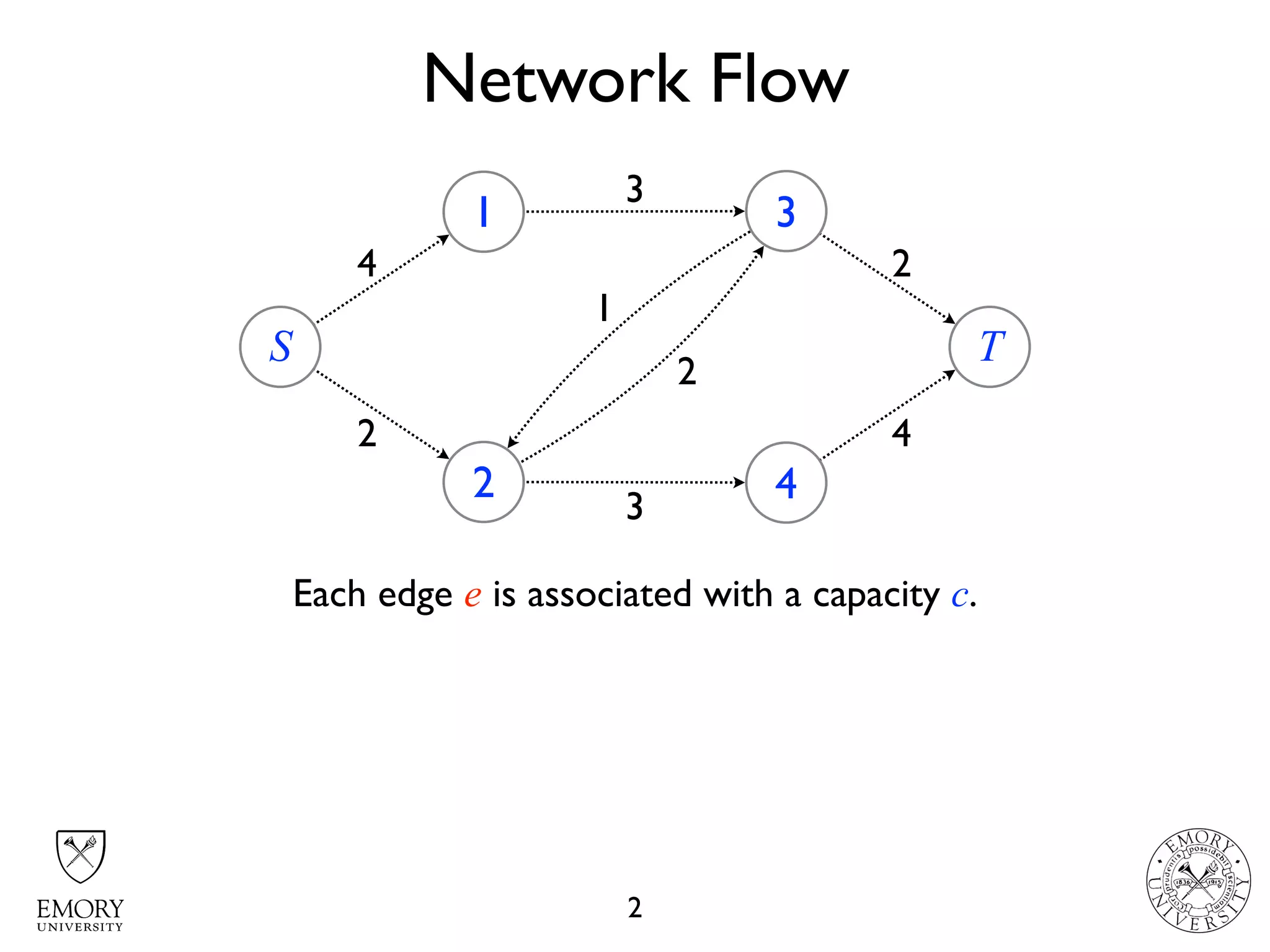
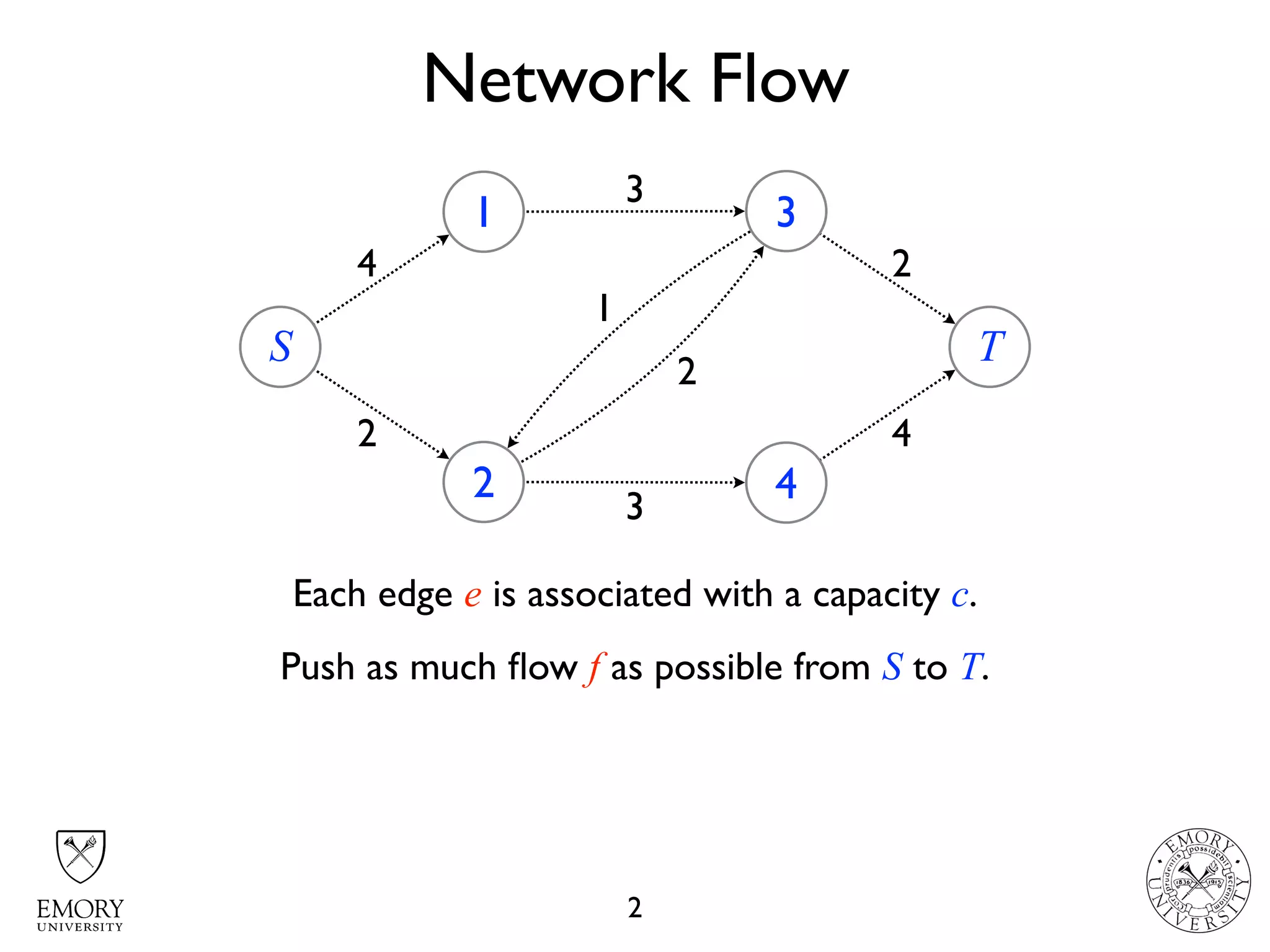
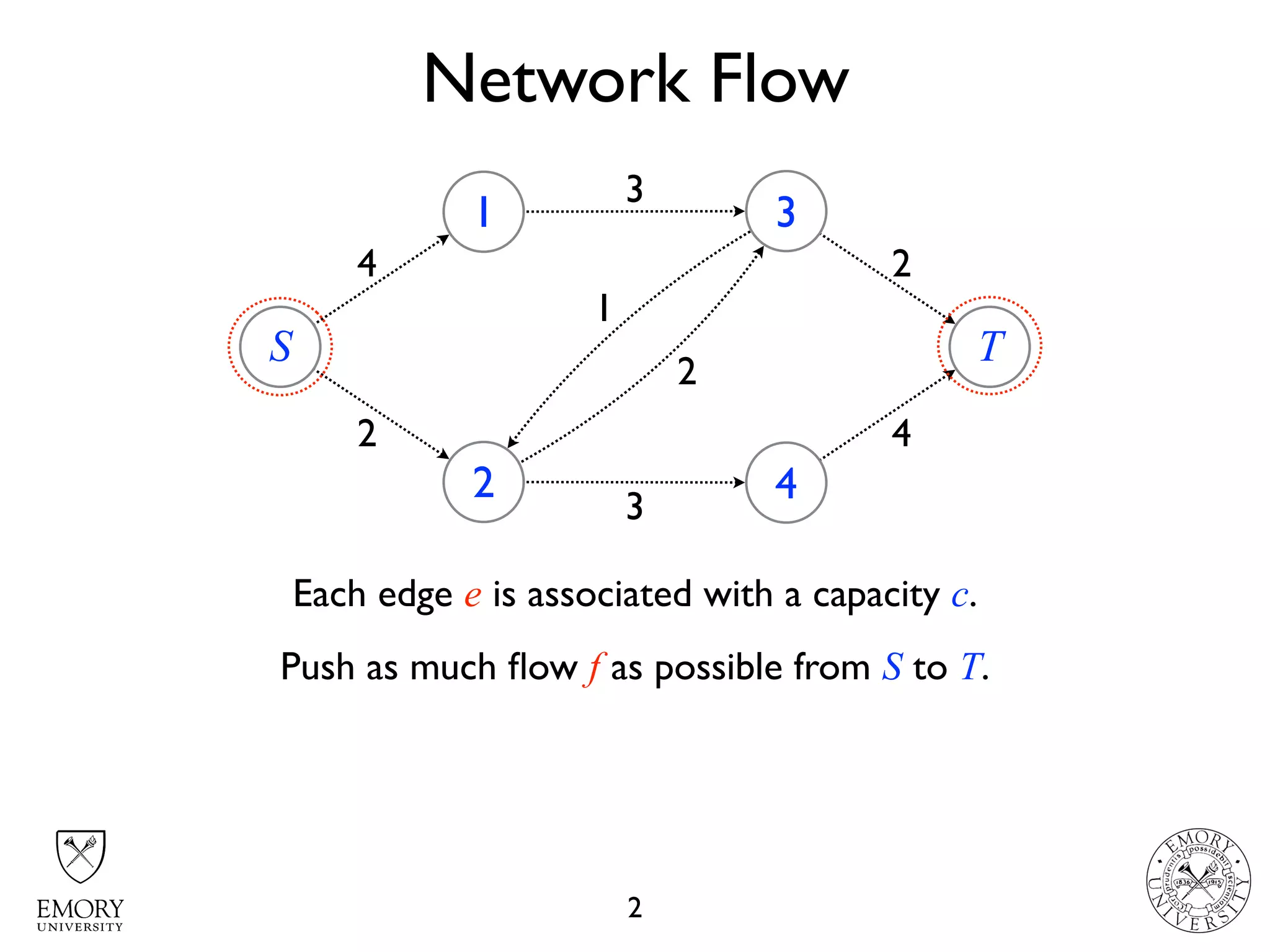
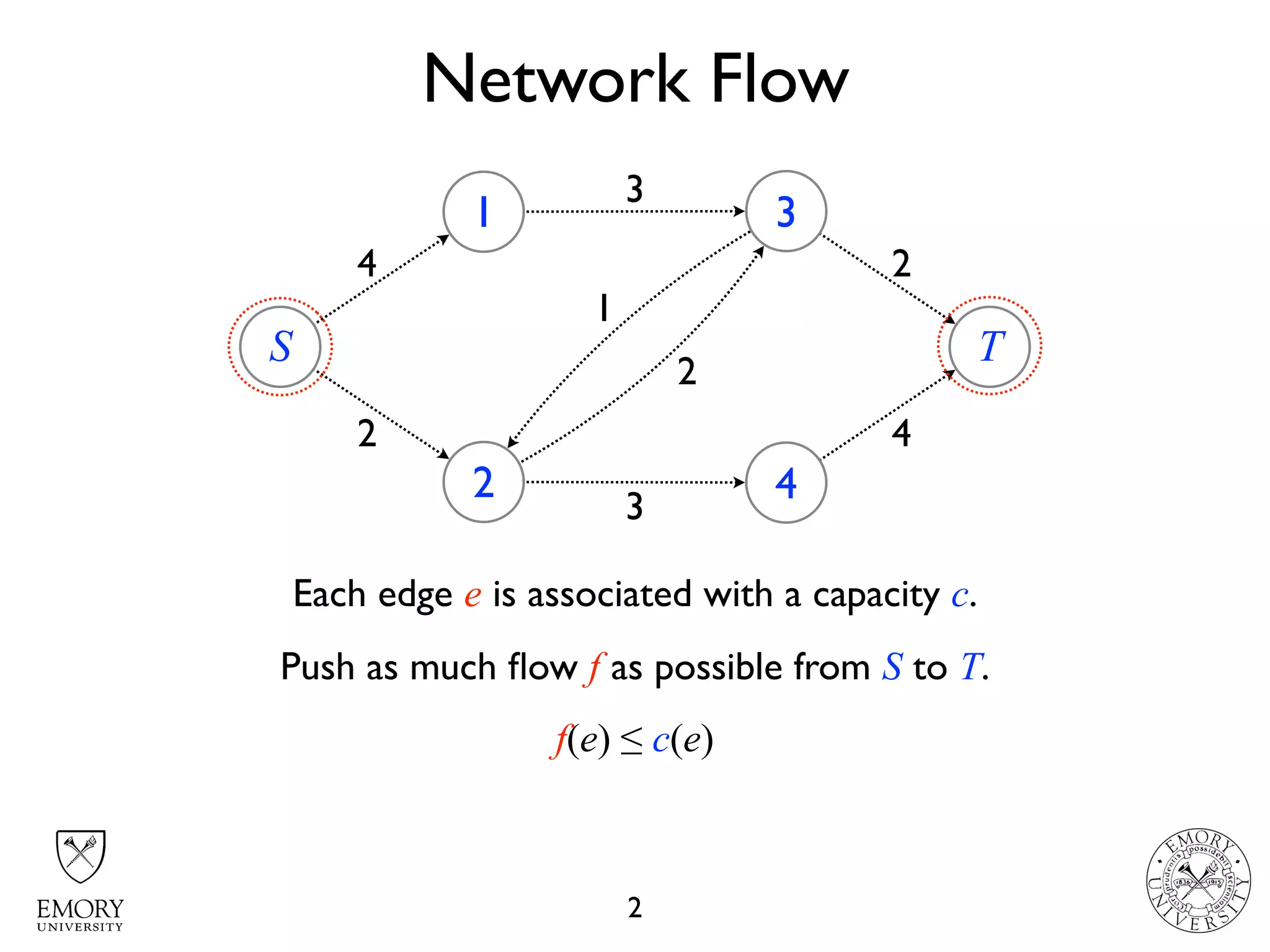
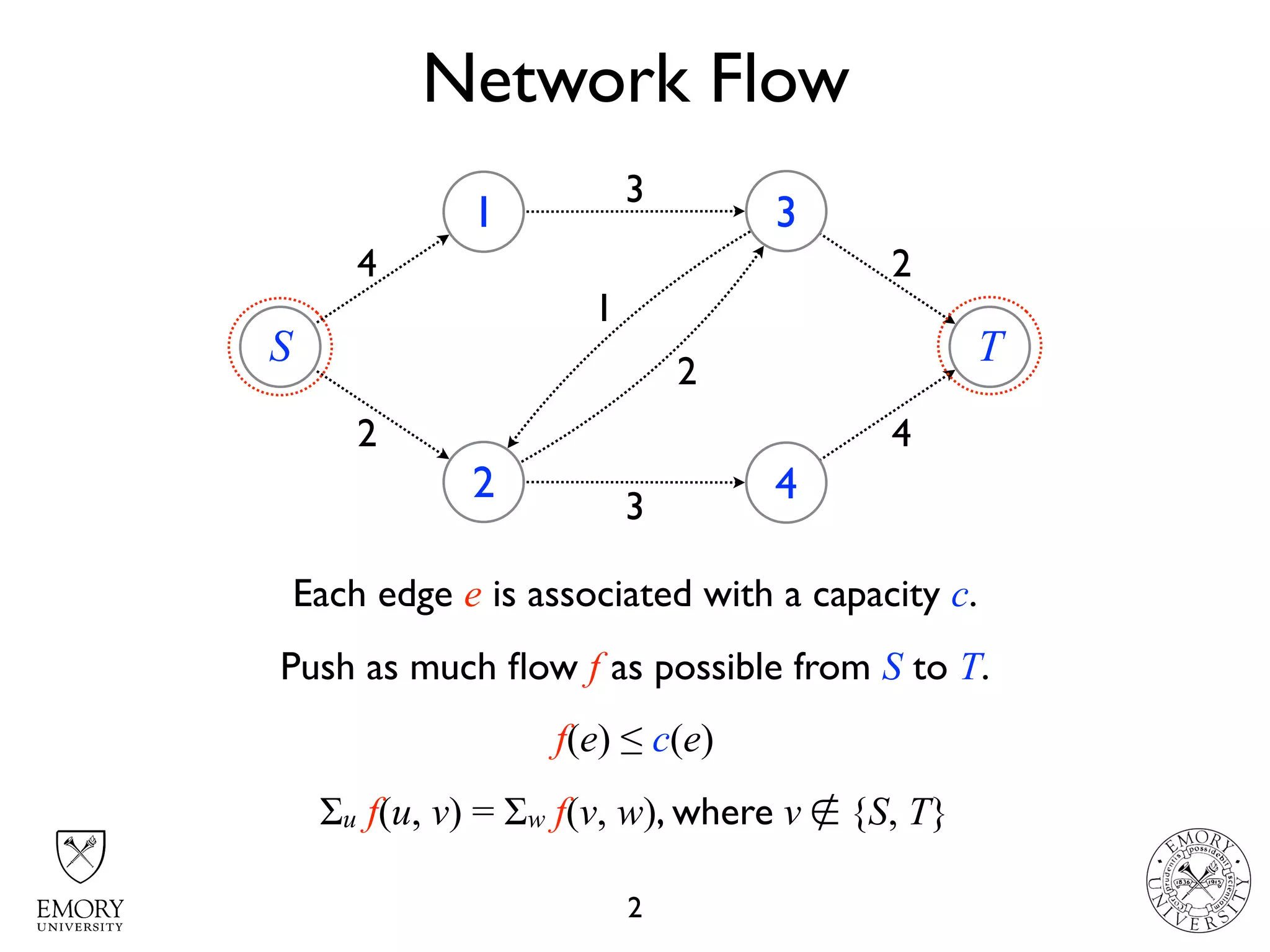
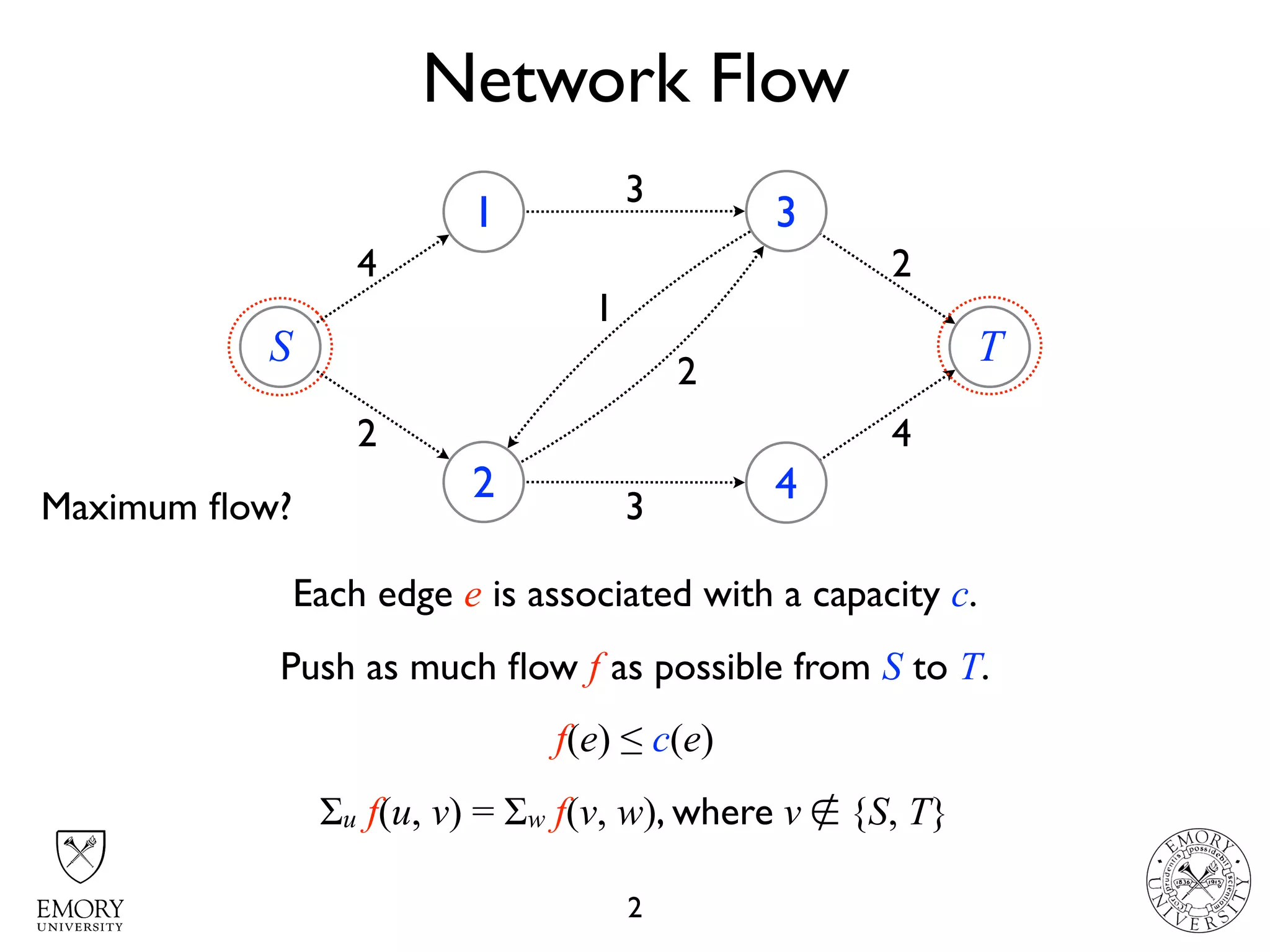
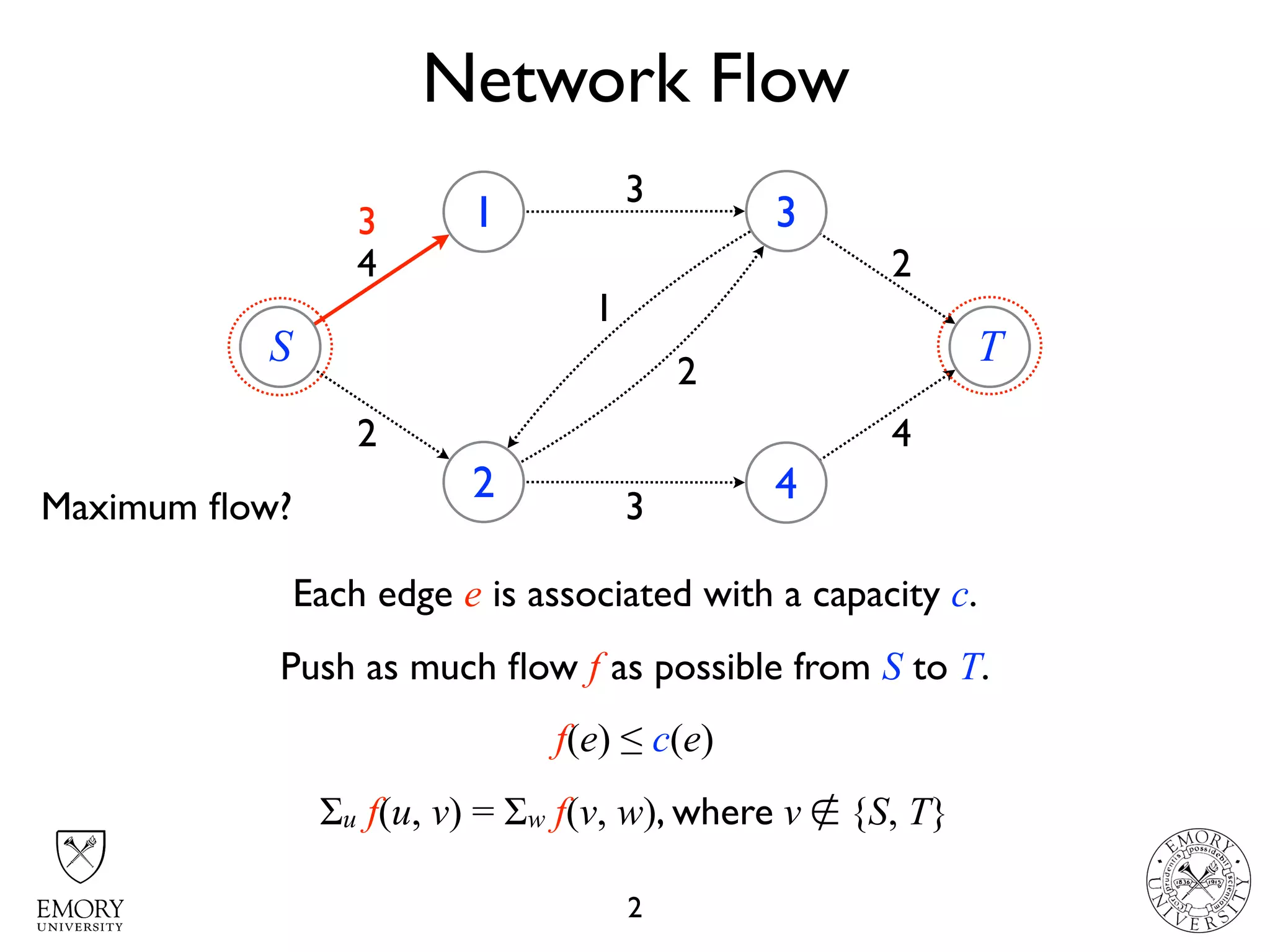
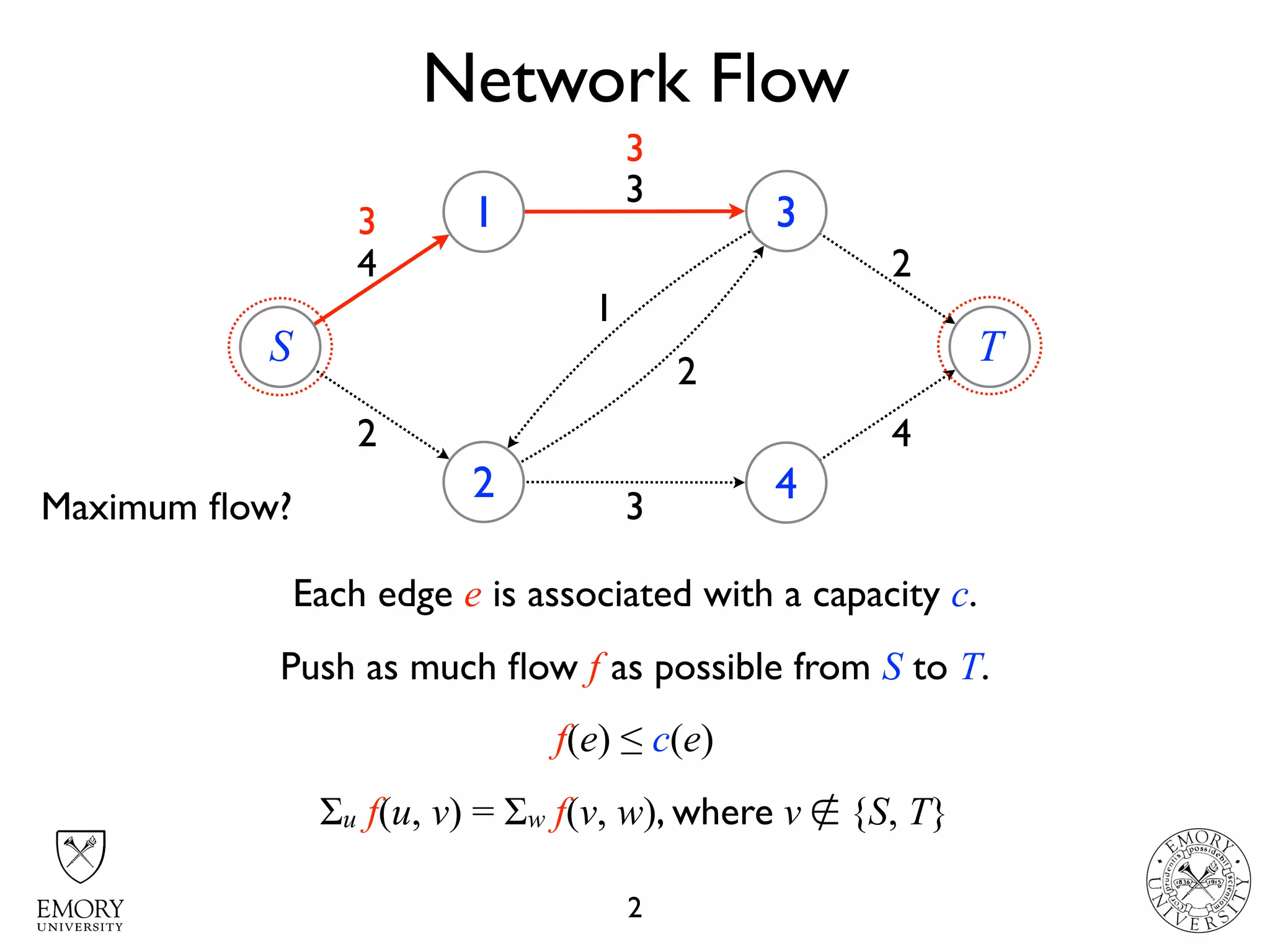
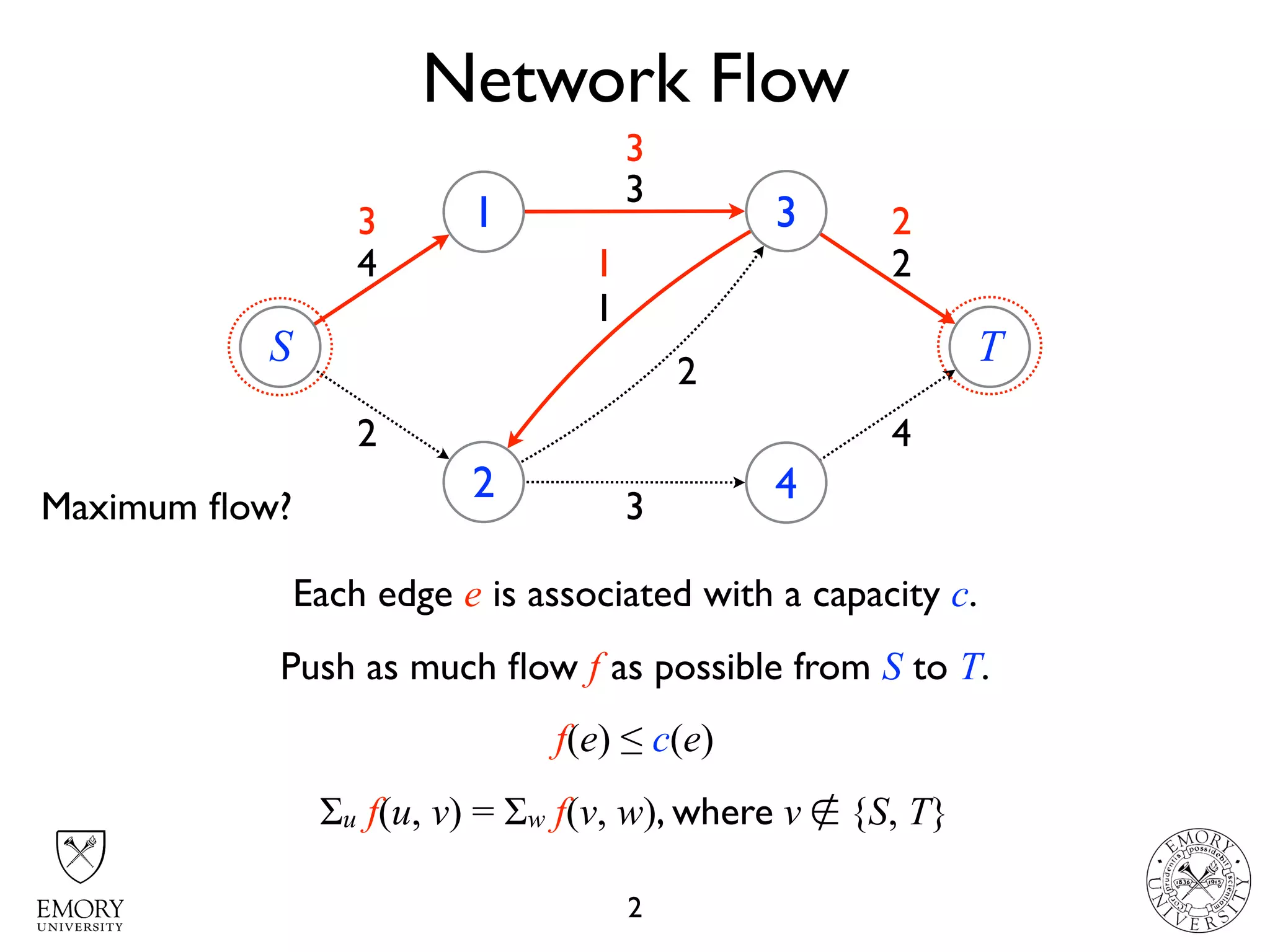
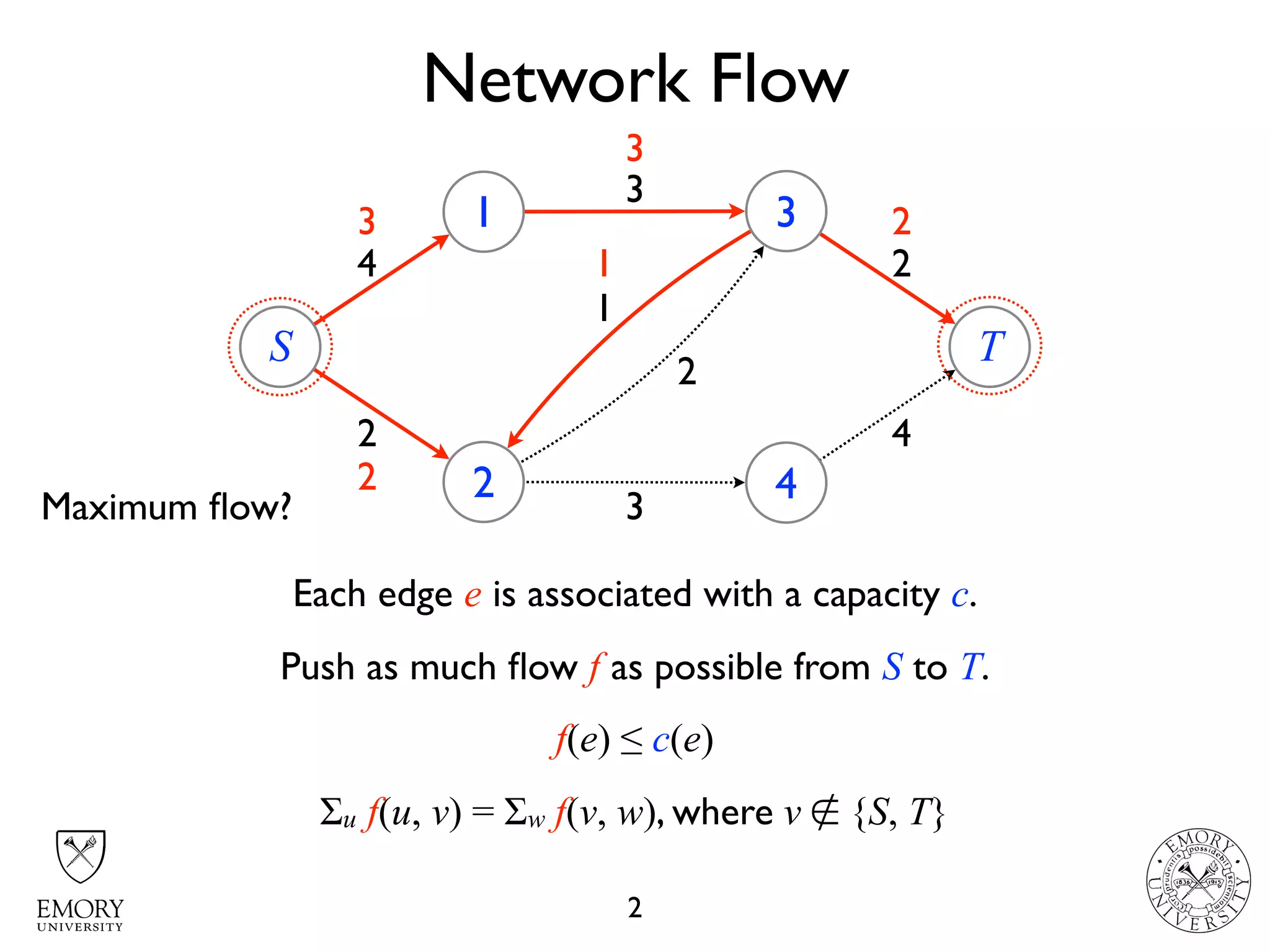
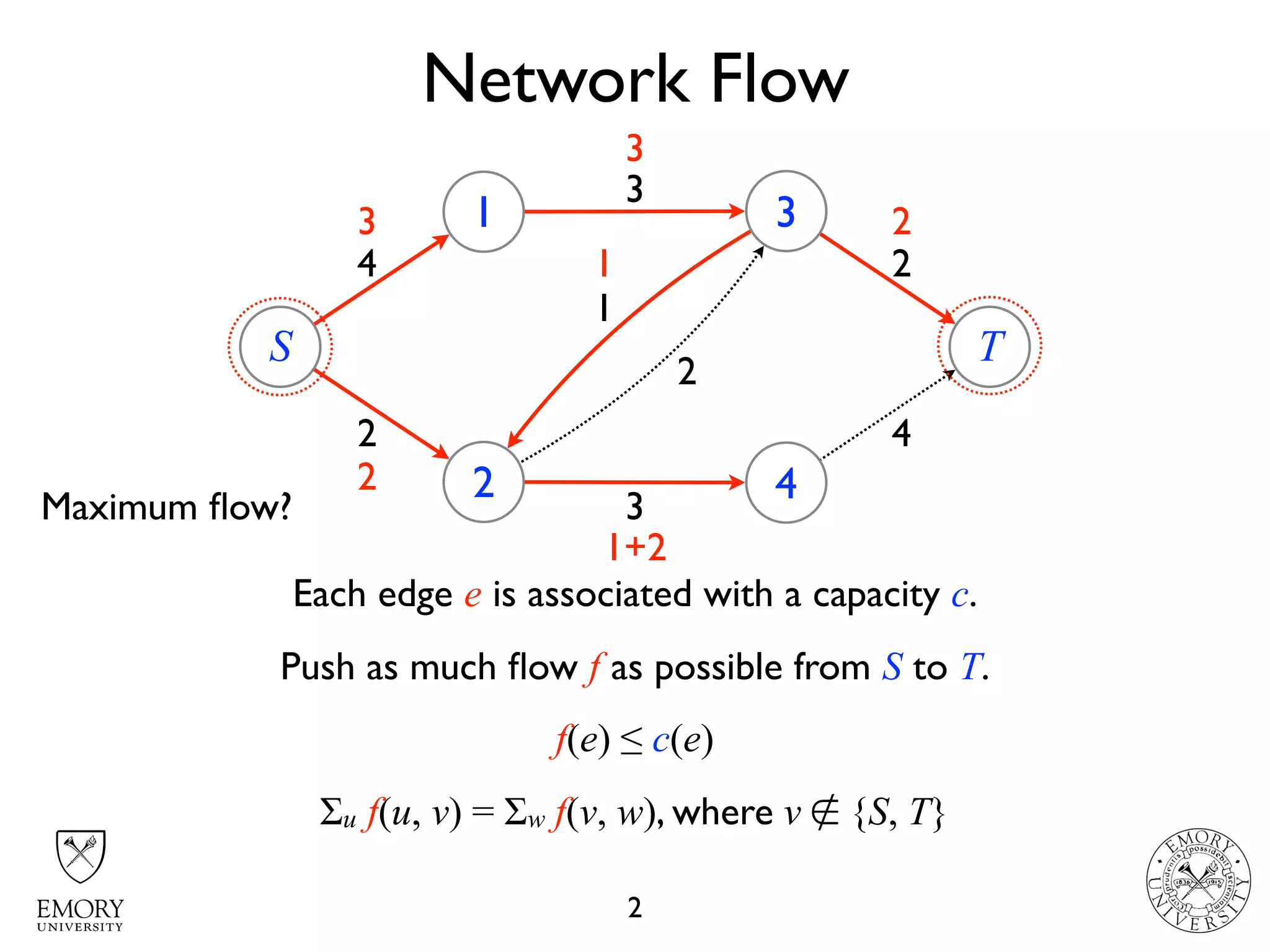
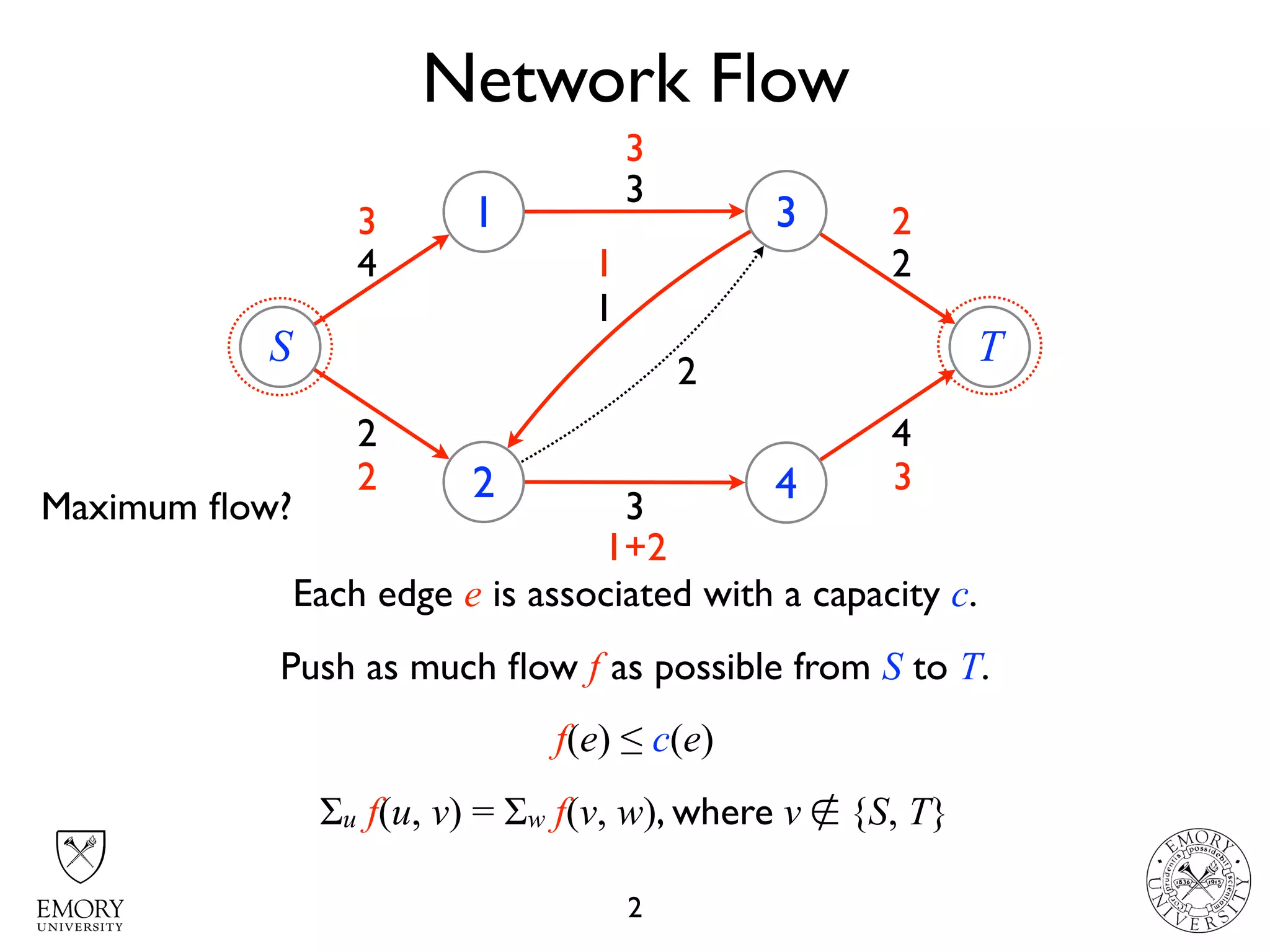
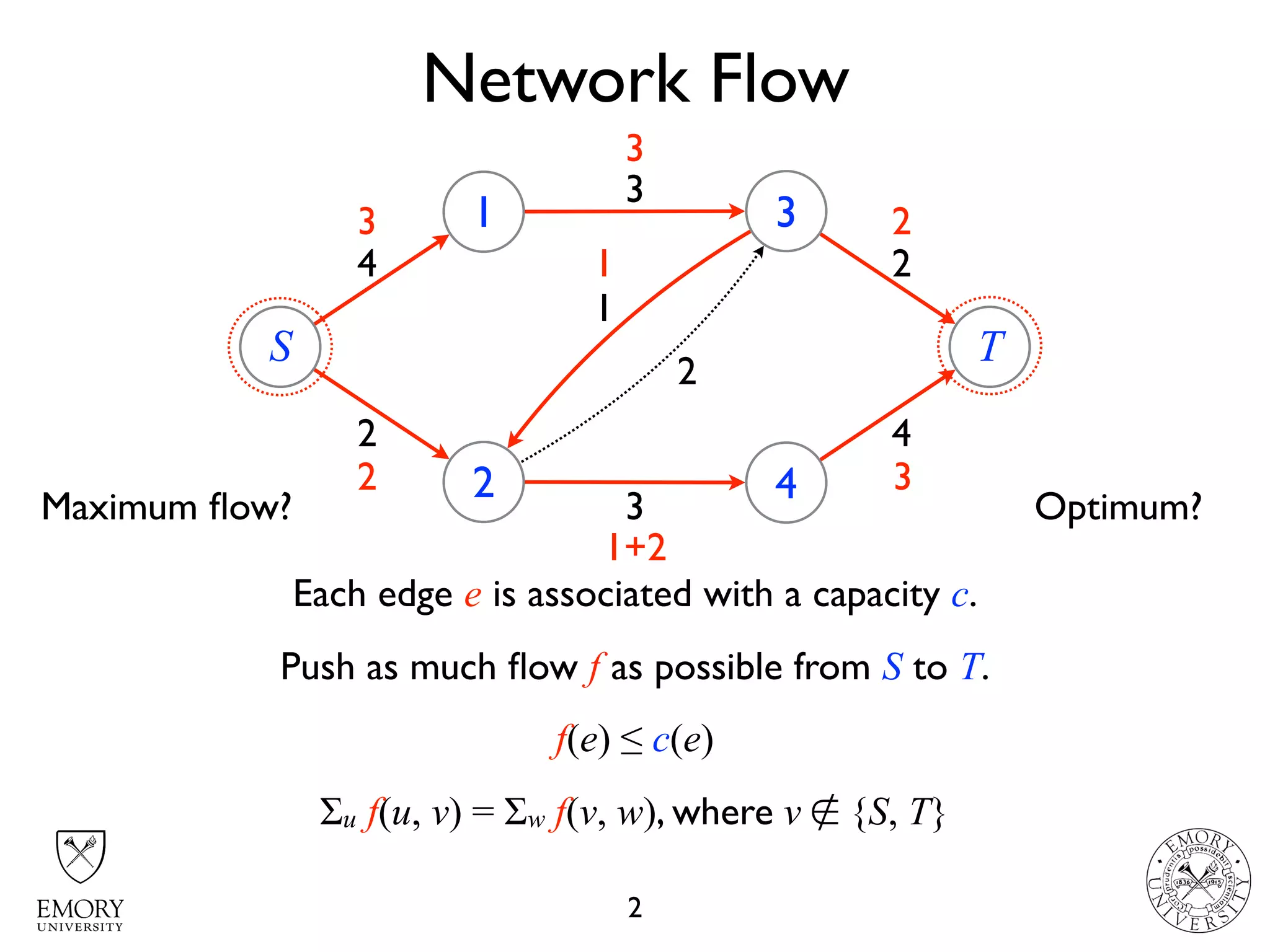
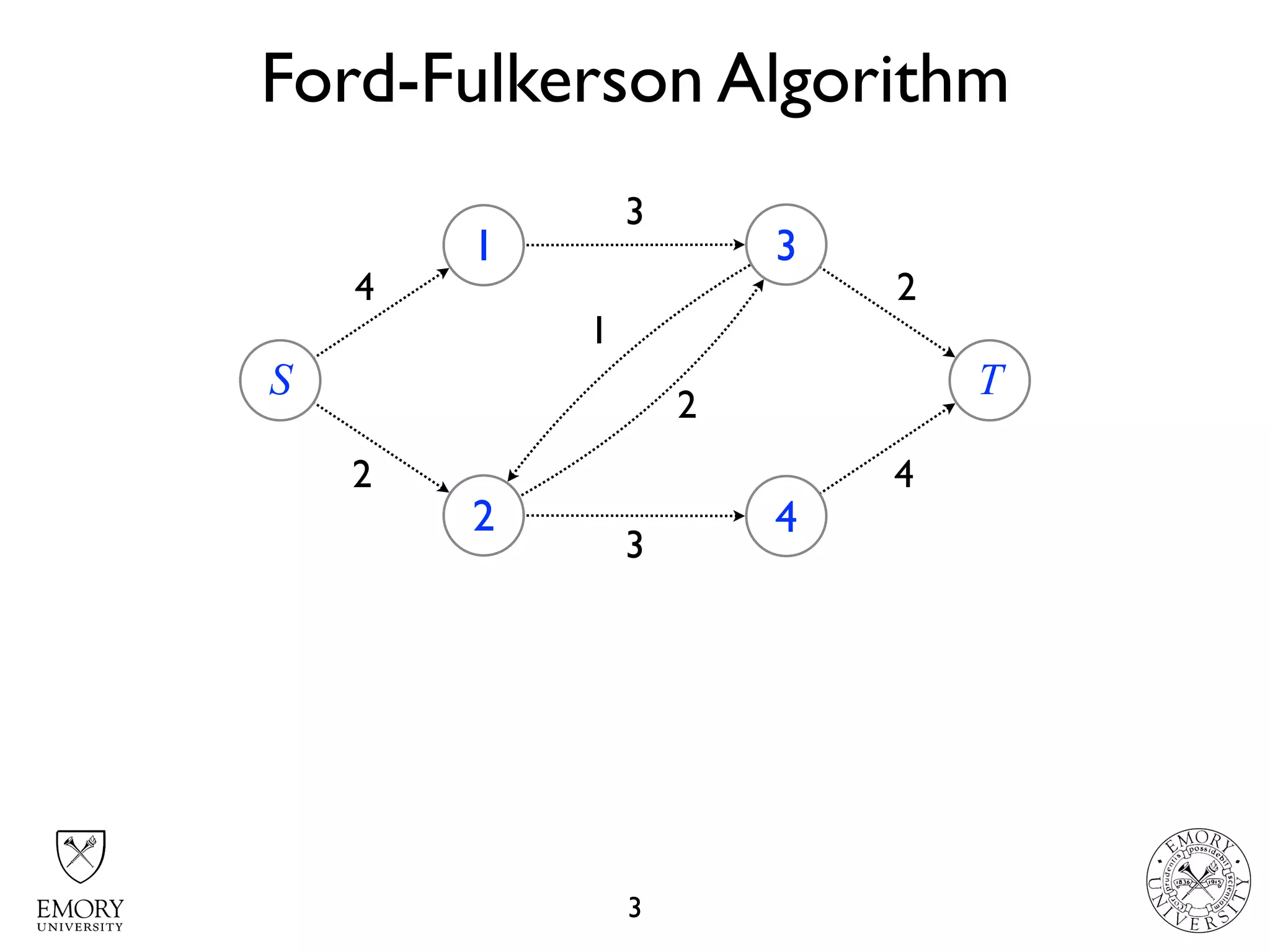
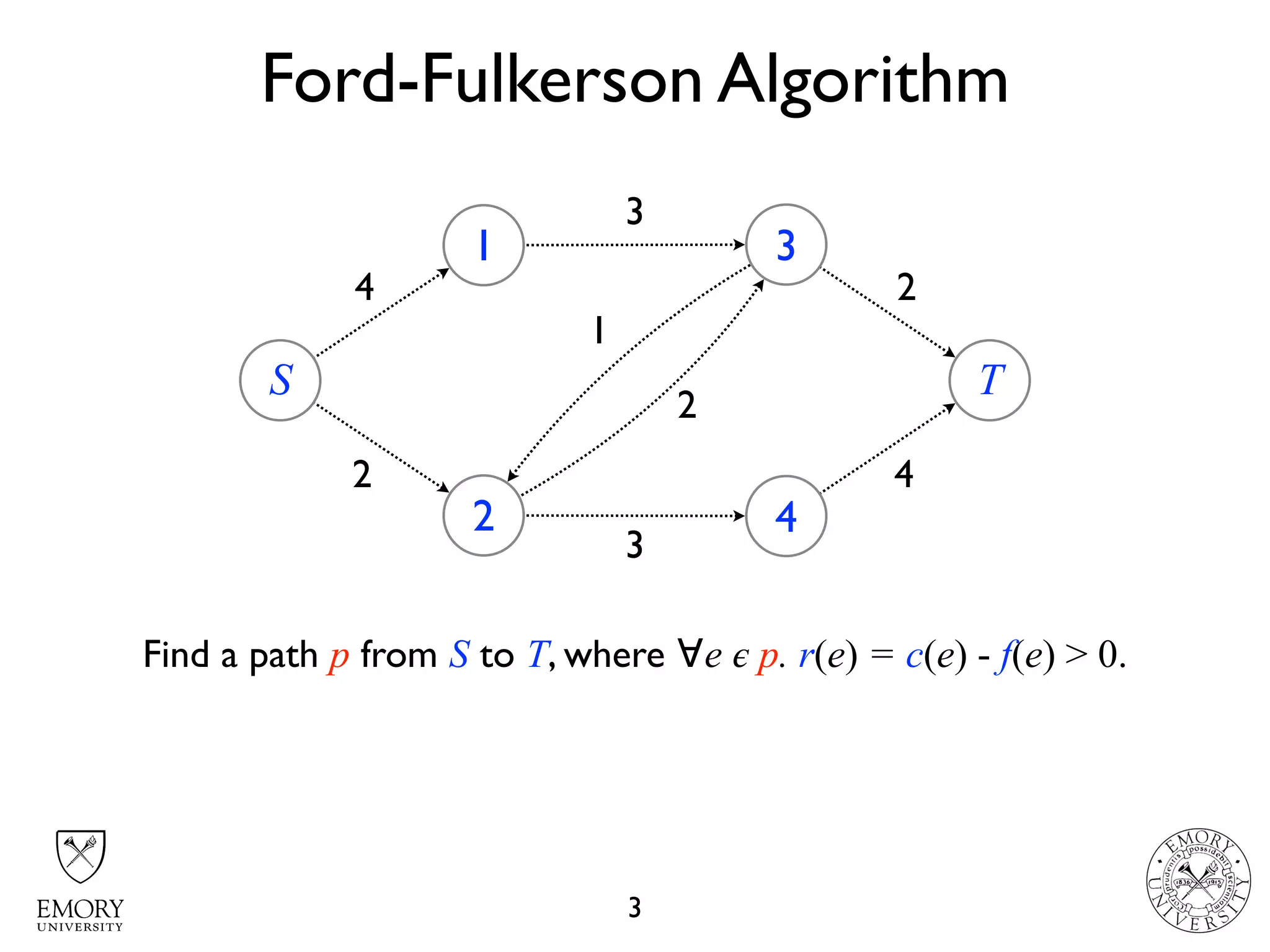
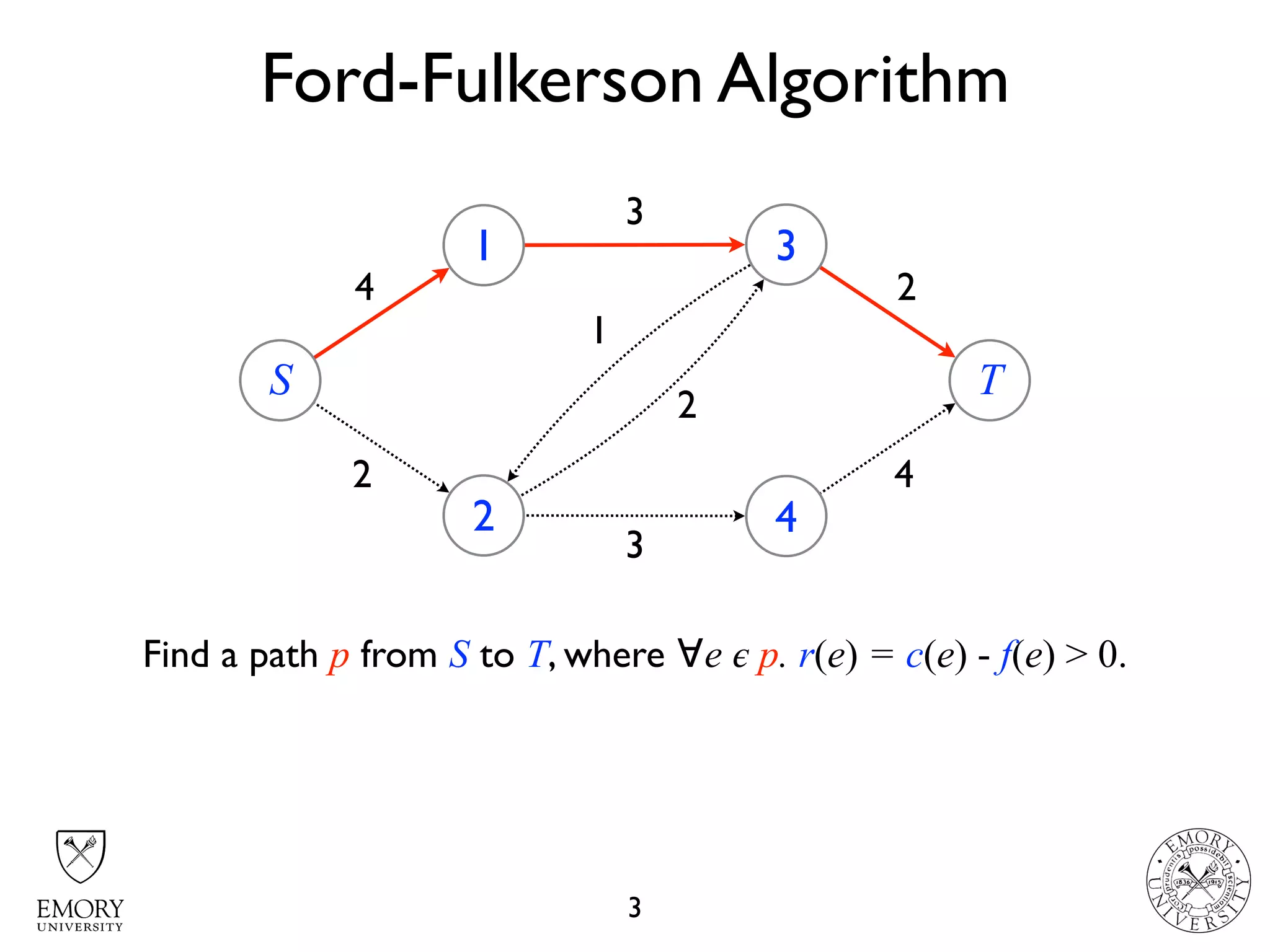
