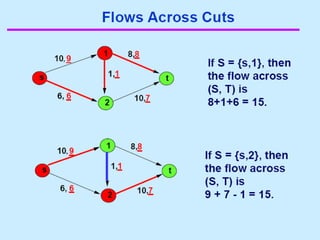
Flow networkFlow networkFlow networkFlow network 1. 2. Flow Network
V
y
V
y
f
v
y
s
f
f
t
s
V
x
y
x
f
V
y
x
x
y
f
y
x
f
V
y
x
y
x
u
y
x
f
R
V
V
f
G
t
s
y
x
u
E
y
x
y
x
u
E
y
x
E
V
G
))
(
(
)
,
(
|
|
}.
,
{
all
for
0
)
,
(
on)
conservati
(Flow
,
,
all
for
)
,
(
)
,
(
symmetry)
(Skew
,
,
all
for
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
constraint
(Capacity
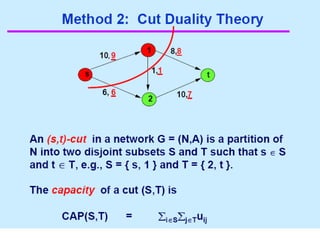
such that
:
function
a
is
in
flow
A
.
sink
a
and
source
a
:
nodes
h two
distinguis
We
.
0
)
,
(
assume
,
)
,
(
For
.
0
)
,
(
capacity
e
nonnegativ
a
ha
)
,
(
edge
each
in which
graph
directed
a
is
)
,
(
network
flow
A
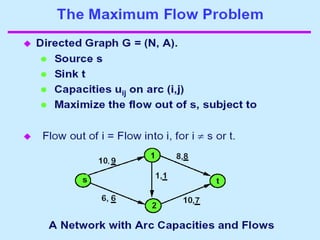
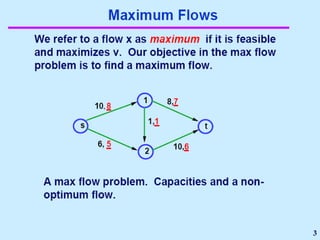
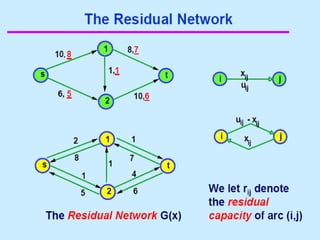
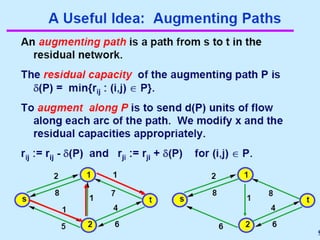
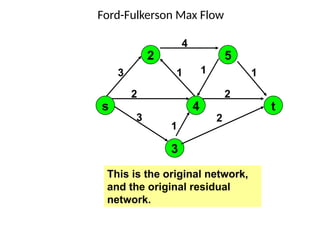
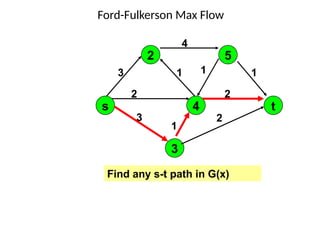
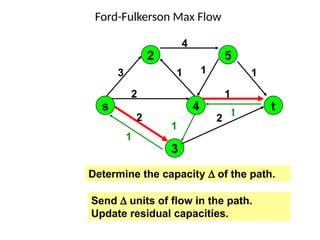
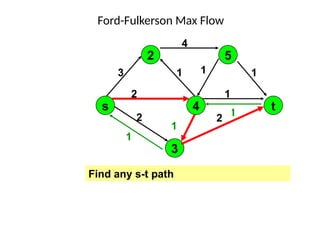
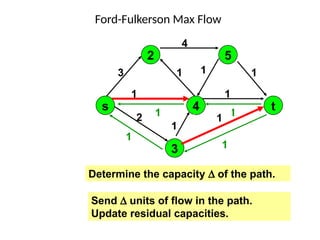
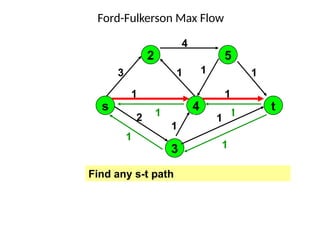
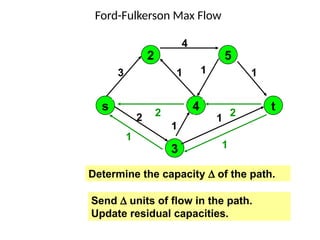
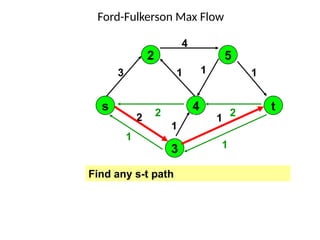
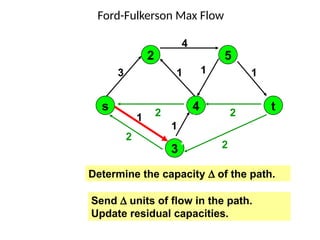
