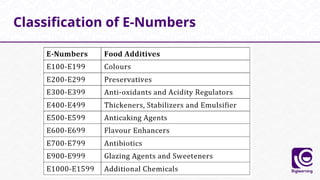
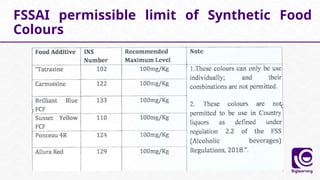
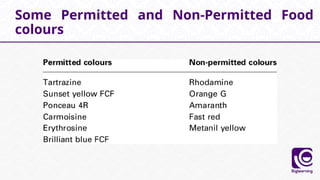
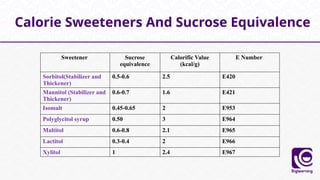
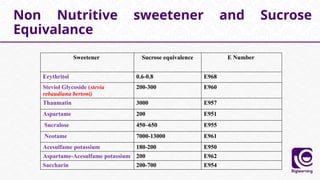
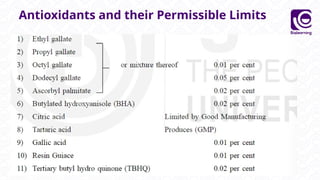
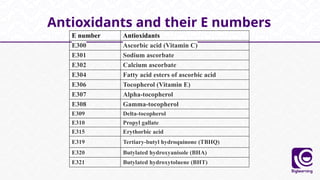
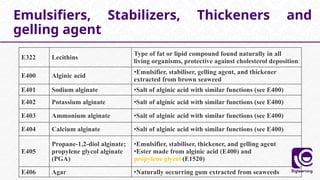
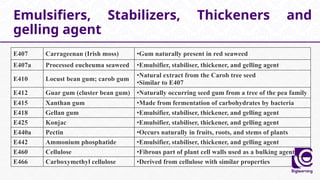
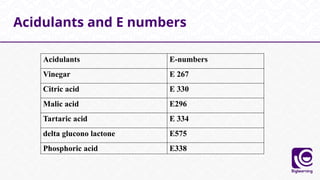
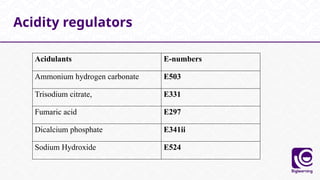
This document discusses food additives, defining them as substances added for technological purposes, excluding contaminants. It categorizes food additives into direct and indirect types, detailing their functions, examples, and potential effects on health. Additionally, it highlights regulations regarding food additives, their classifications, and permissible limits in various regions.