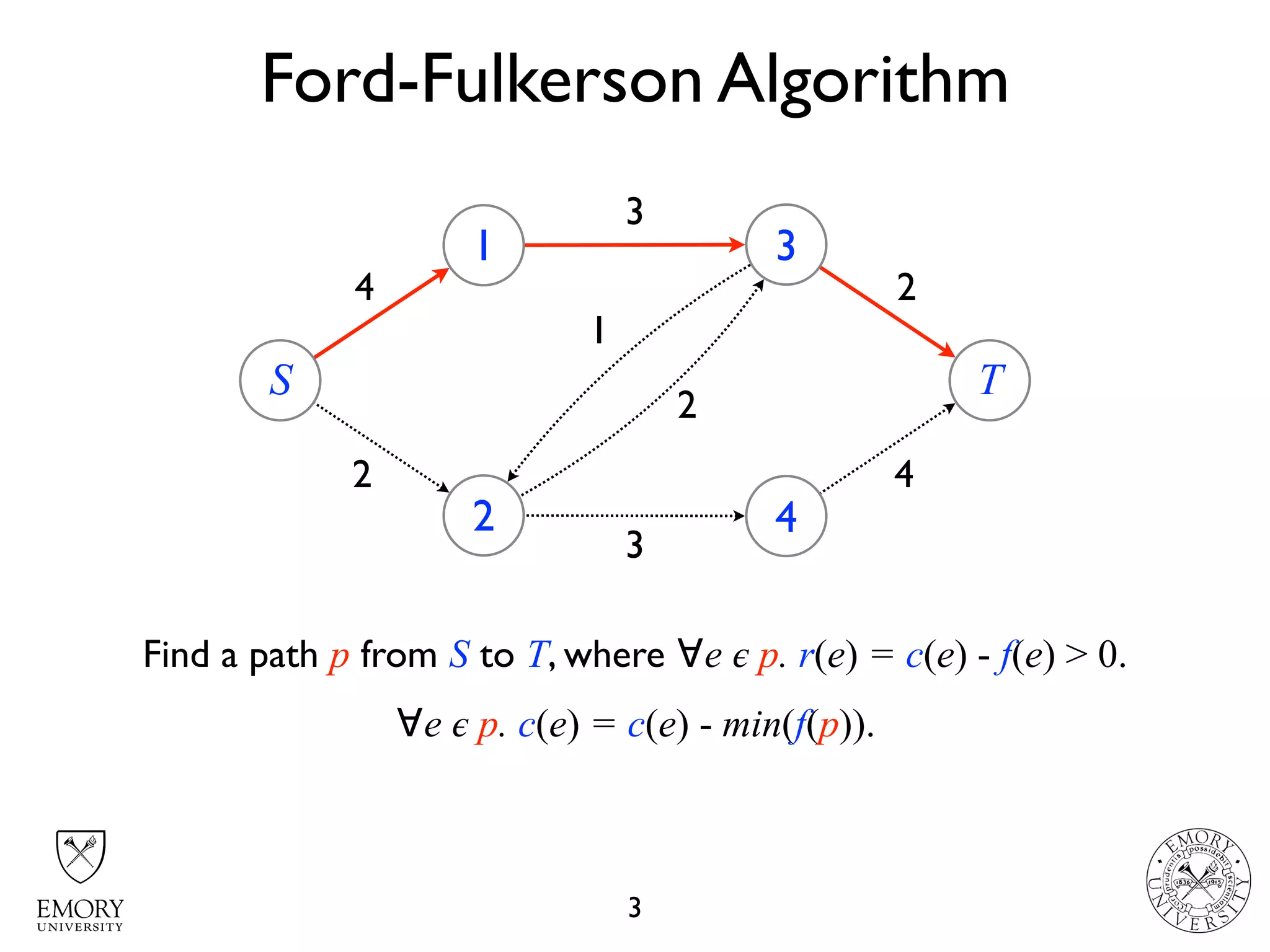
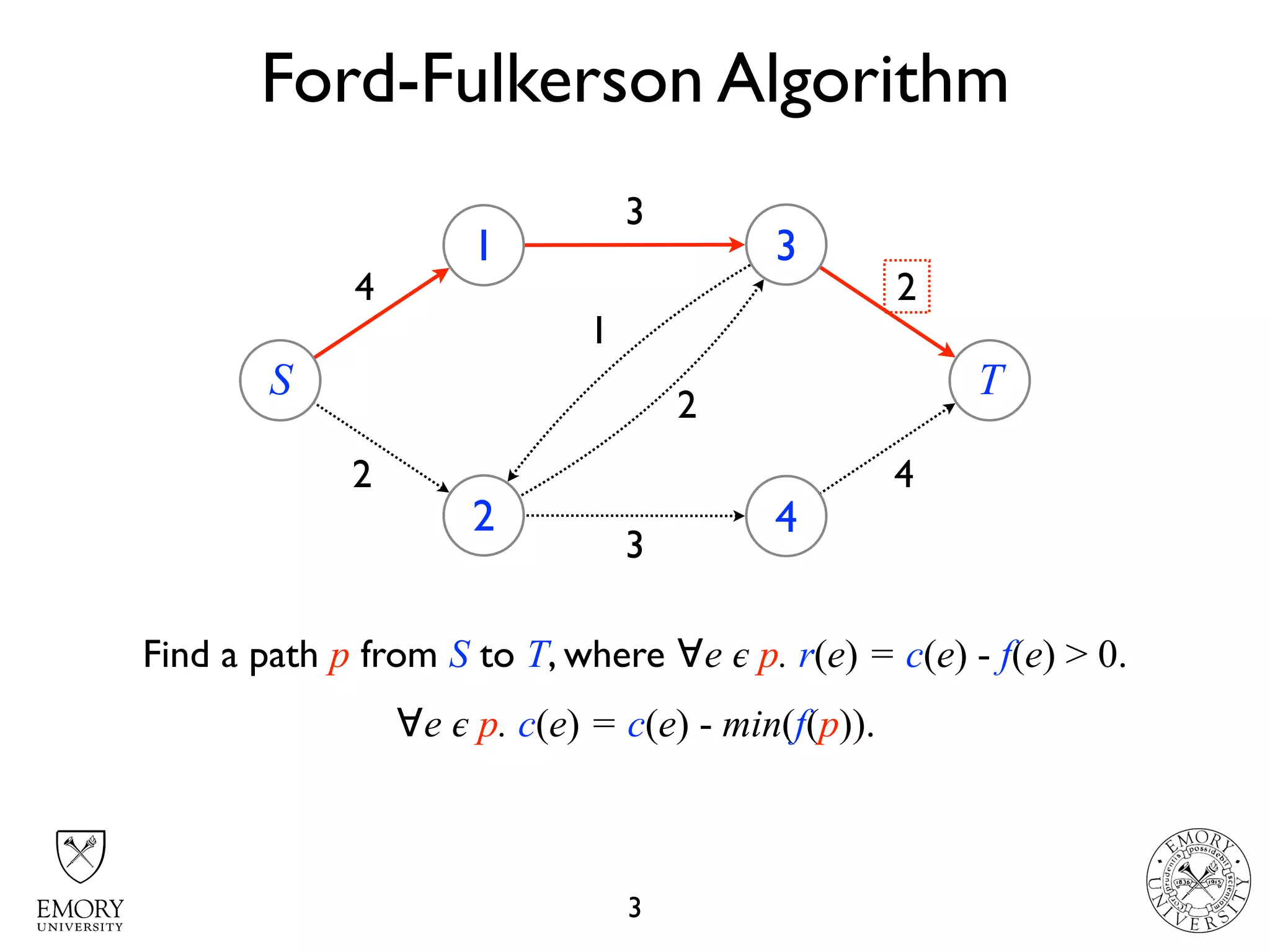
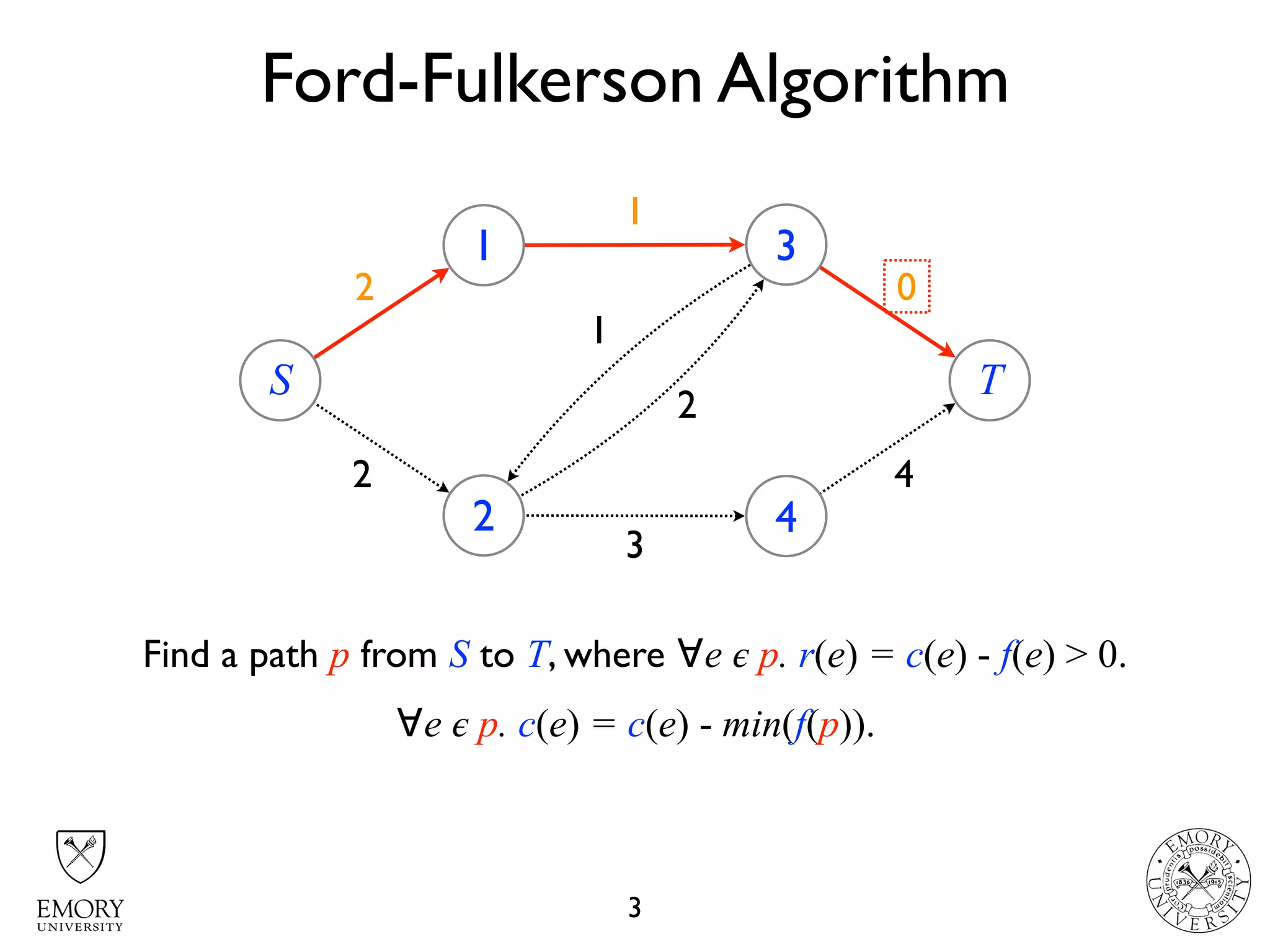
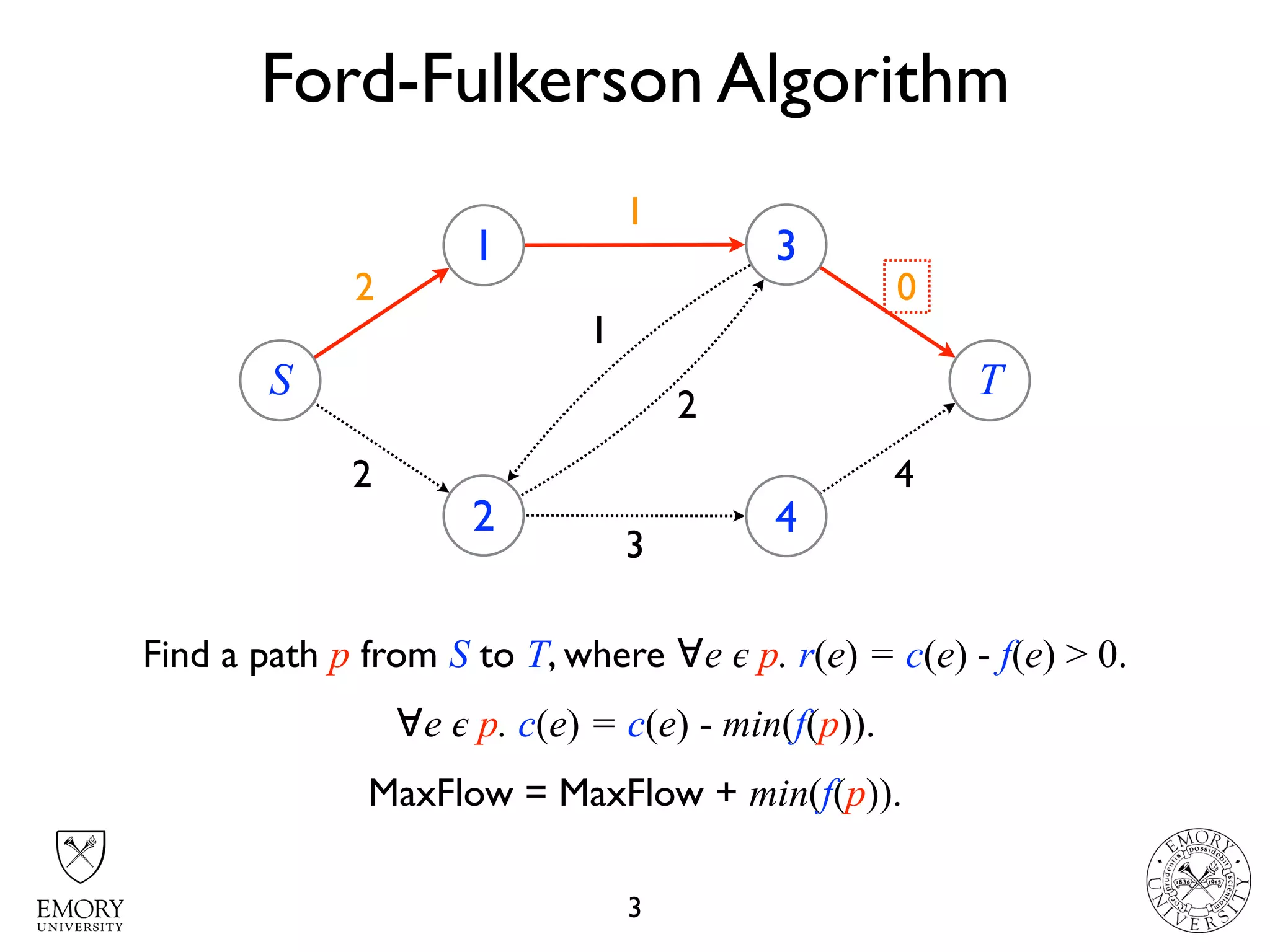
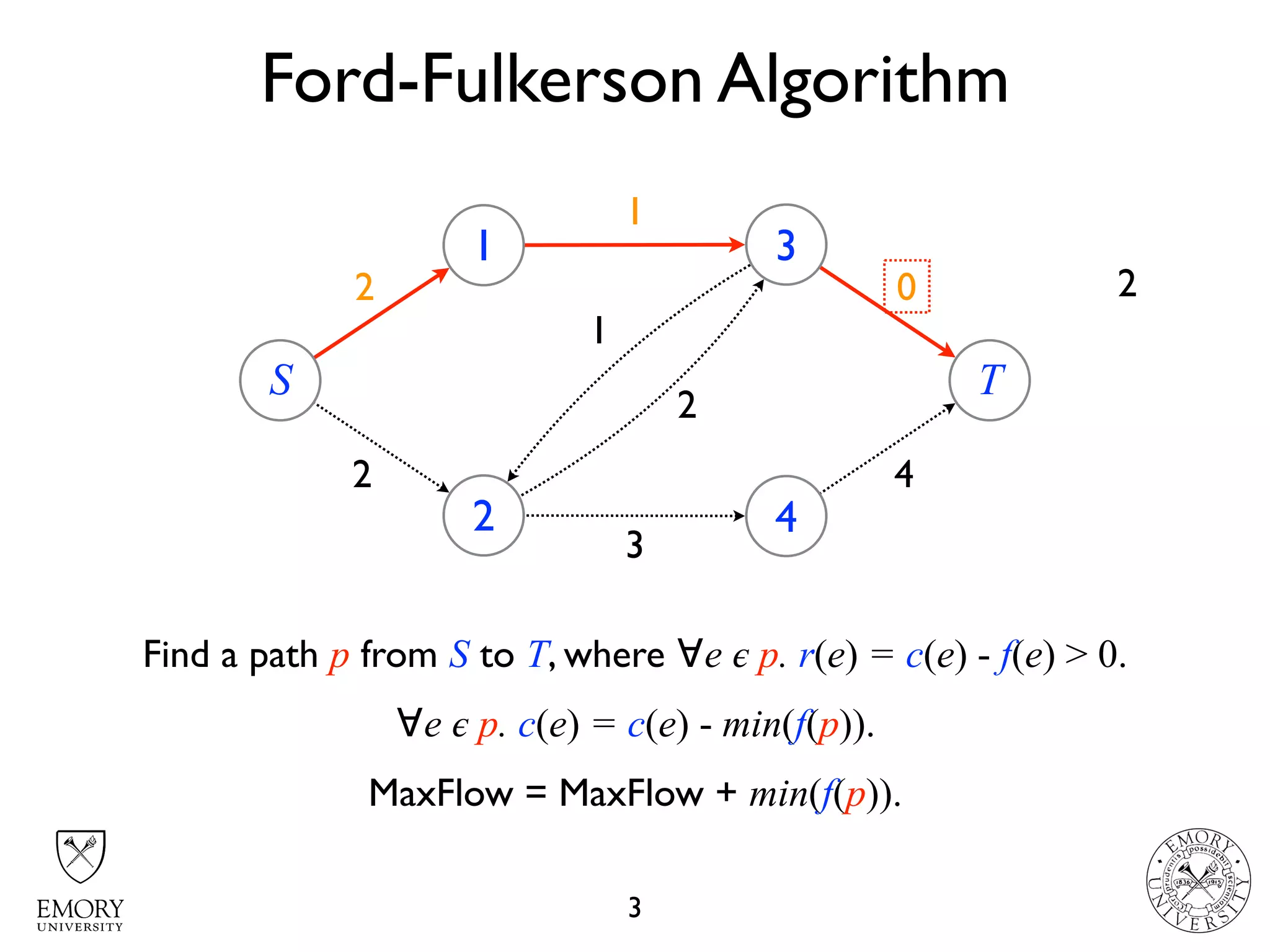
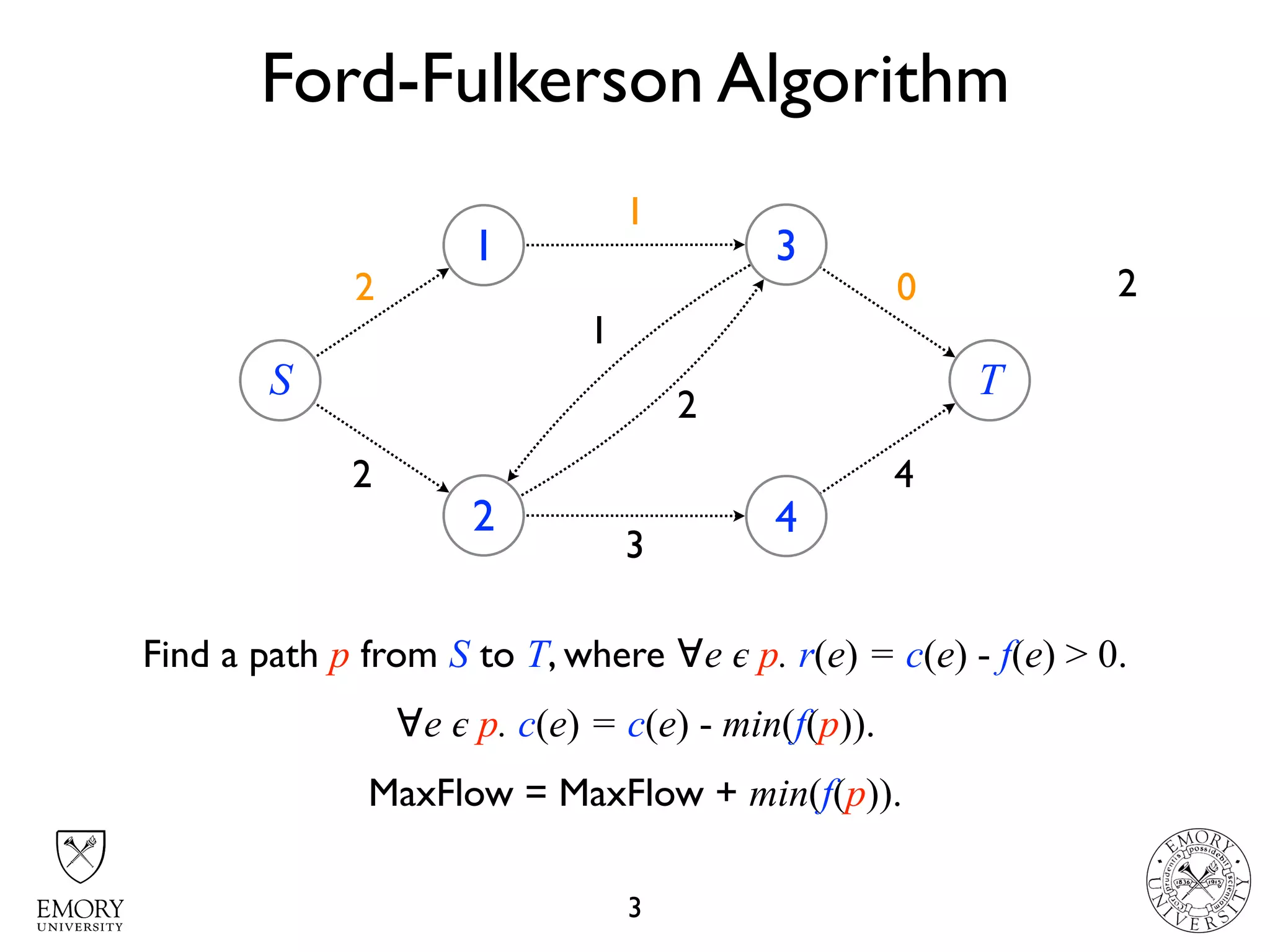
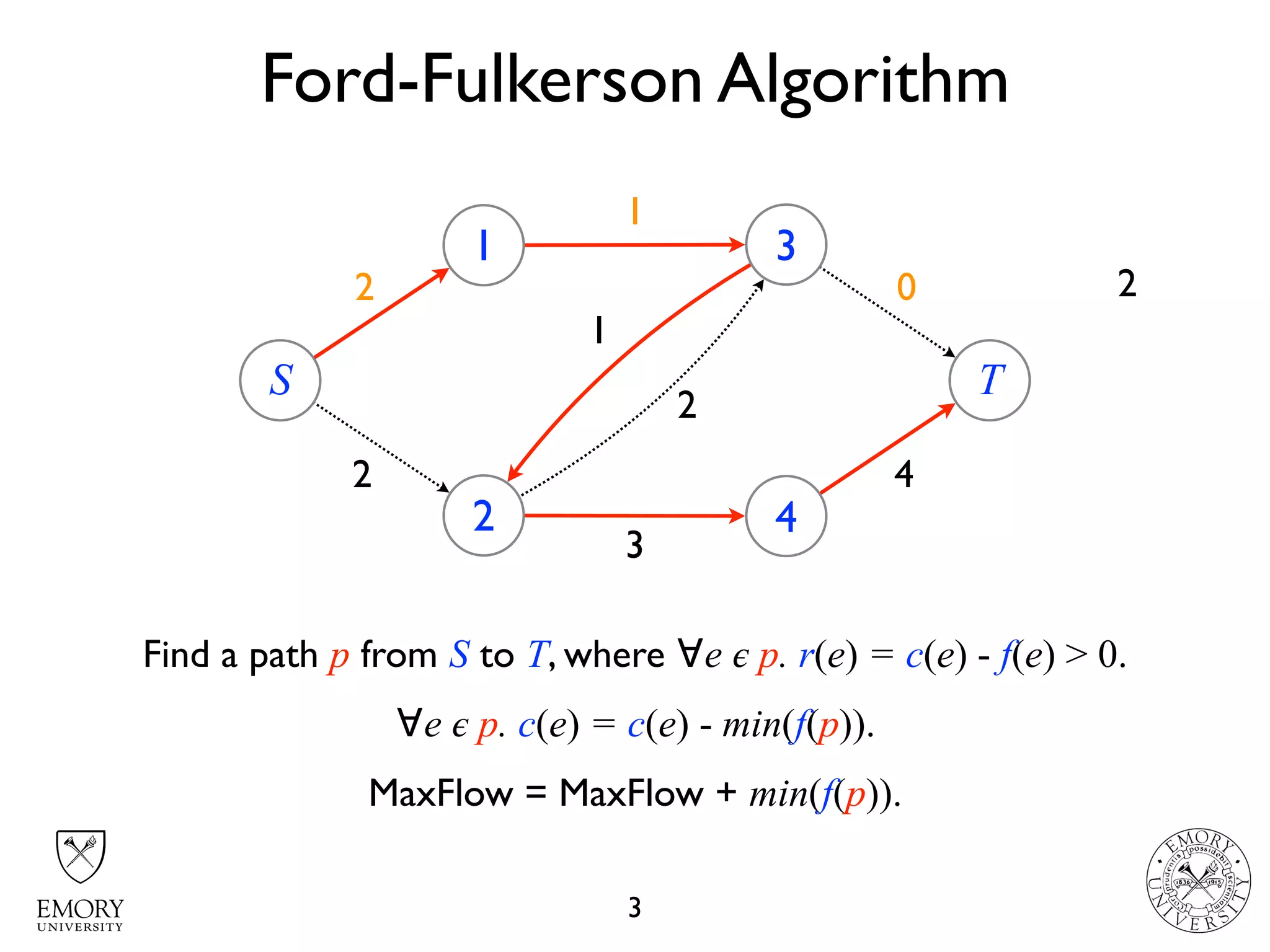
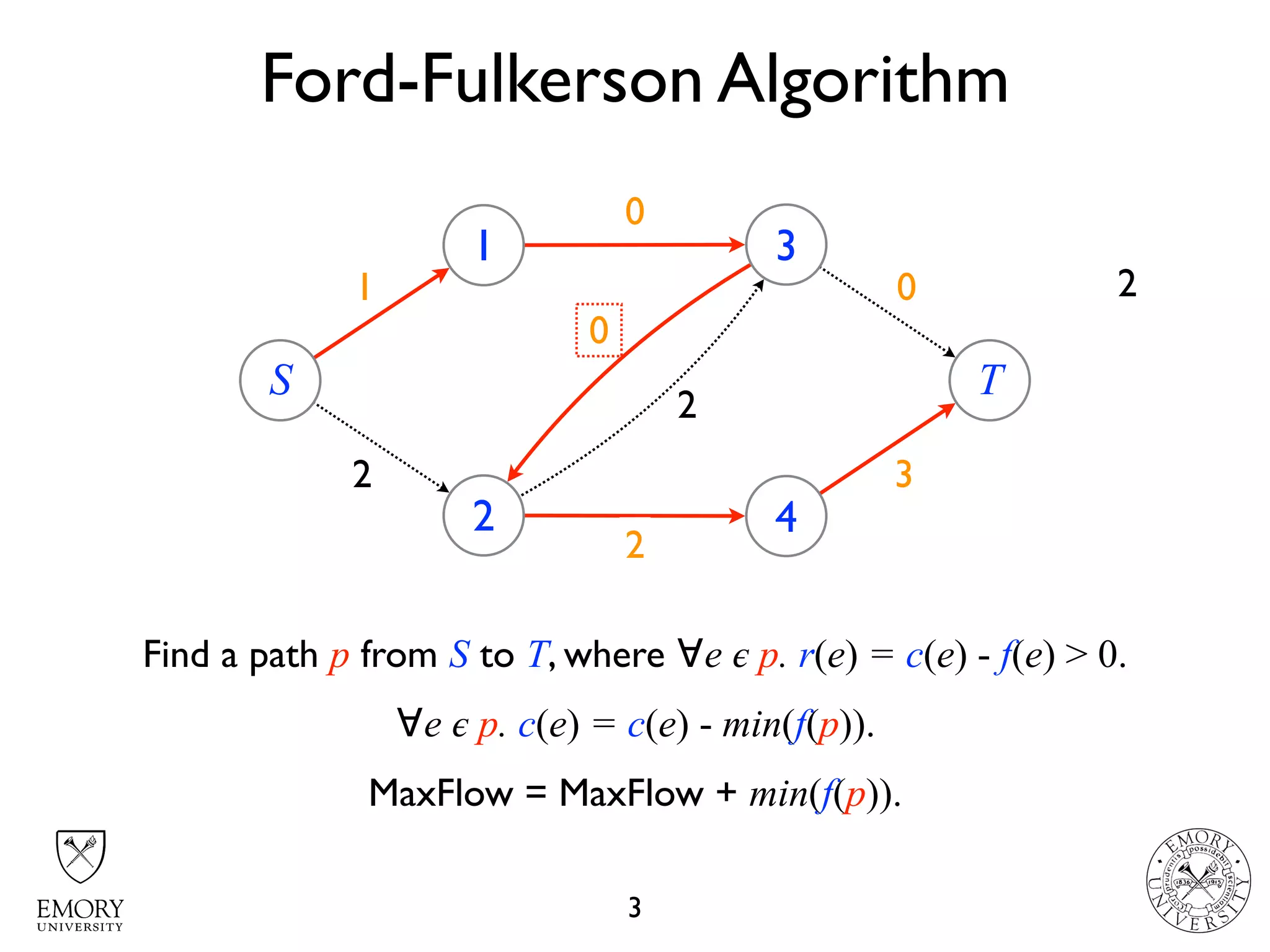
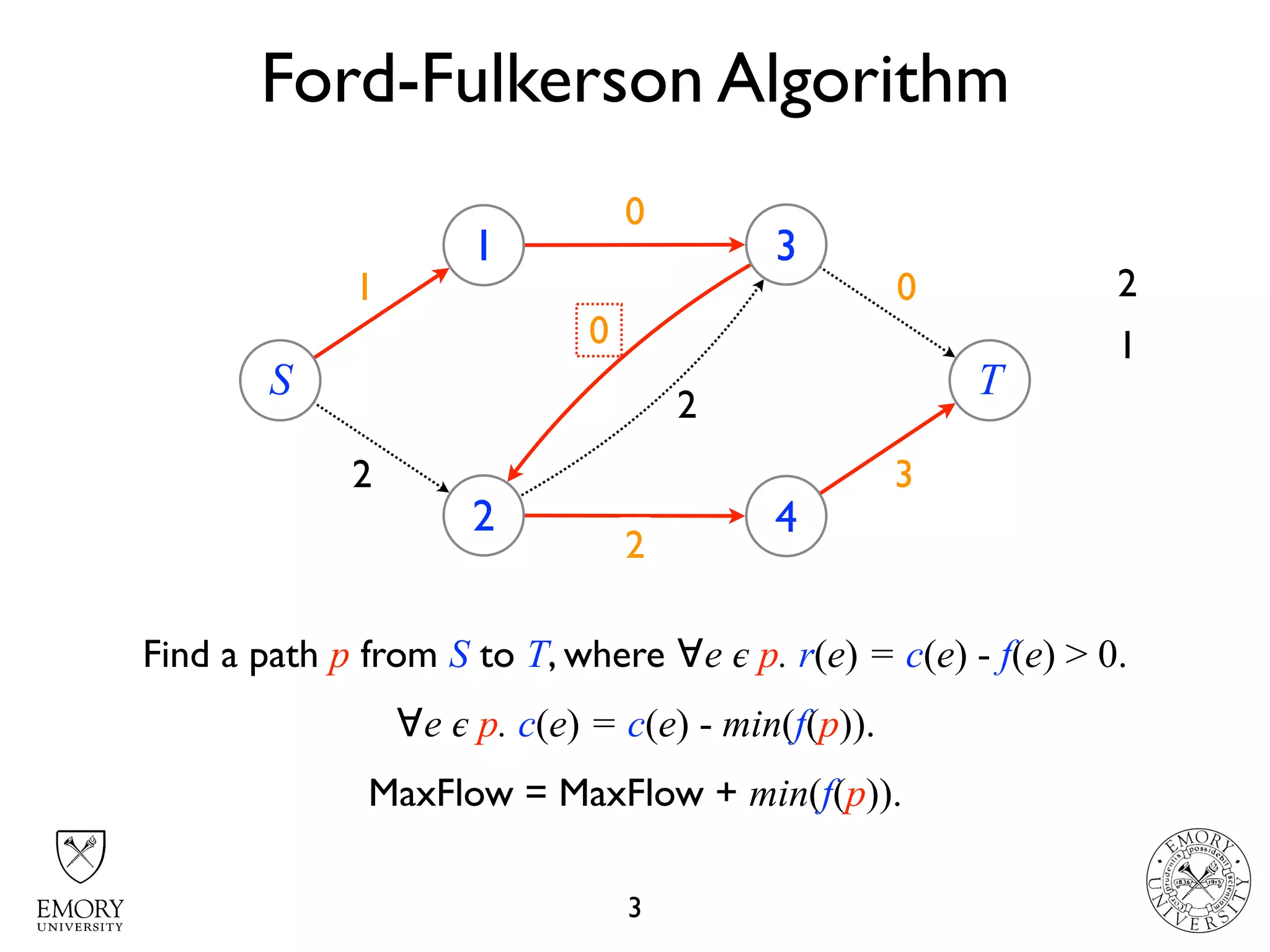
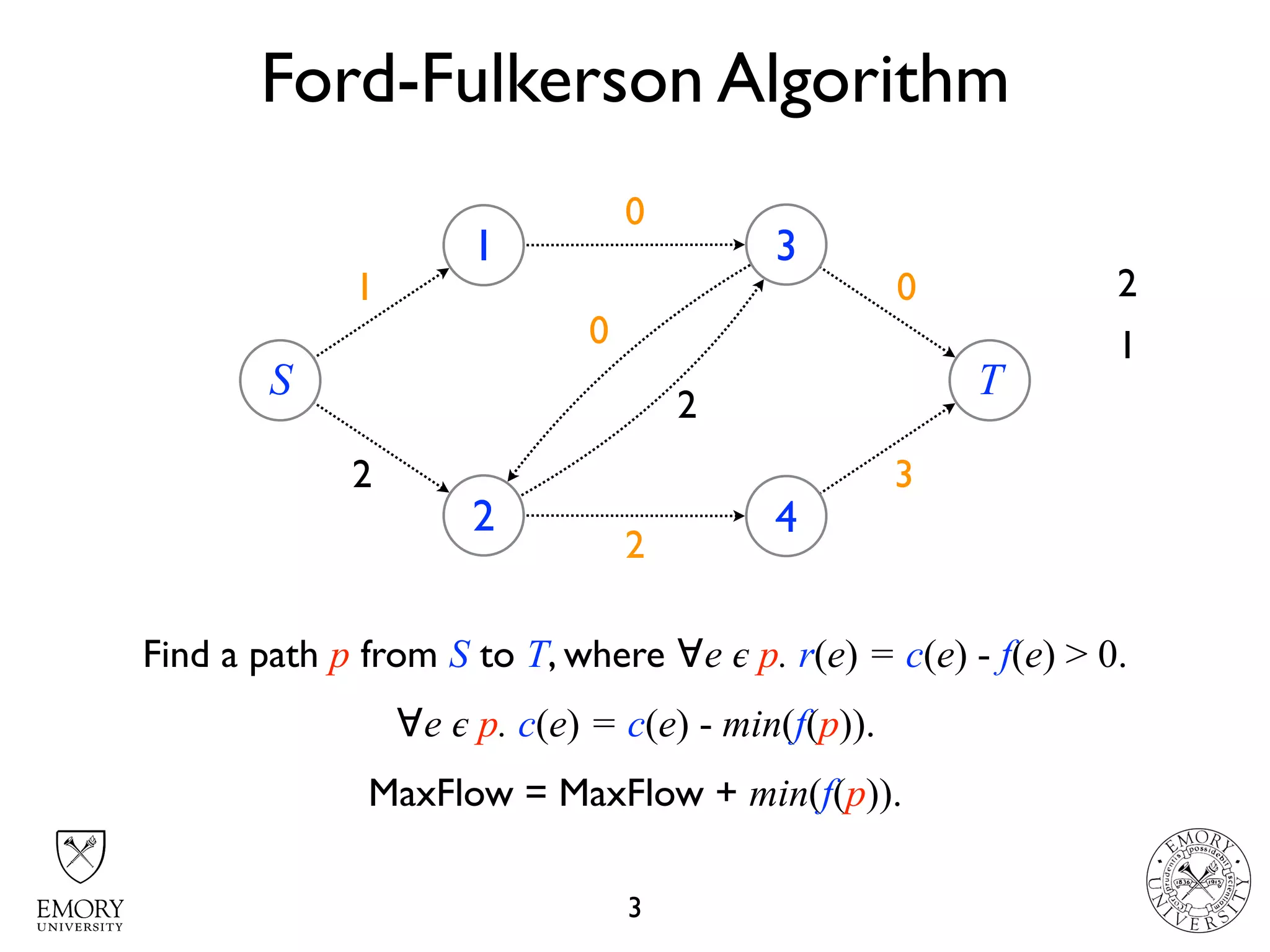
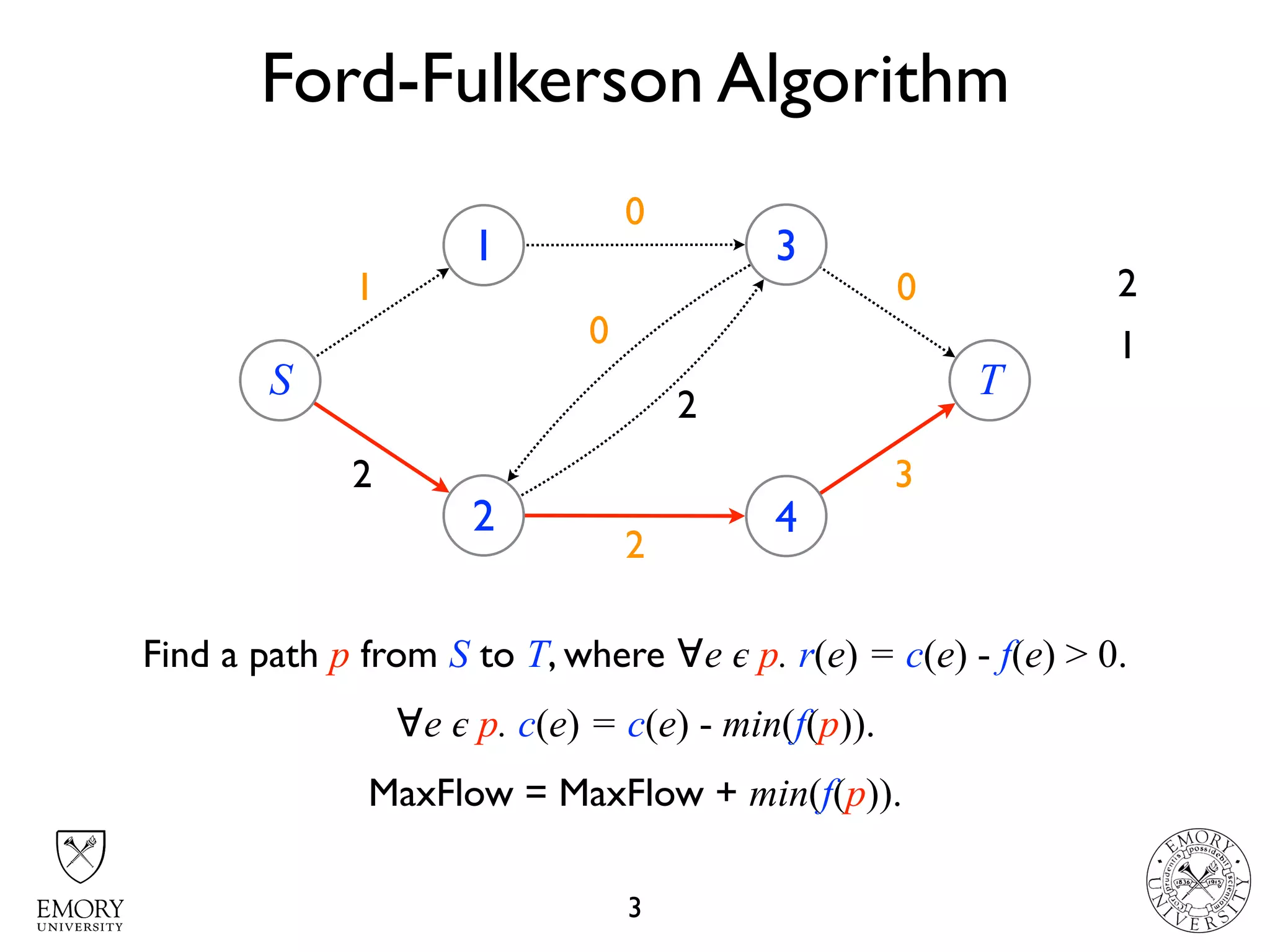
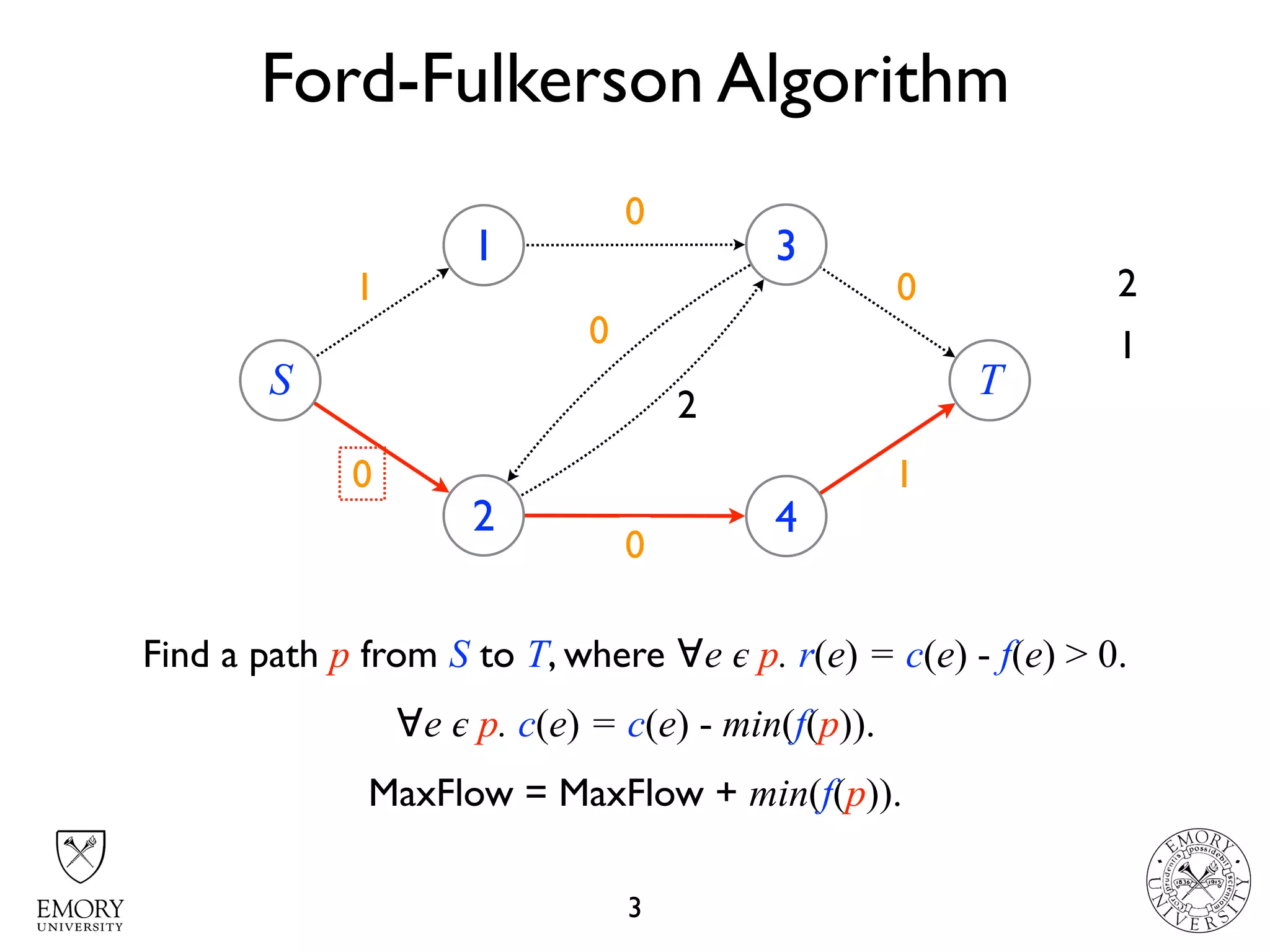
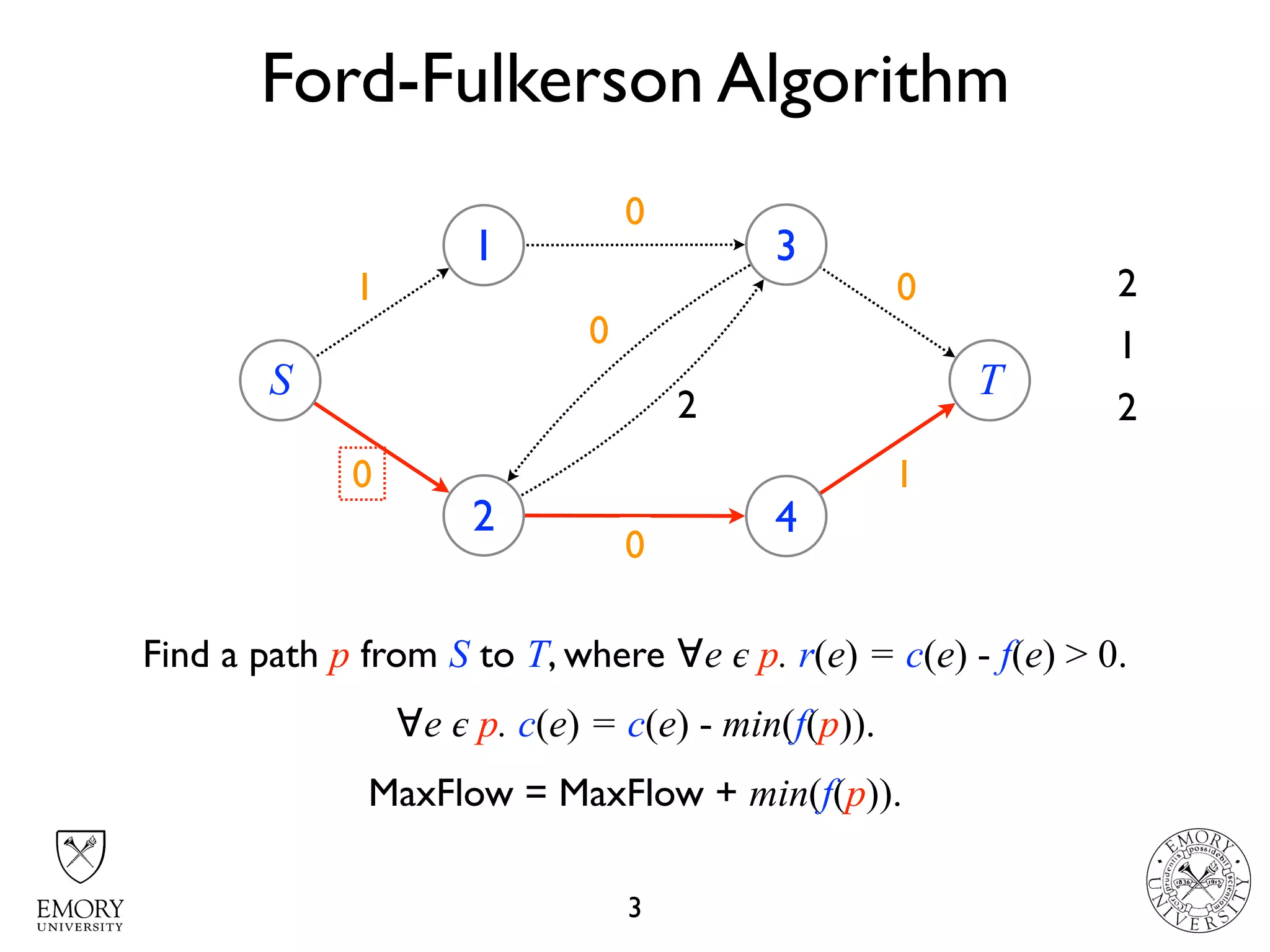
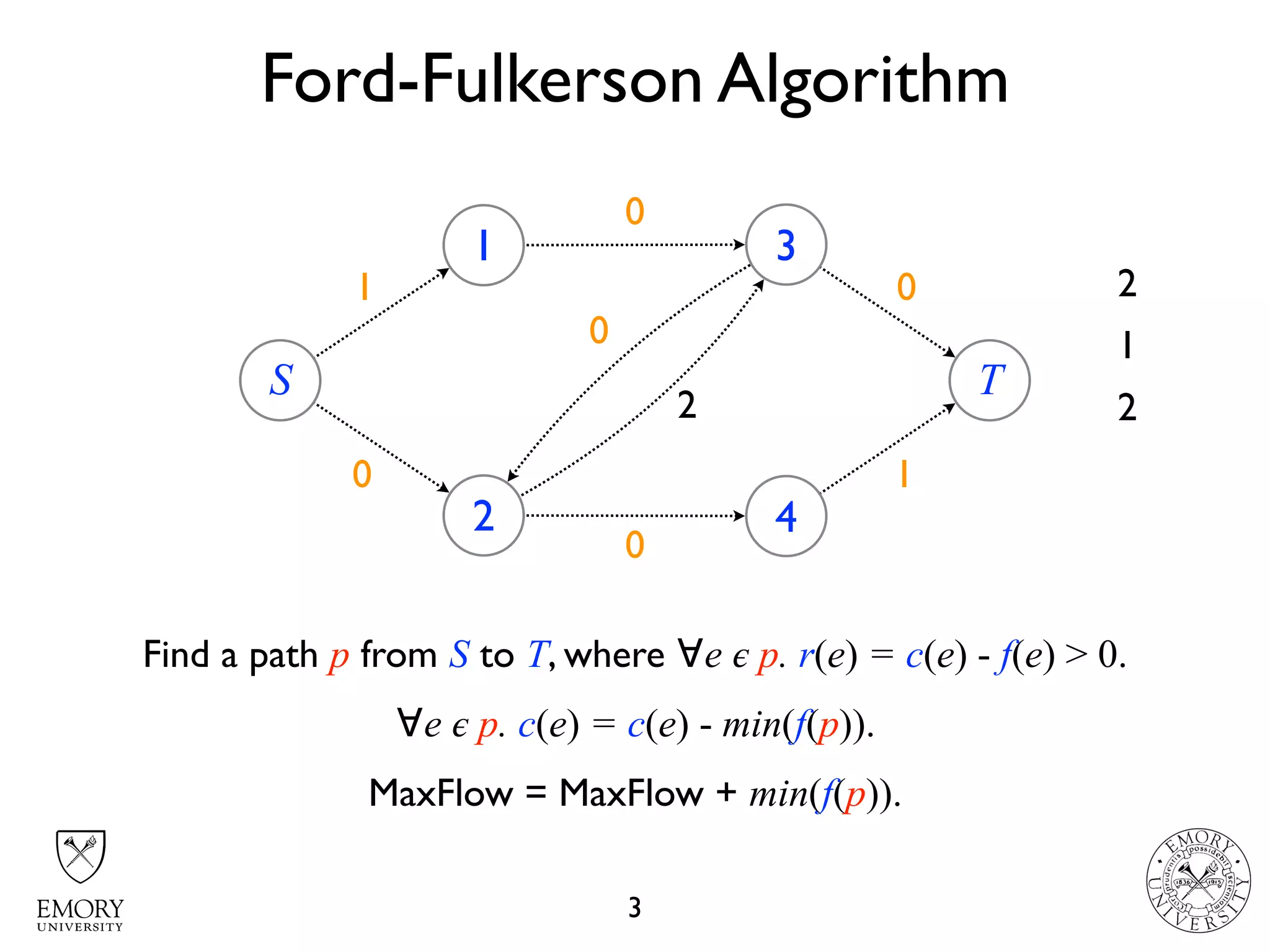
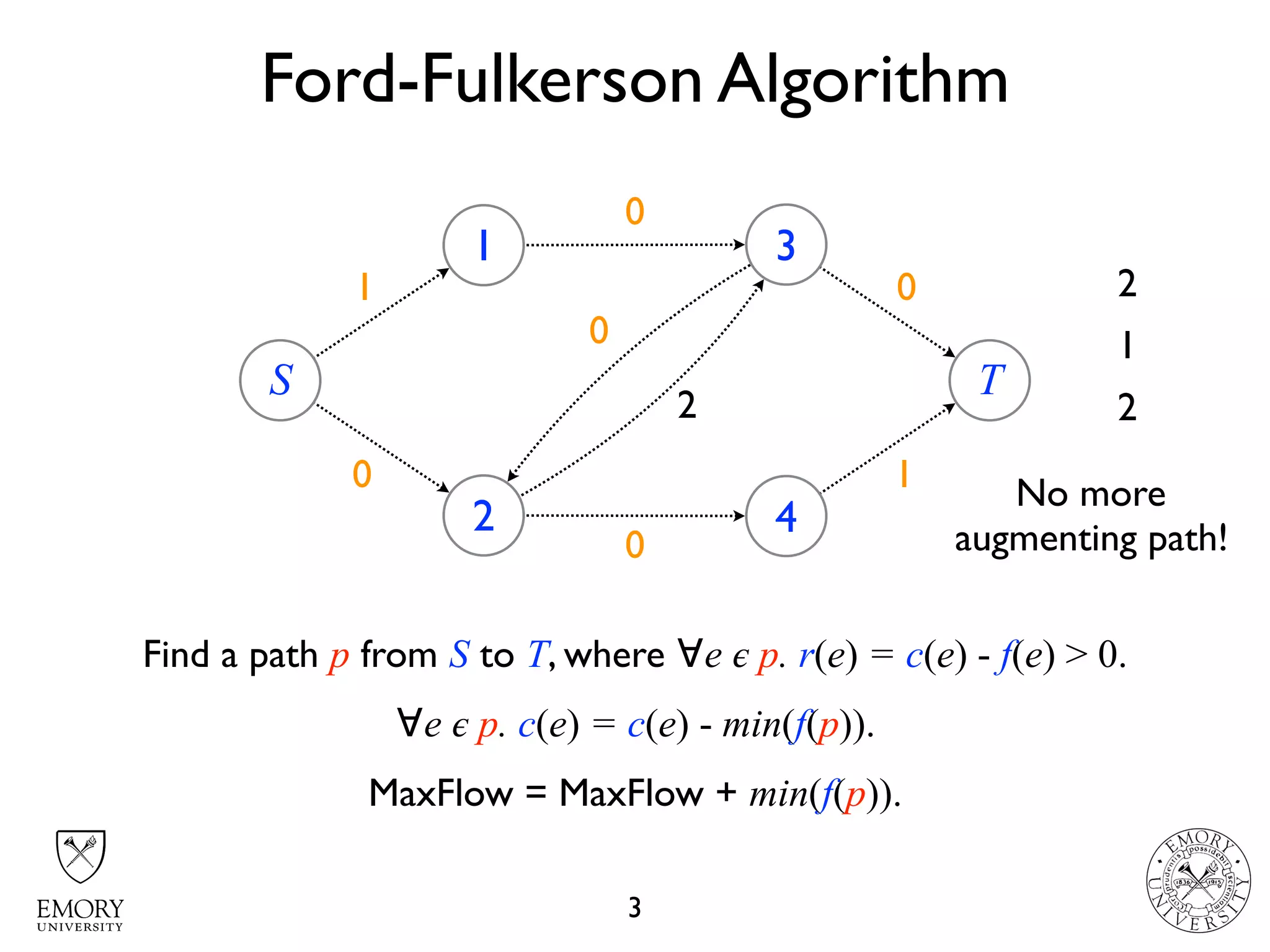
