1. Fluid statics deals with fluids at rest and how they respond to pressure. Pressure is defined as force per unit area.
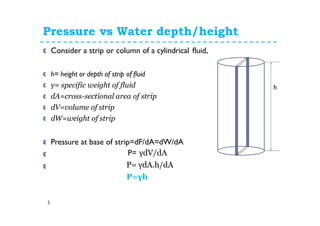
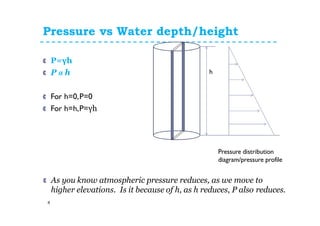
2. Pressure increases linearly with depth or height of a fluid. Deeper locations experience greater pressure due to the weight of fluid above.
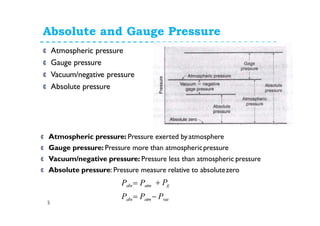
3. There are three types of pressure: absolute, gauge, and vacuum/negative. Absolute pressure is measured from a complete vacuum while gauge omits atmospheric pressure.