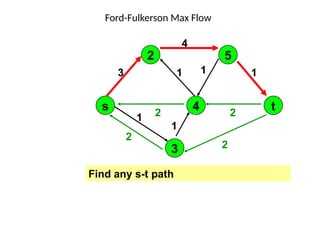
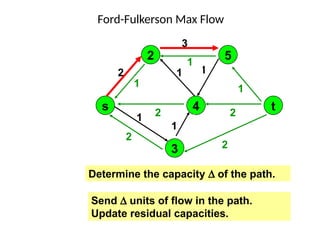
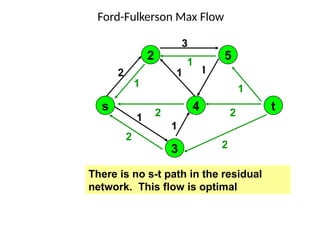
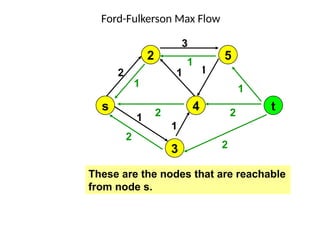
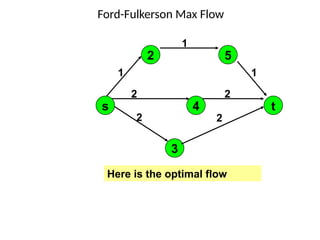
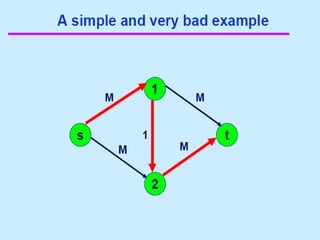
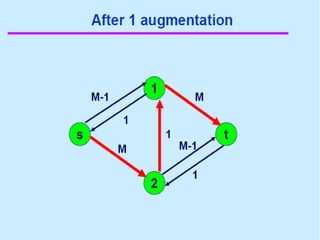
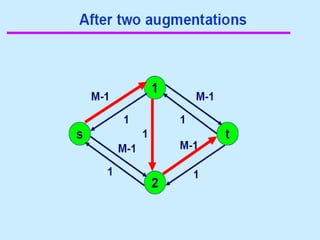
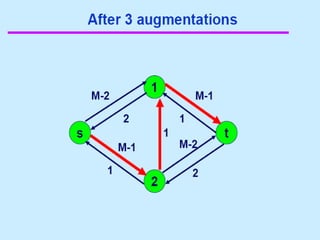
3. 4. 8. The Ford Fulkerson Maximum Flow Algorithm
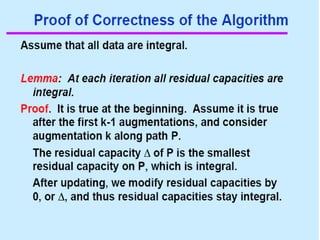
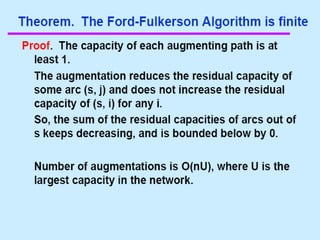
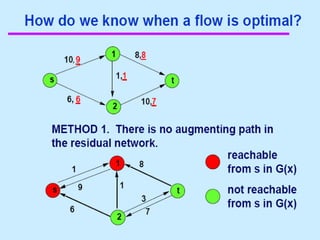
• Begin x := 0;
– create the residual network G(x);
– while there is some directed path from s to t in G(x)
do
• begin
• let P be a path from s to t in G(x);
• ∆:= δ(P);
• send ∆ units of flow along P;
• update the r's;
– End
• end {the flow x is now maximum}.
9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 28. 30. 34. 35. 37. 44. Editor's Notes #9 Obtain a network, and use the same network to illustrate the shortest path problem for communication networks, the max flow problem, the minimum cost flow problem, and the multicommodity flow problem. This will be a very efficient way of introducing the four problems. (Perhaps under 10 minutes of class time.)