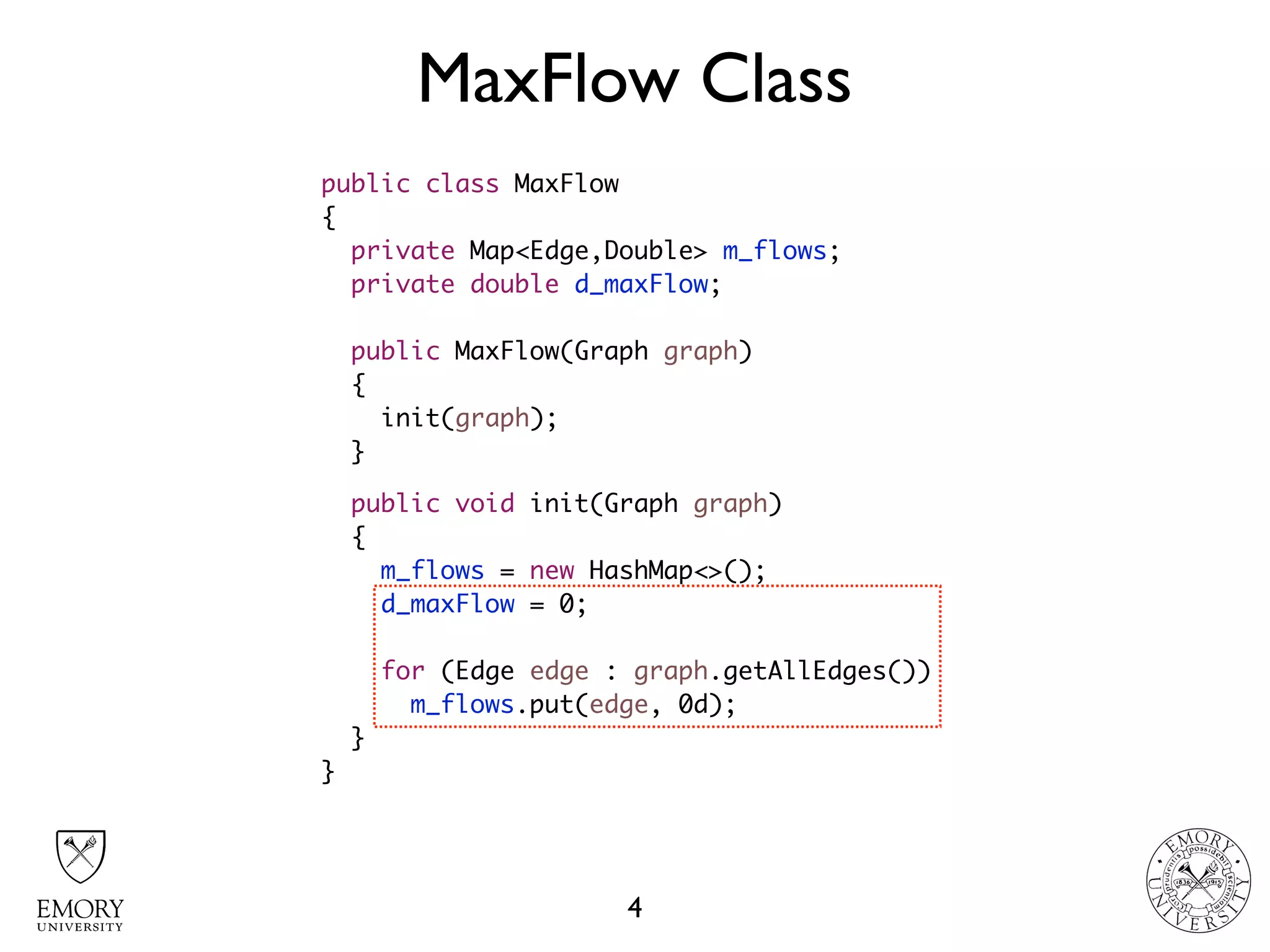
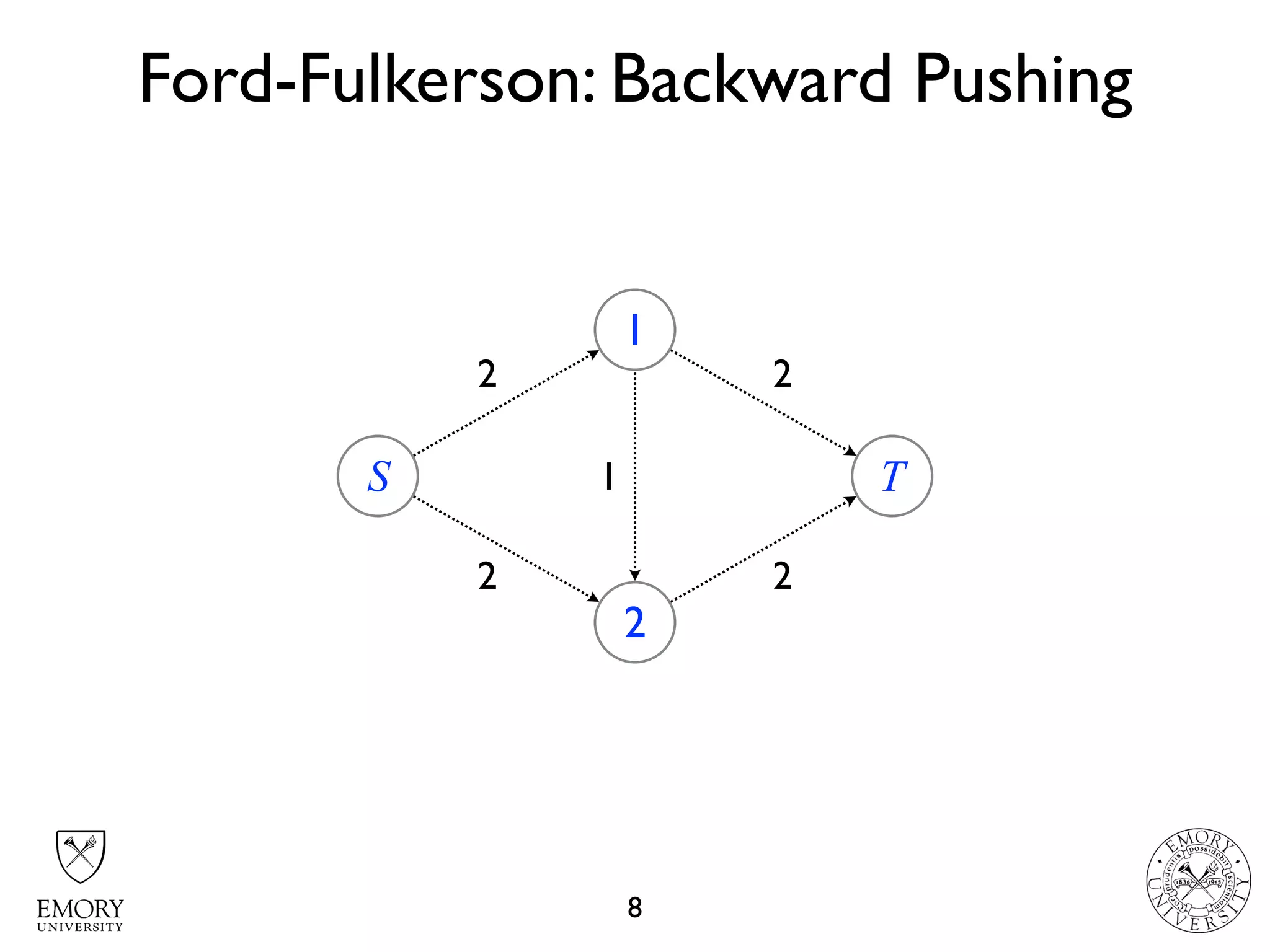
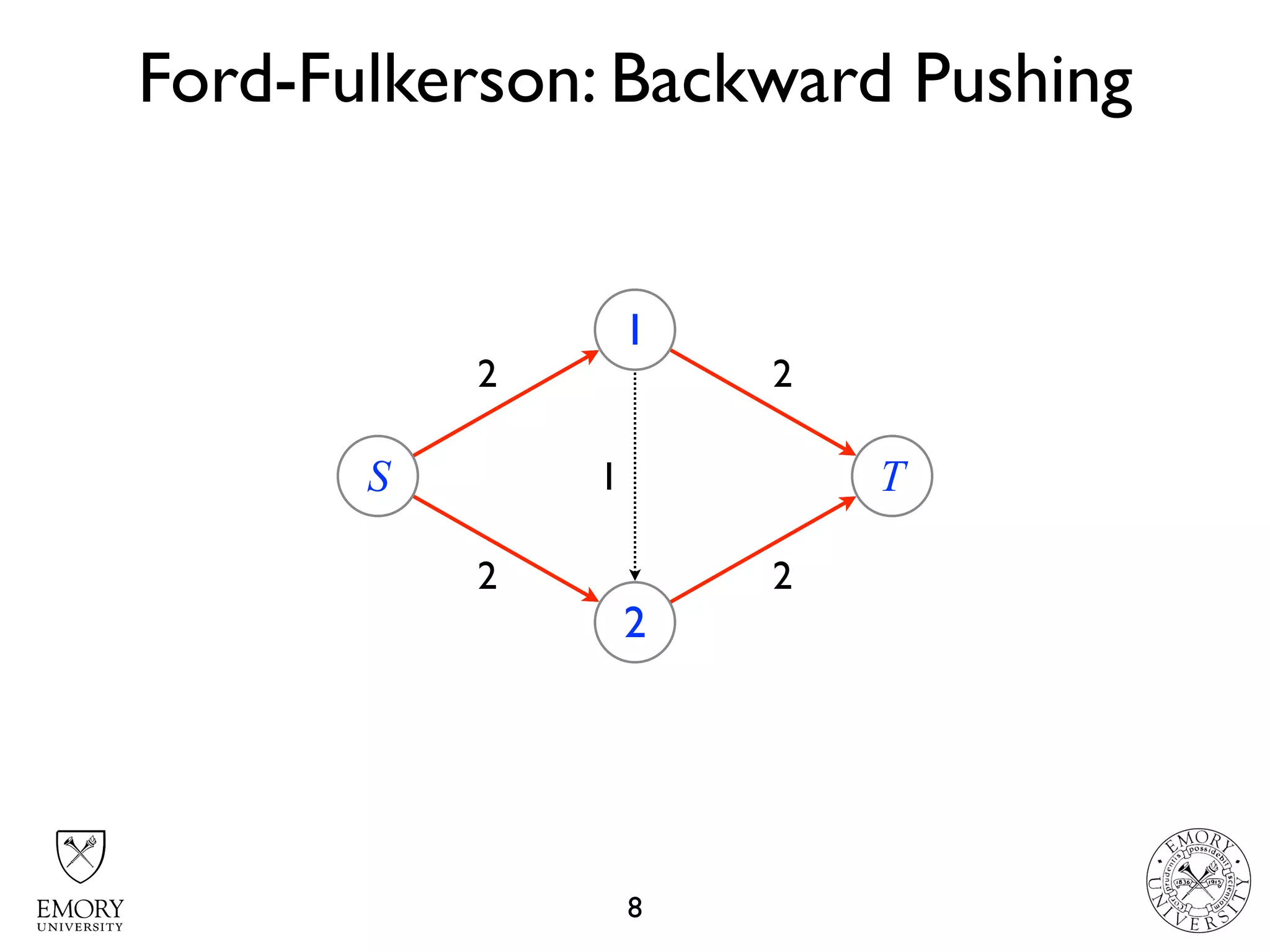
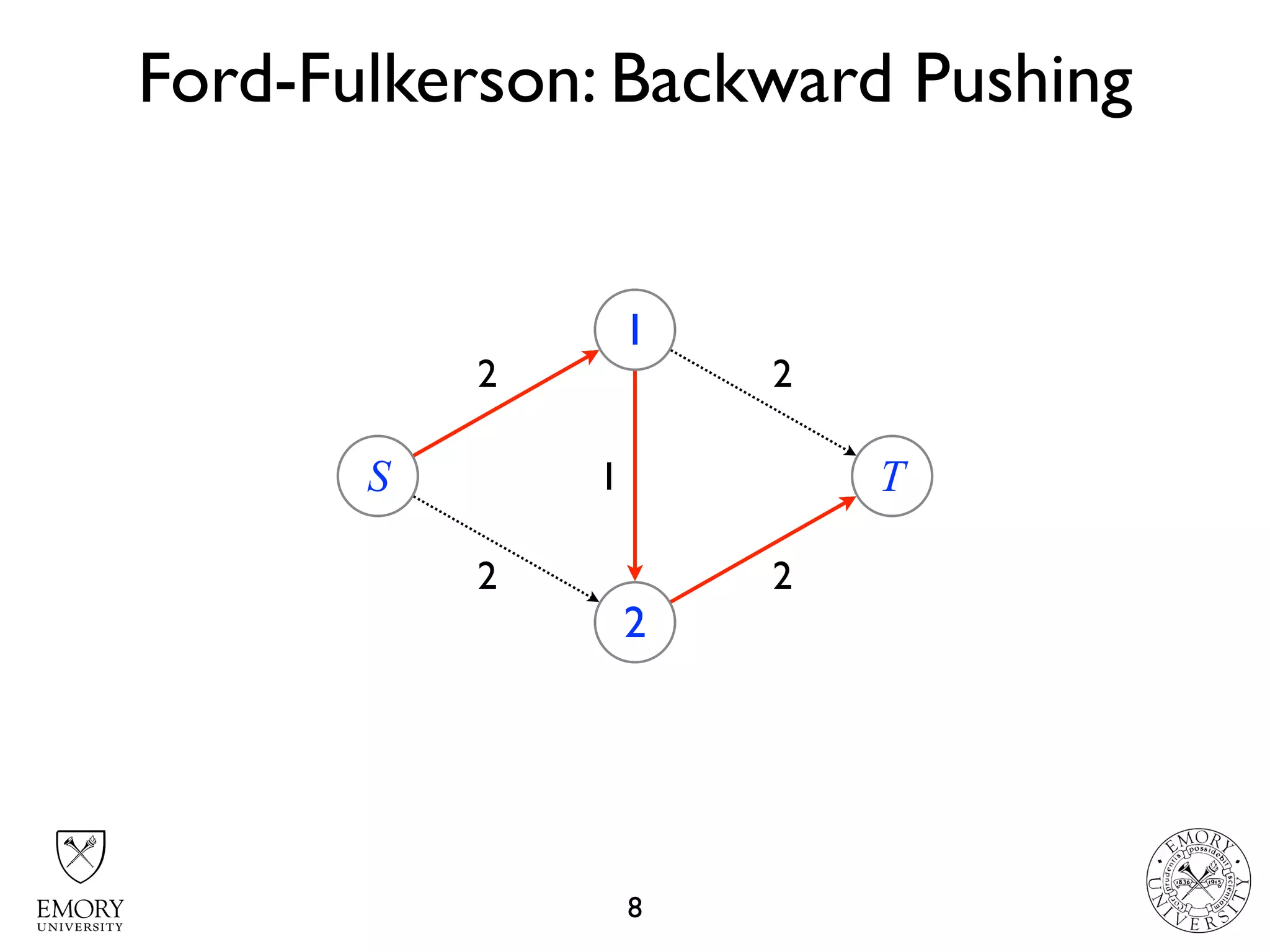
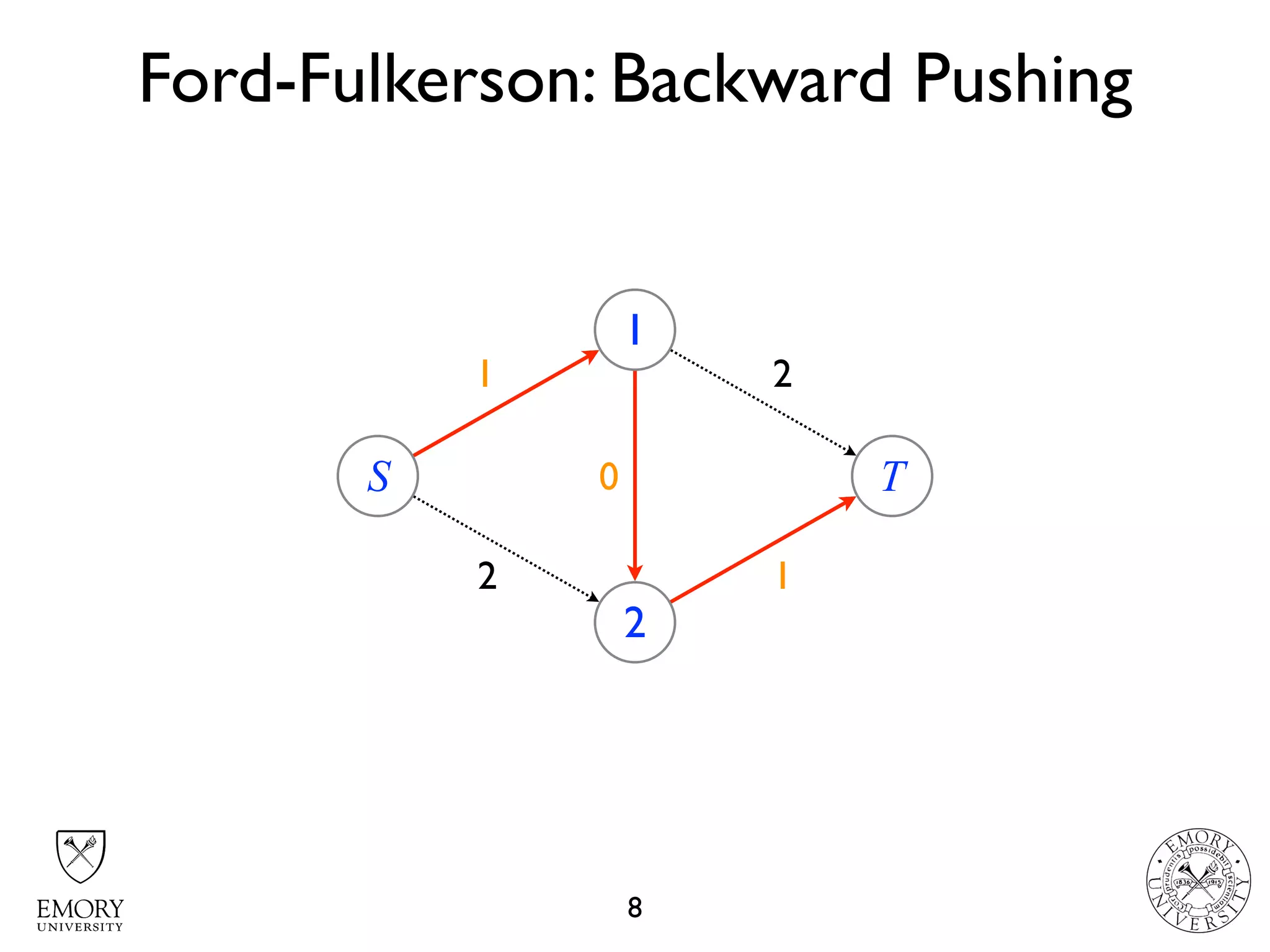
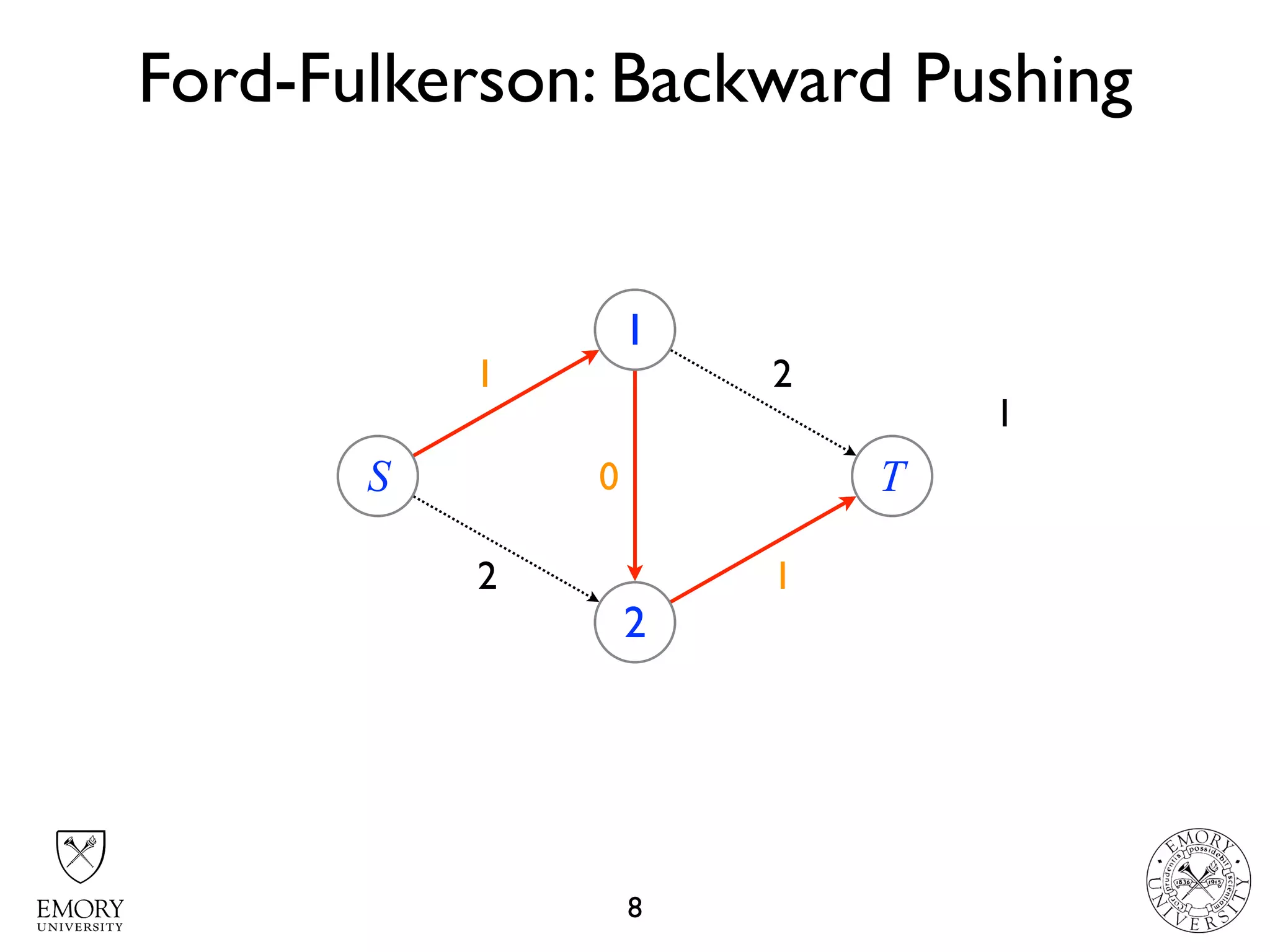
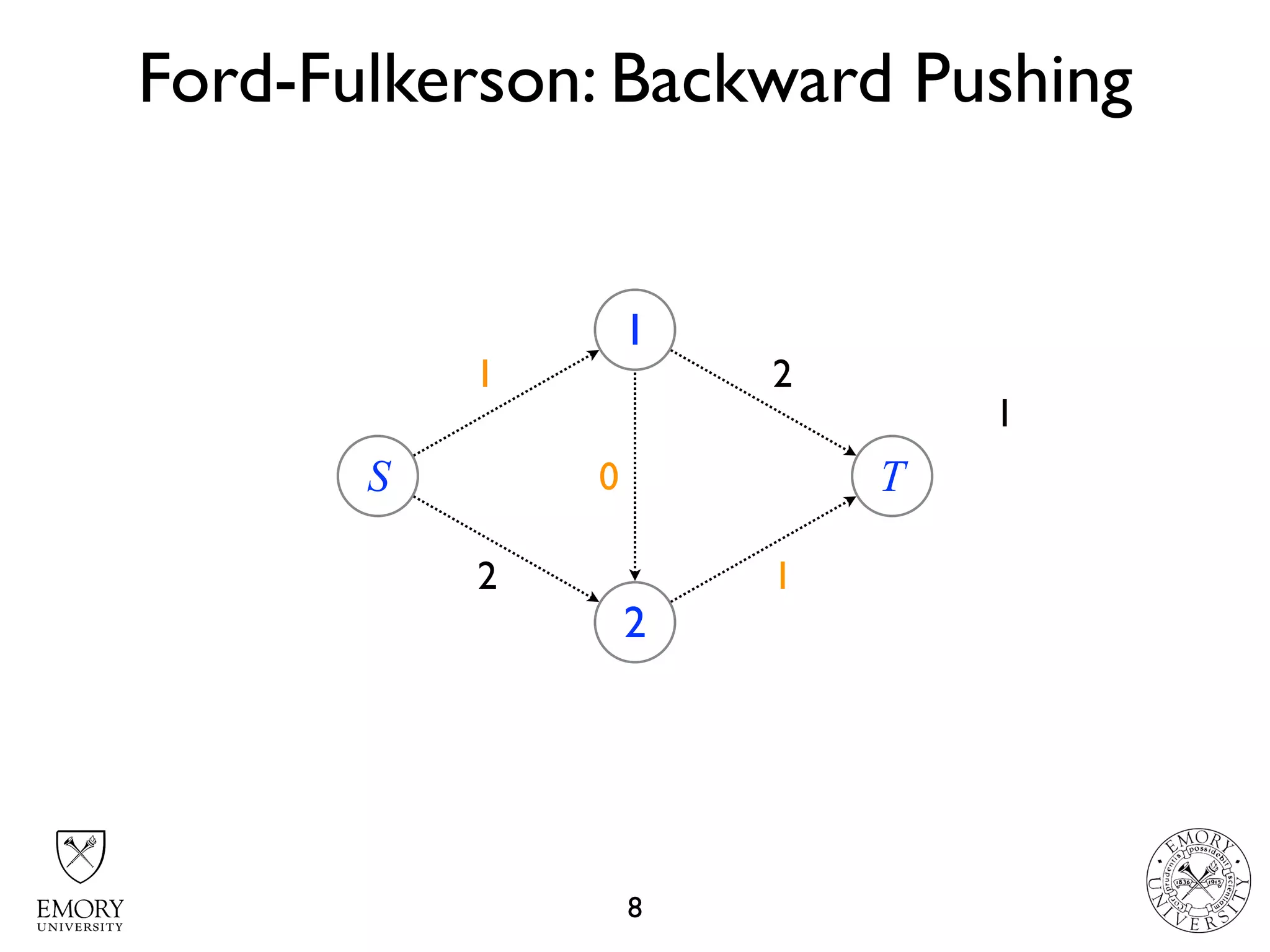
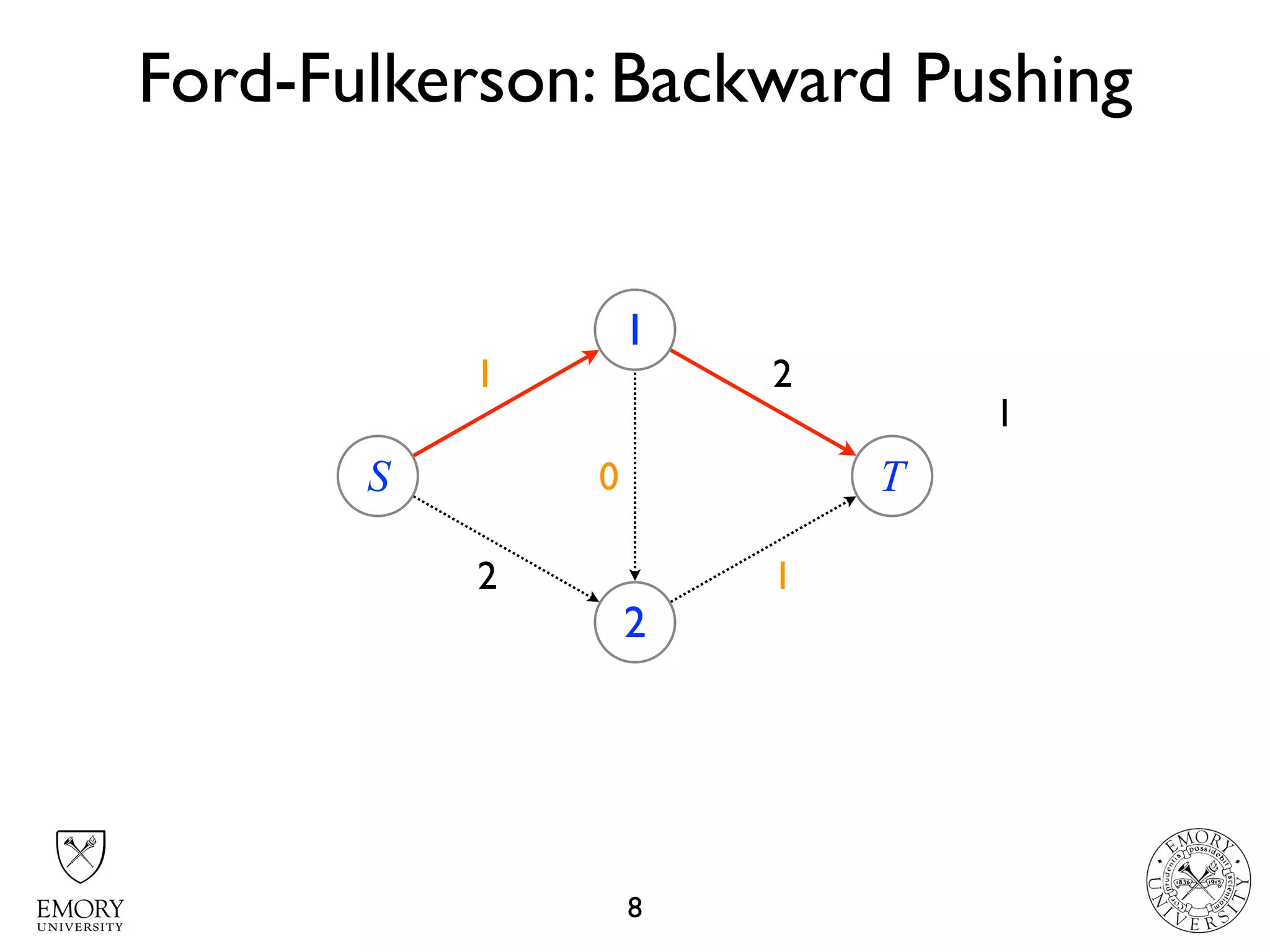
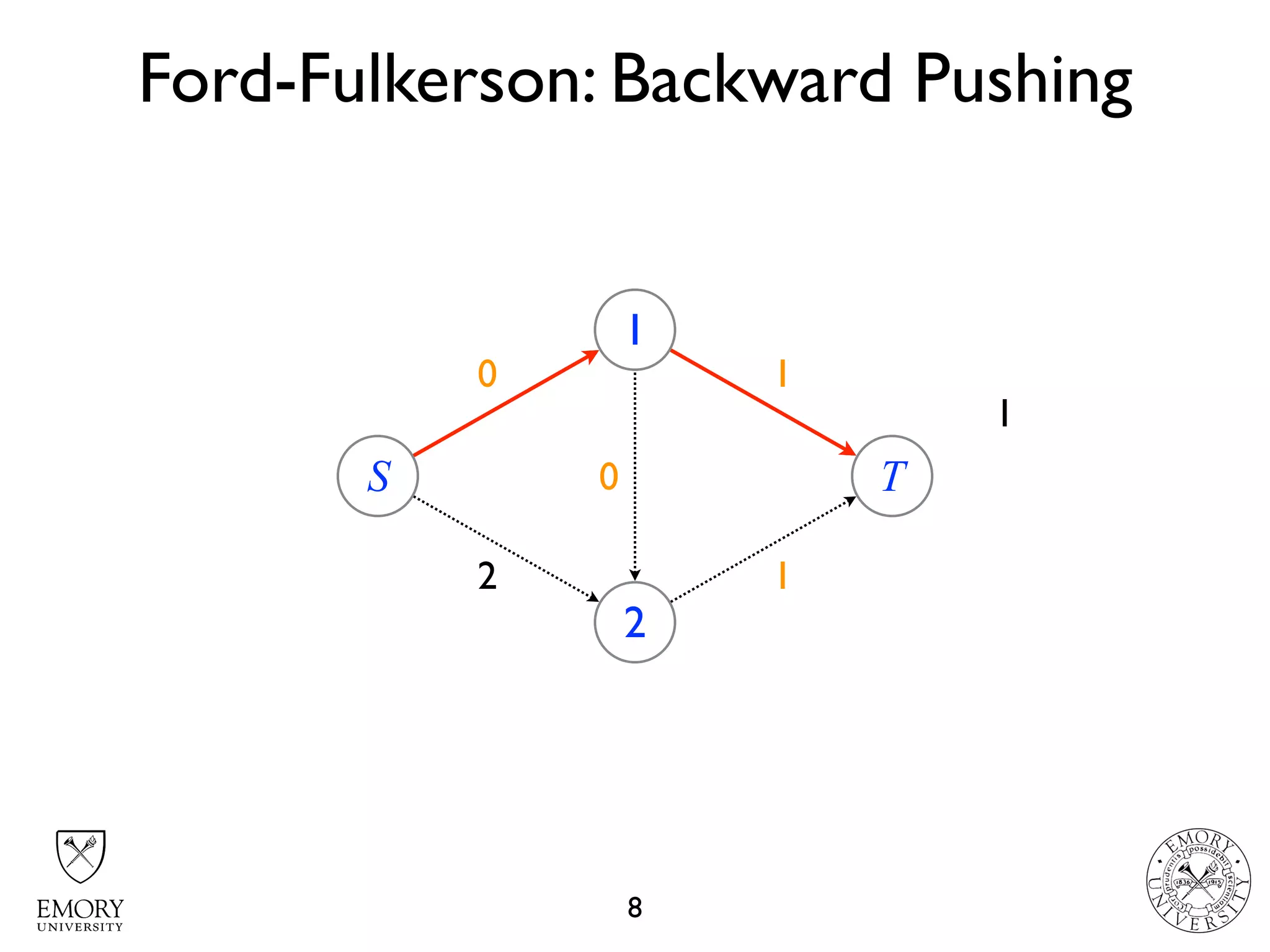
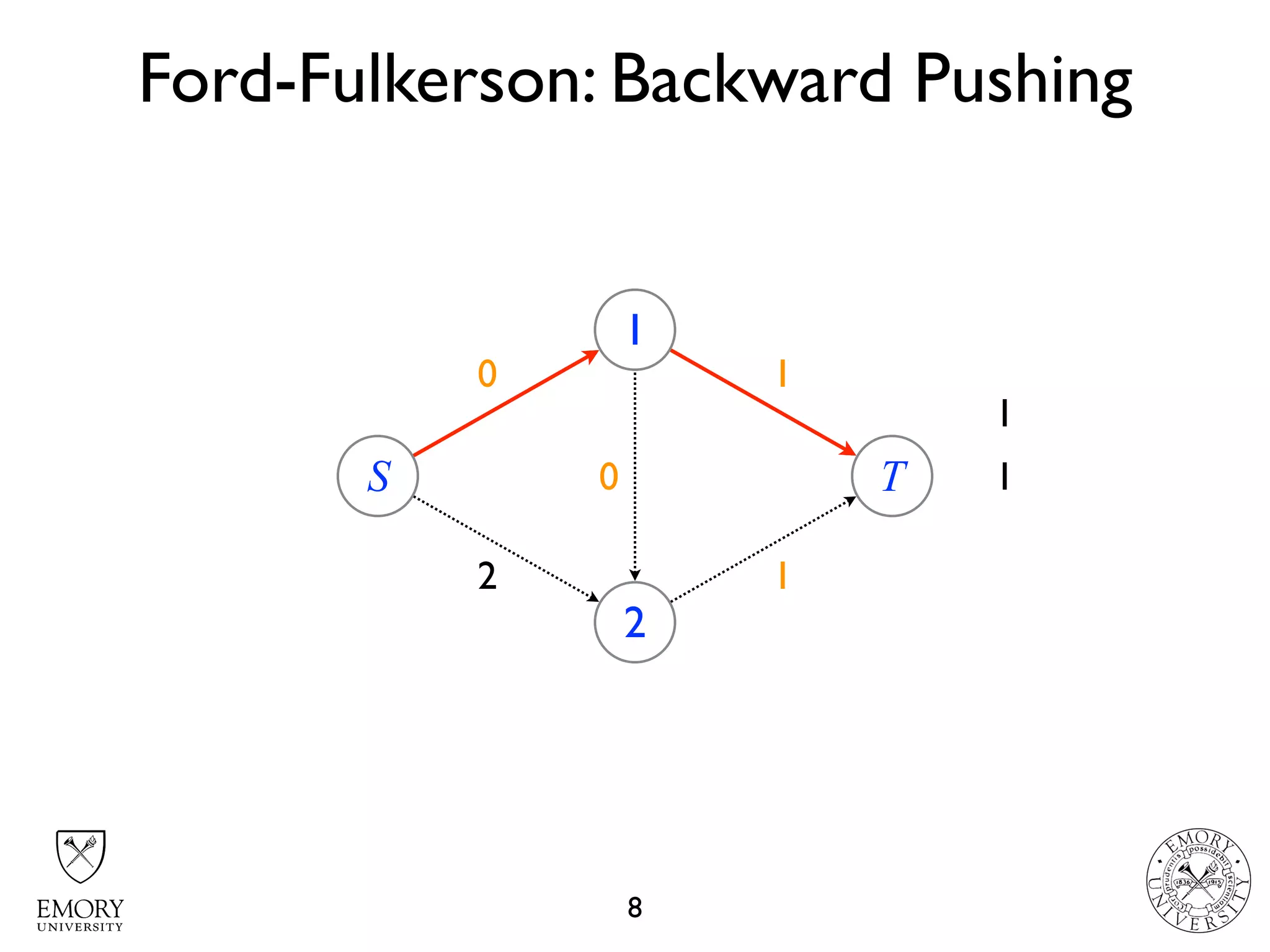
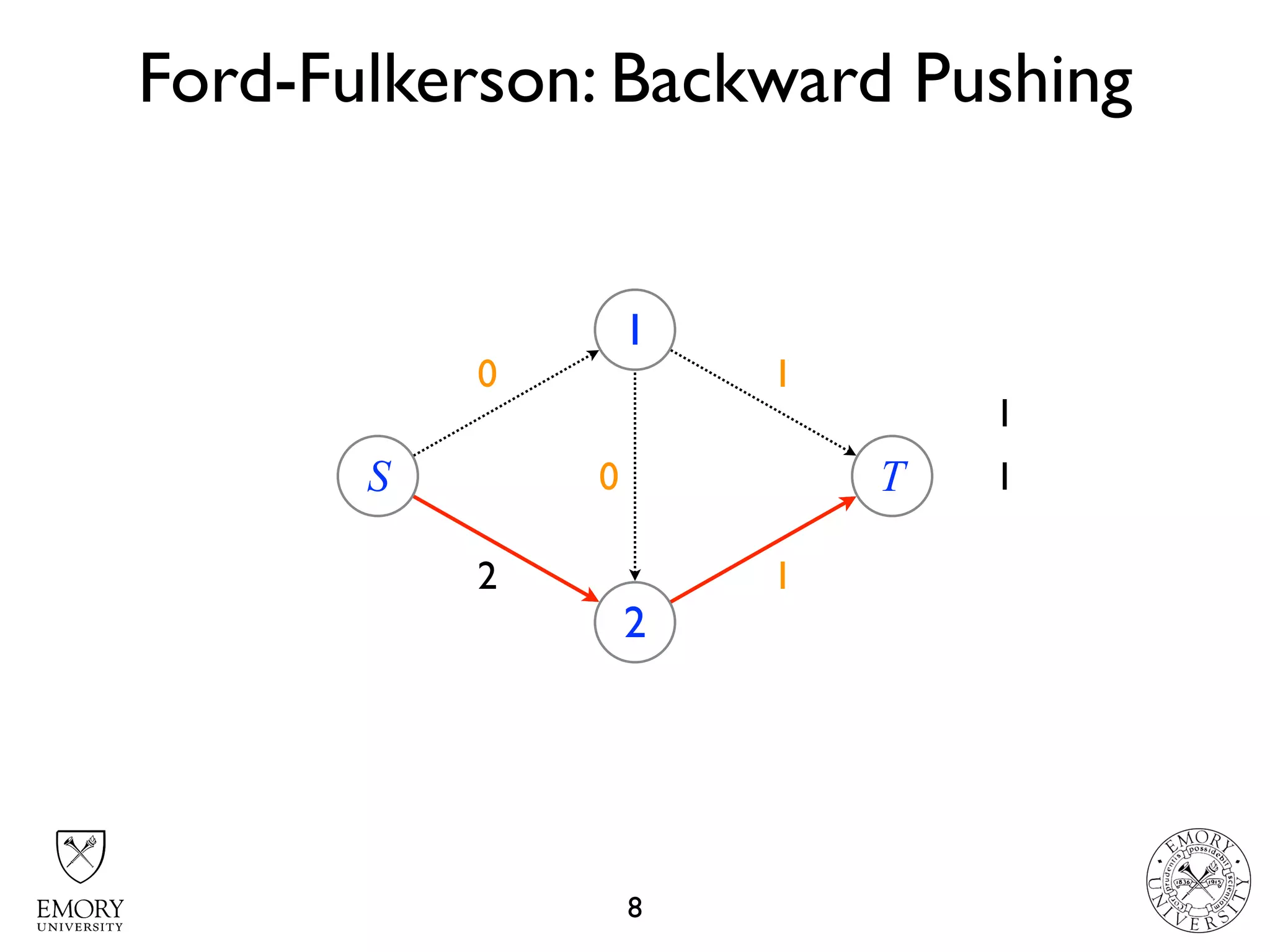
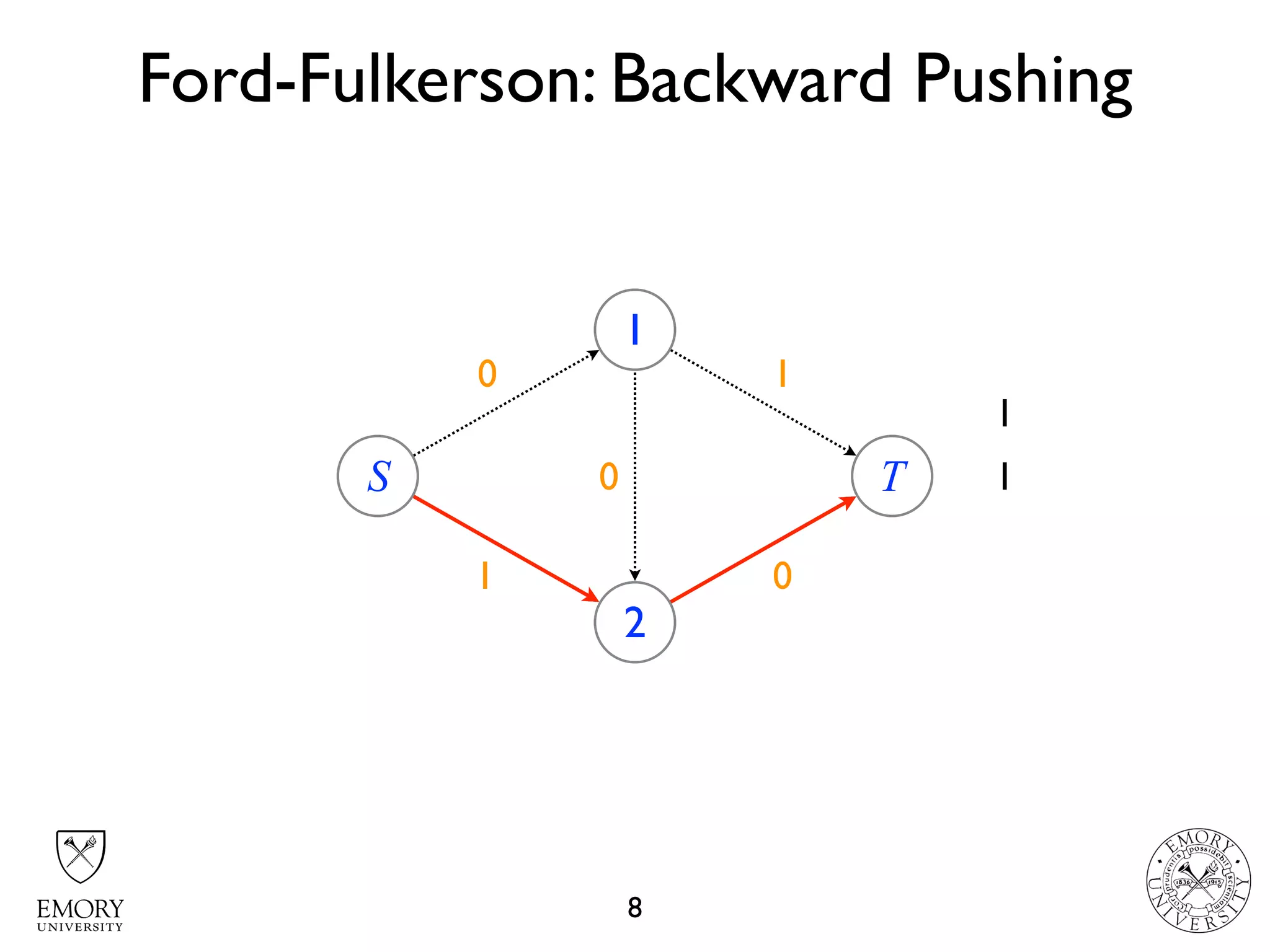
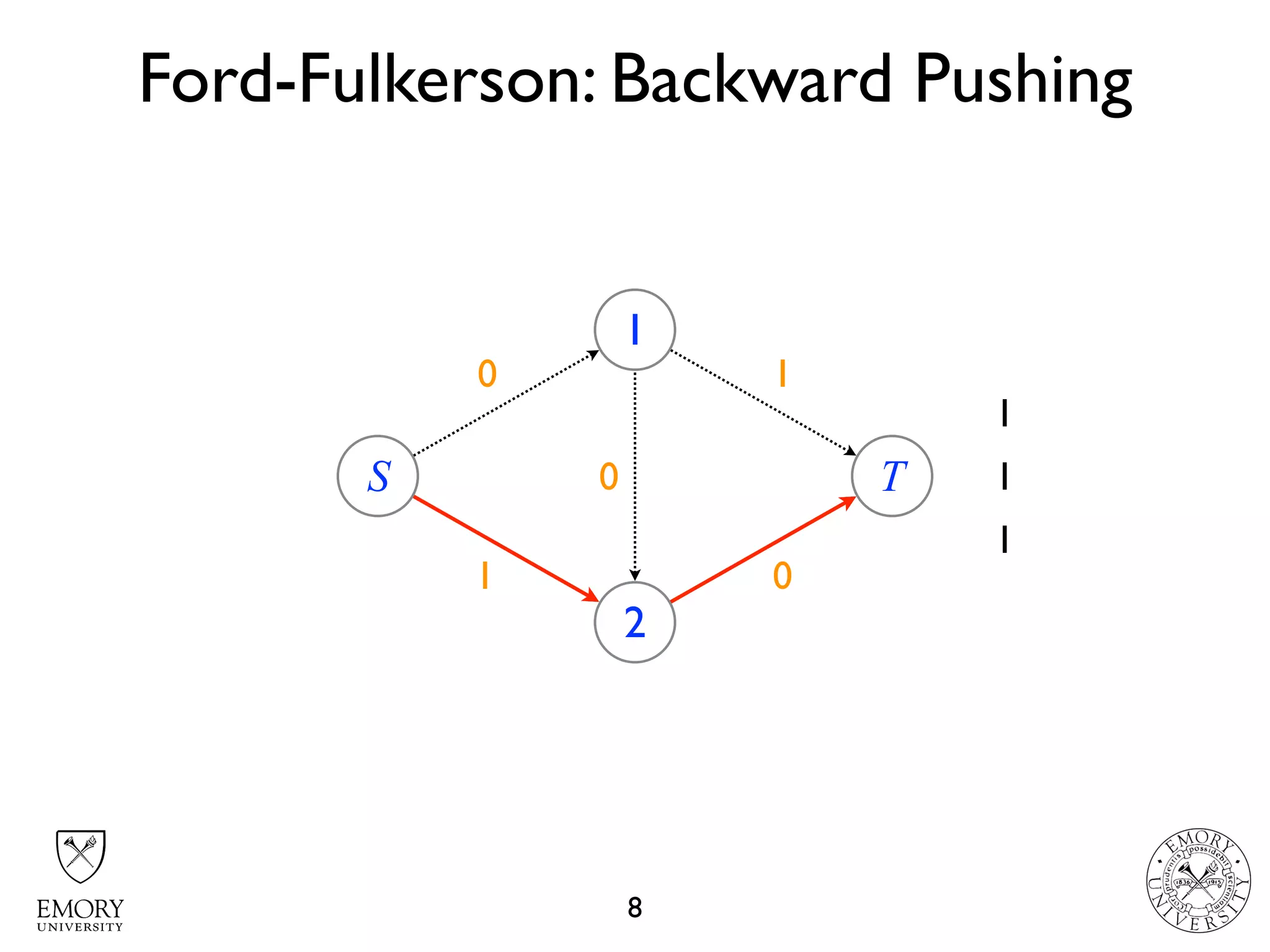
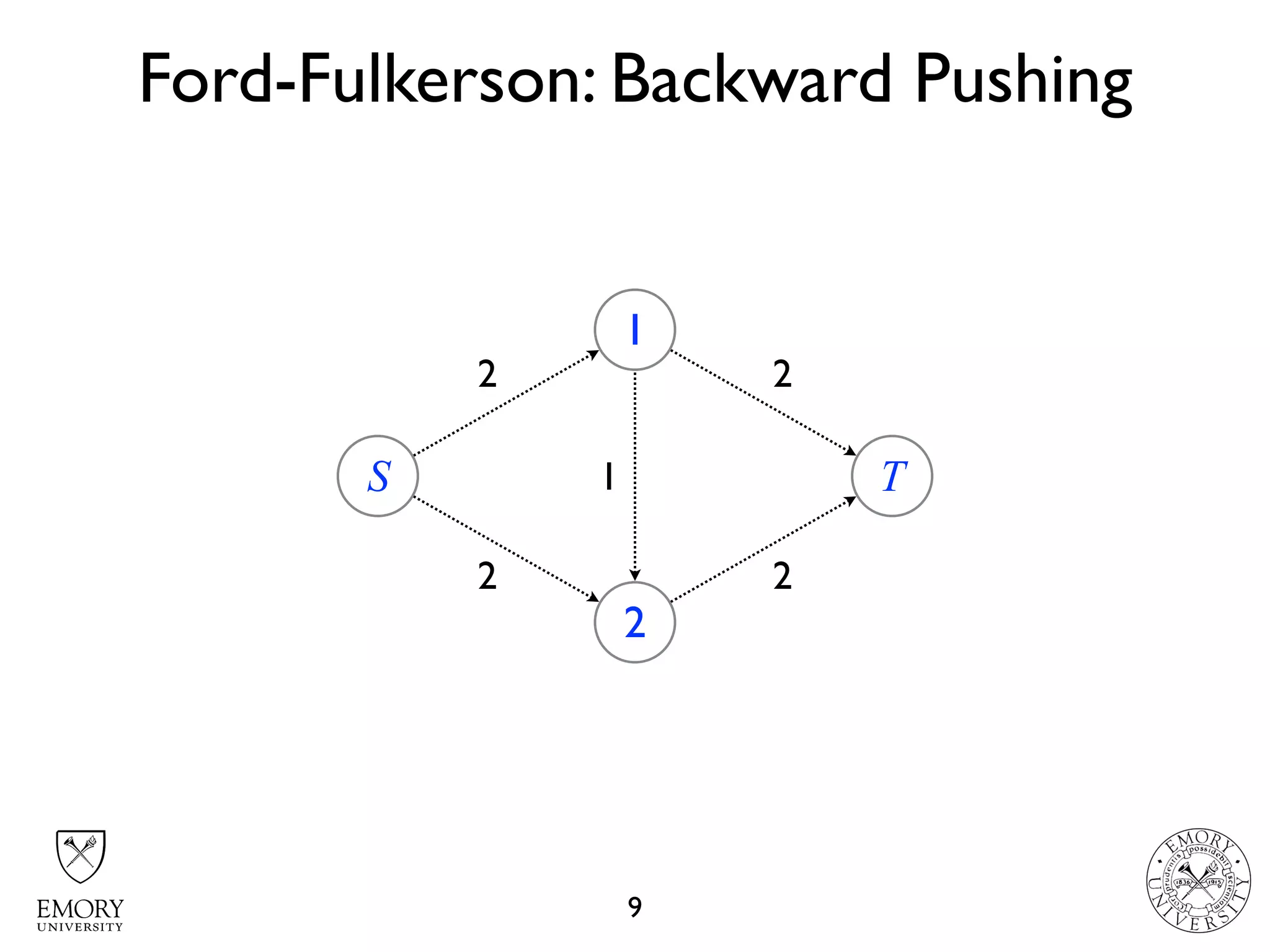
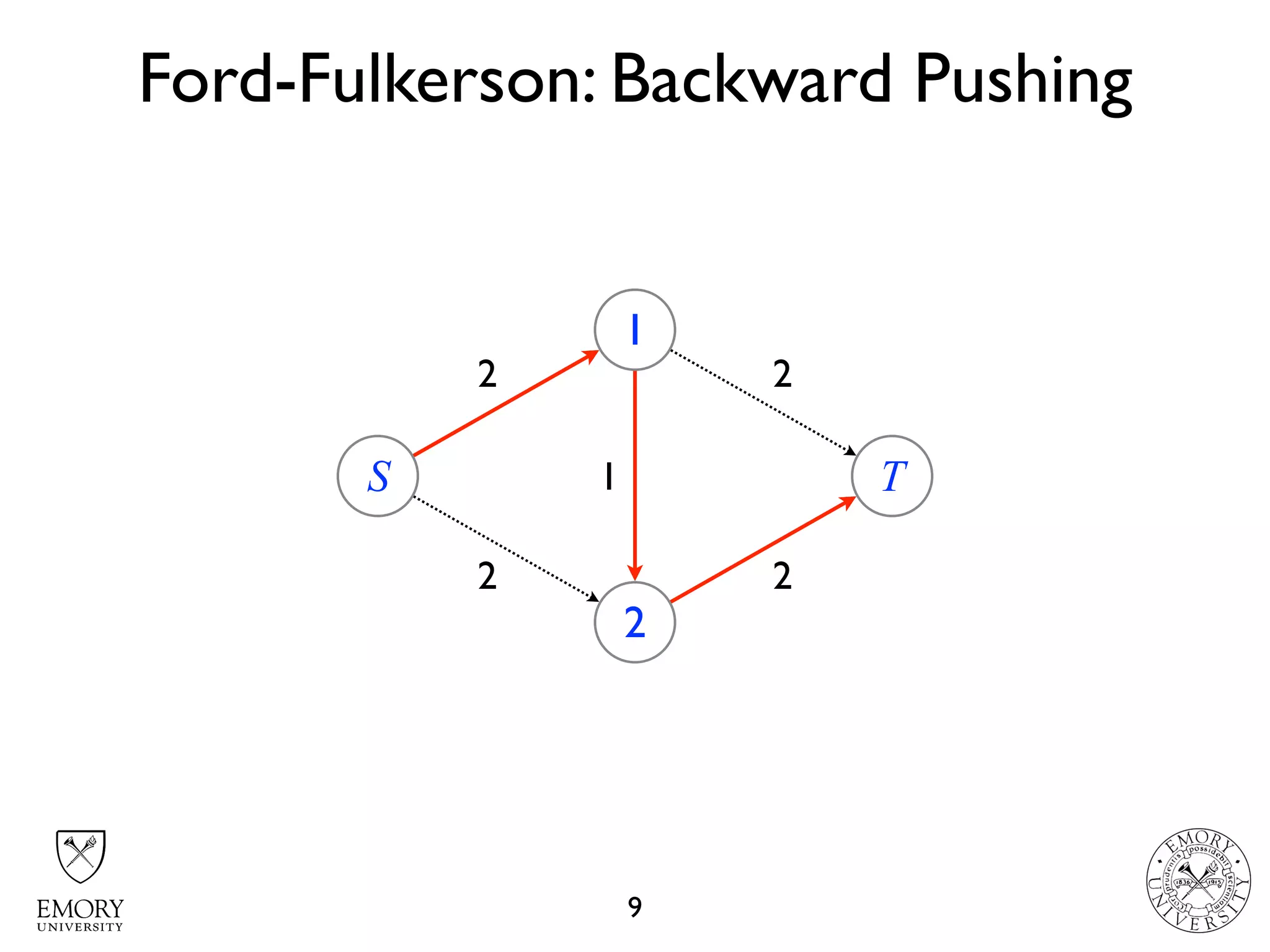
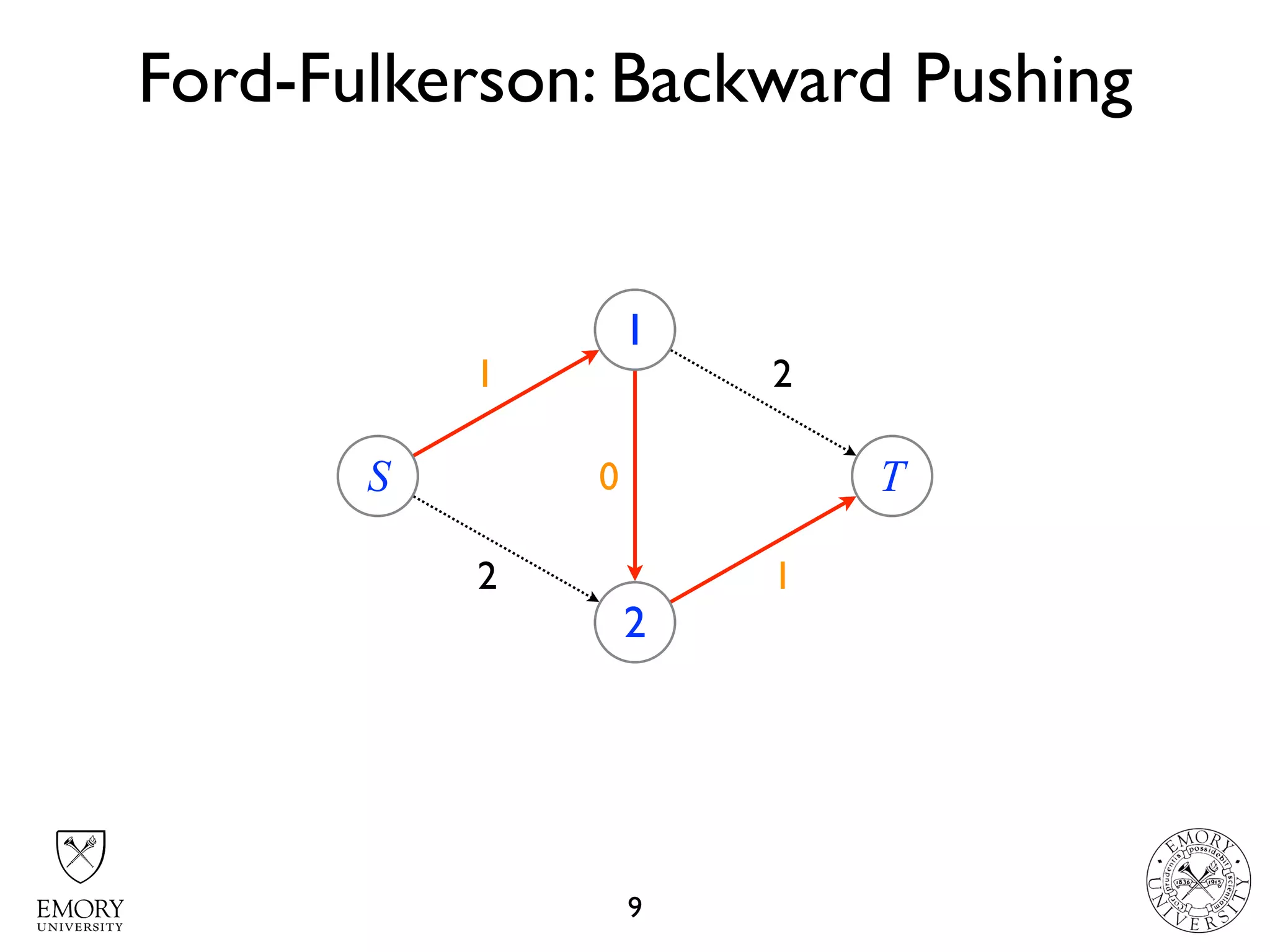
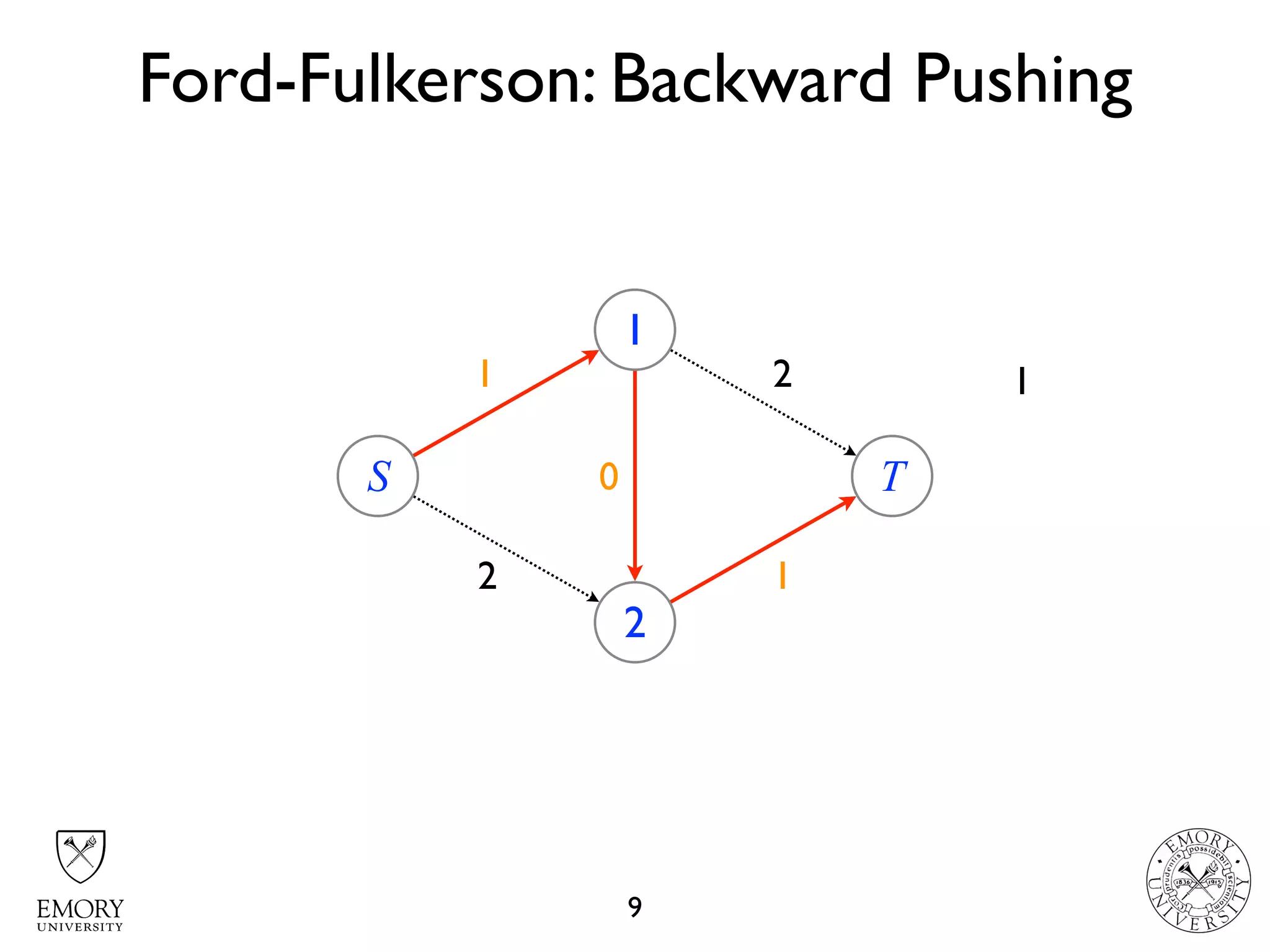
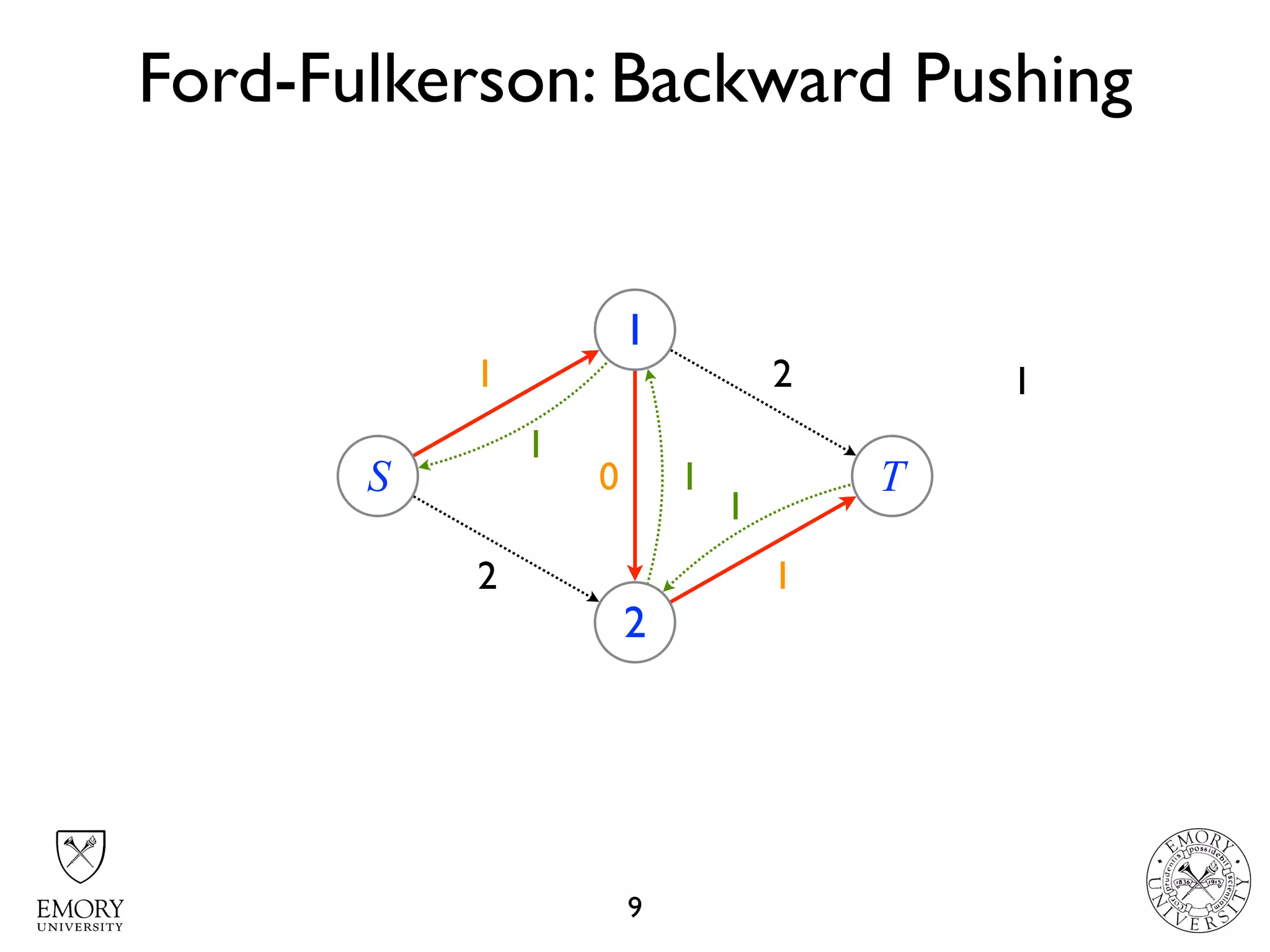
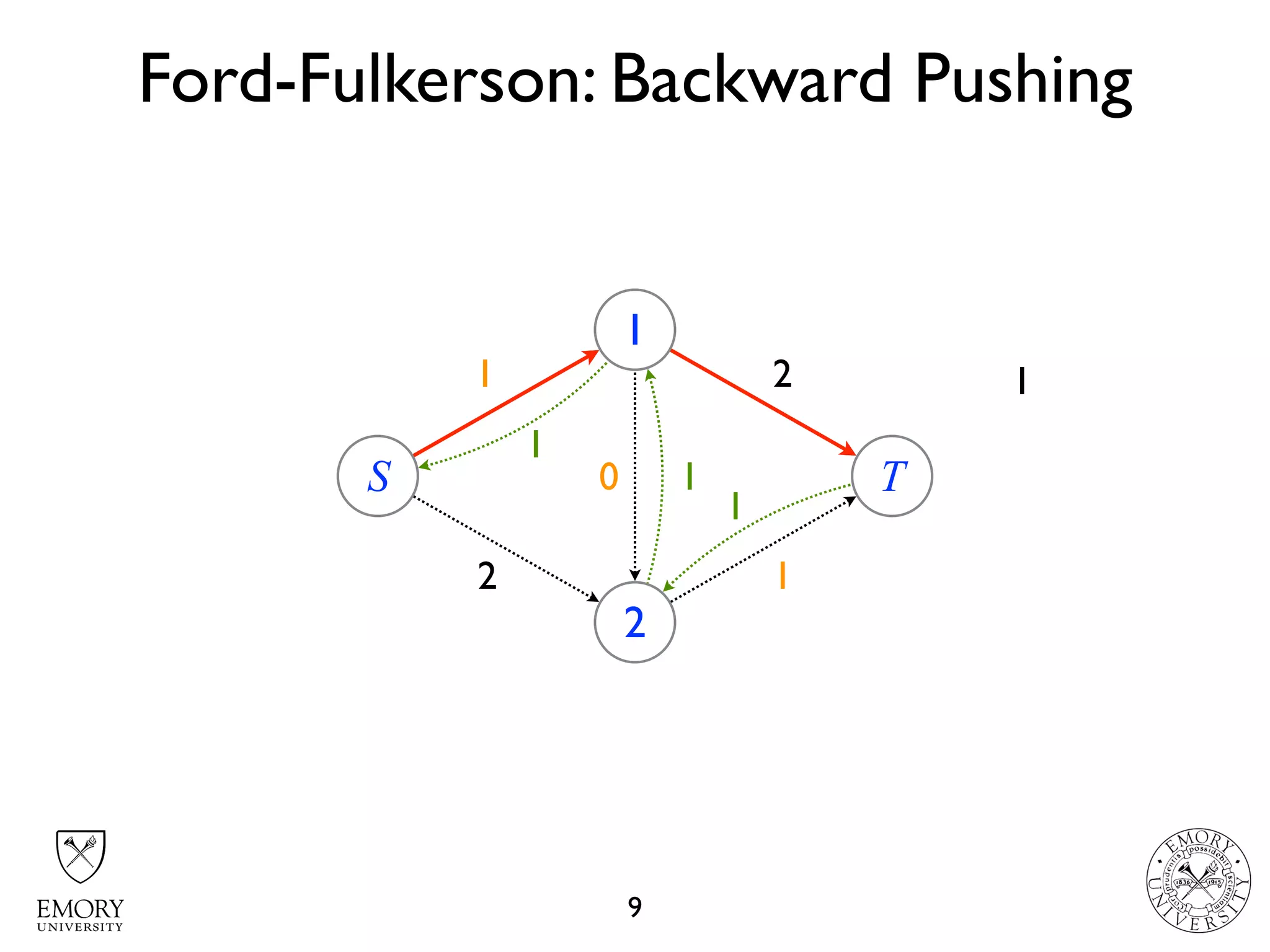
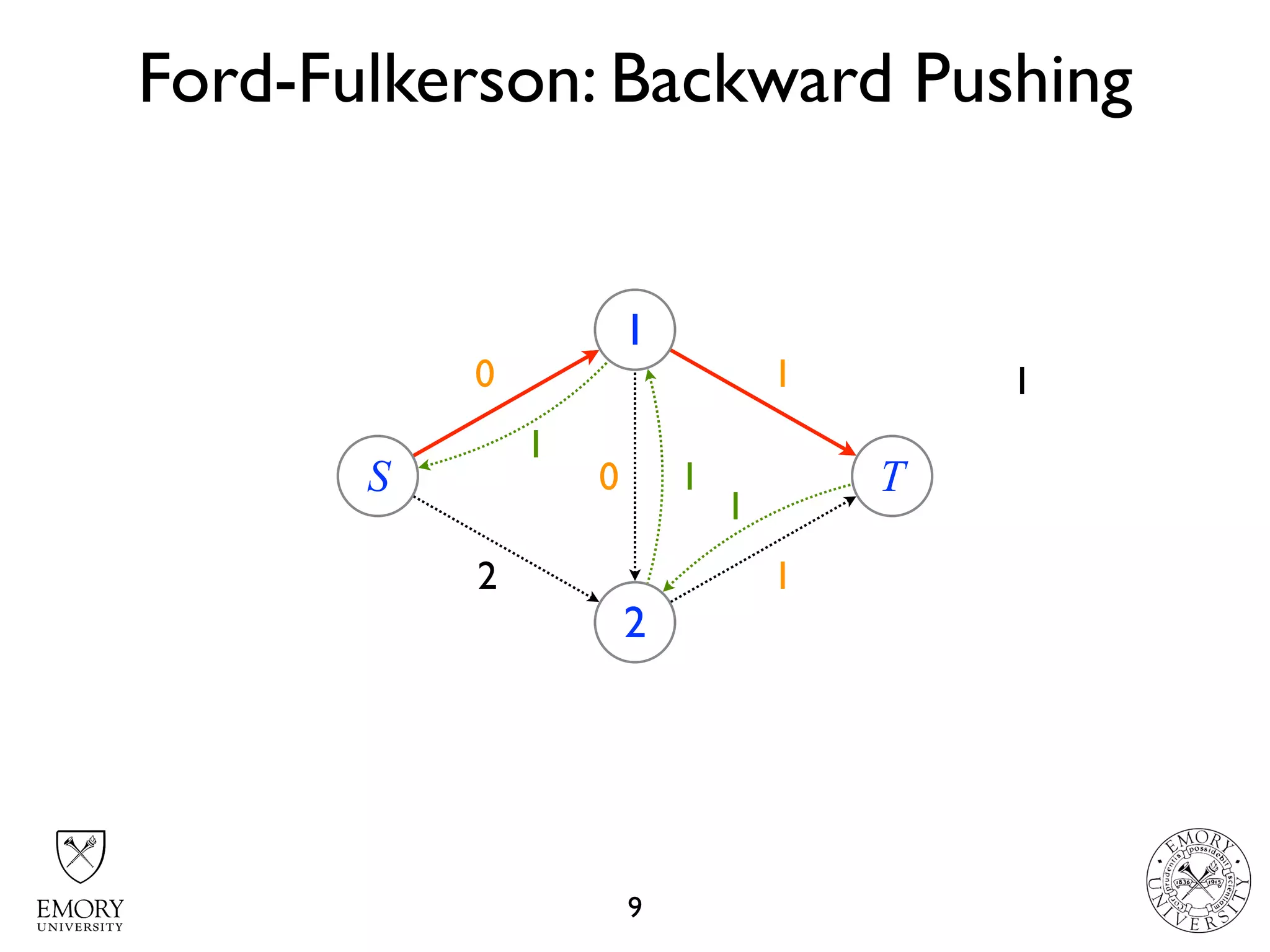
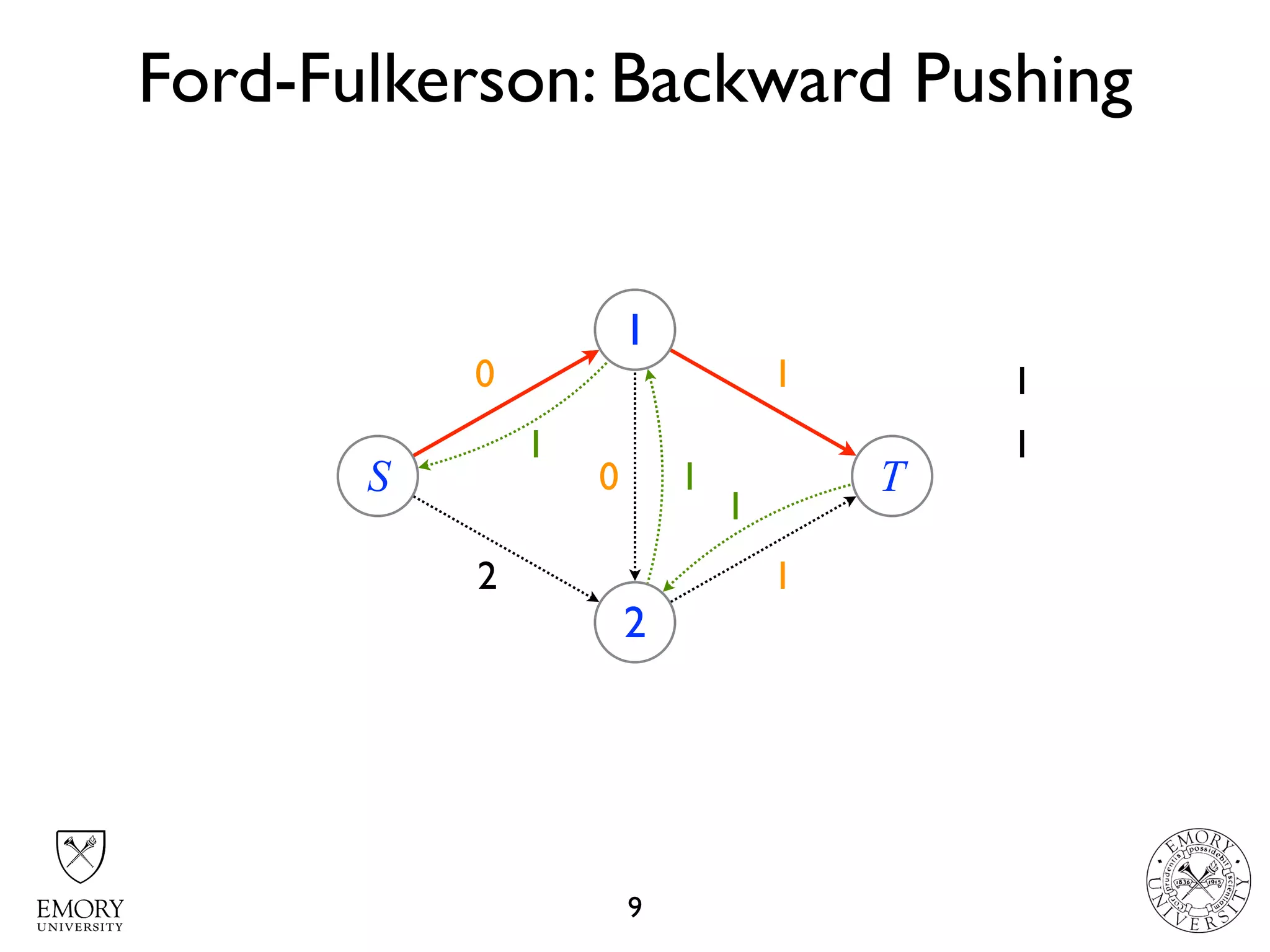
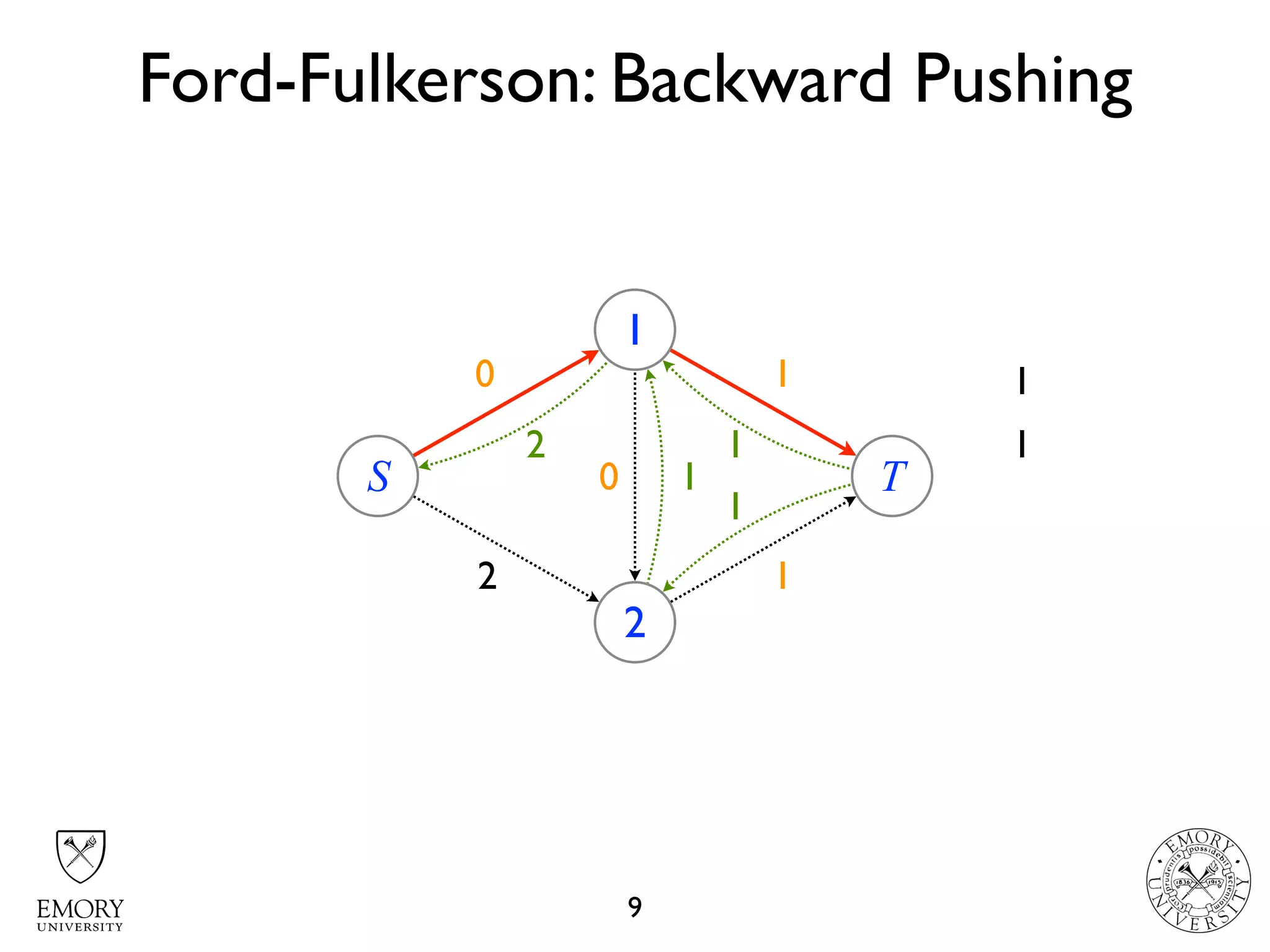
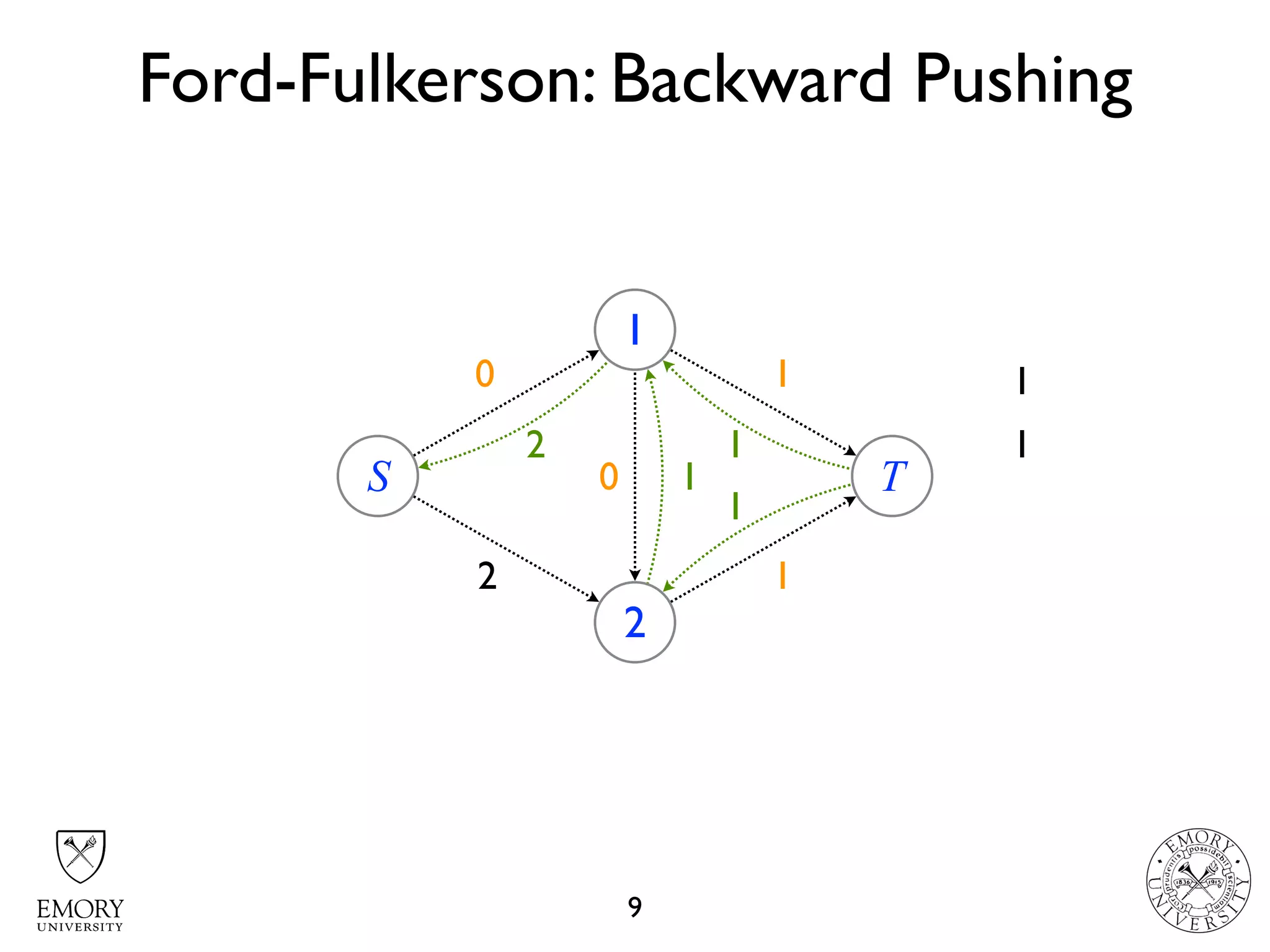
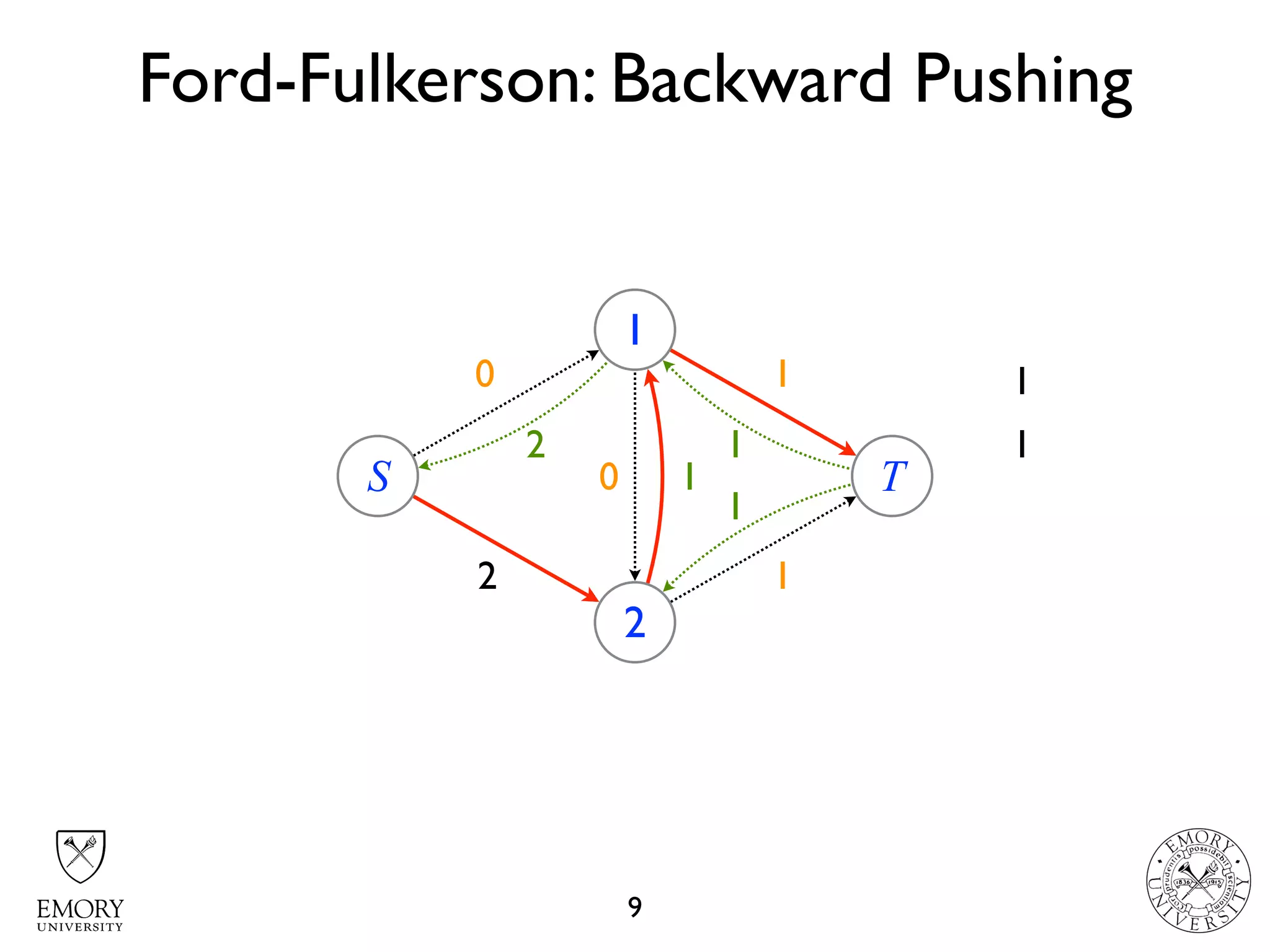
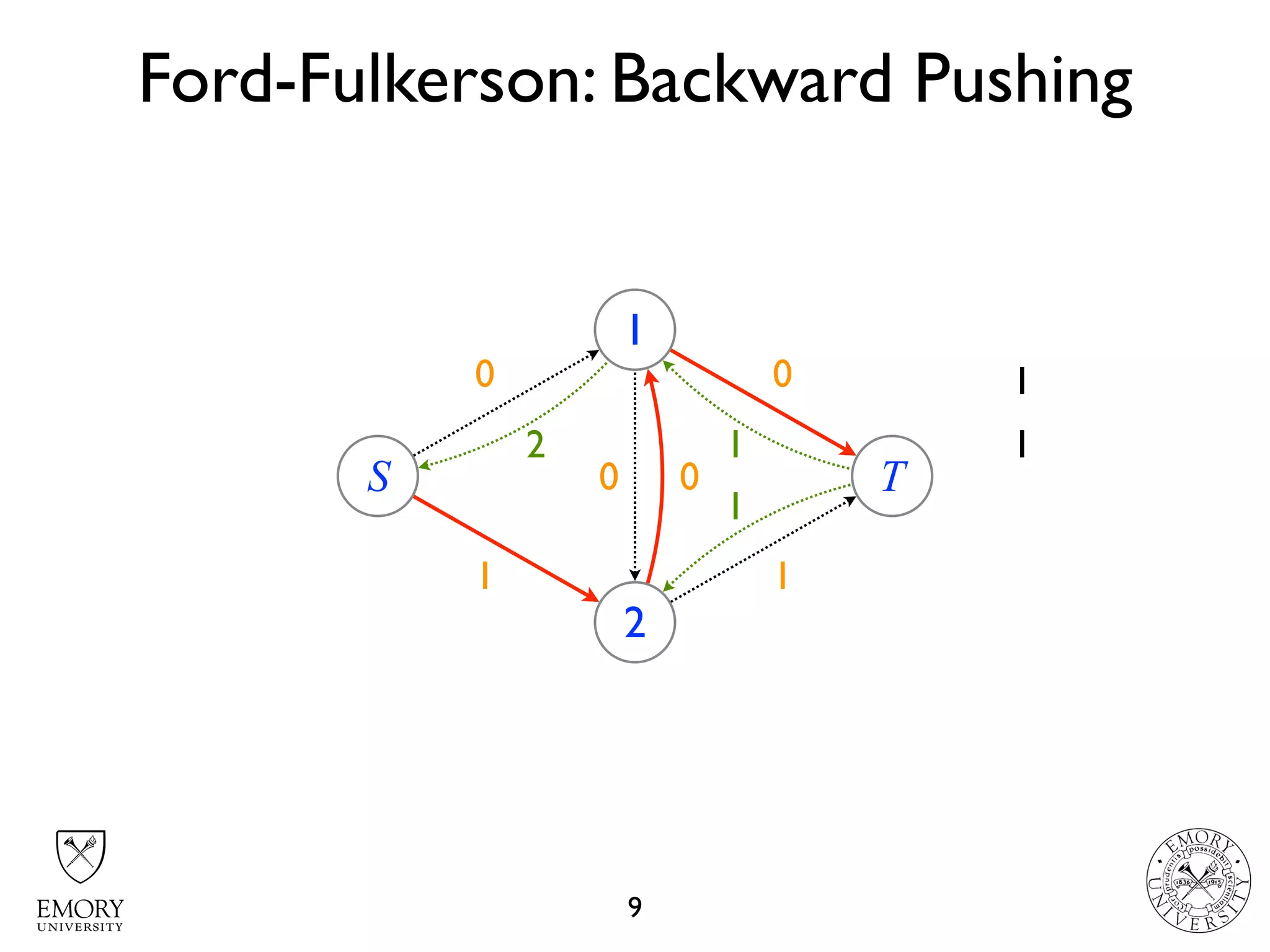
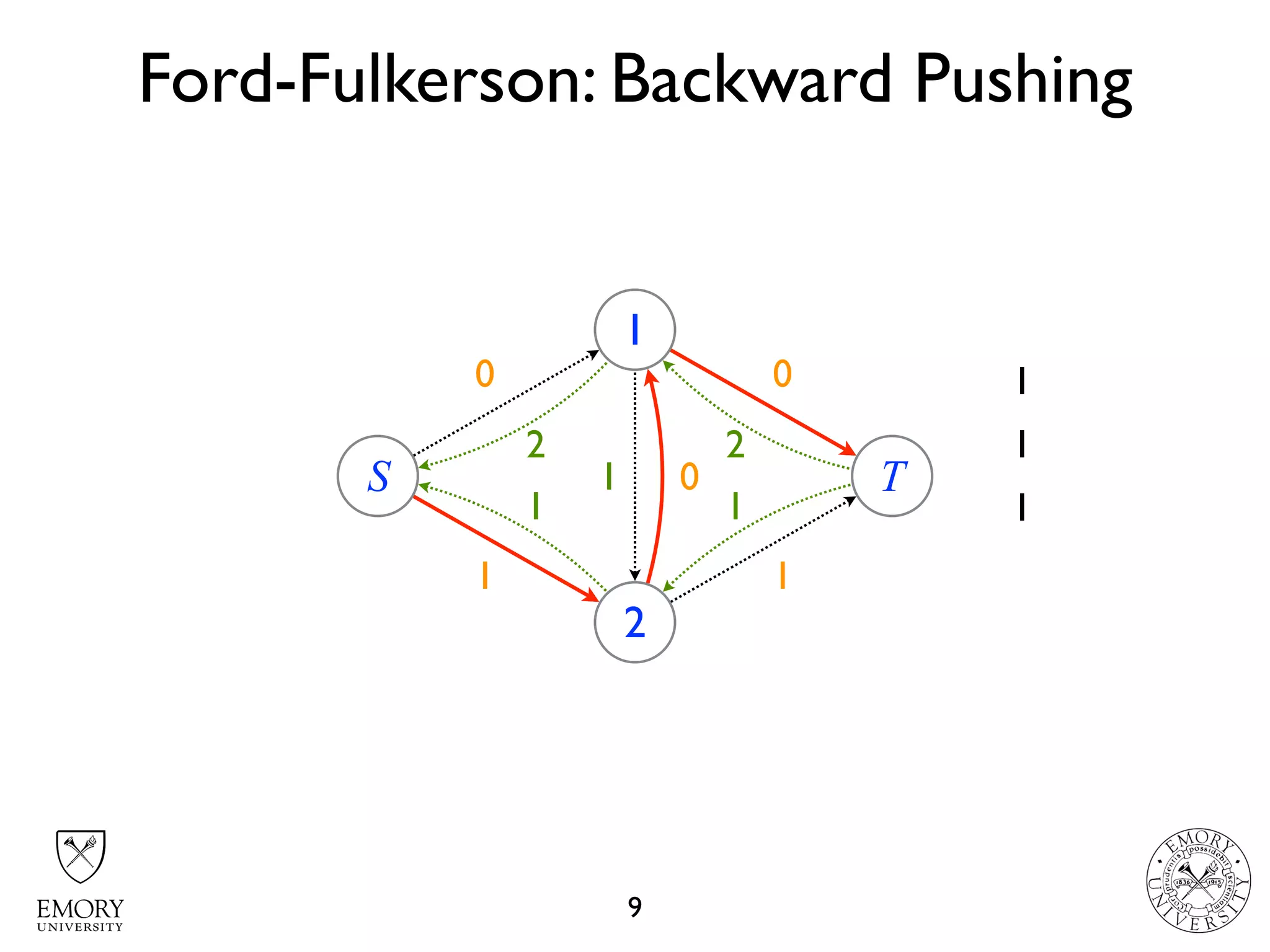
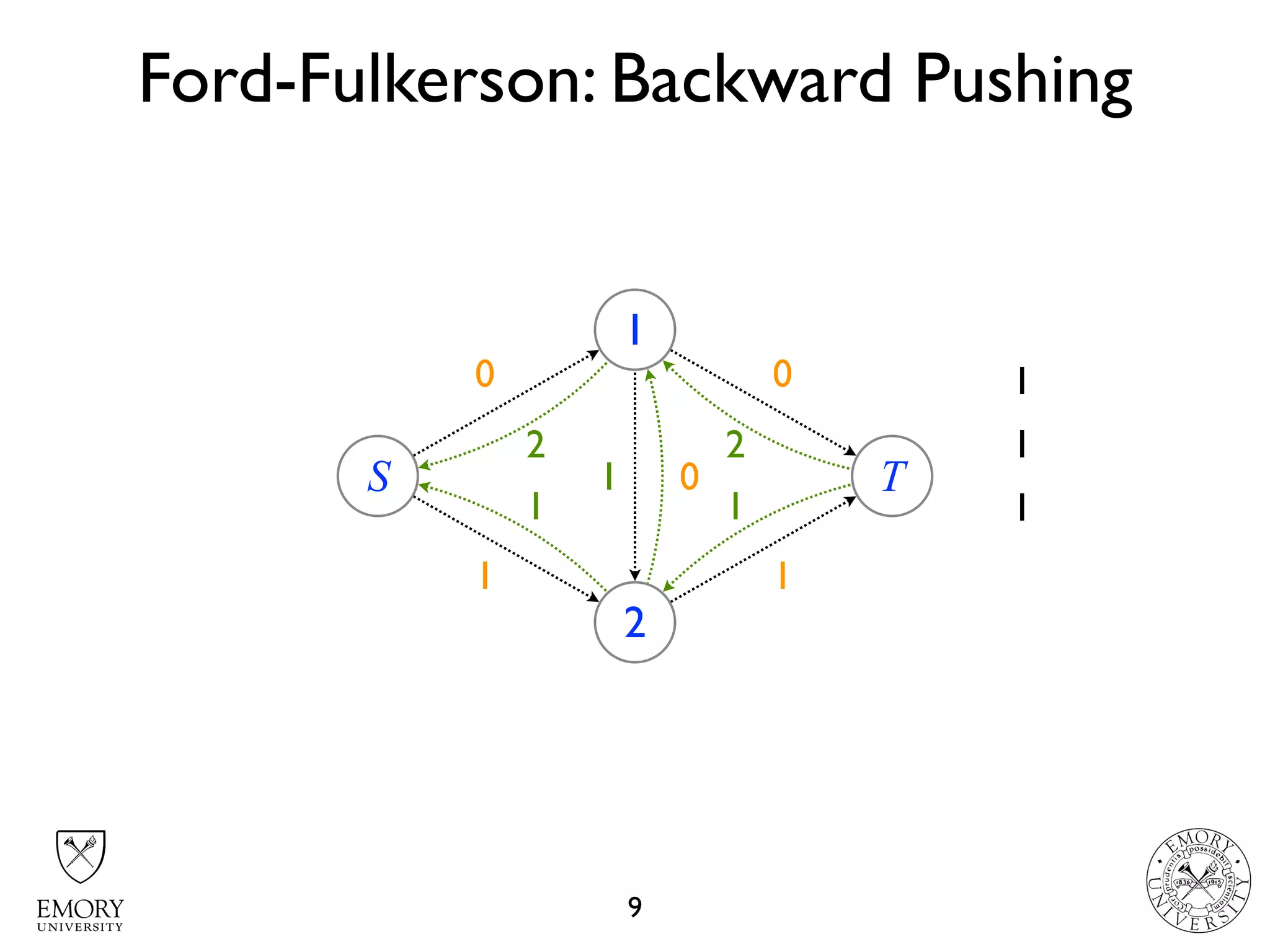
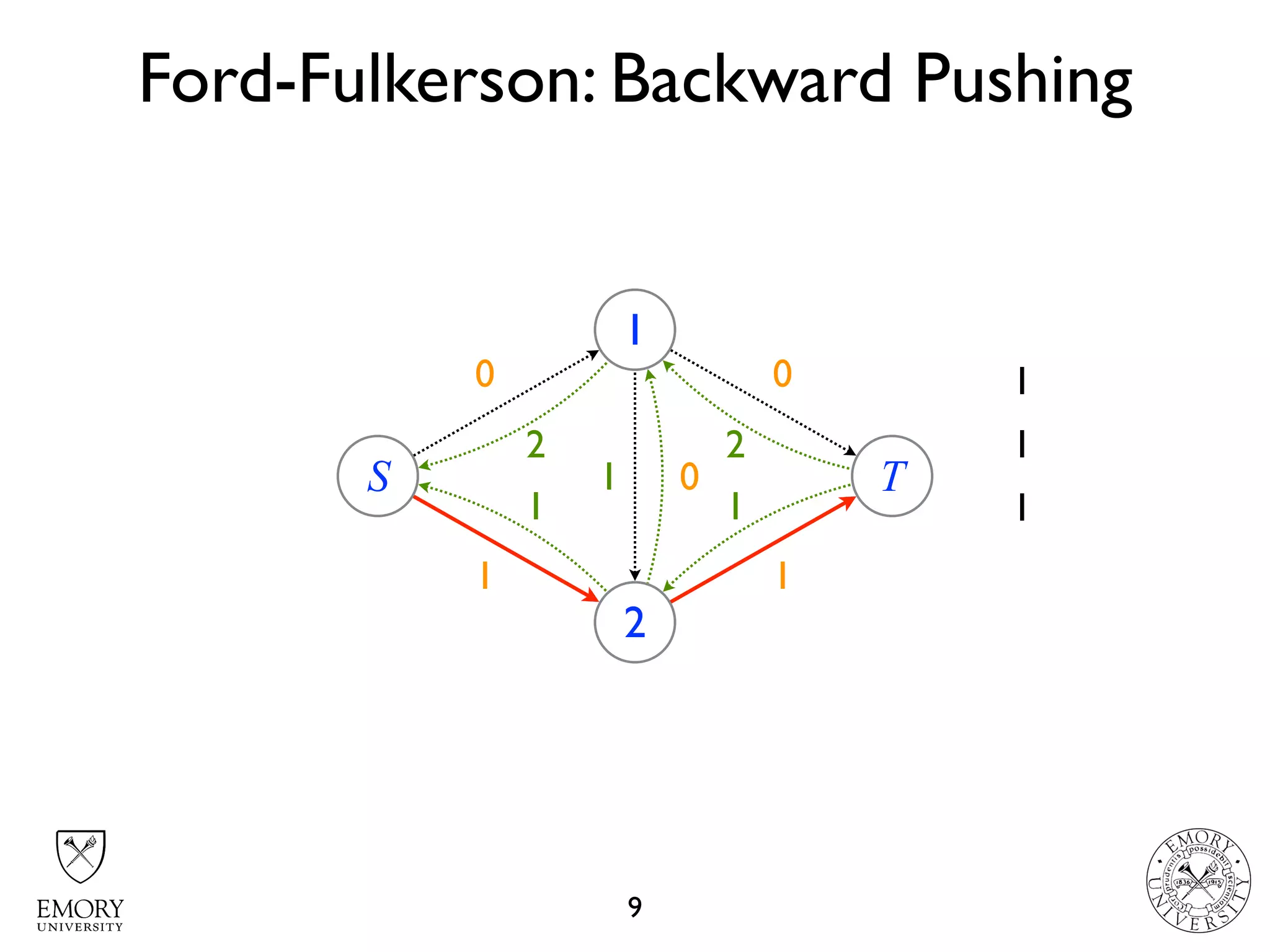
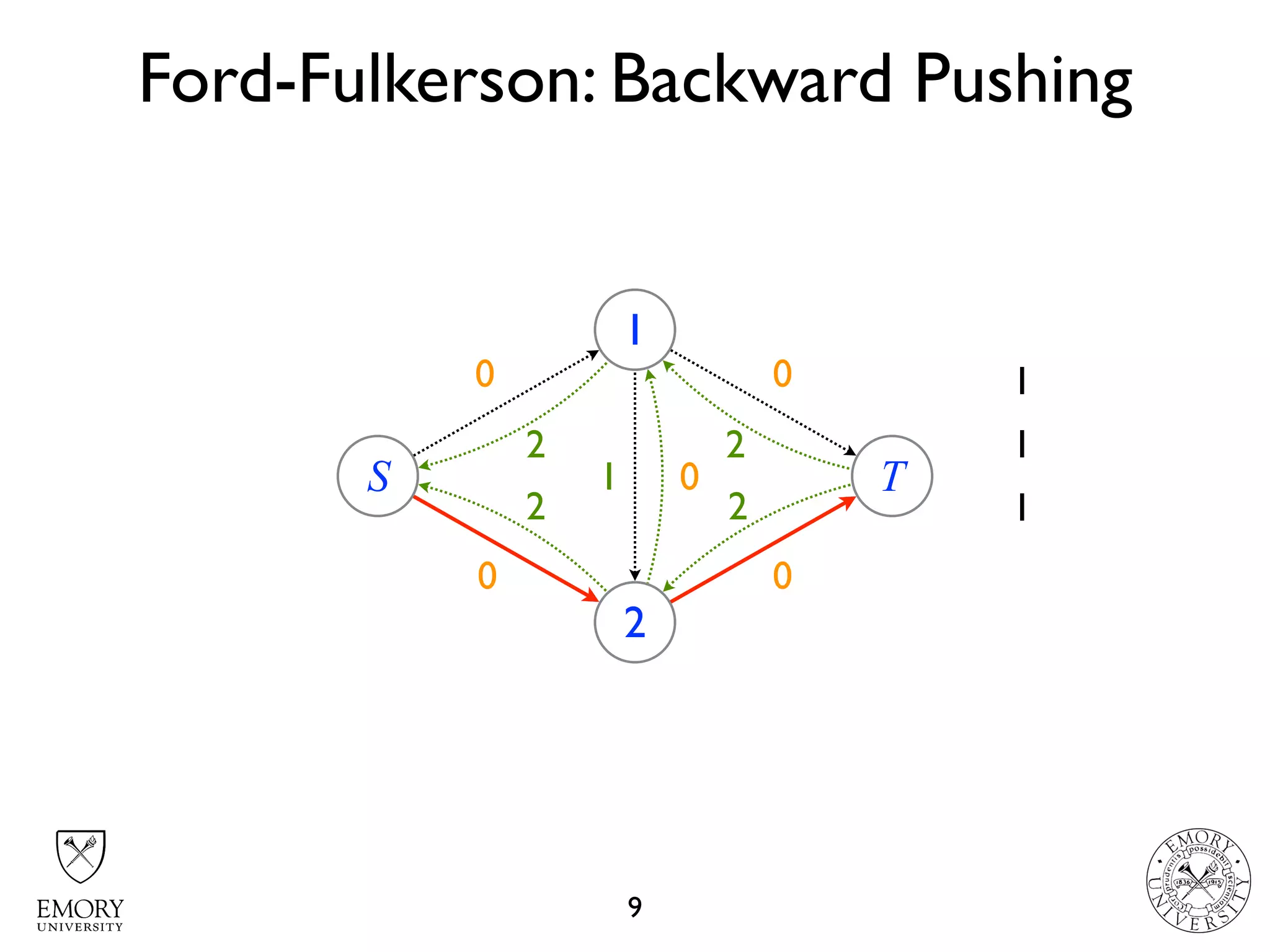
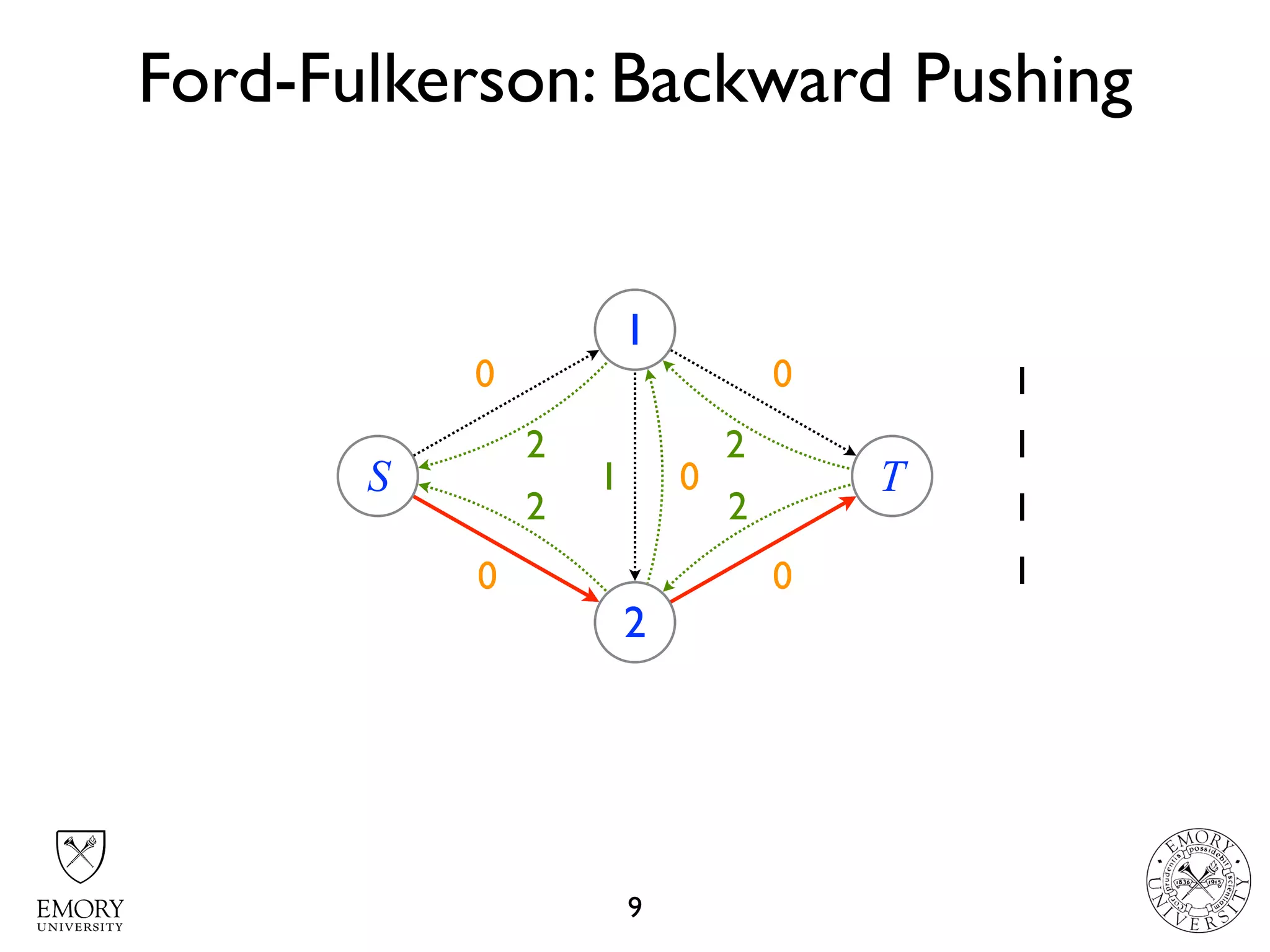
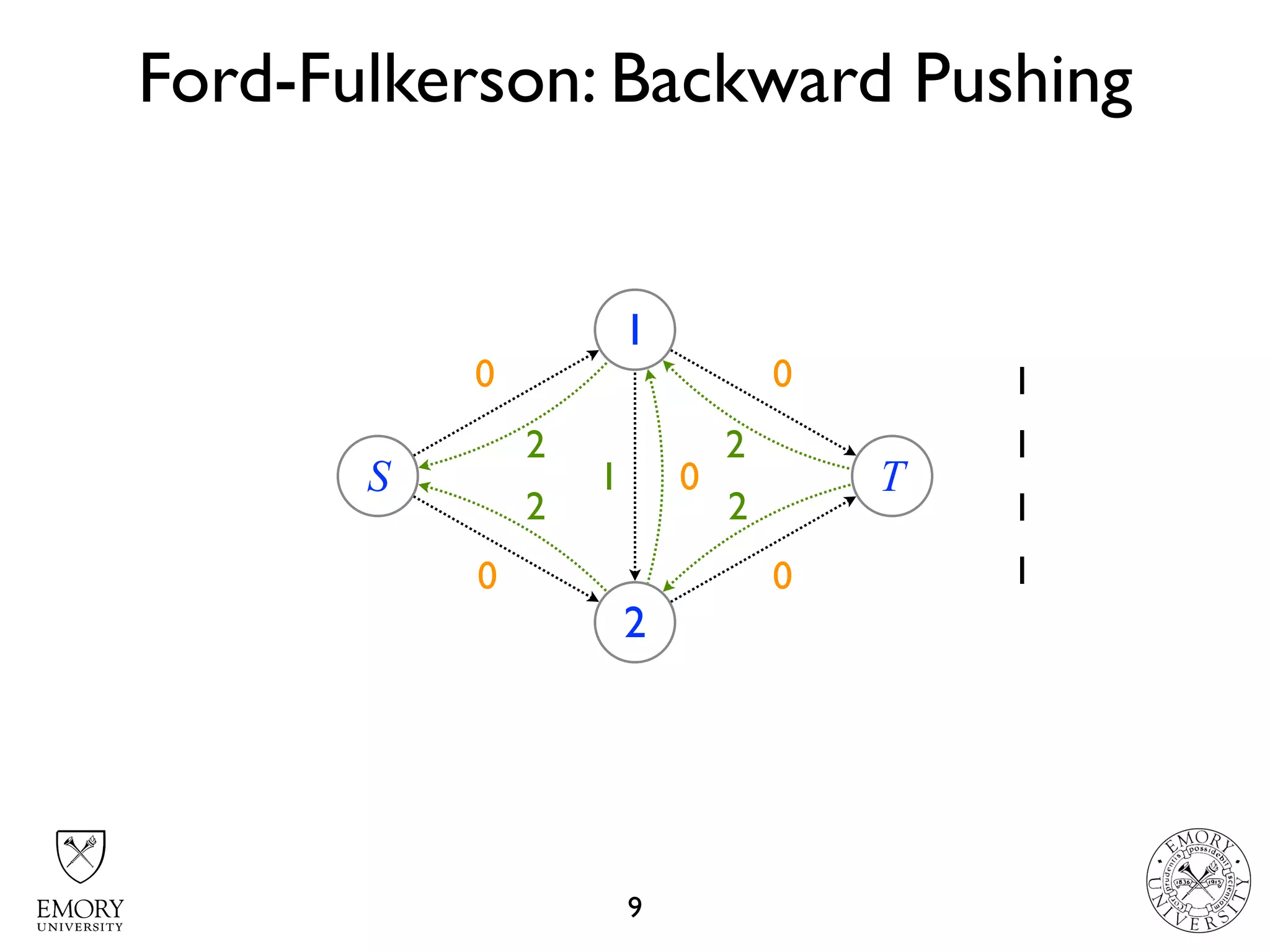
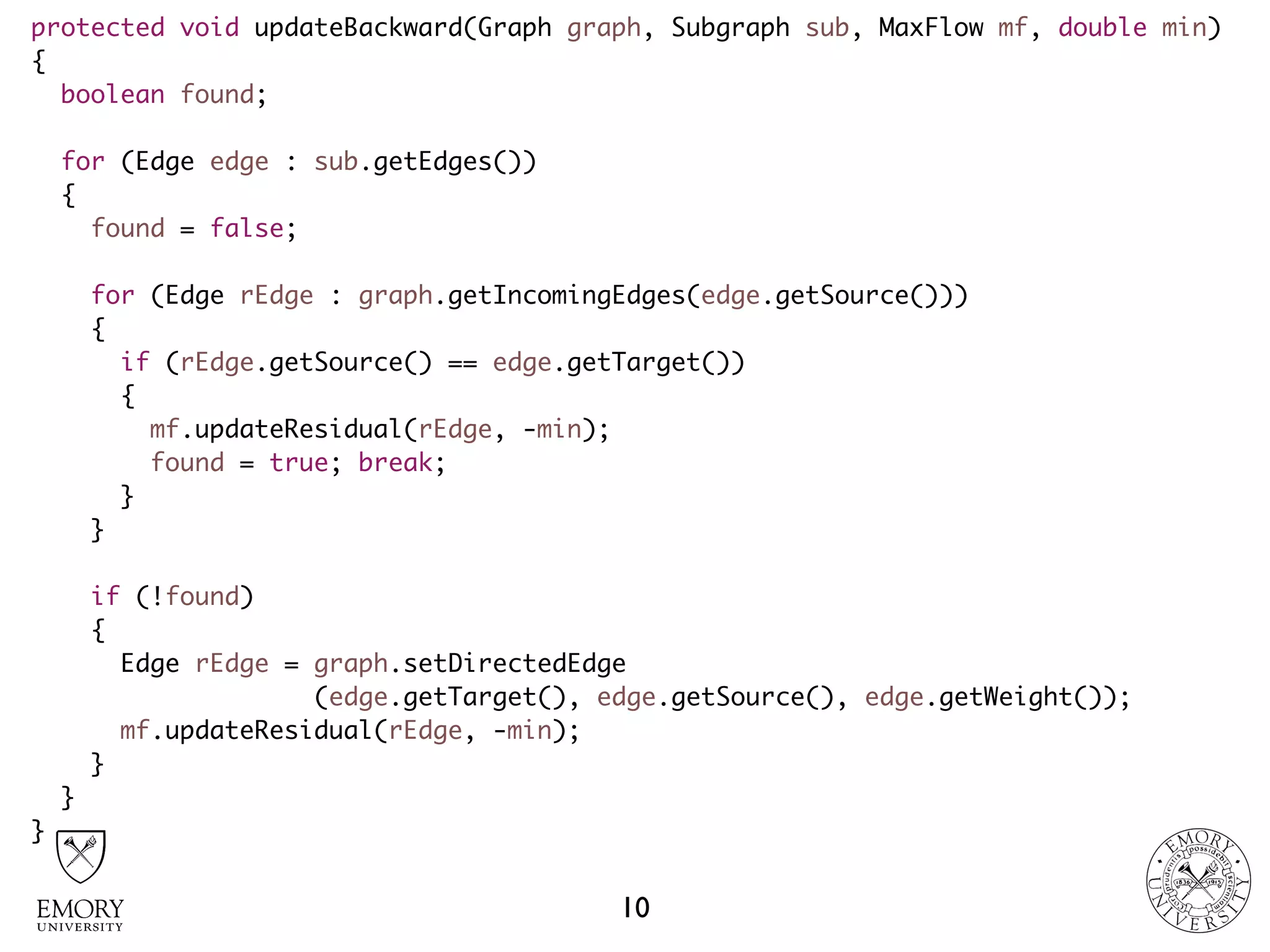
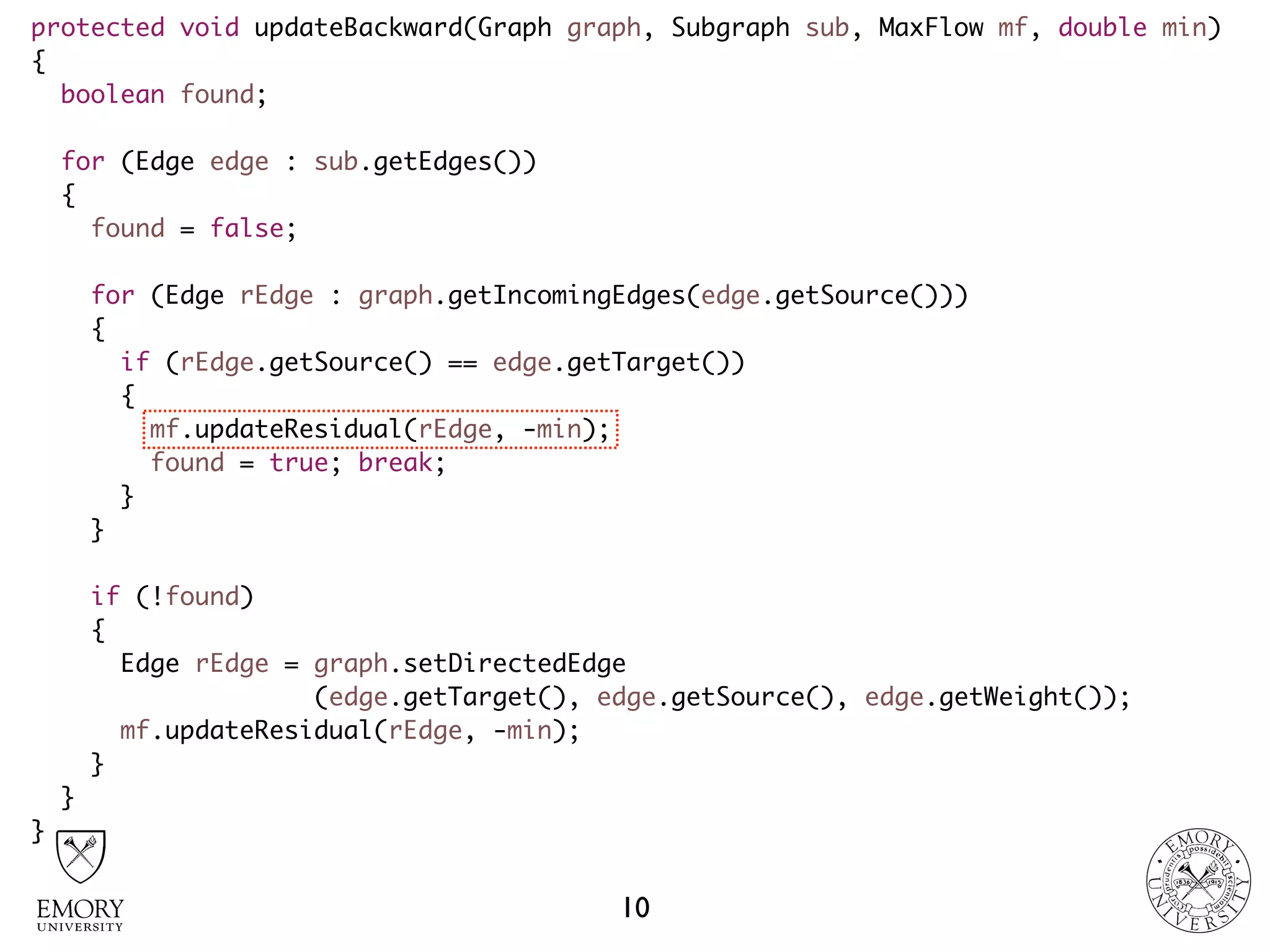
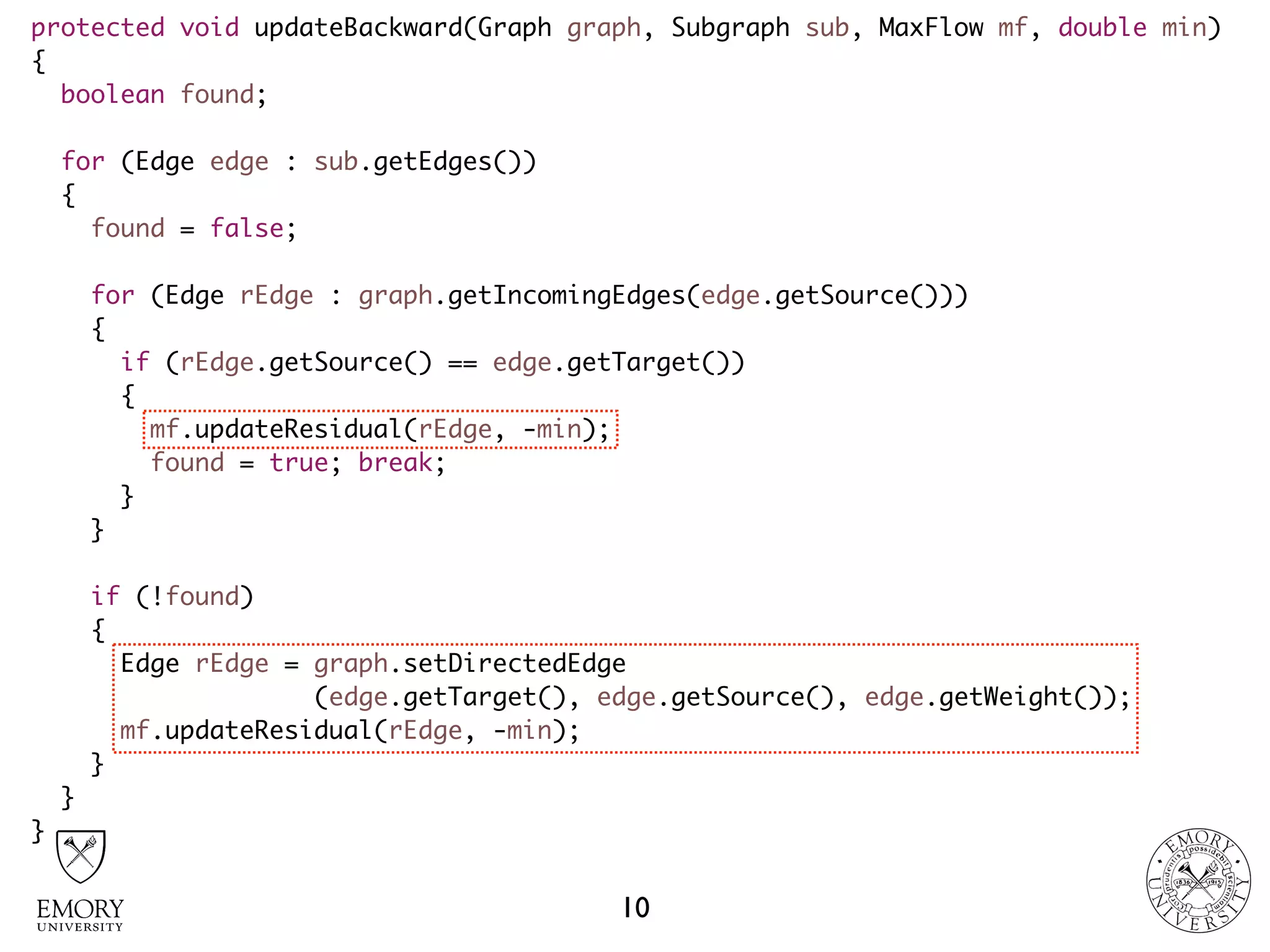
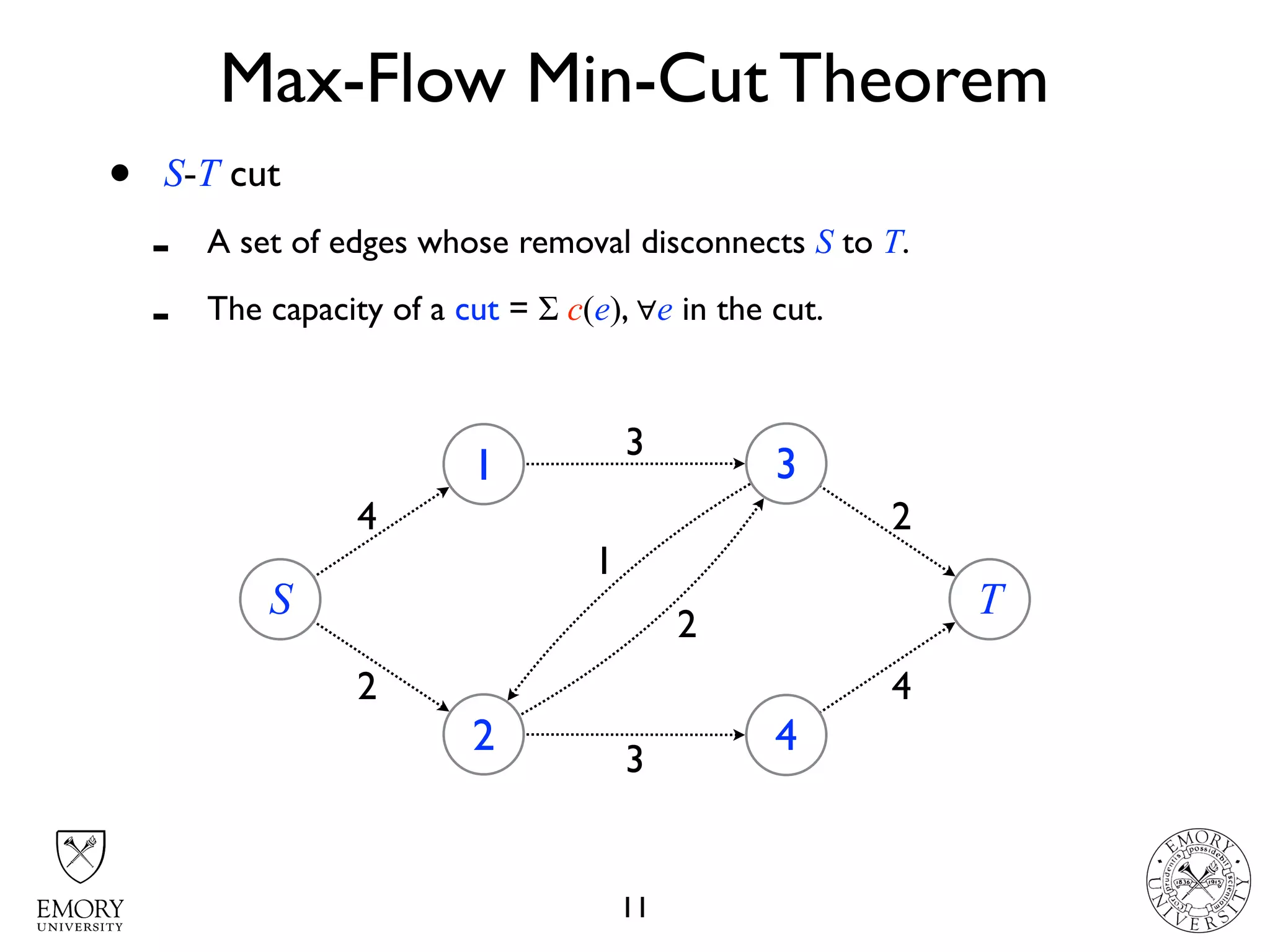
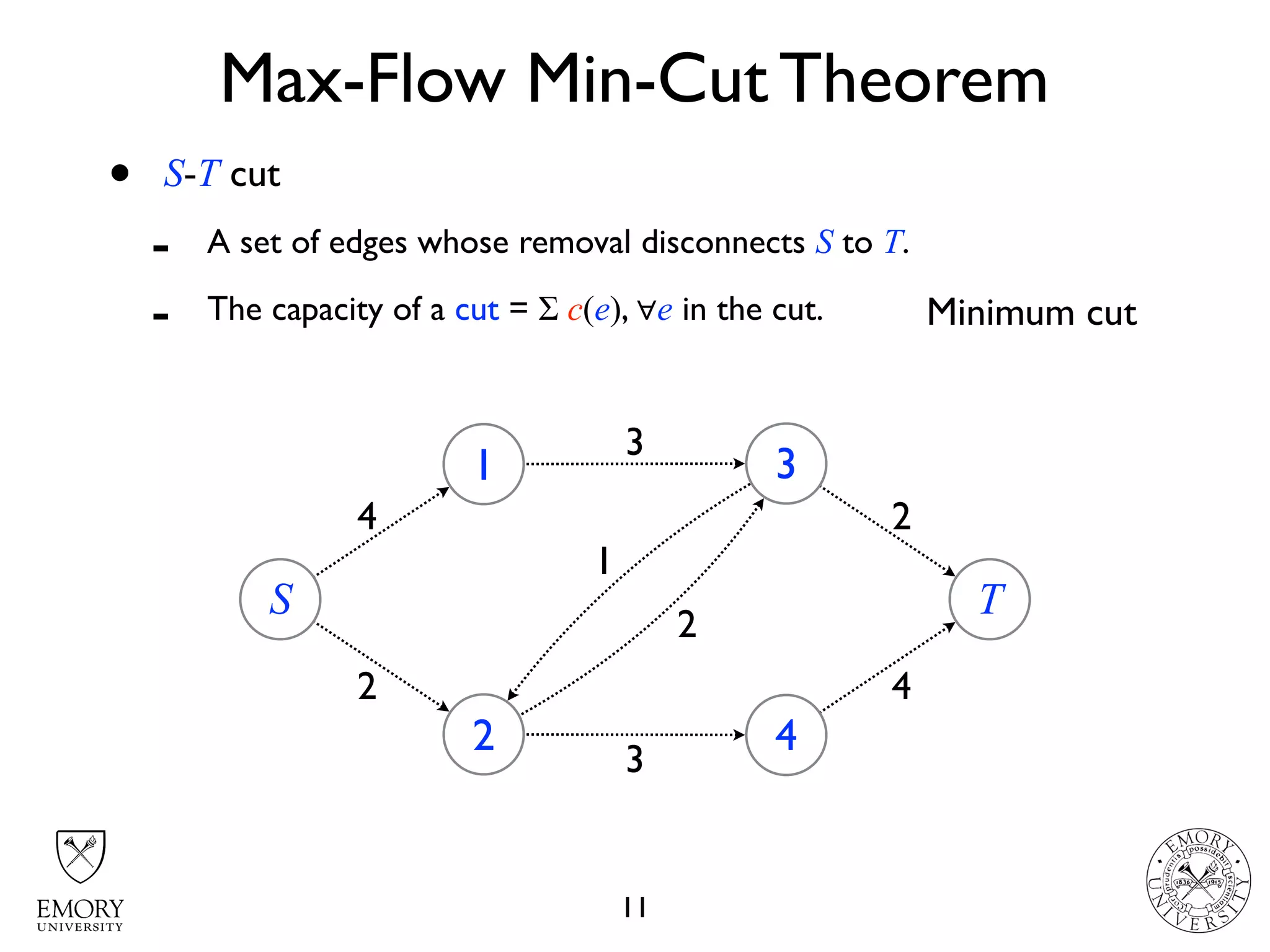
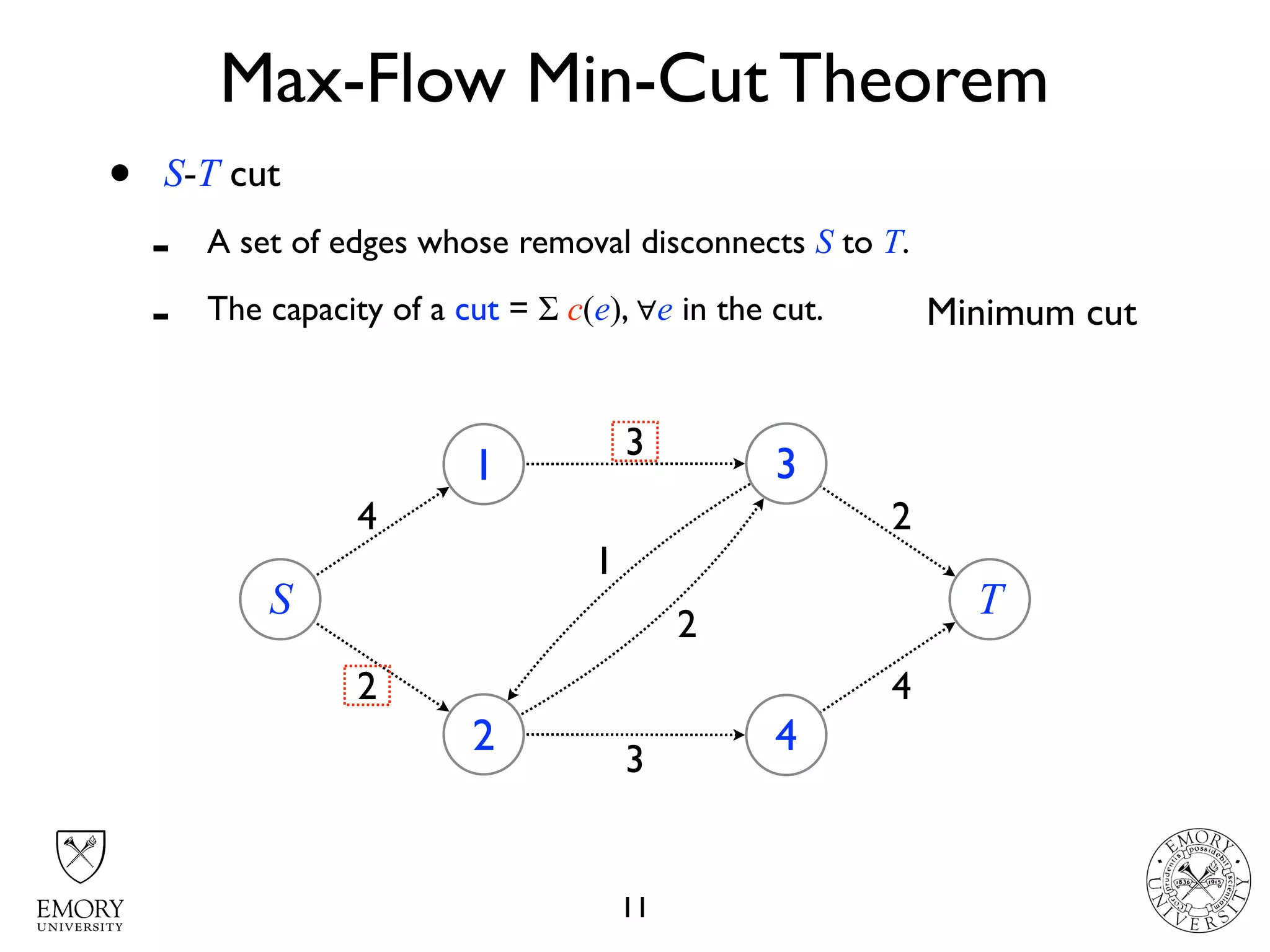
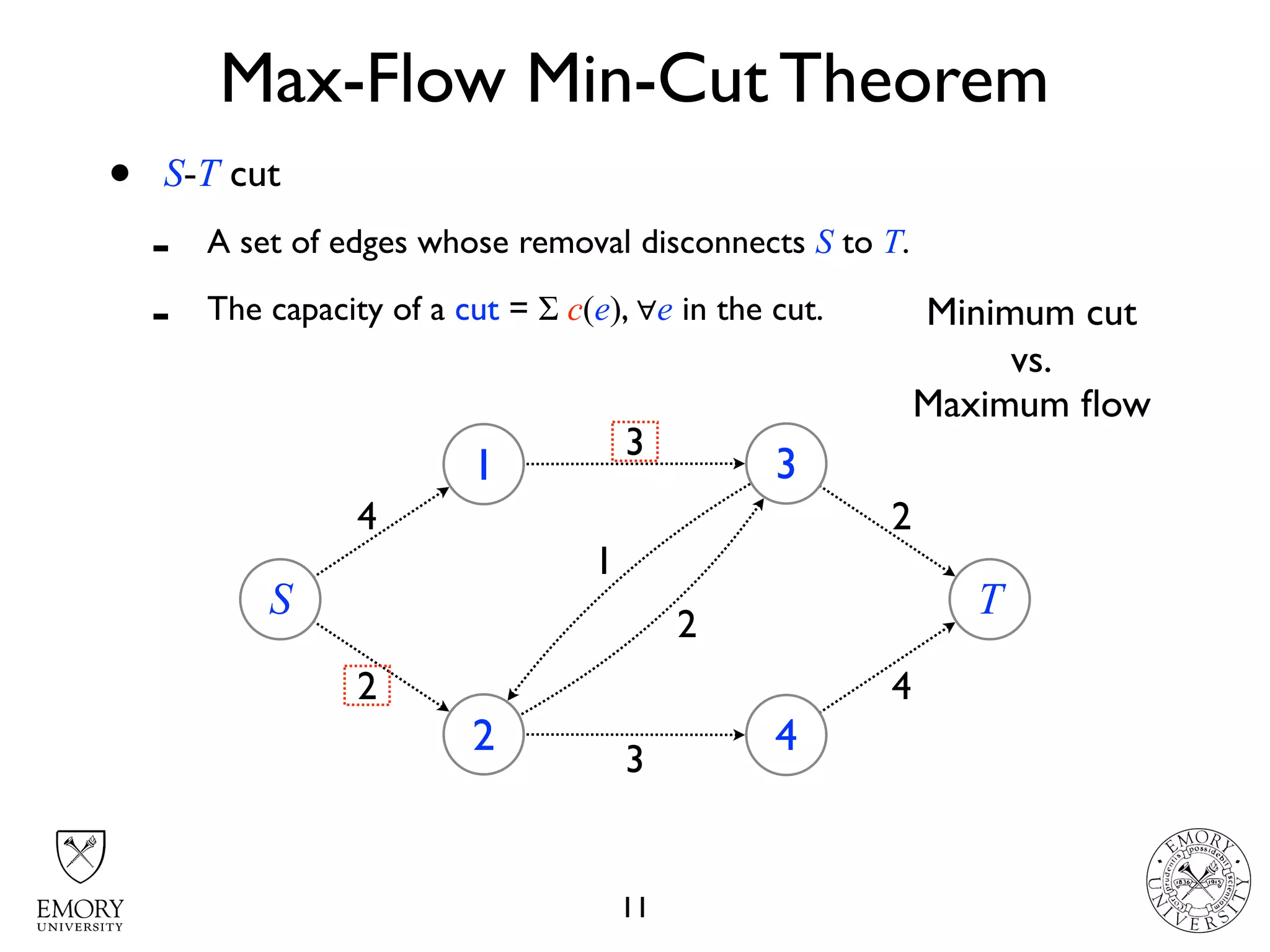
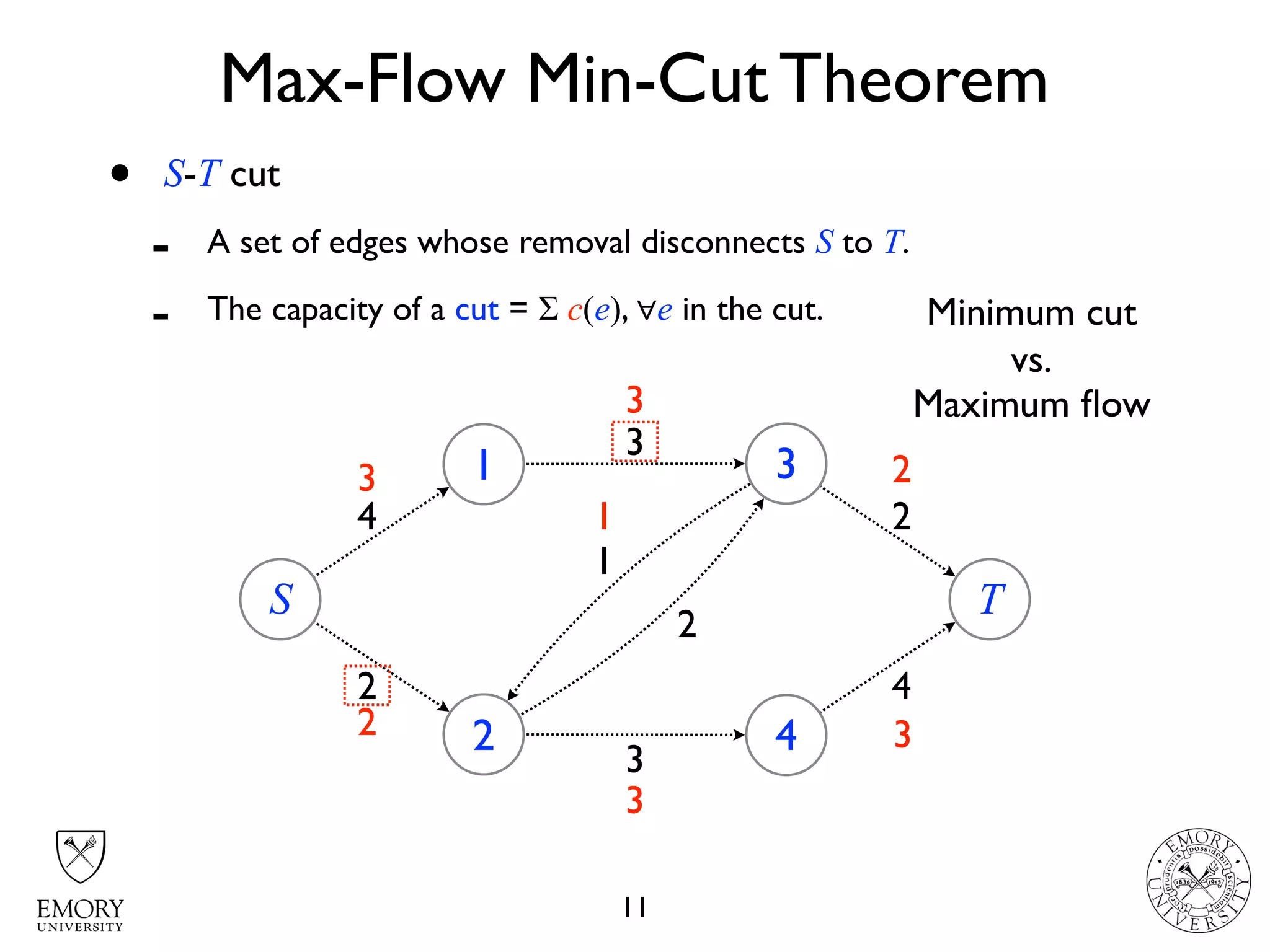
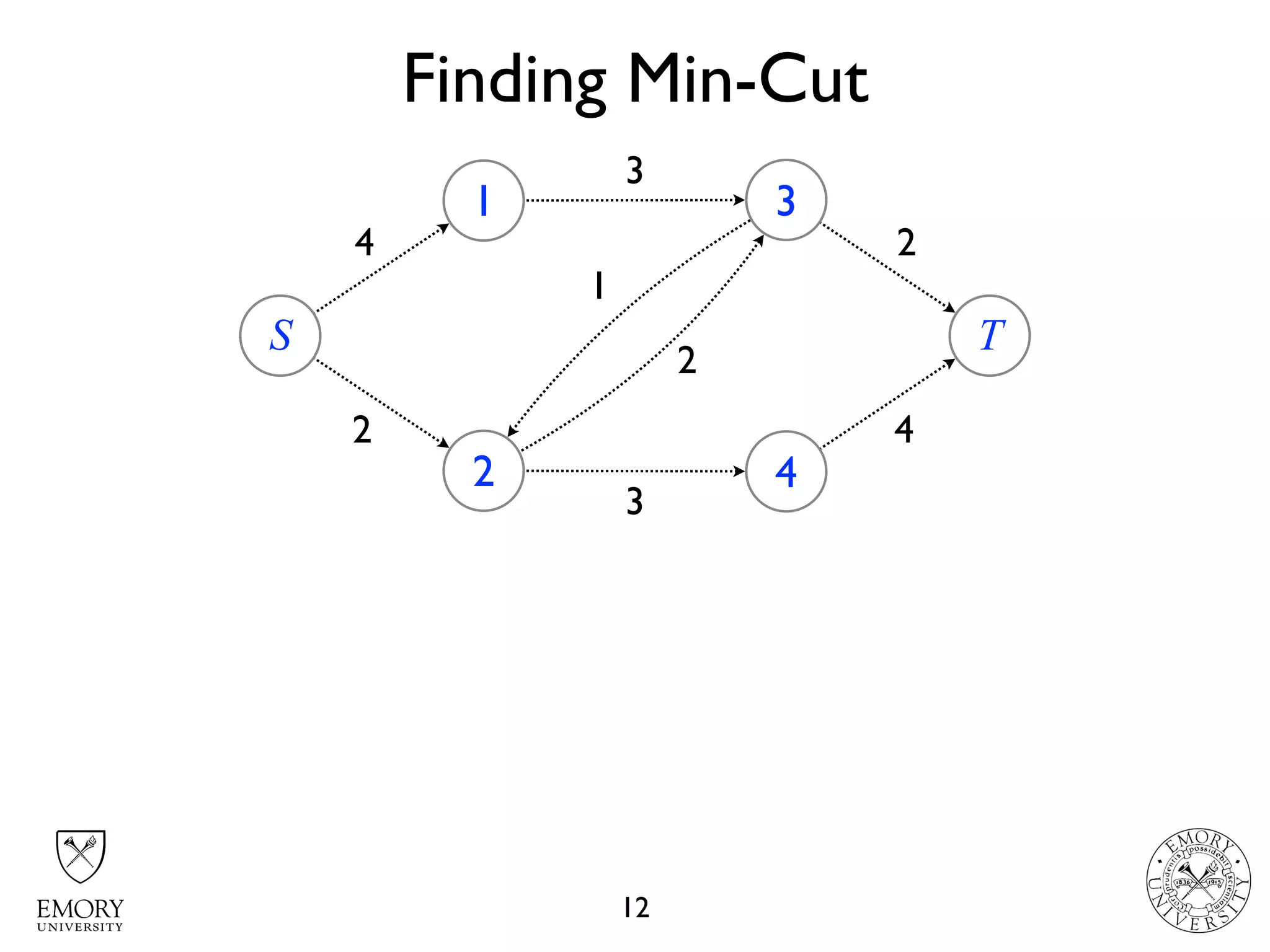
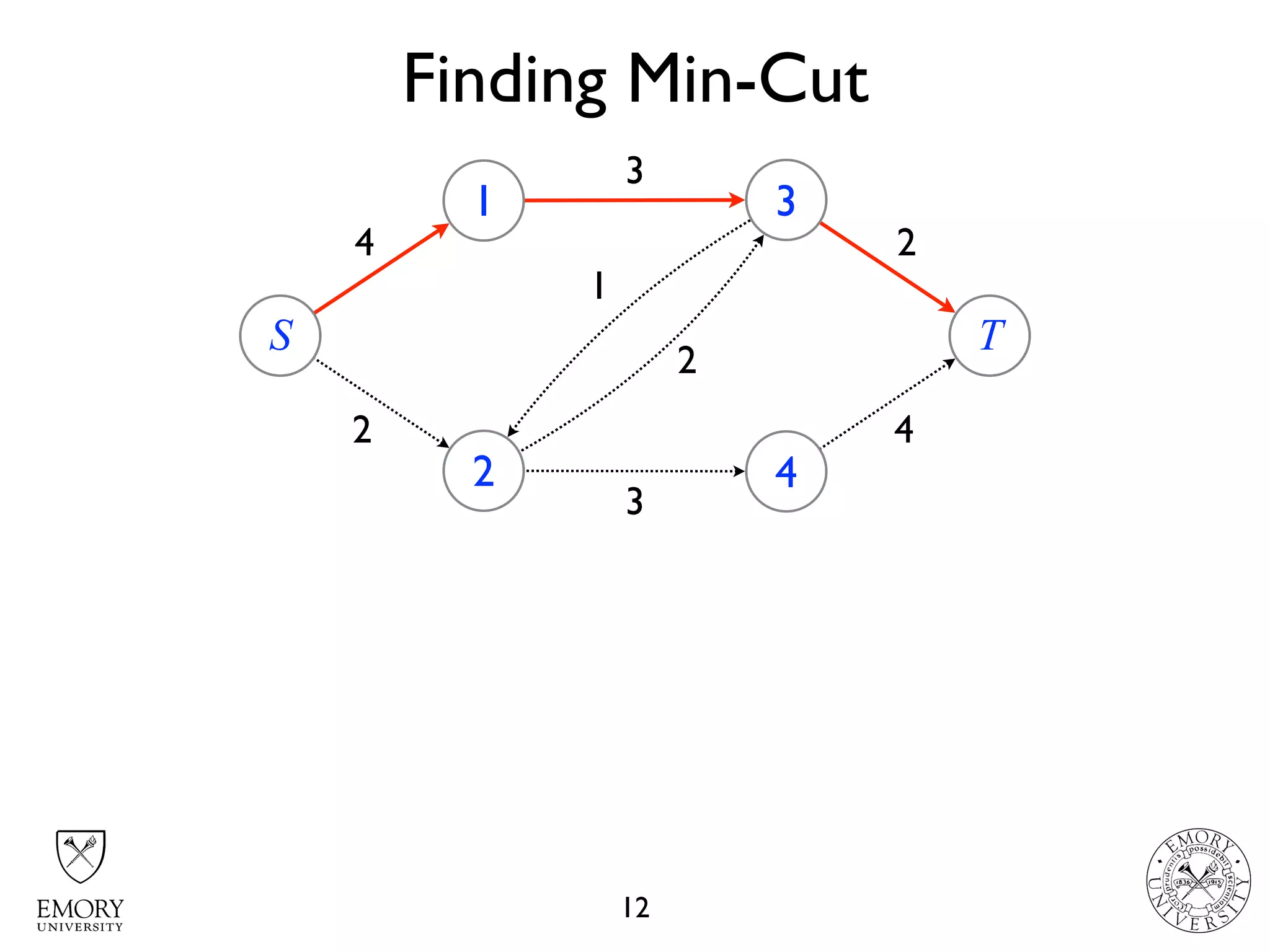
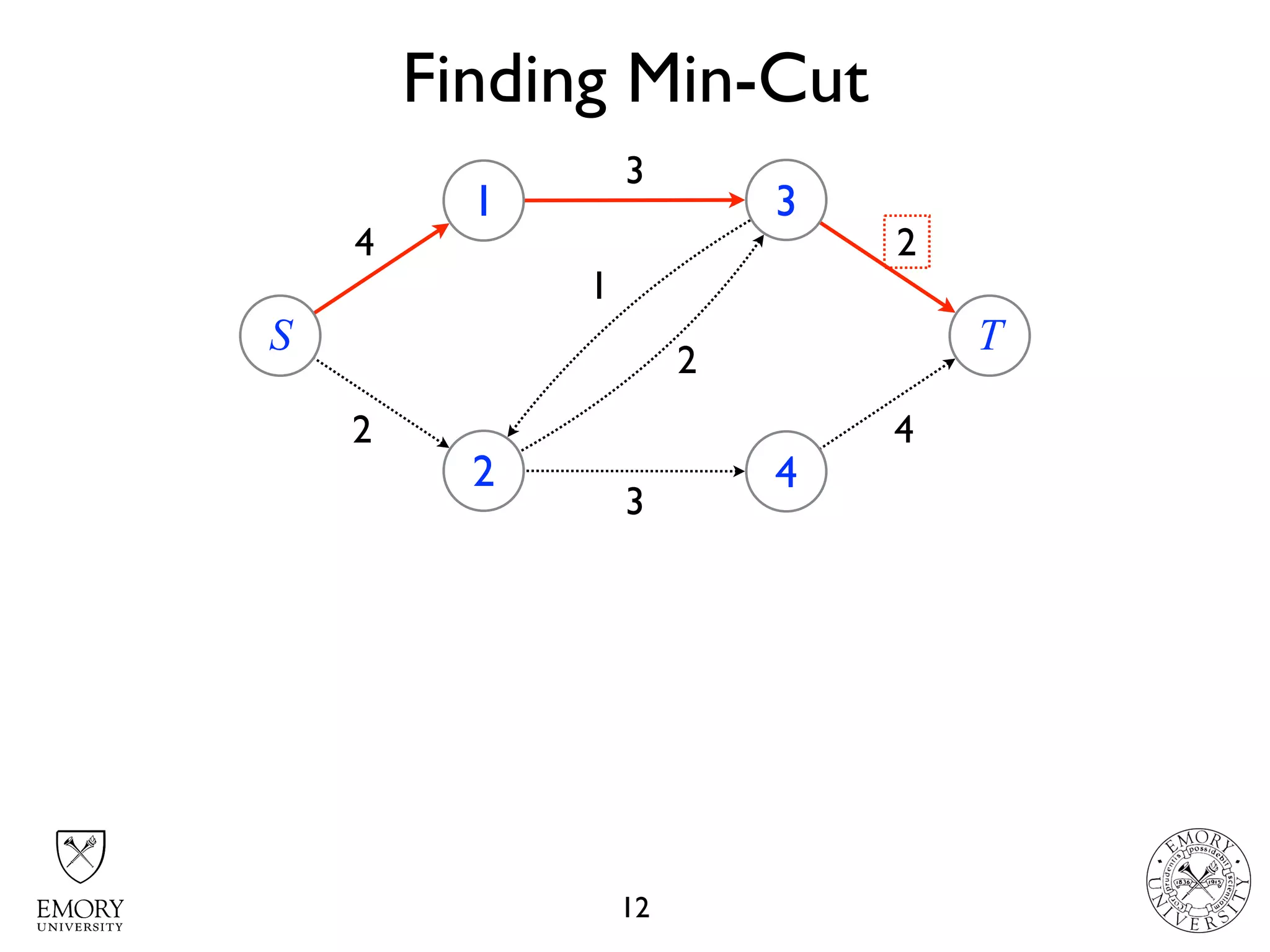
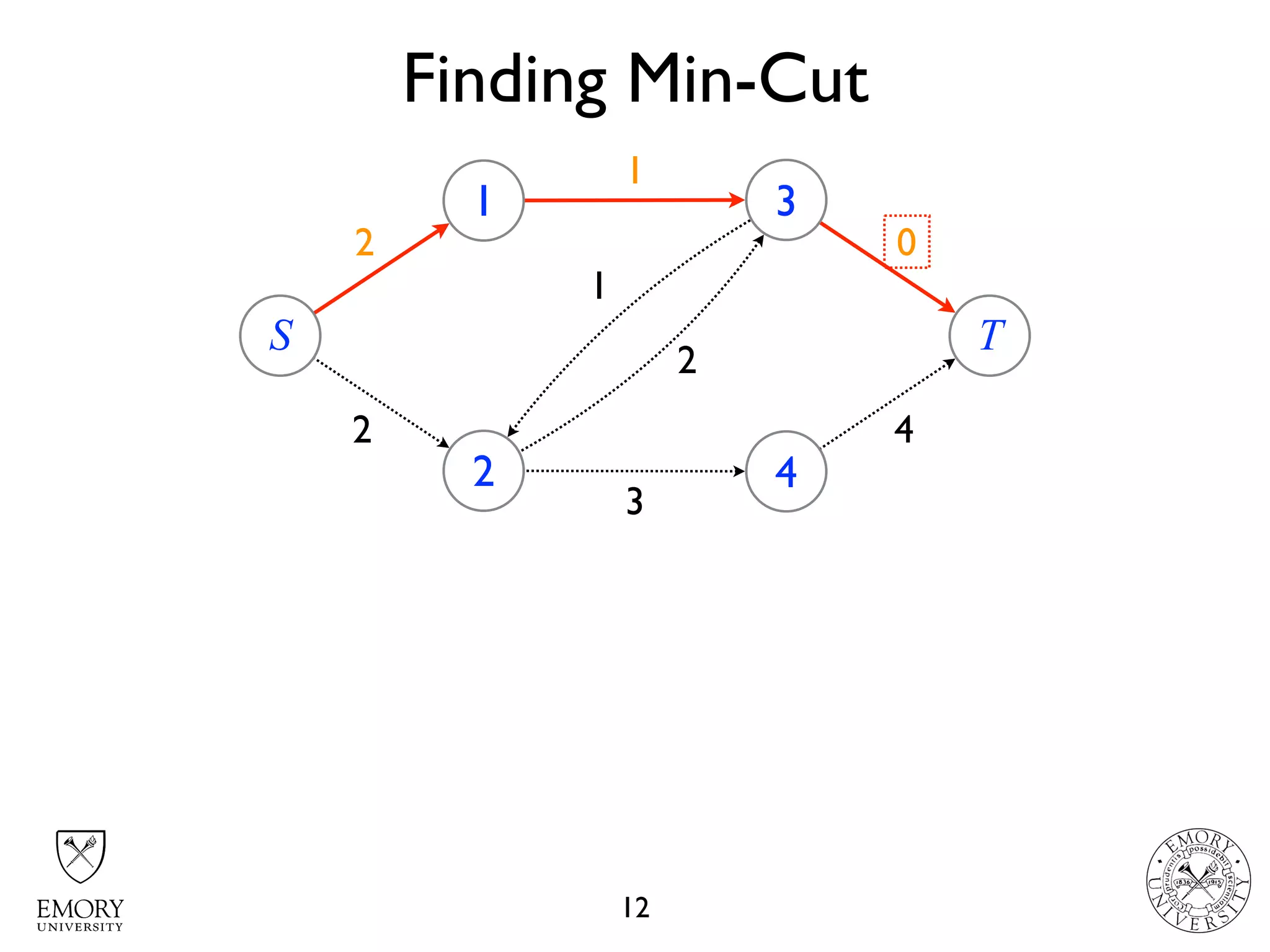
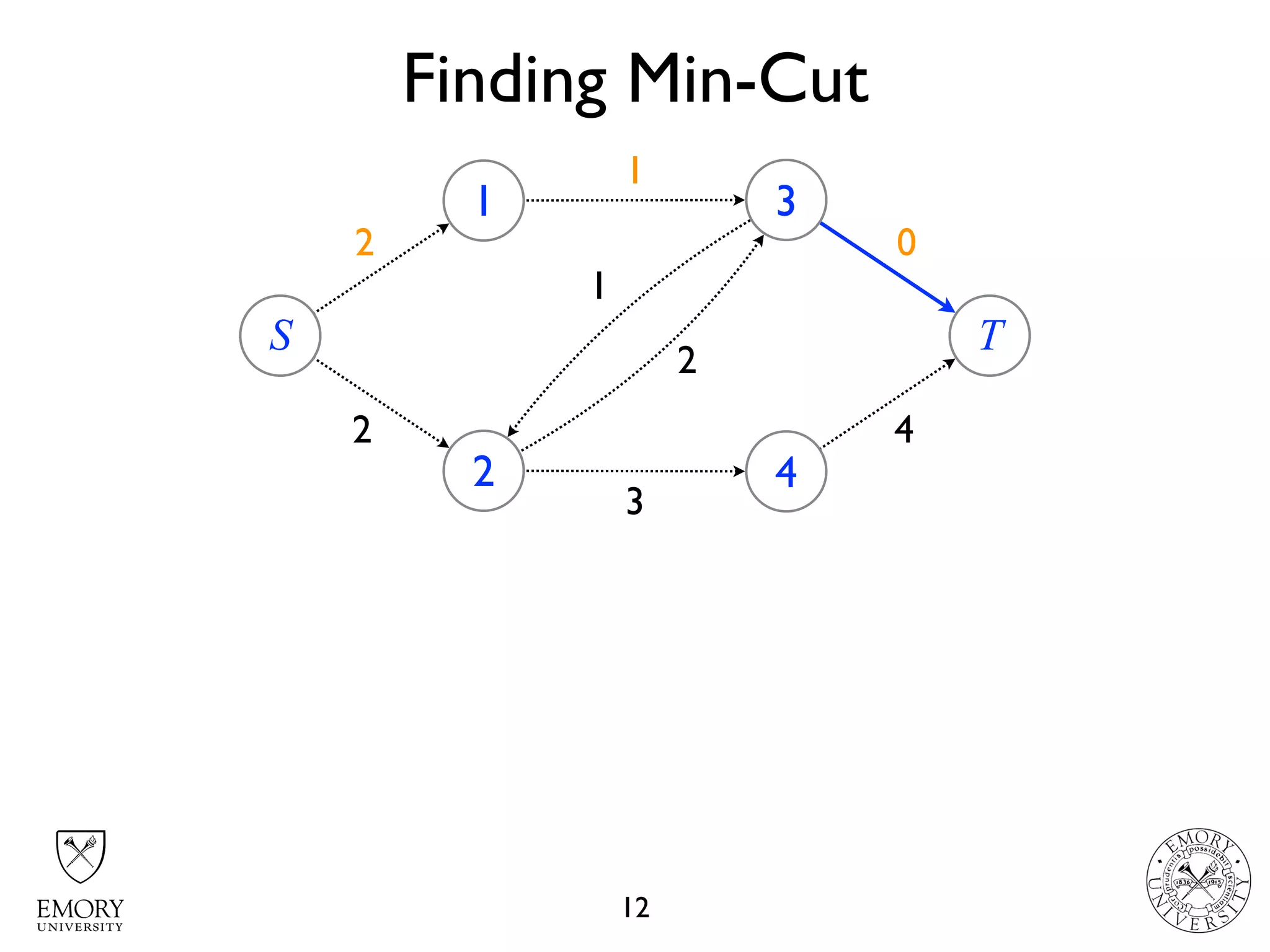
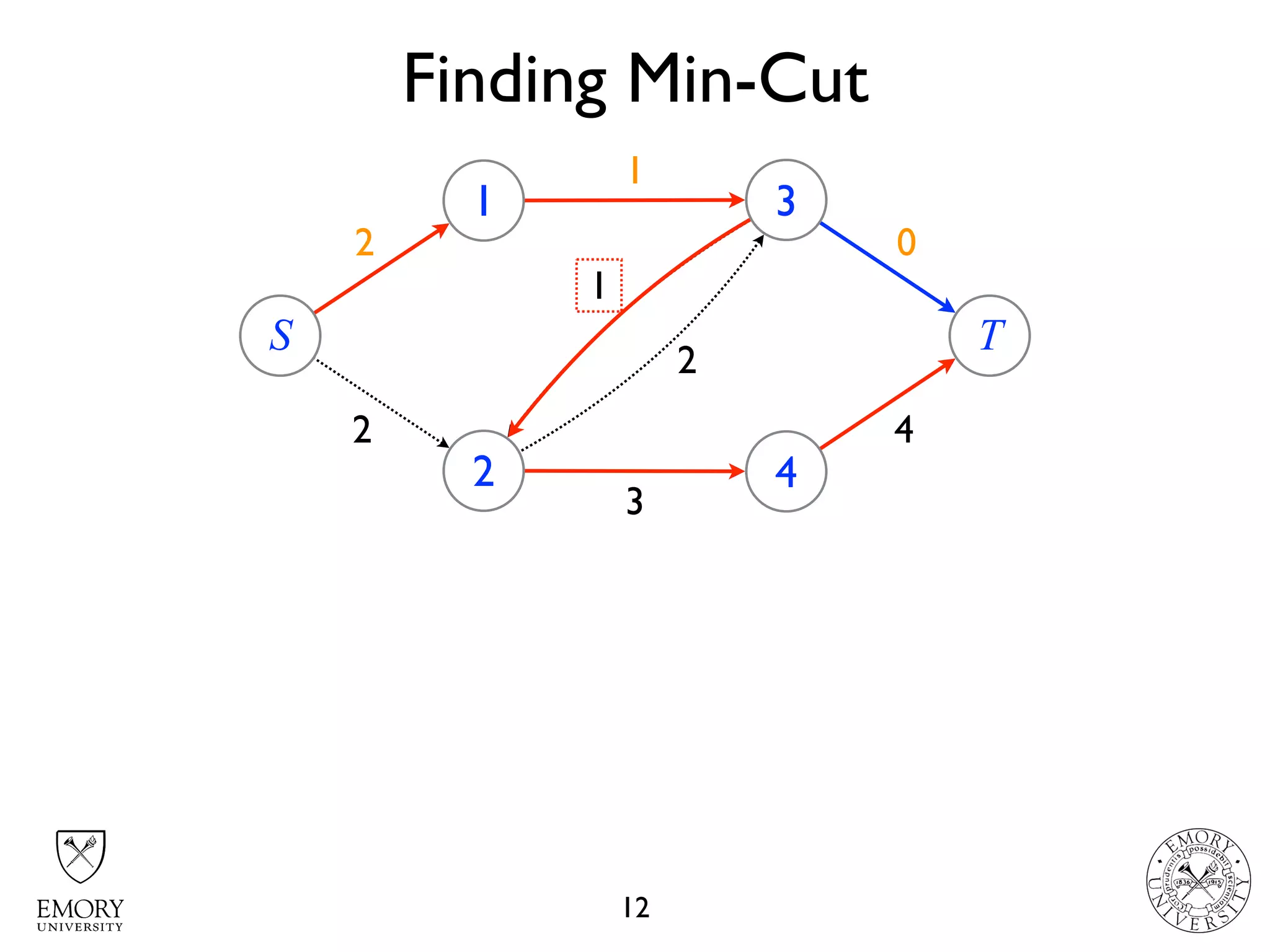
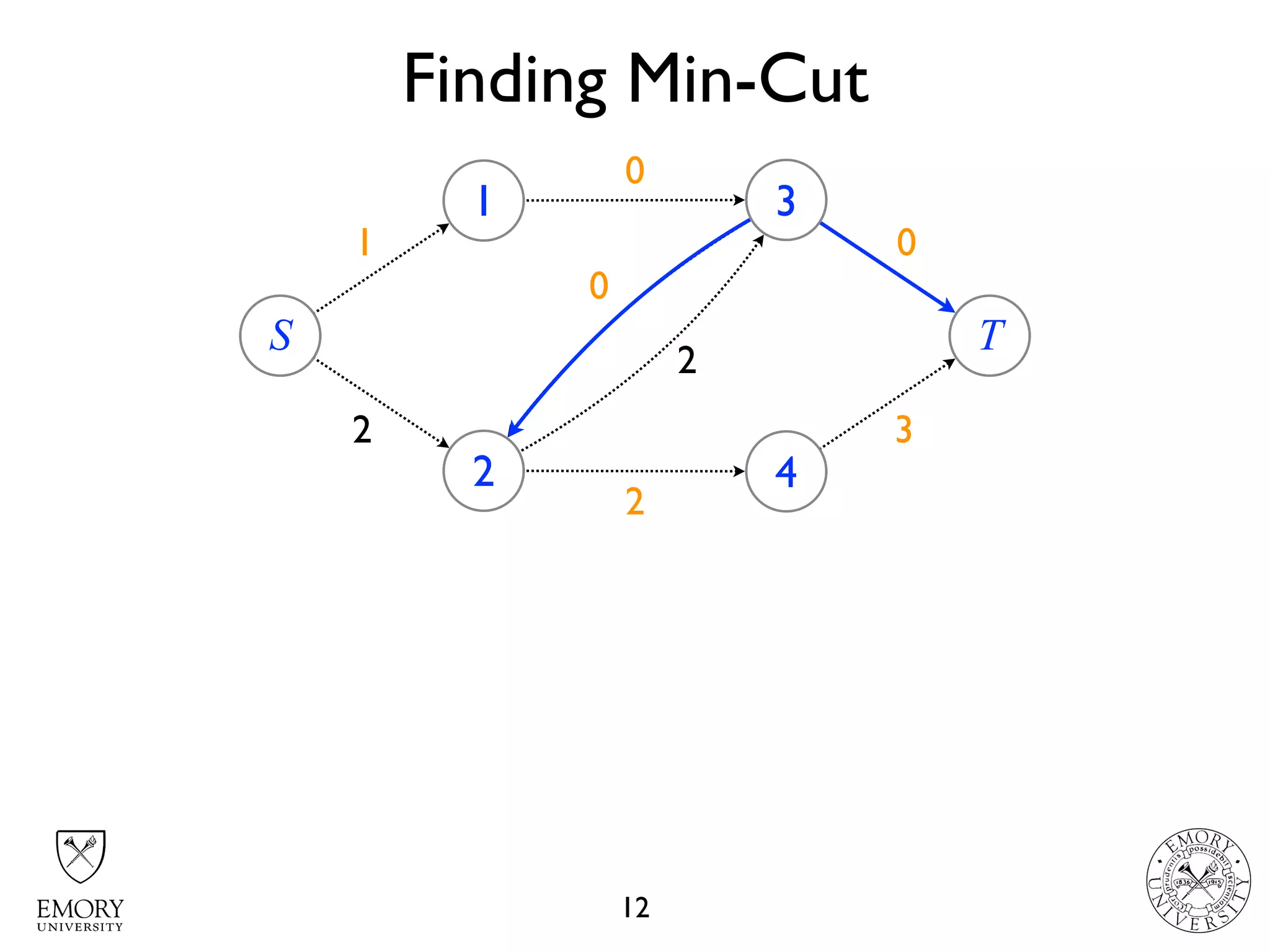
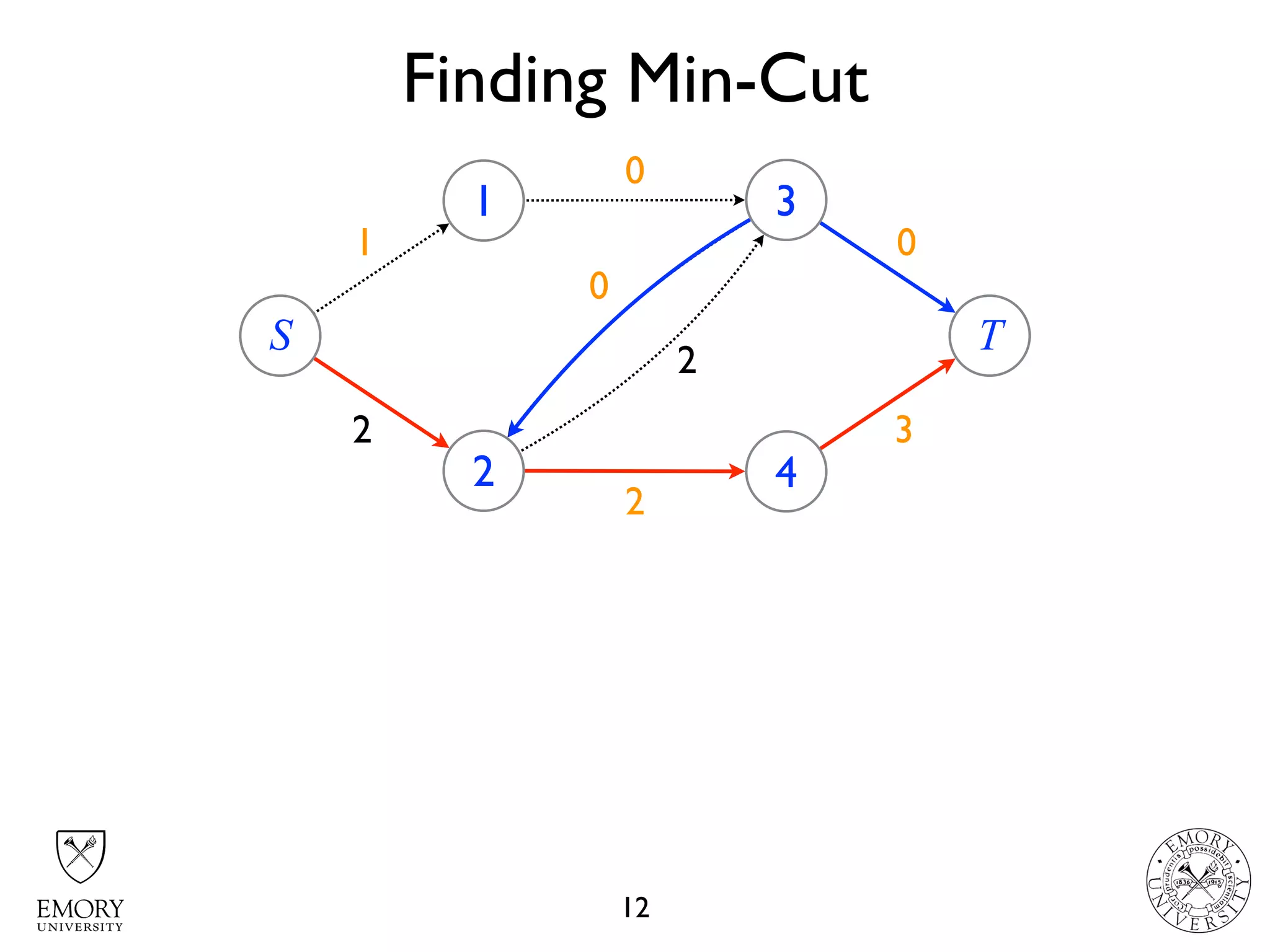
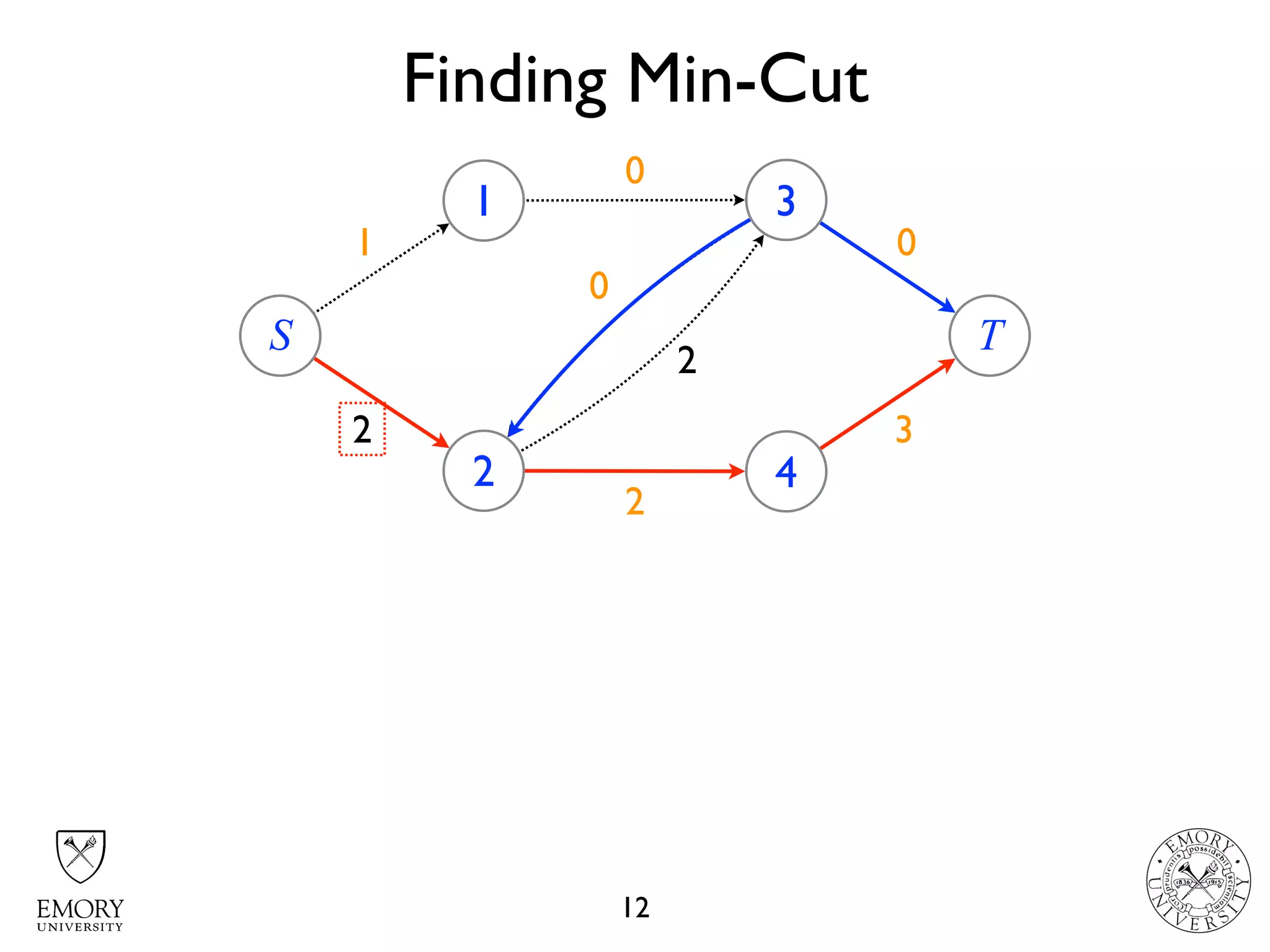
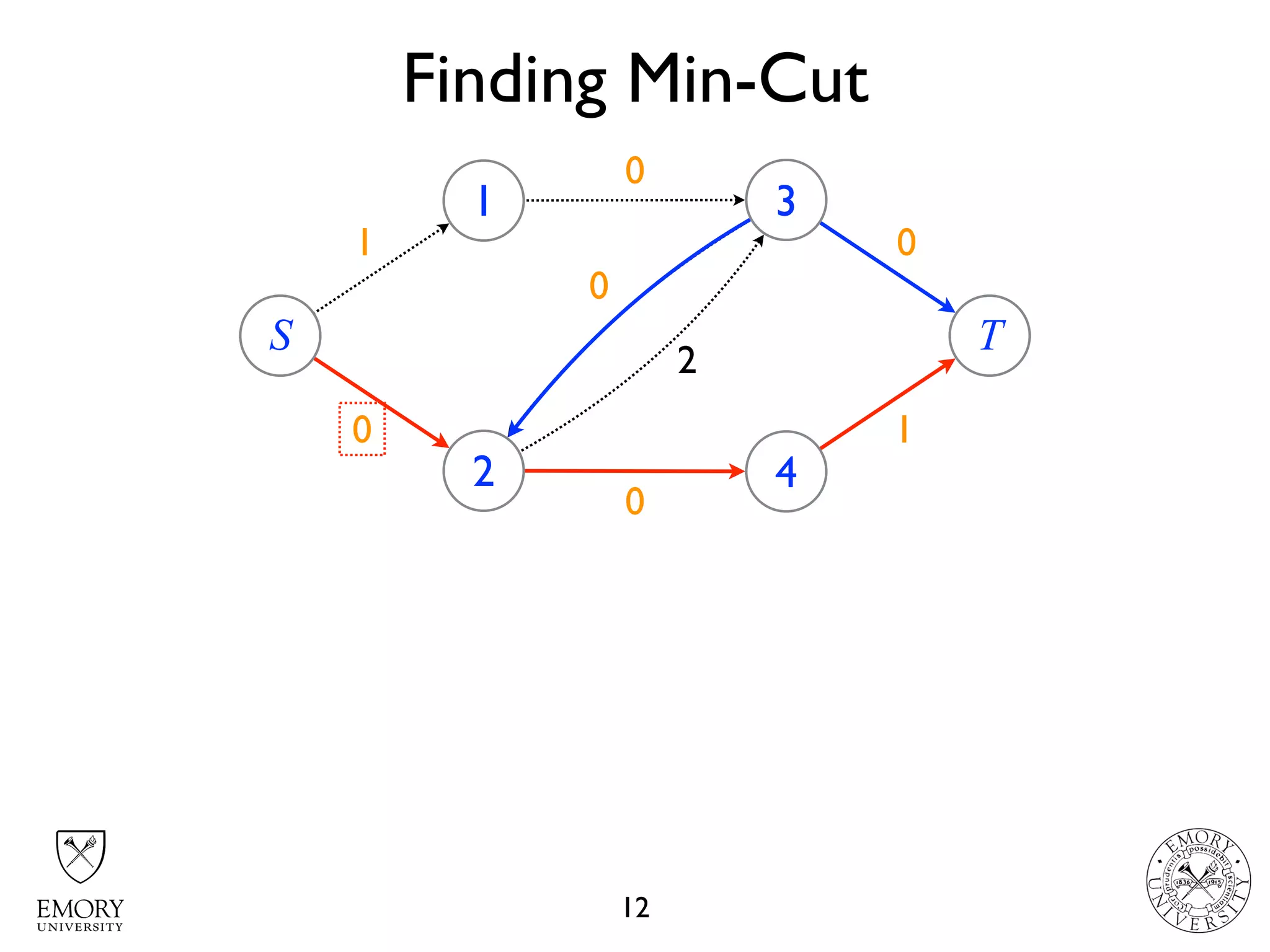
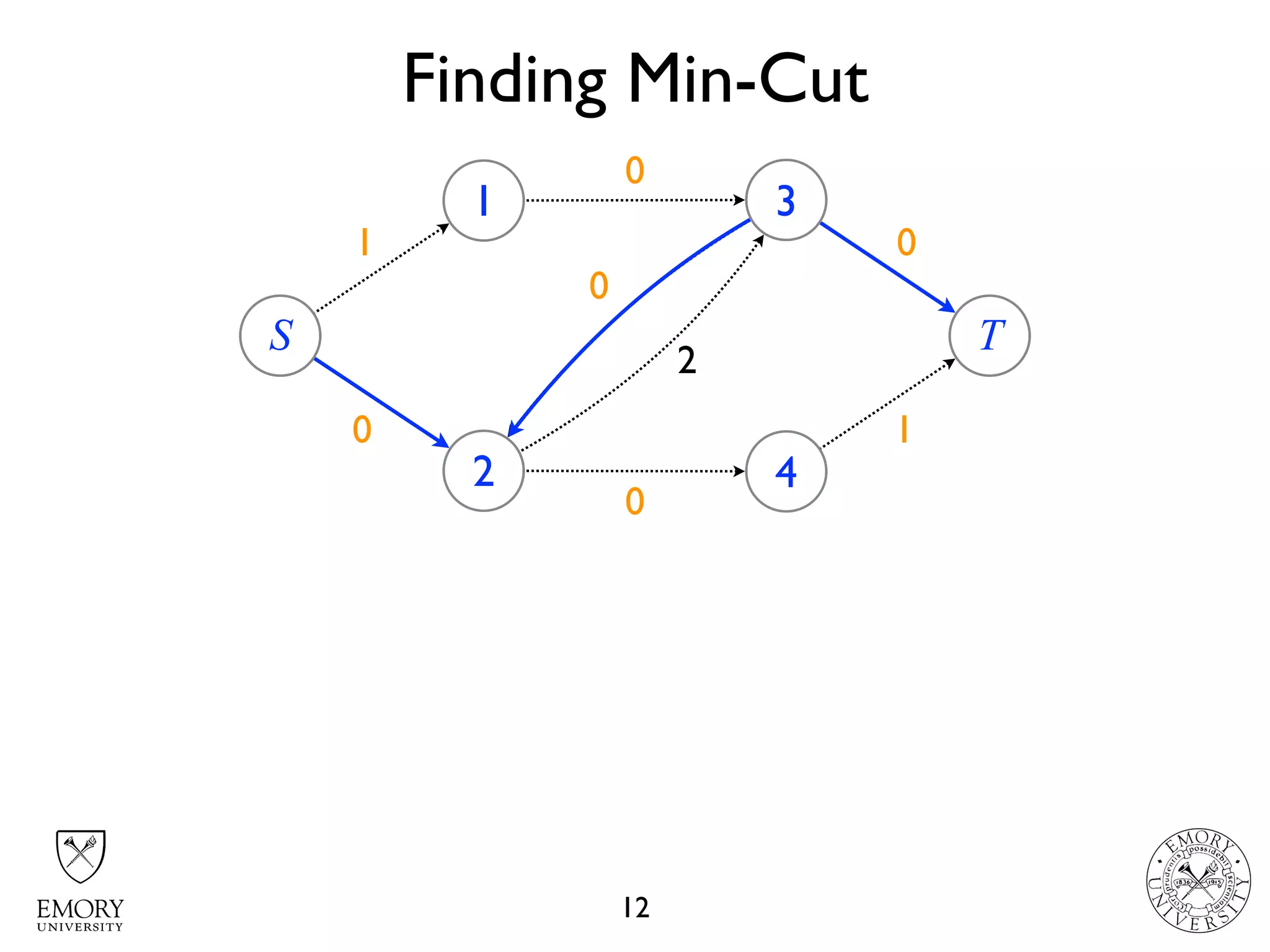
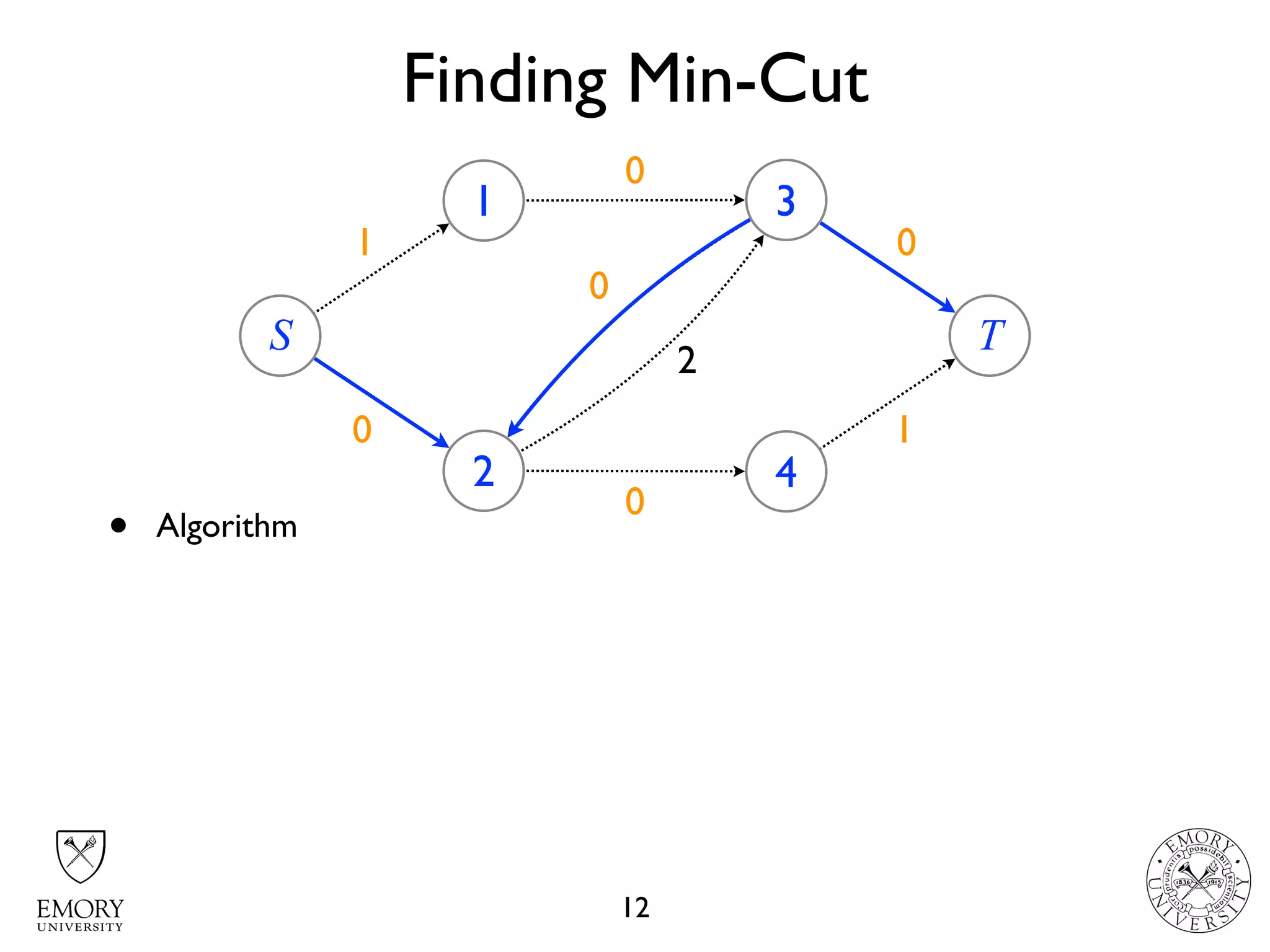
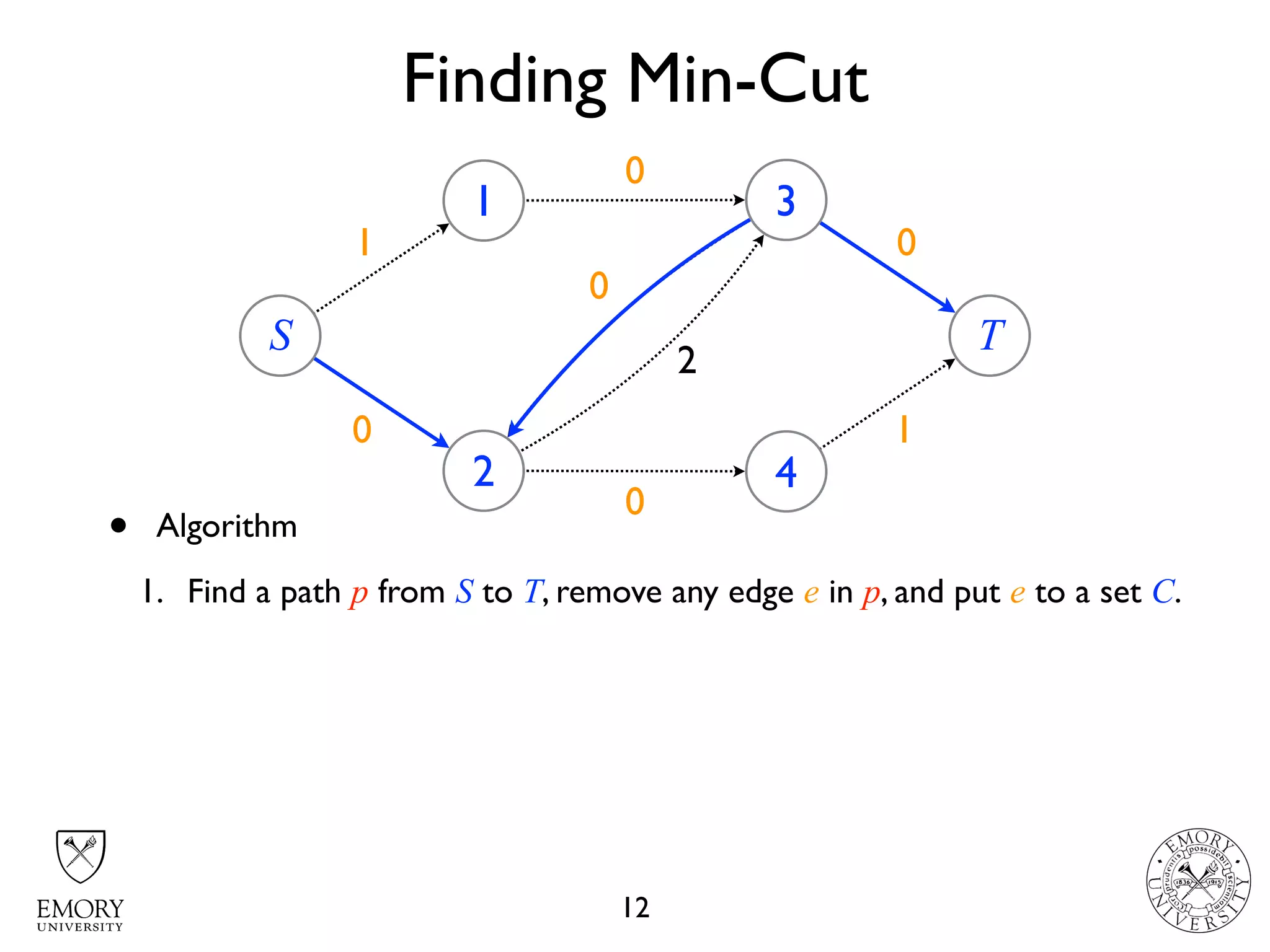
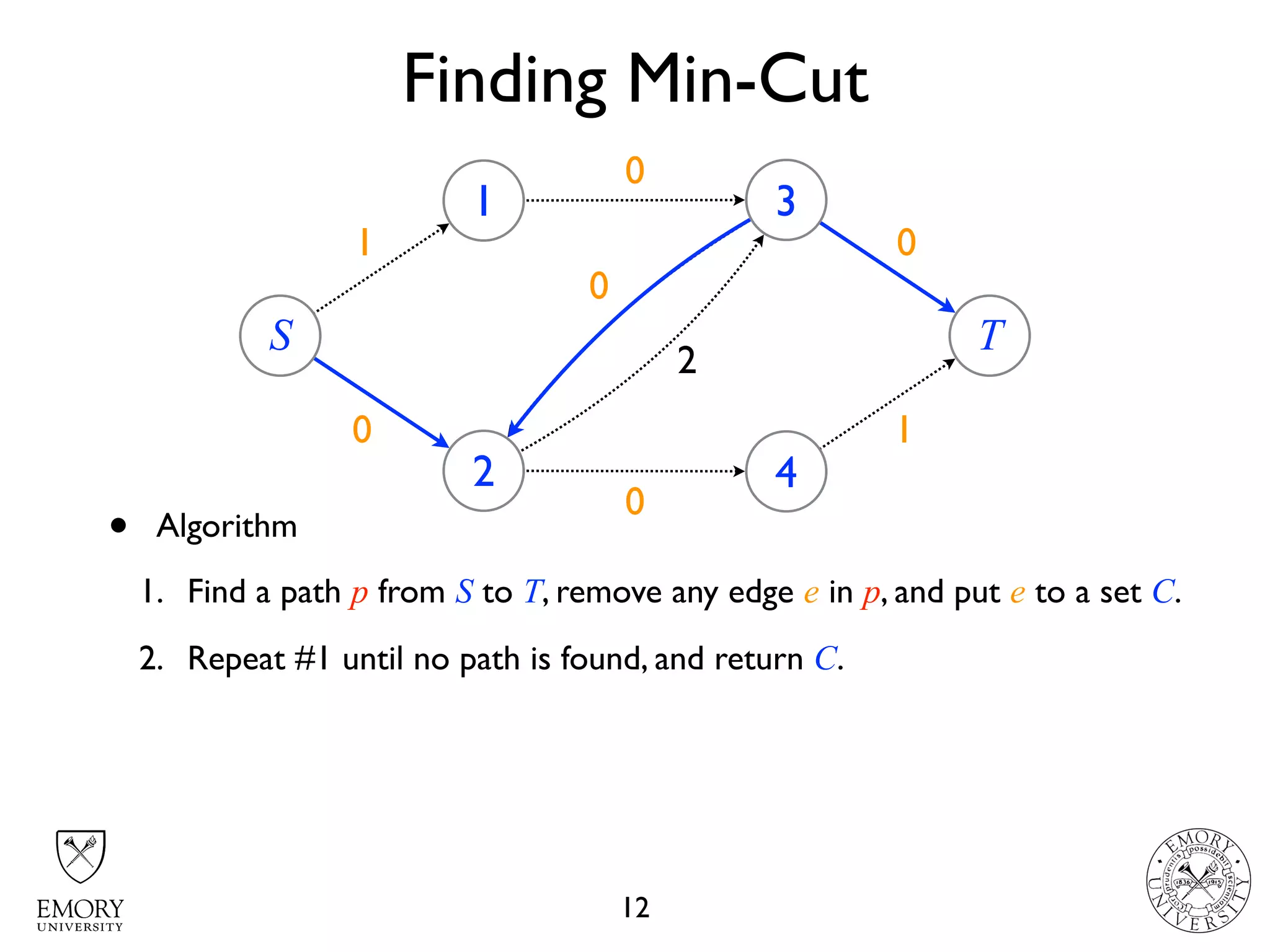
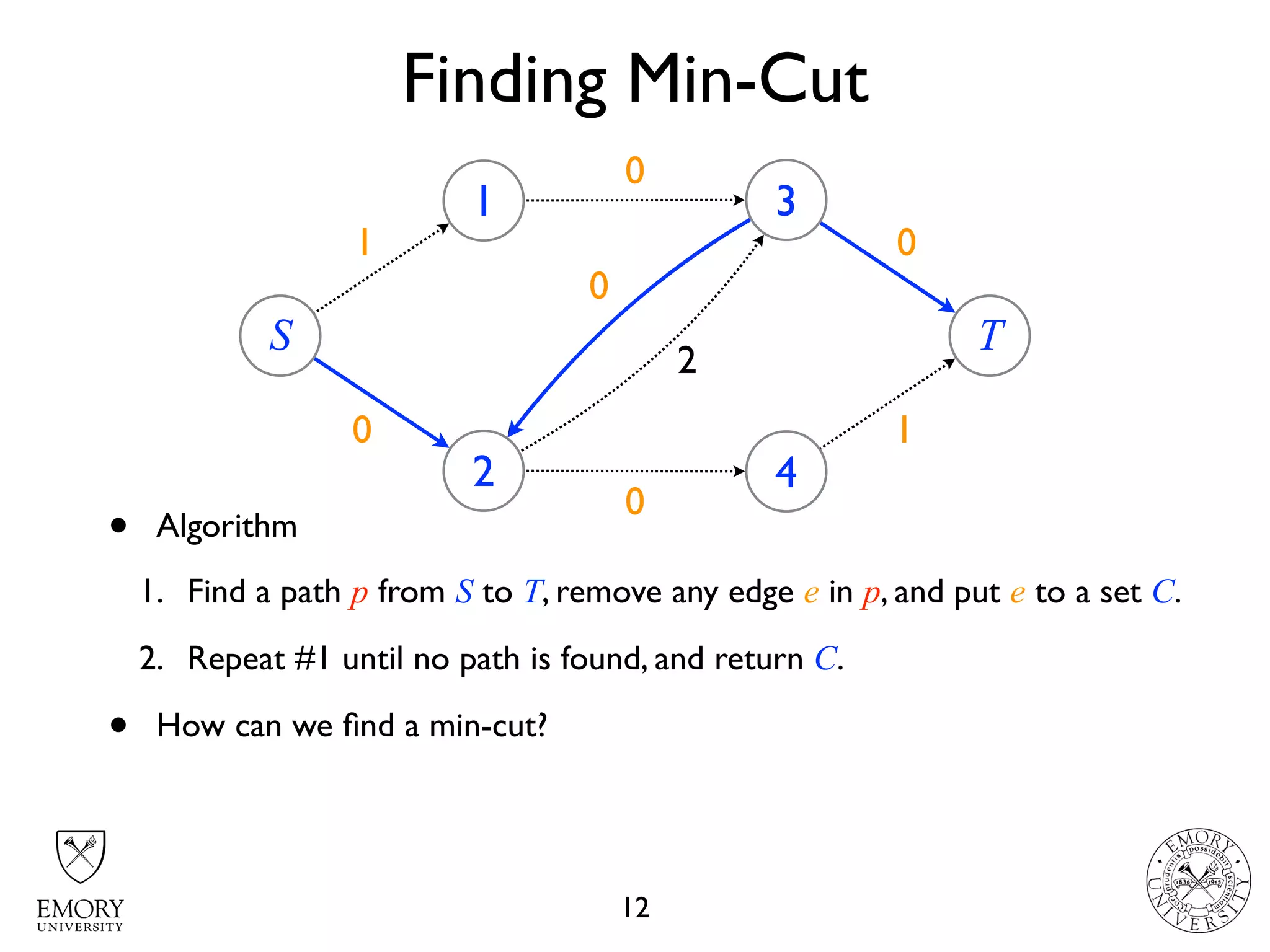
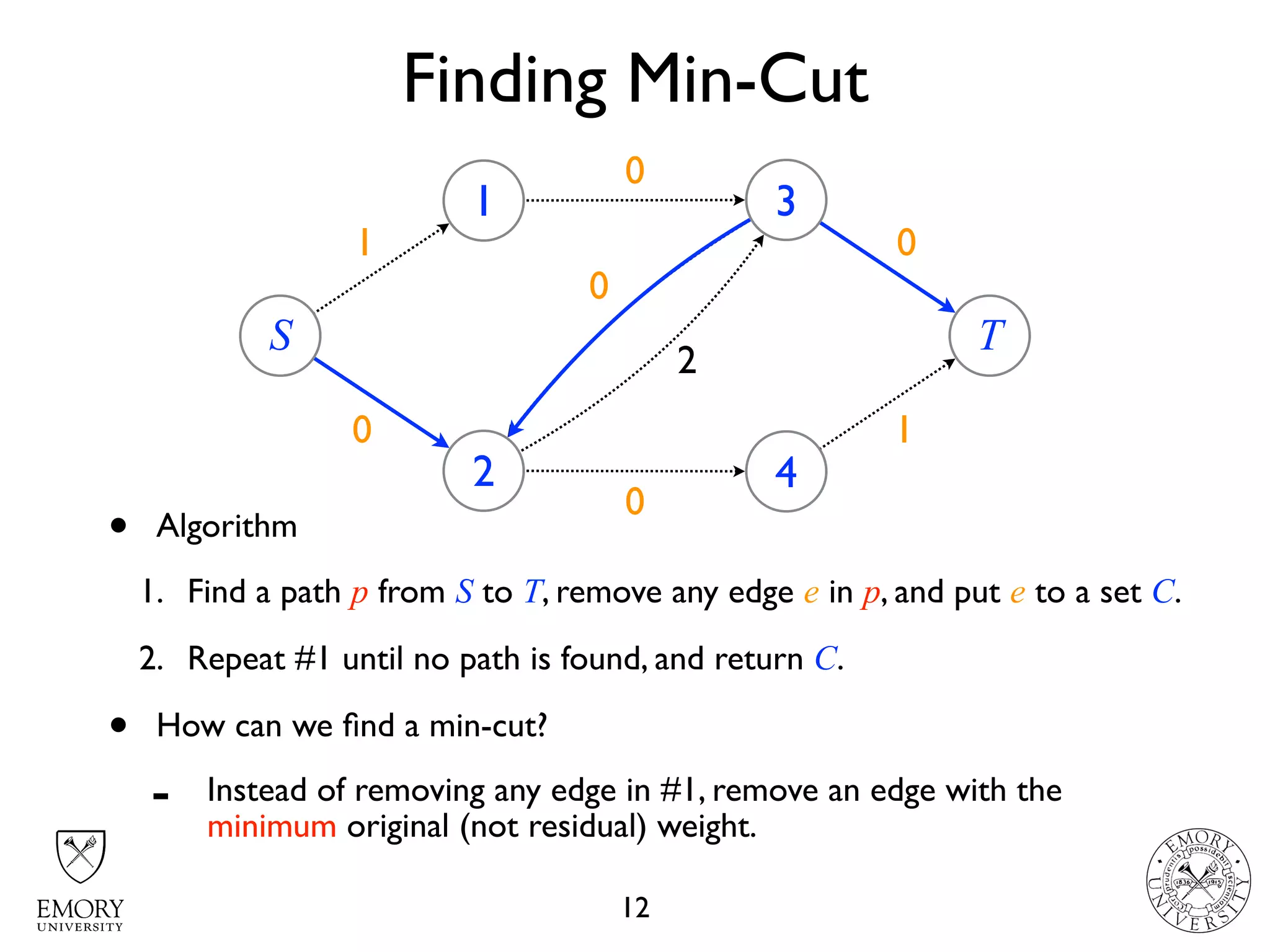
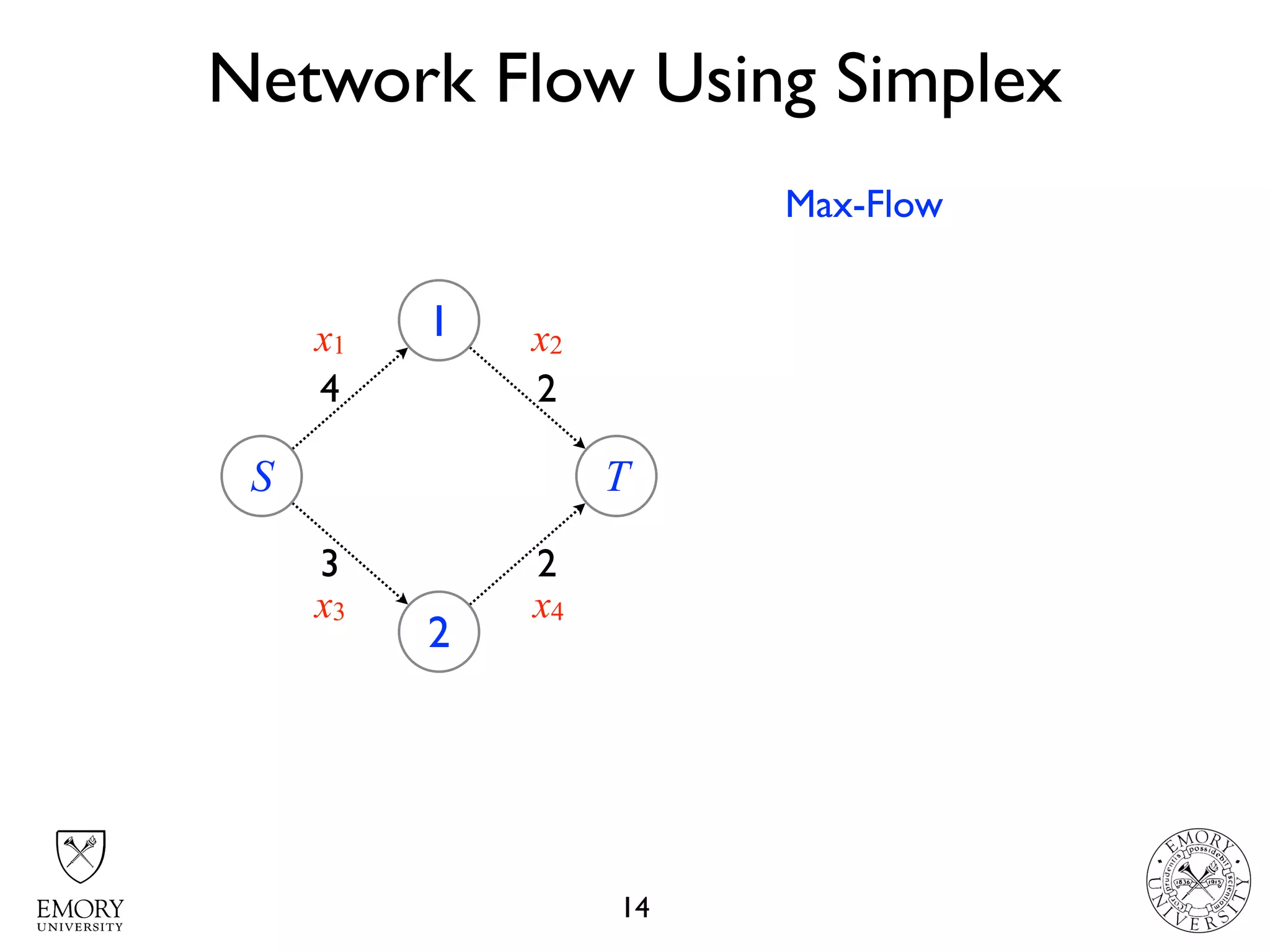
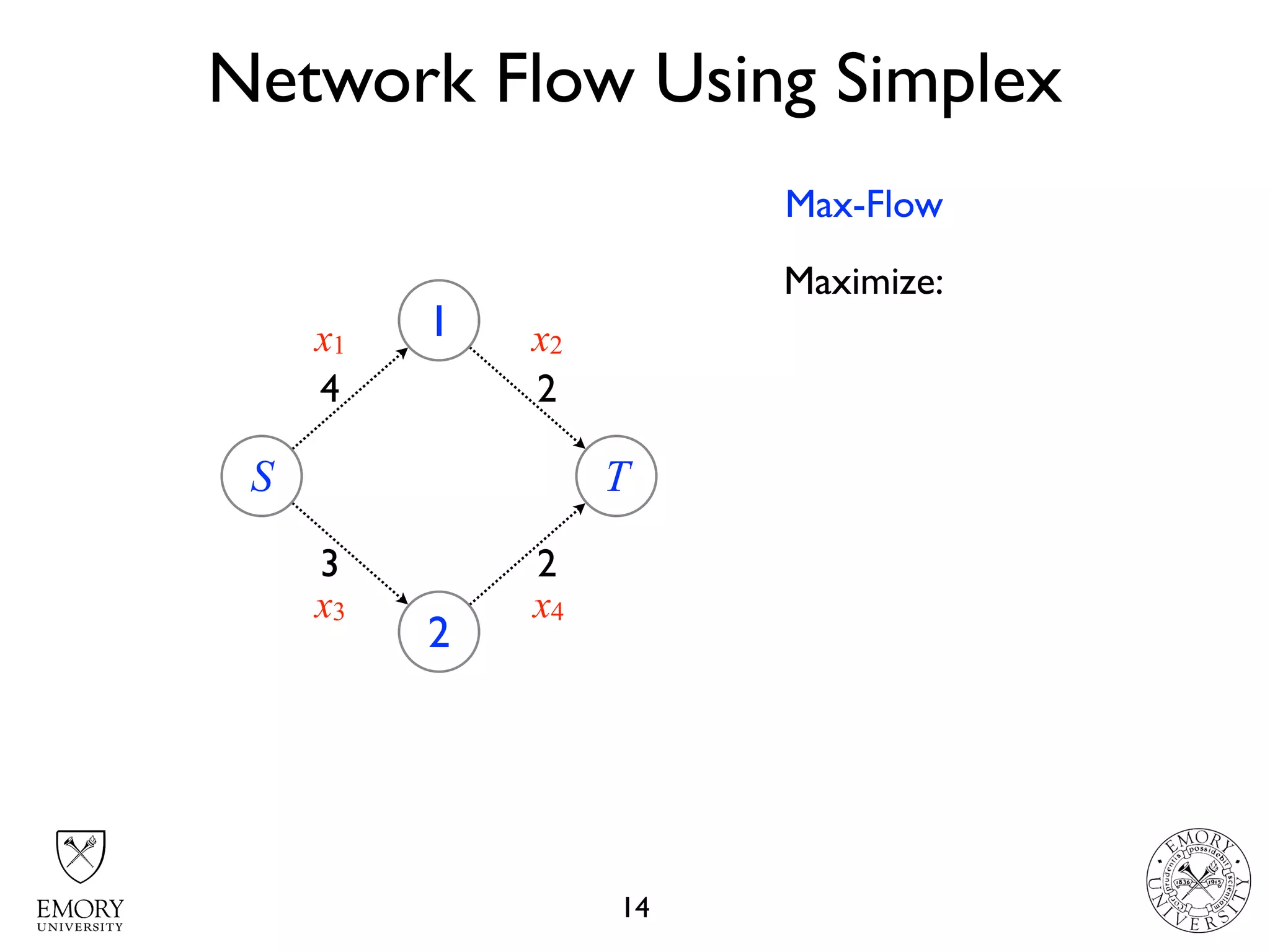
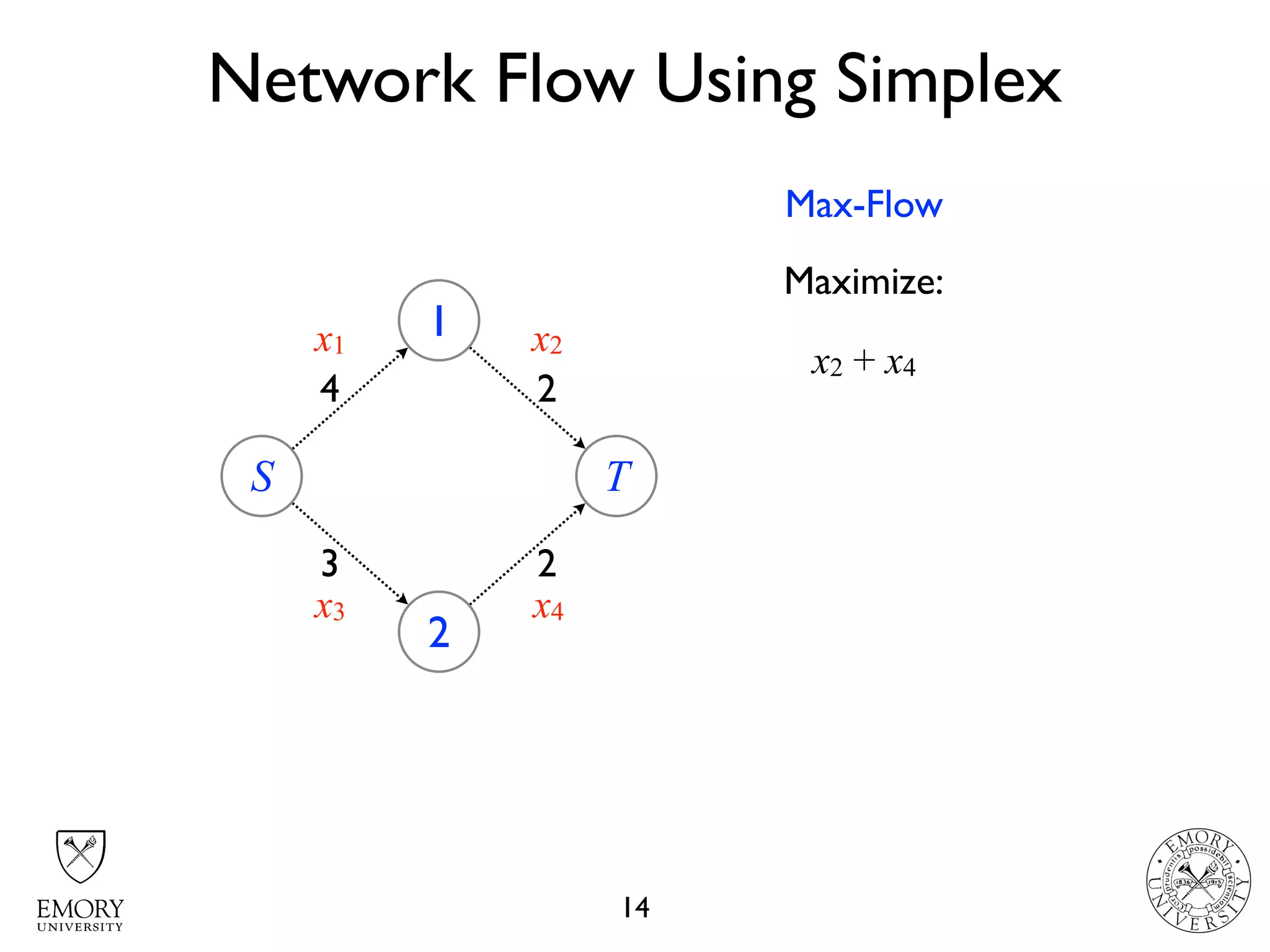
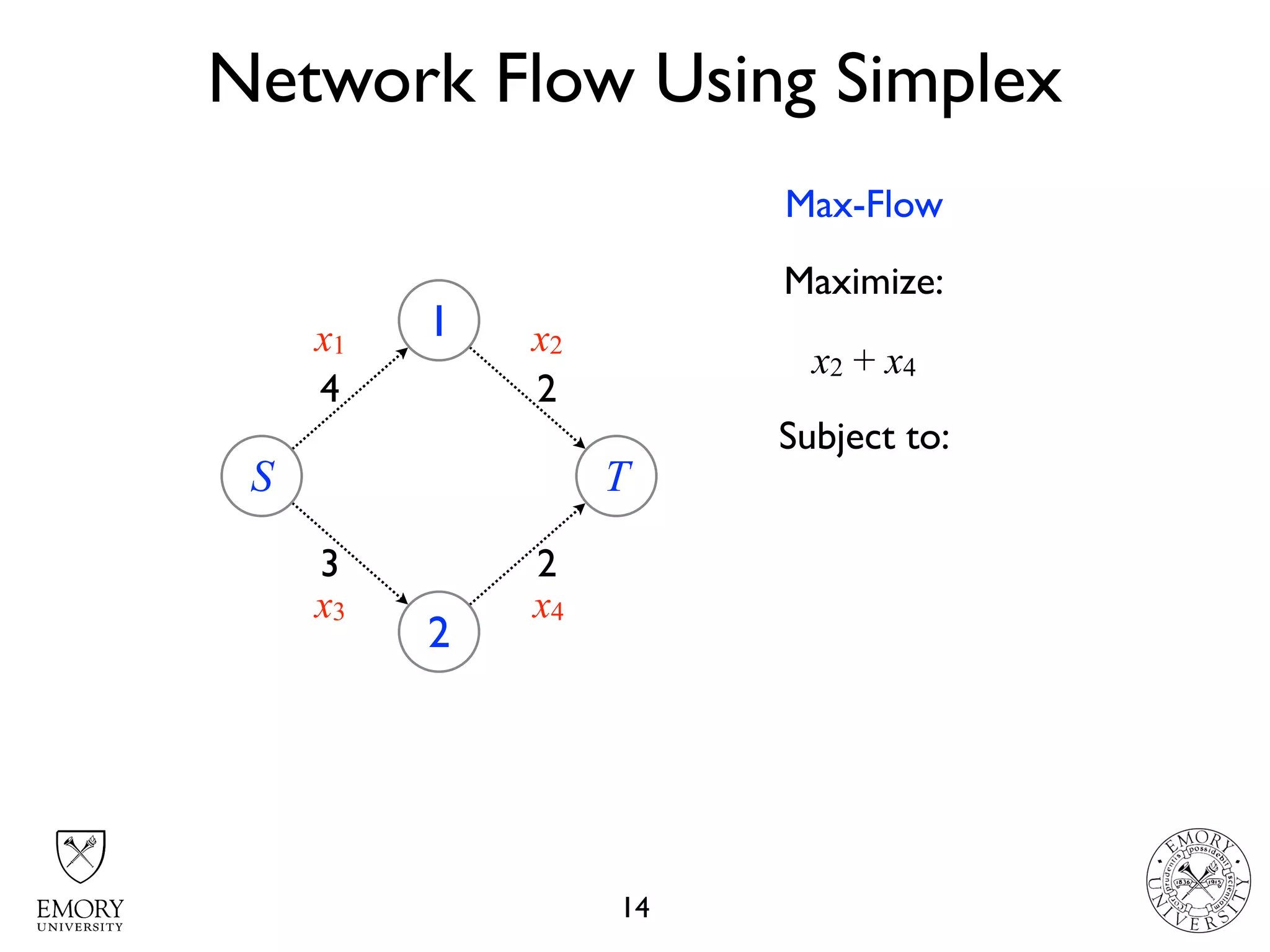
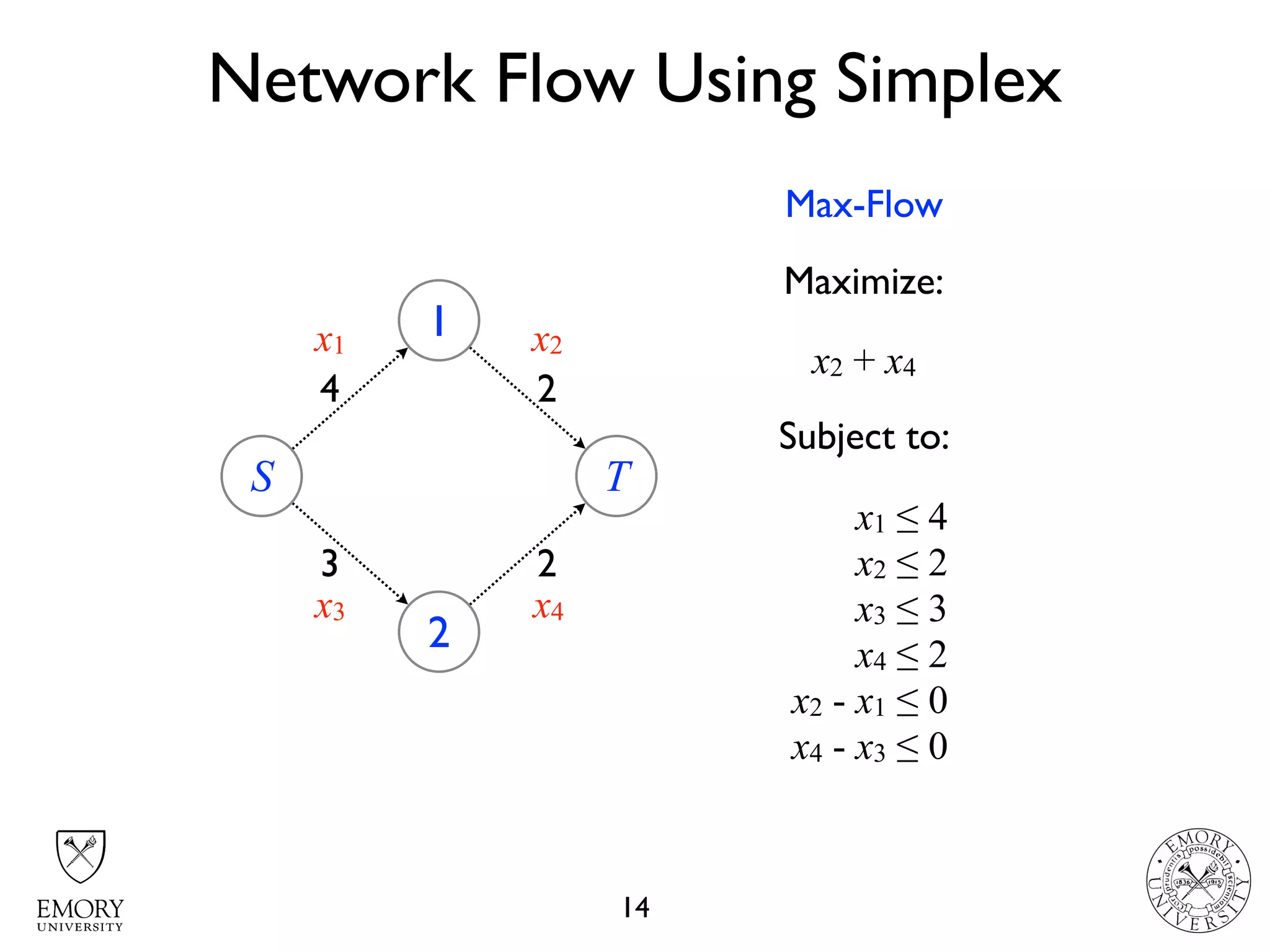
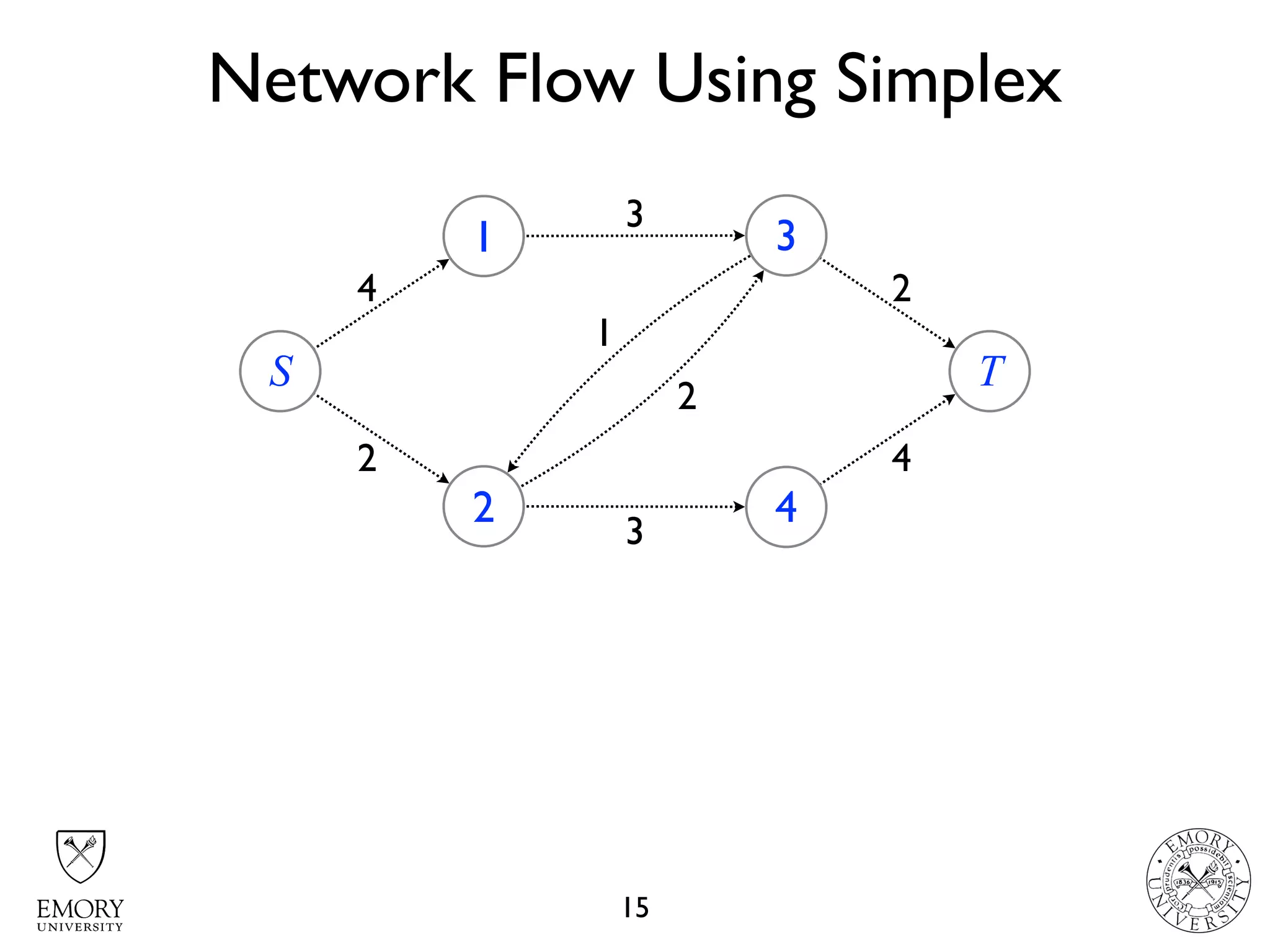
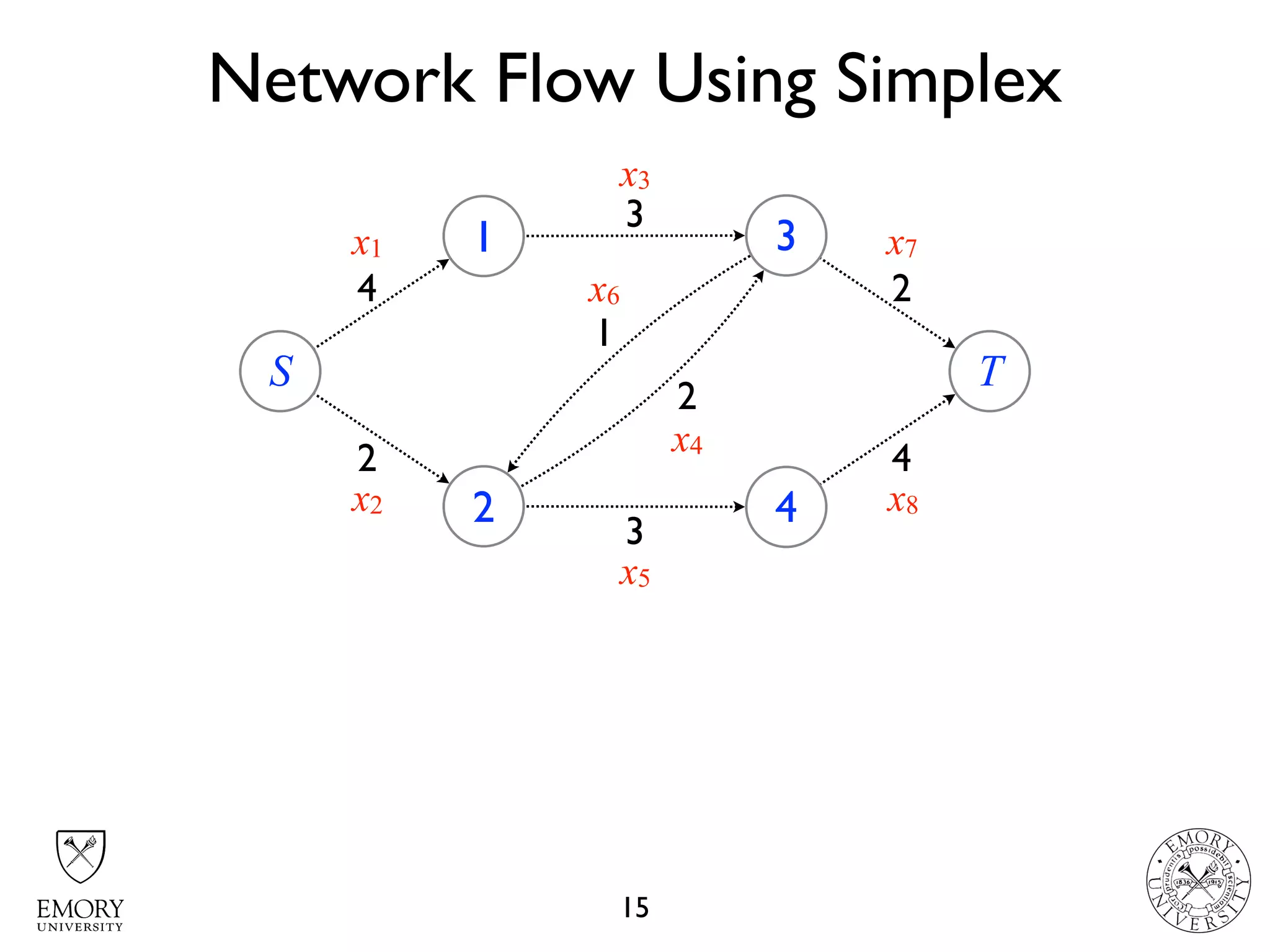
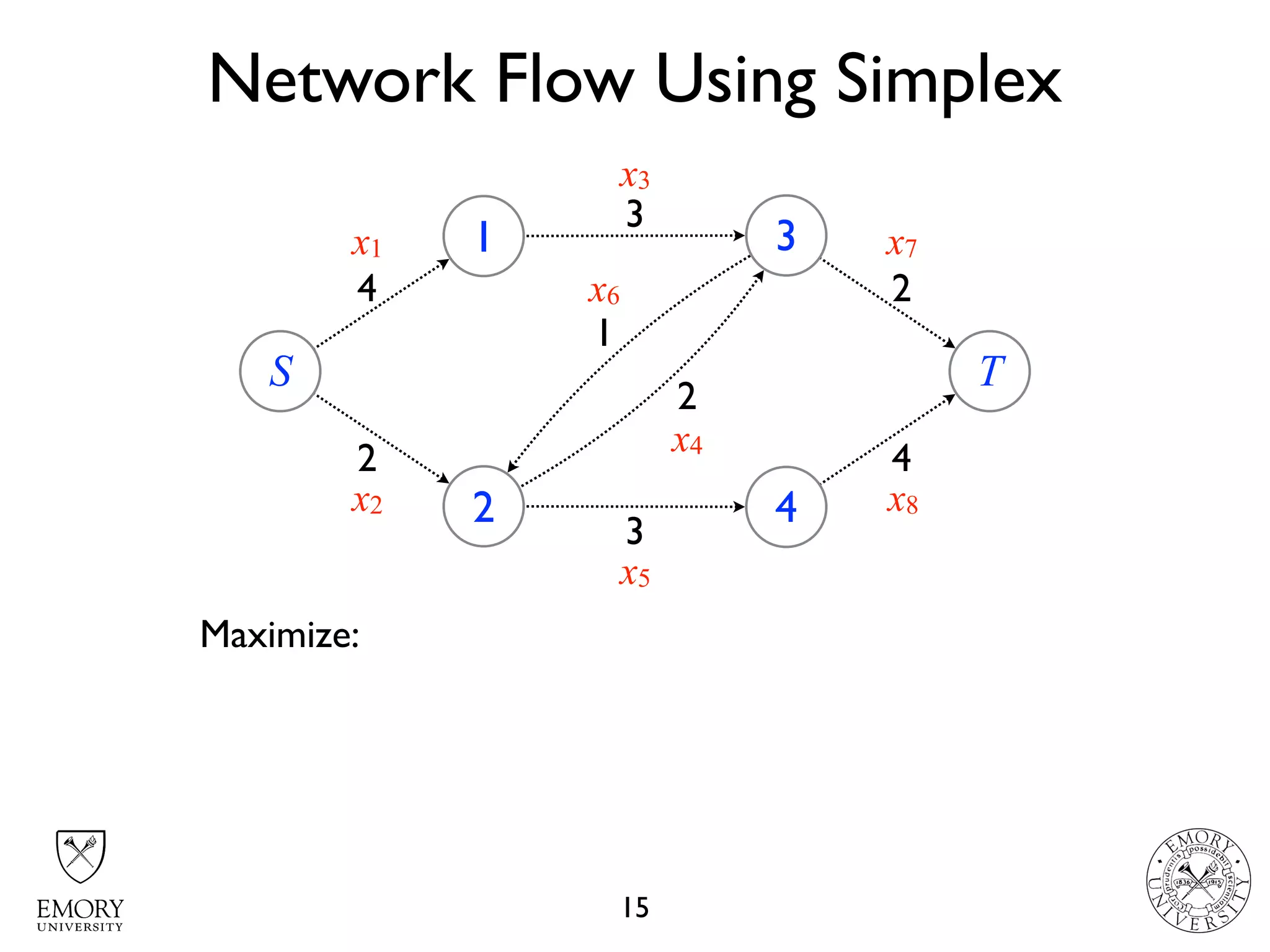
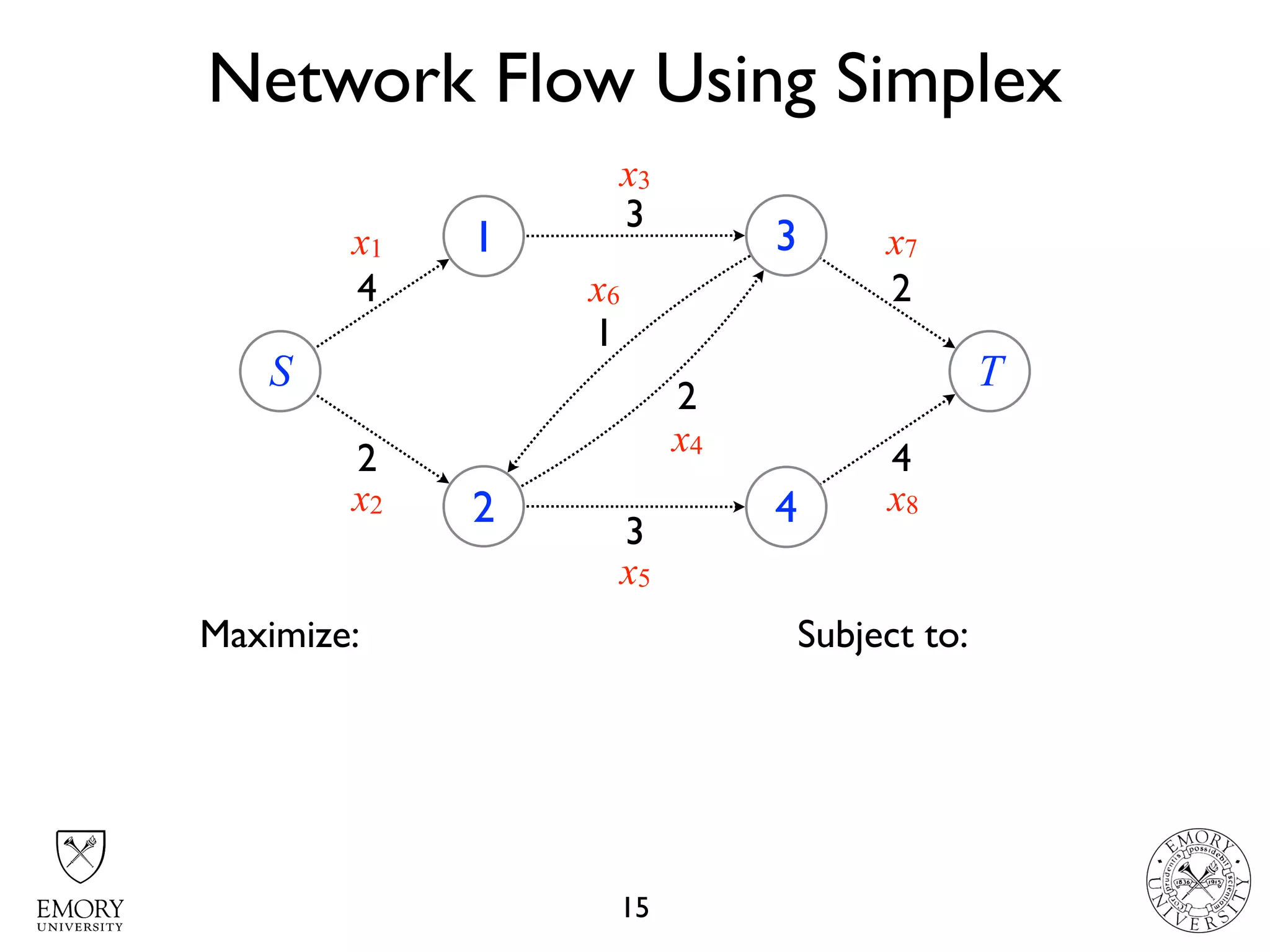
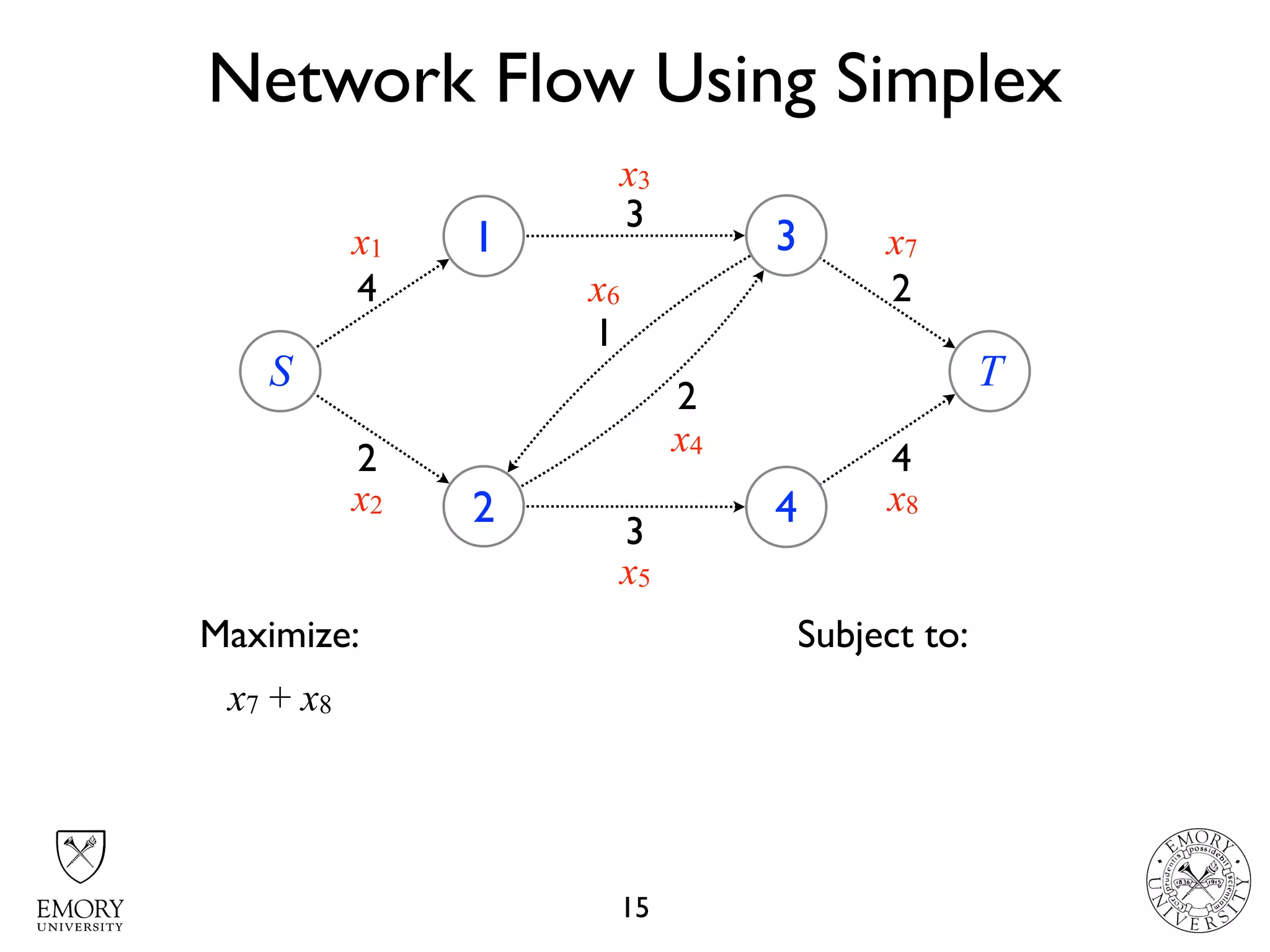
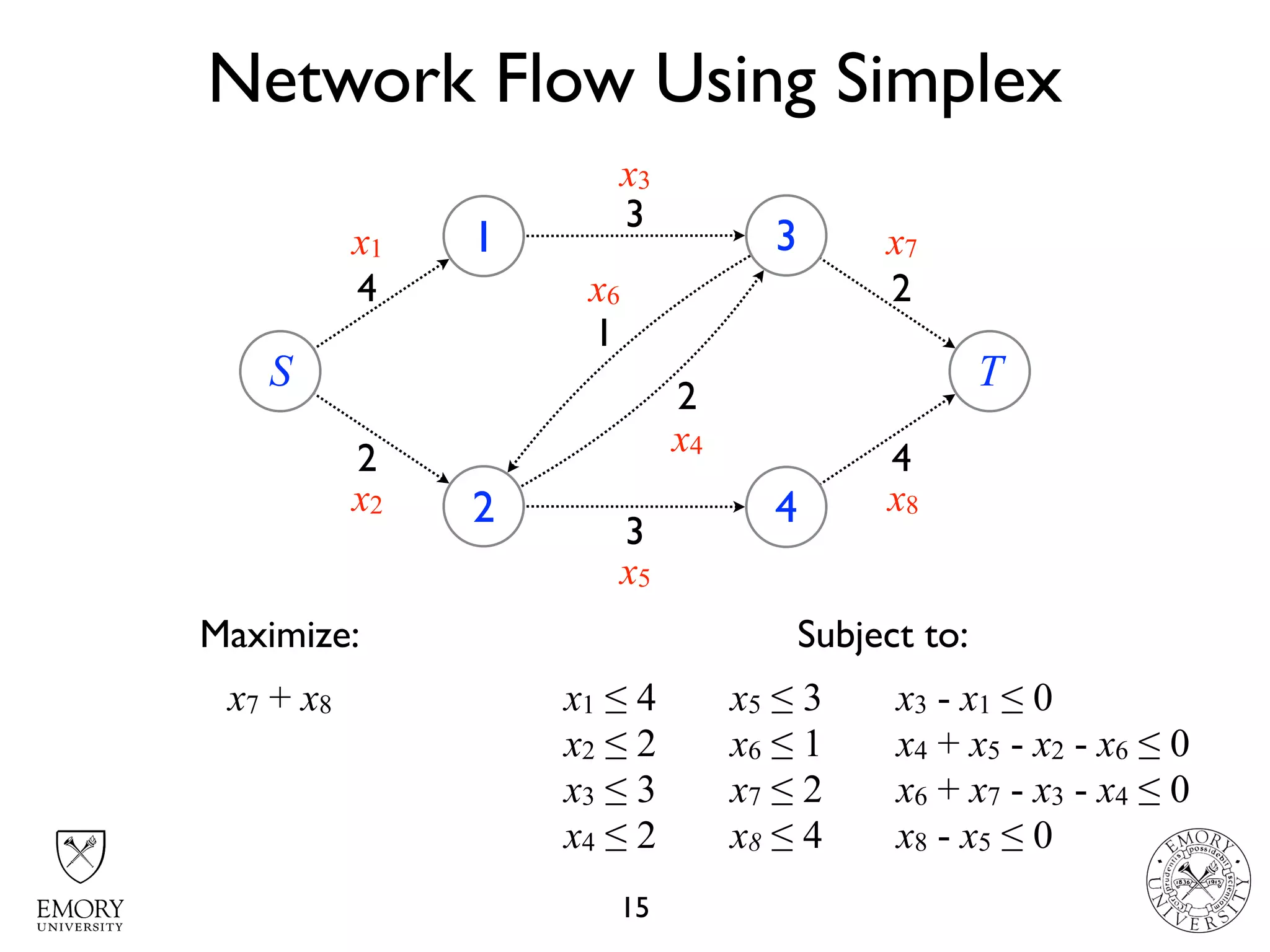
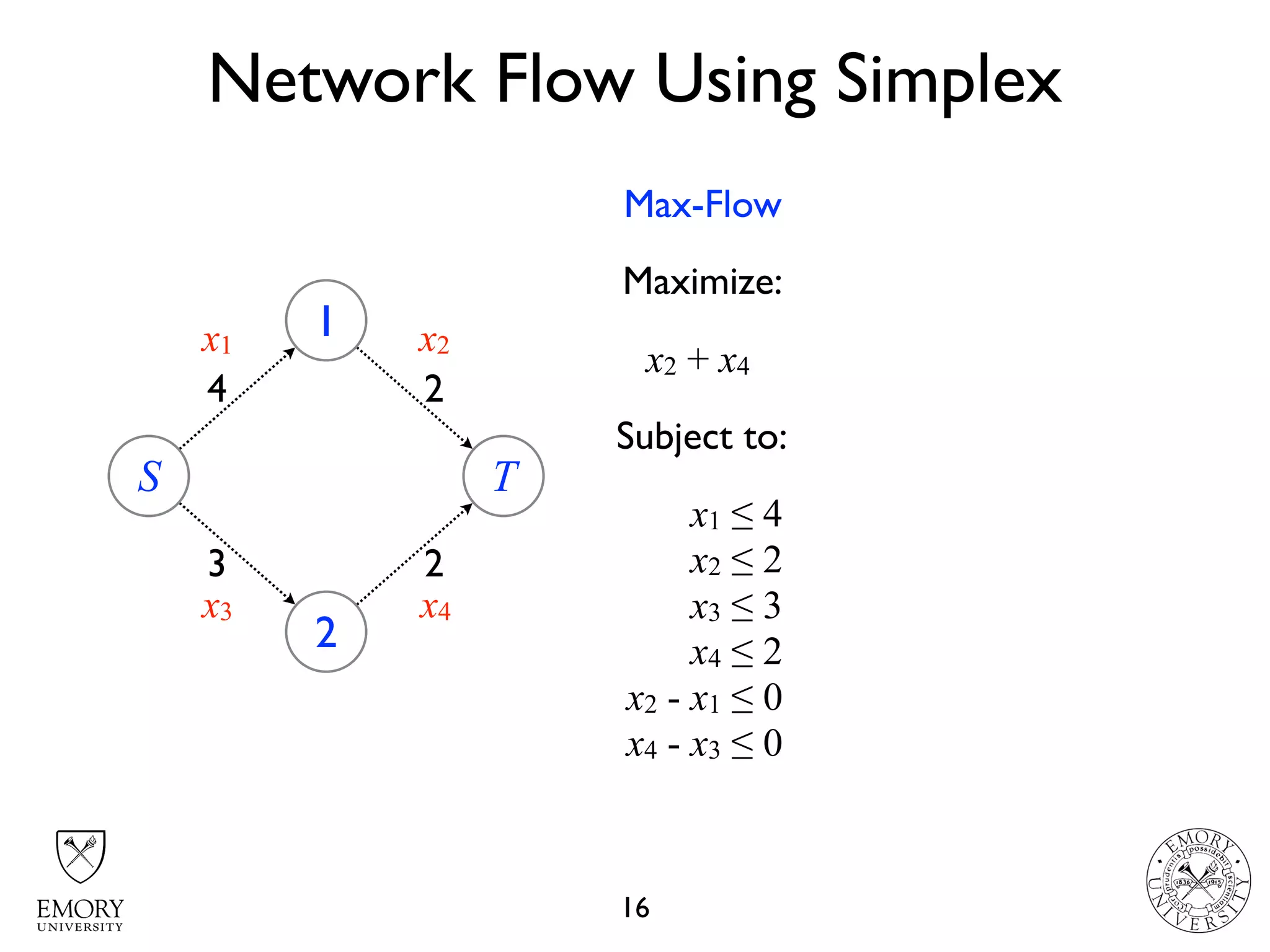
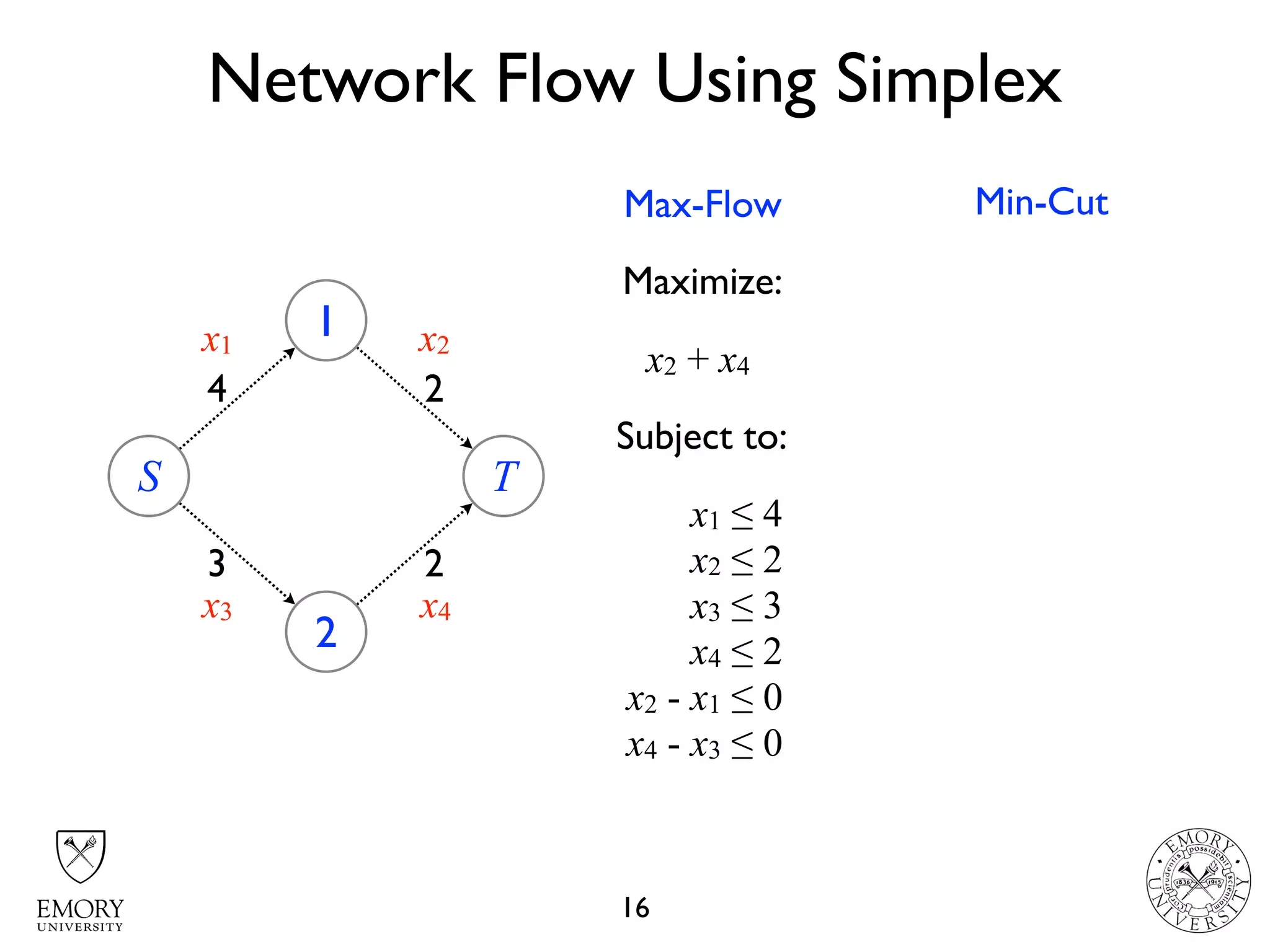
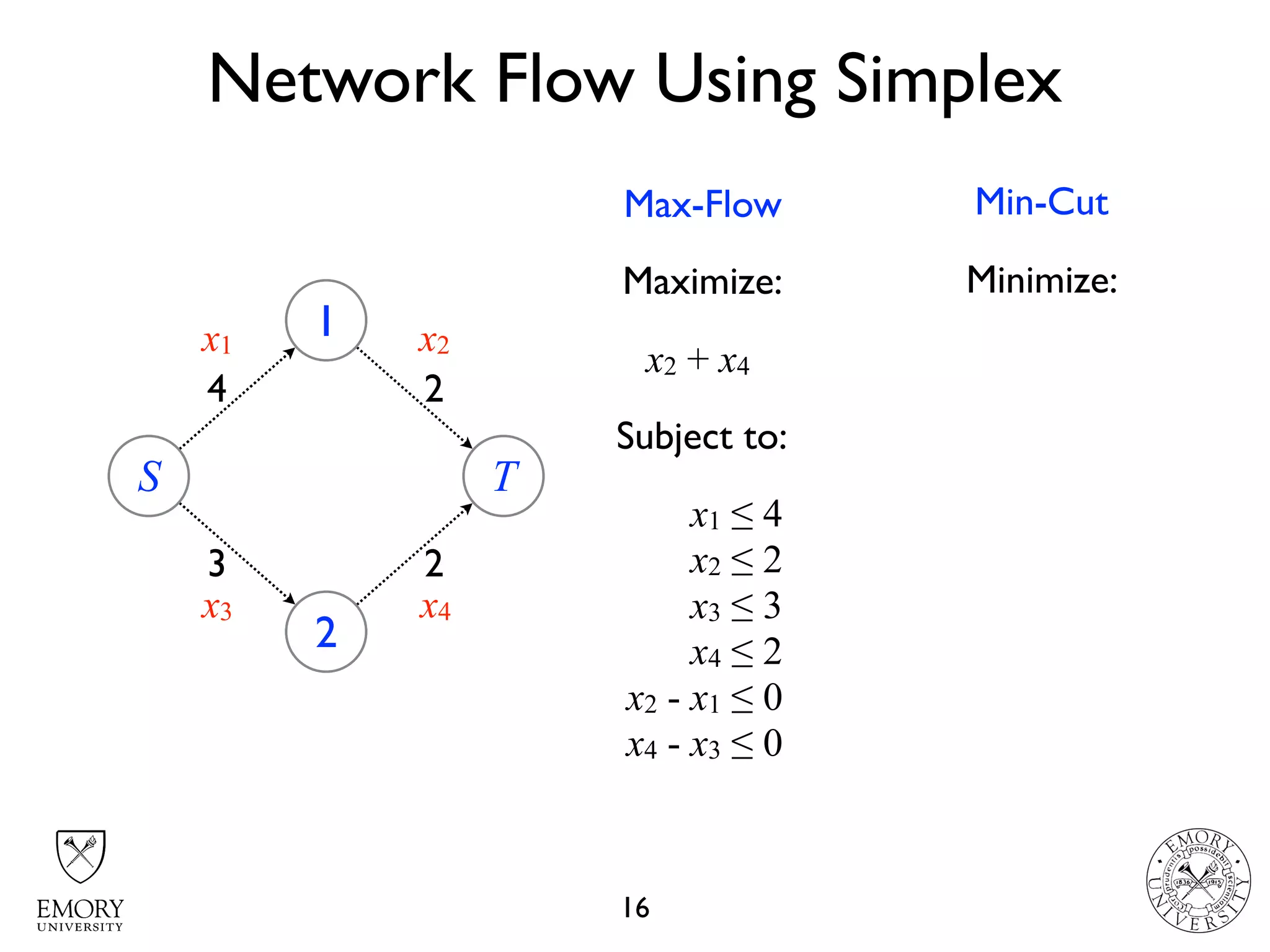
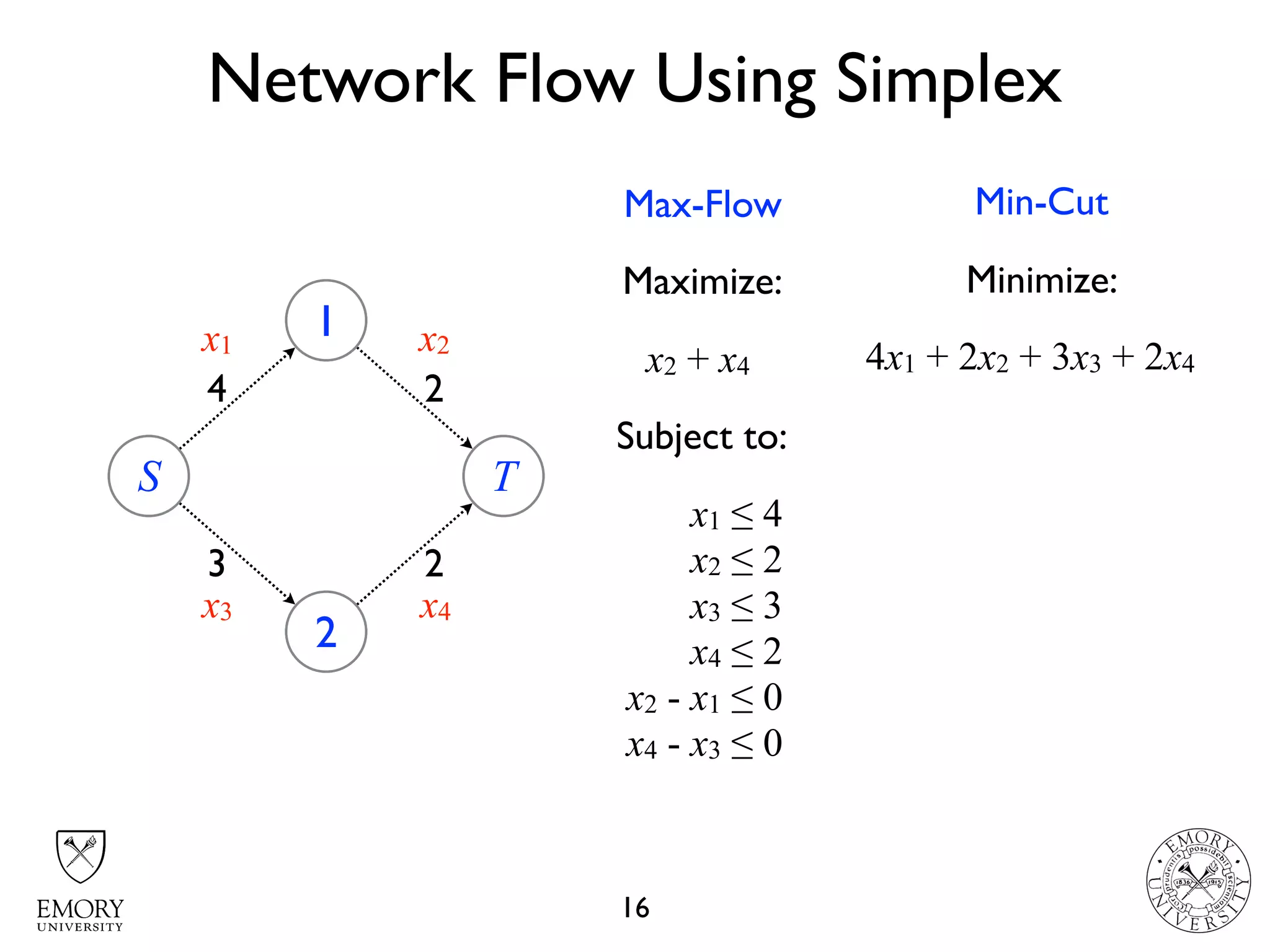
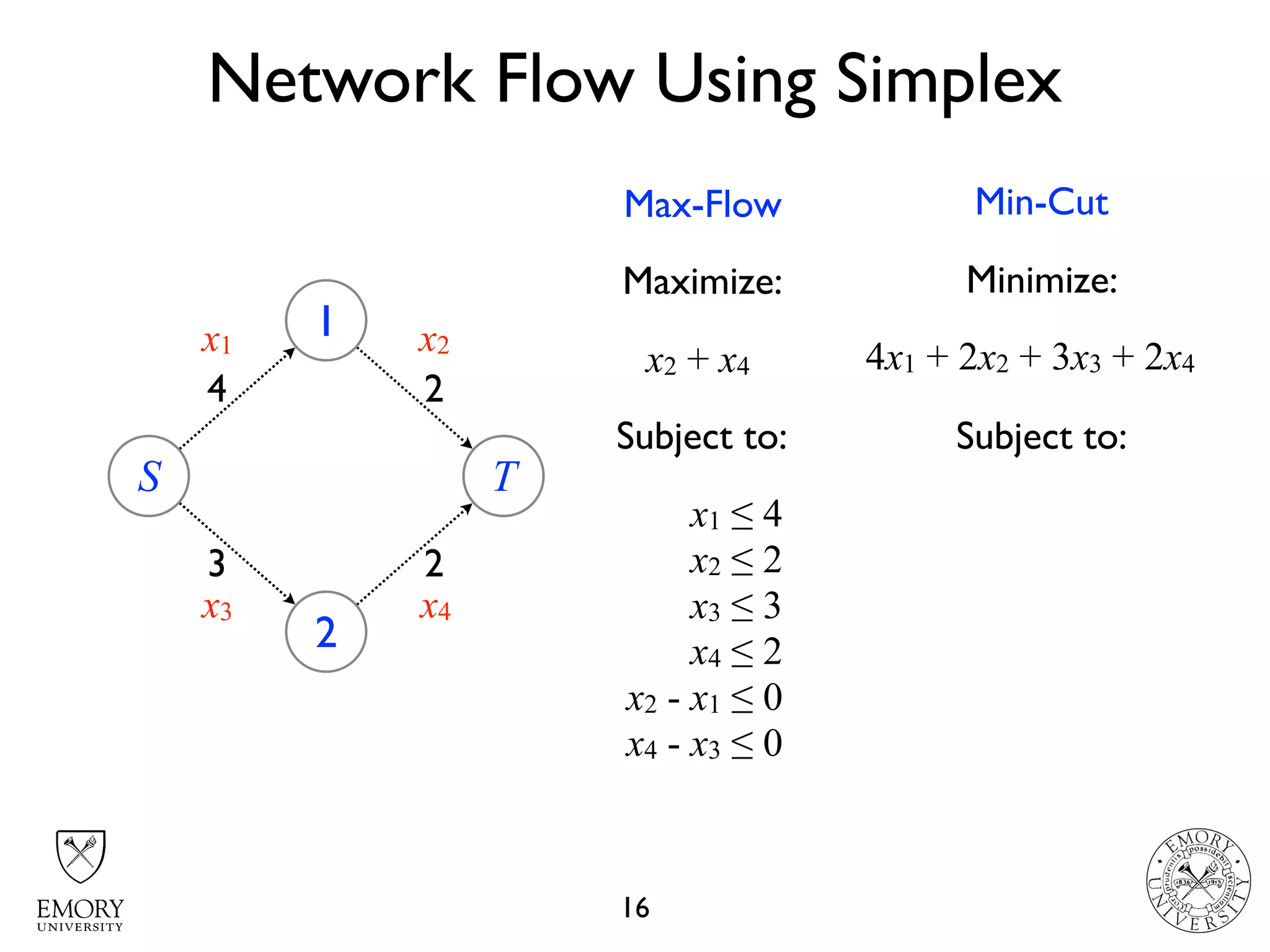
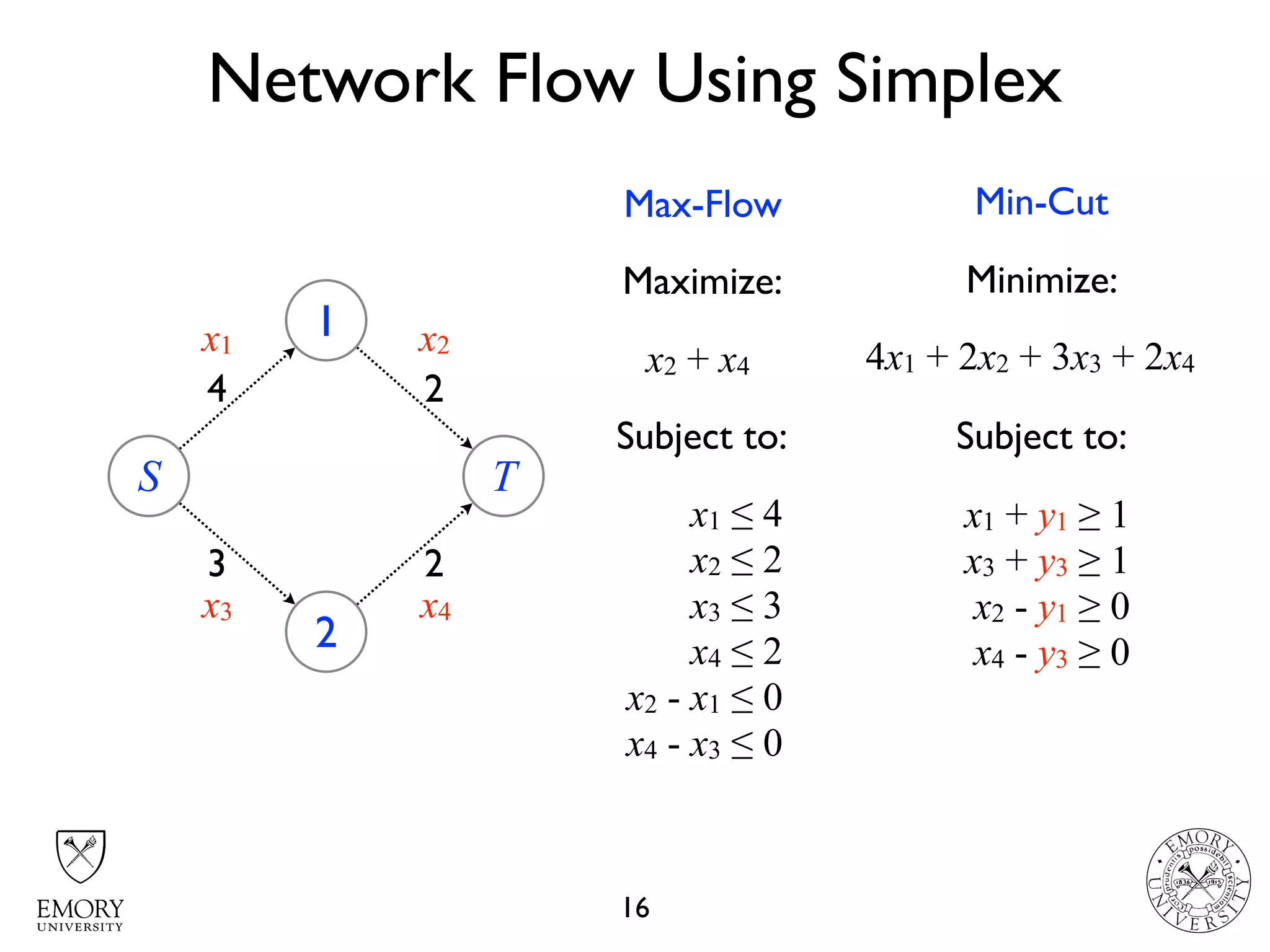
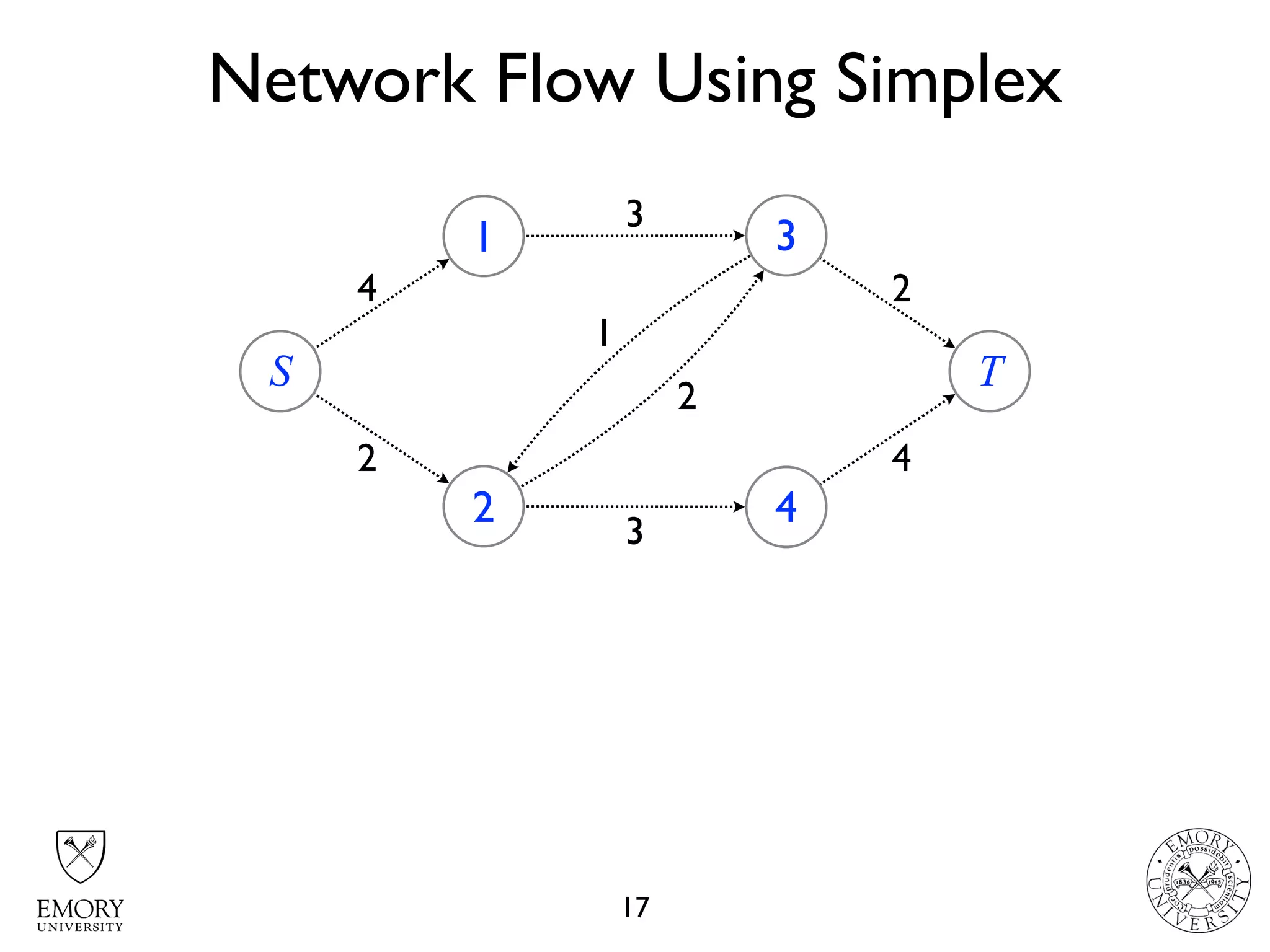
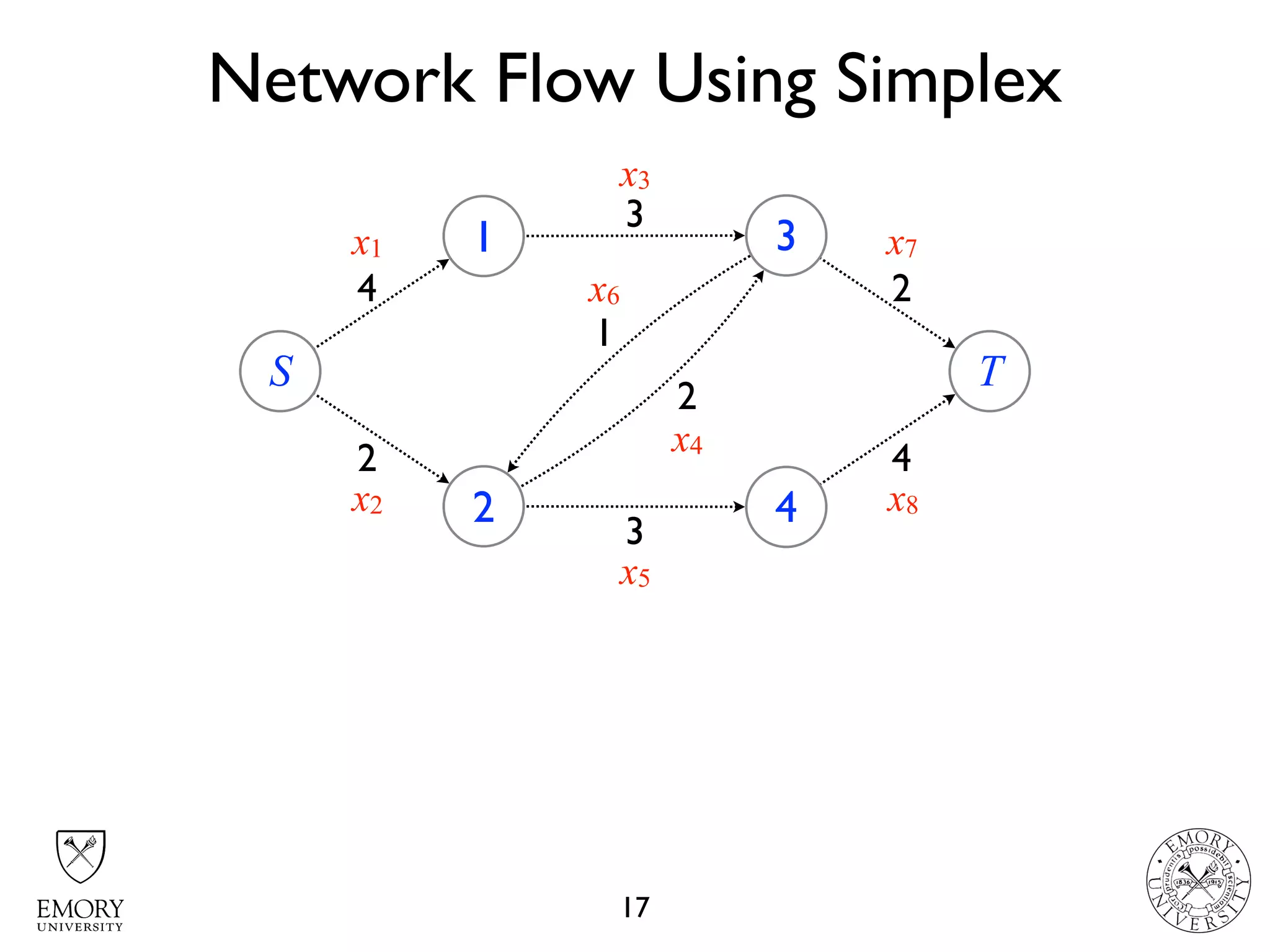
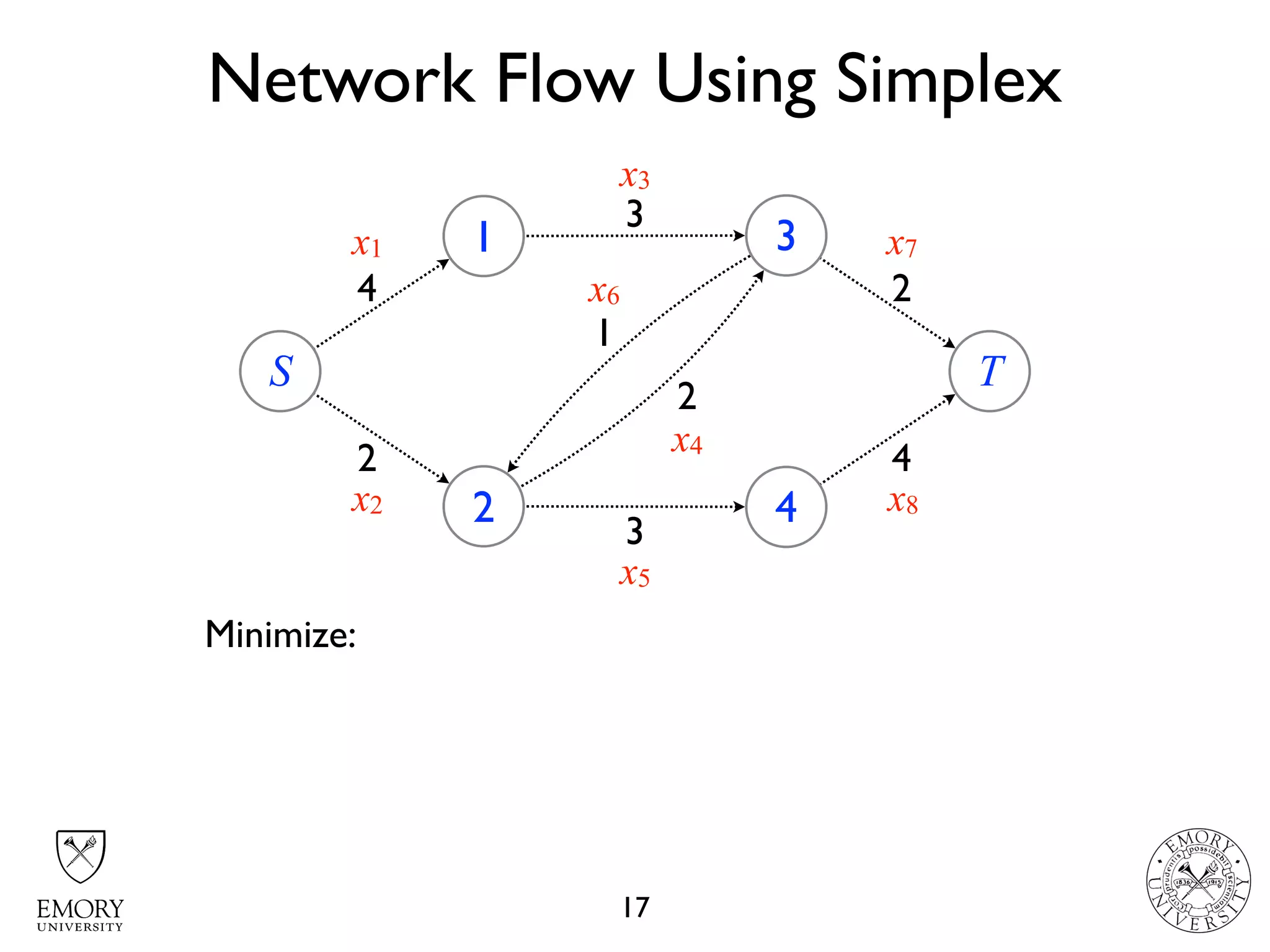
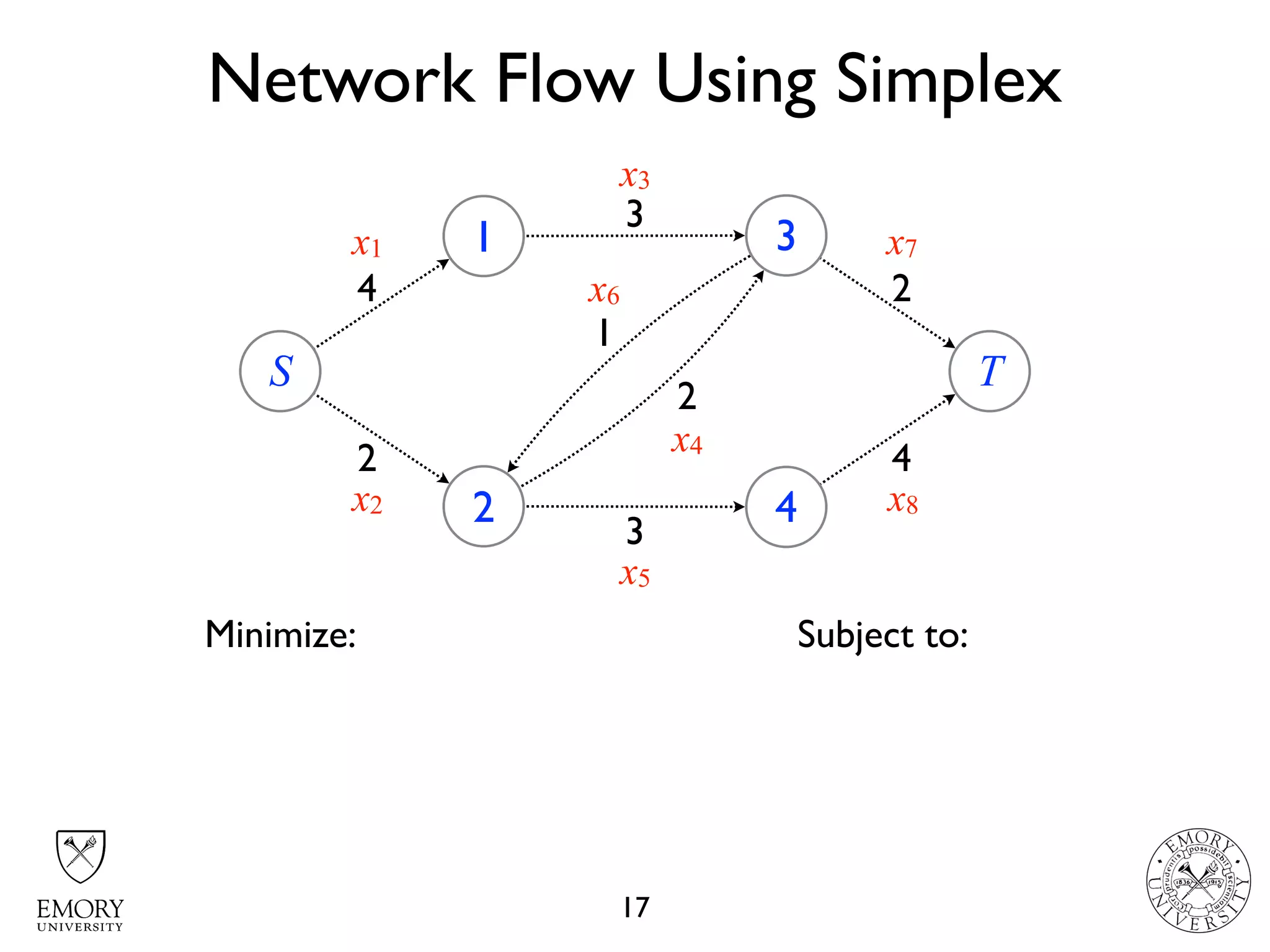
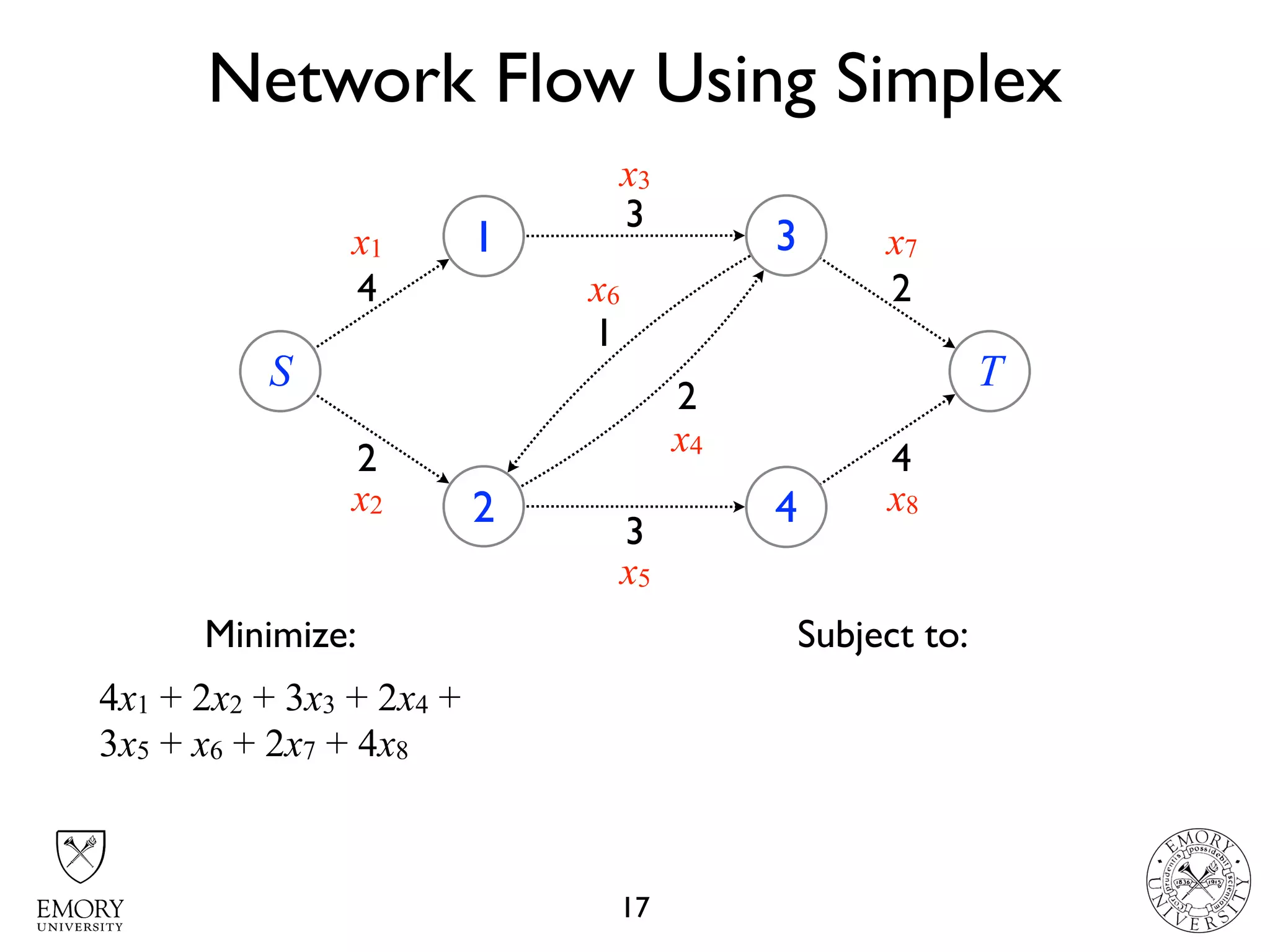
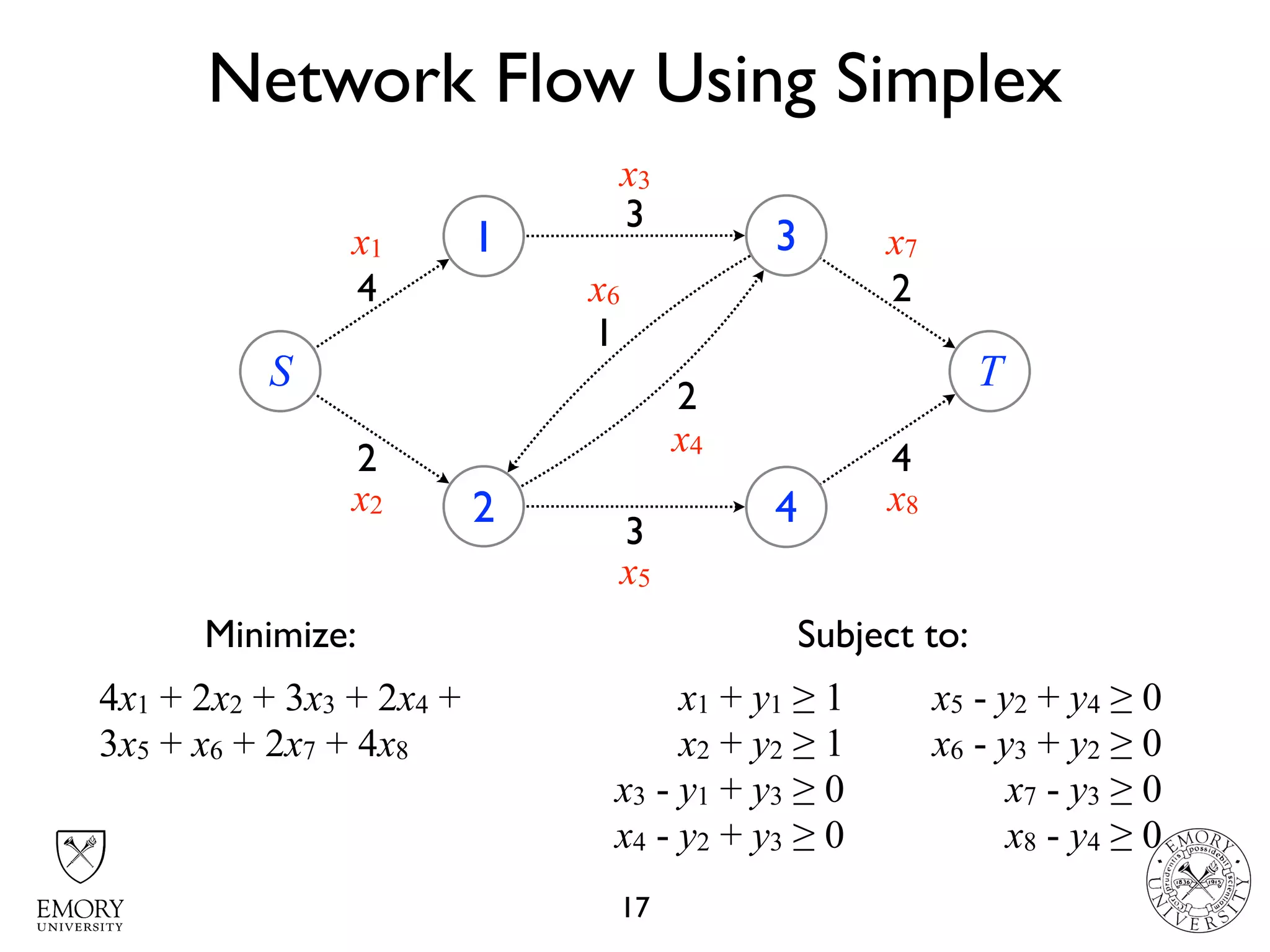
The document describes the maximum flow problem and Ford-Fulkerson algorithm for finding the maximum flow in a flow network. The maximum flow problem involves finding the maximum amount of flow that can be pushed from a source node S to a target node T in a flow network where each edge has a capacity. The Ford-Fulkerson algorithm iteratively finds augmenting paths (paths from S to T with available residual capacity) in the network and pushes flow along these paths until no more augmenting paths exist, giving the maximum flow. Pseudocode is provided for the MaxFlow and FordFulkerson classes that could implement this algorithm.